Velociraptor
Velociraptor mongolienses, Velociraptor osmolskae
Advertisement
Velociraptor Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Family
- Dromaeosauridae
- Genus
- Velociraptor
- Scientific Name
- Velociraptor mongolienses, Velociraptor osmolskae
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Velociraptor Conservation Status
Velociraptor Facts
- Diet
- Omnivore
Velociraptor Physical Characteristics
View all of the Velociraptor images!
What dinosaur was named the “swift seizer” and had a vicious hindfoot claw that could tear into its vulnerable prey?
With appearances in everything from Jurassic World to memes, the Velociraptor is one of the best-known dinosaurs. “Small but vicious” accurately describes the Velociraptor. Standing hunched forward, these speedy carnivores didn’t let their smaller size deter them from taking down larger prey using their claws.

Species, Types, and Scientific Names
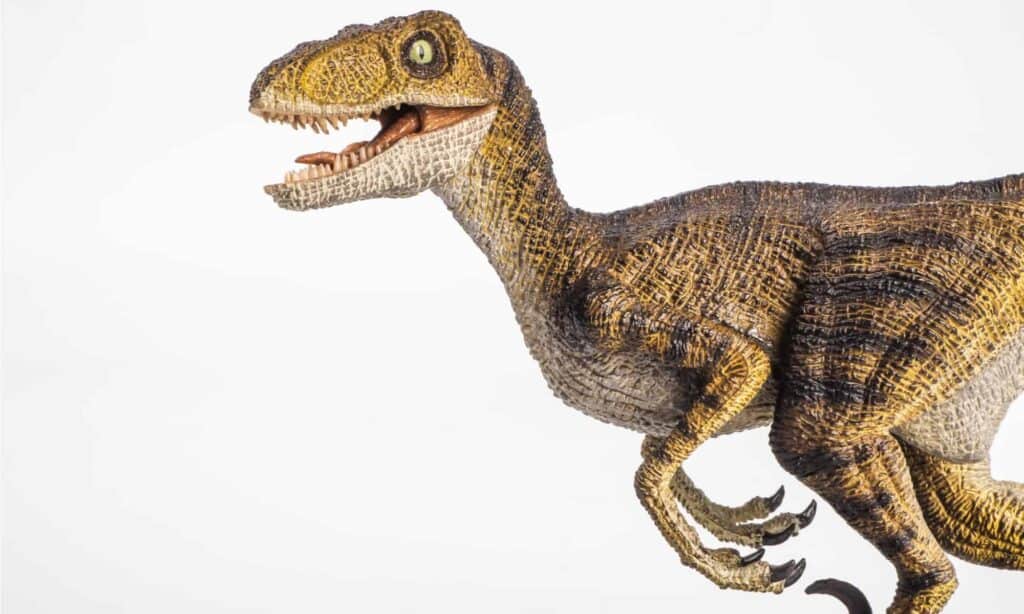

Velociraptors’ notorious stance had them walking on two feet but hunched over.
©kamomeen/Shutterstock.com
Velociraptor is a genus with two distinct species. The Velociraptor mongolienses is the type species that lived in Mongolia. The other species, Velociraptor osmolskae, was very similar and lived in Inner Mongolia, China. They belong to the Velociraptorinae subfamily of the Dromaeosauridae family. Dromaeosauridae includes other feathered therapods.
These dinosaurs are part of the Therapoda clade, also known as Therapods. All therapods have three-toed limbs and hollow bones. Other notable therapods include Tyrannosaurus rex and Allosaurus. Modern birds are also therapods and are much more closely related to these carnivorous dinosaurs than most people realize!
These creatures belonged to the phylum Chordata and the kingdom Animalia. They were dinosaurs and part of the Dinosauria clade. The complete taxonomy of the Velociraptor is outlined below.
Velociraptor
| Kingdom | Animalia | |
| Phylum | Chordata | |
| Clade | Therapoda | |
| Family | Dromaeosauridae | |
| Subfamily | Velociraptorinae | |
| Genus | Velociraptor | |
| Species | Velociraptor mongolienses, Velociraptor osmolskae |
Description and Size

Velociraptors had wings that were probably too small to use for sustained flight.
©kamomeen/Shutterstock.com
Velociraptors were much longer than they were tall. Adults were over 6 feet long and over 1.5 feet tall when measured at the hip, which was the tallest part of their stature. They stood on two legs but leaned far forward, even when they were standing still. Their front hands were more like wings in flexibility, although it is likely that they did not fly.
They could weigh over 30 pounds and were considered mid-sized in their family. However, there were plenty of larger carnivorous therapods, such as the T. rex.
One of the most interesting things about these creatures is actually their similarity to modern birds. They had feathers on most of their bodies and probably had visible wings. Quill knobs are visible in some Velociraptor specimens. This tells scientists that these dinosaurs definitely had feathers. It cannot tell scientists whether or not they were capable of flight, however. Even some modern birds with feathers do not have the ability to fly, such as ostriches.
The large body size and small wing size meant that Velociraptors probably didn’t fly. They would not have had wings large enough to generate the lift required to get their bodies off the ground.
Diet

Scientists believe that Velociraptors were carnivores that ate small protoceratops (shown here) and lizards.
©Dotted Yeti/Shutterstock.com
These creatures were carnivores with sharp teeth capable of tearing into the flesh of their meals. Their teeth were serrated and could cut through even tough, fibrous meat. Scientists believe that they were two means through which Velociraptors found and ate their meals.
The sharp, curved talon on the Velociraptor’s hindfeet was a formidable weapon. A Velociraptor could have used it to attack other small dinosaurs, small prehistoric mammals, insects, and lizards. It worked similarly to talons on today’s birds of prey to hook into their prey. They could have hooked into the softer parts of their prey, including the belly or throat.
One specimen showed a Velociraptor in combat with the herbivore Protoceratops. Unfortunately for both dinosaurs, a sandstorm or landfall buried them both before either could win the match. It does teach scientists a lot about how these dinosaurs attacked and fought, however.
Other specimens show that Velociraptors scavenged and fed on prey that was already taken down. Bite marks on the bones of another Protoceratops showed that the raptor ate the remaining meat and chewed on the bones of the carcass.
Habitat – When and Where It Lived
Mongolia was home to Velociraptors 80 million years ago.
©Johnstocker Prodution/Shutterstock.com
Velociraptors lived during the Cretaceous Period, between 85.8 to 70.6 million years ago. It was alive at the same time as the Triceratops, Spinosaurus, and formidable Tyrannosaurus rex. Scientists do not know exactly when it went extinct.
These dinosaurs lived in modern-day Mongolia. V. mongolienses specimens have only been found in Mongolia, specifically in the Djadochta Formation. This area of the Gobi desert is full of fossilized remains. V. osmolskae remains have been discovered in the nearby Barun Goyot Formation, also in Mongolia.
These locations were sandy and dry in the Velociraptor’s time, similar to the way that they are today. Researchers know this due to the conditions and evidence that is present on the buried fossils in these formations.
Threats And Predators
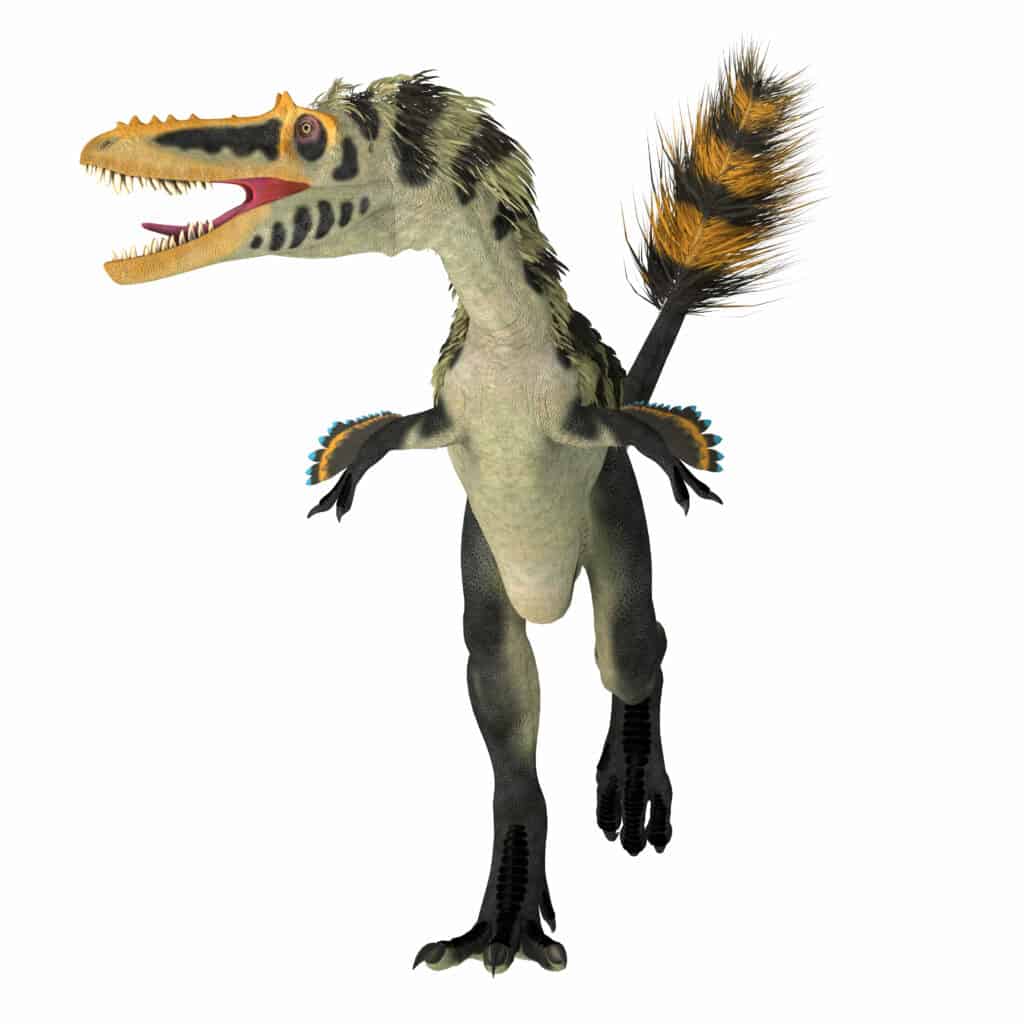

The
Alioramuswas larger than the Velociraptor and one of its main predators.
©Catmando/Shutterstock.com
Other carnivores were the biggest threat to Velociraptors. While their talon was effective in a fight or when hunting prey, it was no match for the larger size and speed of big carnivores that walked the earth during the late part of the Cretaceous. It is likely that Alioramus, Tarbosaurus, Oviraptorosaurs, and Troodontids ate Velociraptors.
Velociraptors fought with each other as well, resulting in injuries that could be life-threatening. One fossil shows other Velociraptor bite marks on its bones. Because these bite marks do not show signs of healing, the Velociraptor that was bitten probably died from the injuries.
Young Velociraptors
Like all dinosaurs, Velociraptors laid eggs. Their young were particularly vulnerable while still in their shell or when newly hatched. They were smaller and less able to run or defend themselves from predators. Some dinosaurs even hunted for eggs as a tasty treat.
Discoveries and Fossils – Where It was Found

Megatherium americanum and Velociraptors can be viewed at the
American Museum of Natural History.
Velociraptor fossils are some of the most fascinating that show how these dinosaurs lived and fought. The “Fighting Dinosaurs” discovery made in 1971 in the Djadochta Formation shows a Velociraptor and a Protoceratops in combat. The Velociraptor’s hindfoot claw is in the neck of the Protoceratops, probably going for its jugular vein or other vital part of the body. The Protoceratops had broken the right arm of the Velociraptor.
The two dinosaurs were preserved in such an interesting way because of the way that they died. Surprisingly, neither dinosaur emerged victorious from their fight. Instead, a sandstorm buried them so quickly that they weren’t even able to disengage from their fight. Because of this, scientists know how these two animals fought.
Extinction – When Did It Die Out?
Velociraptors went extinct at the end of the Cretaceous period, along with most other species on Earth. This extinction event is attributed to an asteroid strike in present-day Mexico that dramatically changed the Earth’s environment in a short time. Most species were unable to survive the new environment, which led to over 75% of species on Earth becoming extinct.
Similar Animals to The Velociraptor
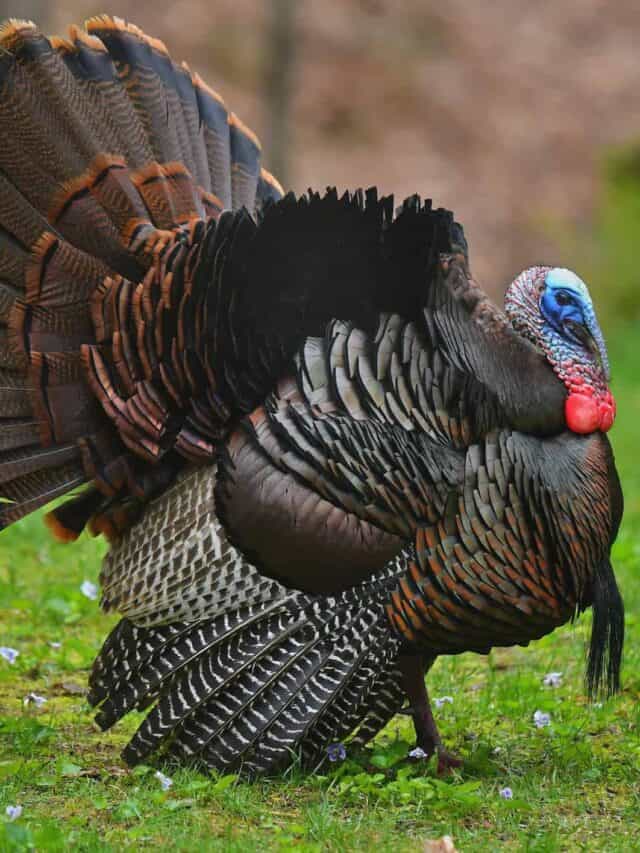

Modern-day turkeys and chickens are descendants of Velociraptors.
©iStock.com/Robert Winkler
- Chickens: Believe it or not, Velociraptors are some of the dinosaurs most closely related to modern-day birds. They had wing-like arms, feathers, and hollow bones. Velociraptors were also closer in size to chickens and turkeys than some other therapods.
- Deinonychus: The dinosaurs portrayed in the book and film Jurassic Park as Velociraptors are more similar to Deinonychus, another member of the Dromaeosauridae family. They also had feathers and a similar build, although they were larger than Velociraptors.
Velociraptor FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
When did Velociraptor live?
Velociraptor lived during at the end of the Cretaceous Period, between 85.8 to 70.6 million years ago. Scientists believe that it went extinct around 66 million years ago as part of a specific extinction event.
How big was a Velociraptor?
The medium-sized raptors were just over 30 pounds and over 6 feet long. They stood leaning forward and were just over 1.5 feet tall measured at their hip.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.