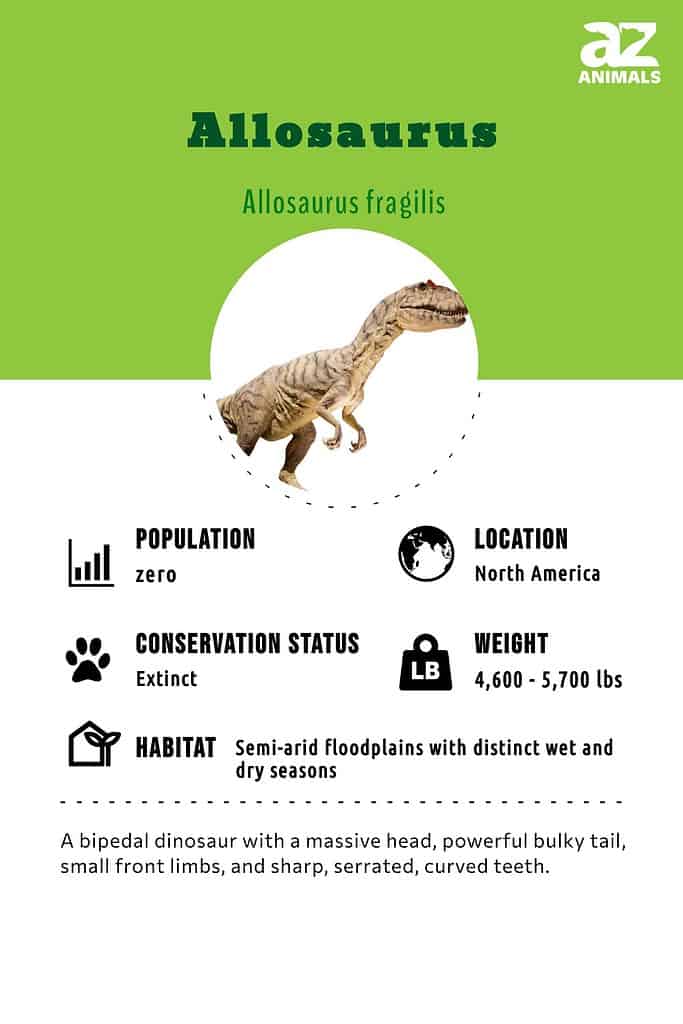
Allosaurus
Allosaurus fragilis
Differnt Lizard” or Allosaurus weighed around two tonnes that is almost equal to a car.
Advertisement
Allosaurus Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Reptilia
- Order
- Saurischia
- Family
- Allosauridae
- Genus
- Allosaurus
- Scientific Name
- Allosaurus fragilis
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Allosaurus Conservation Status
Allosaurus Facts
- Prey
- Stegosaurus, Brachiosaurus
- Group Behavior
- Social
- Fun Fact
- Differnt Lizard” or Allosaurus weighed around two tonnes that is almost equal to a car.
- Biggest Threat
- Allosaurus
- Most Distinctive Feature
- Small horn and ridges on the skull
- Gestation Period
- 6 months
- Litter Size
- 10-20 eggs
View all of the Allosaurus images!
Description and Size
Allosaurus fragilis is a species whose Greek translation is “different lizard.” It is considered a main part of the Theropod group, meaning it preys on flesh.
Fun Allosaurus Facts
They are one of the most dominant fossils found around the world which is why paleontologists had a lot to study. Here are a few facts related to its physical attributes.
- Allosaurus weighed about 4600 lbs or 2.3 tons and it had an average length of approximately 12 meters.
- The female Allosaurus (3.2 meters) was slightly shorter in height compared with the male Allosaurus (3.8 meters).
- The skull of the Allosaurus was quite large in comparison to its neck. In addition, it was elongated and carried ridges from the nose to the eyes. On top of the eyes, there were small curved horn-like structures.
- The teeth of Allosaurus were sharp, dagger-like, and five to ten centimeters long. But an interesting thing is that they were curved on the inside, helping them in hunting and holding down their prey.
- It had bigger hind limbs in comparison with its forelimbs but the difference is not that large. It was a bipedal organism with three fingers on each hand and three toes on each foot. But there was another short toe on the inner side of each of its feet.
- It had quite a heavy tail and a relatively light build that helped it to maintain balance.
- The tail of the Allosaurus was quite large and pointy. It is made up to be half the length of the whole organism.
- Another interesting thing about this dinosaur is that it had vertebrae, unlike any other dinosaur. It had a series of concave bones that resembled an hourglass-type structure.
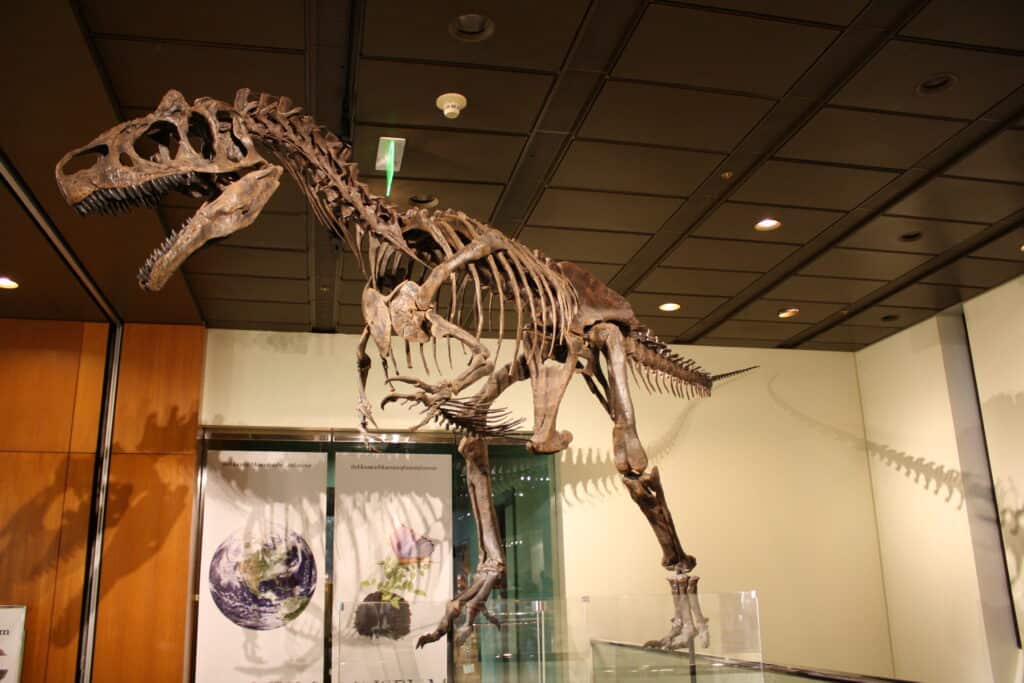

(Big Al II) was discovered in the Morrison Formation.
Evolution
Not much is known of the evolution of Allosaurus, but allosaurus fragilis may have evolved from allosaurus jimmadseni, since it occurred a few million years before. Allosaurus fragilis had adapted improvements in vision and strength. There is no concrete evidence of the animals’ origin at present.
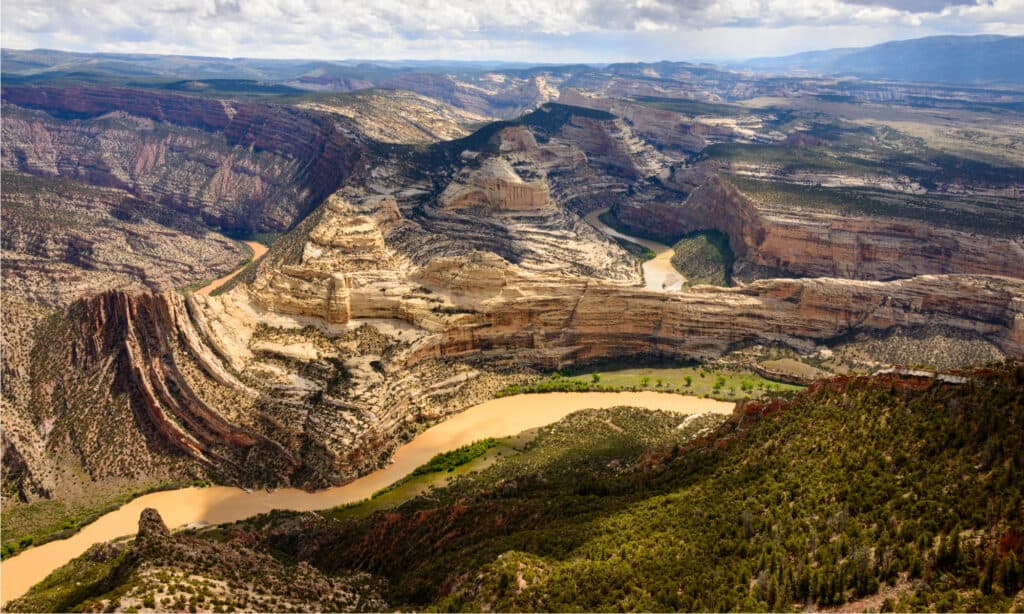

Dinosaur National Monument, Colorado, is part of the Morrison Formation.
©Zack Frank/Shutterstock.com
The Morrison Formation
Many allosaurus fossils have been discovered in the Morrison Formation, a rock unit from the Late Jurassic (155 million years ago – 148 million years ago). It extends throughout the Western United States and often contains the fossils of dinosaurs including Apatosaurus, Stegosaurus, Allosaurus, and others. The river channels of the formation contain the most dinosaur bones. The almost complete skeletons of two Allosaurus jimmadseni – “Big Al” and “Big Al II” were found in the Morrison Formation.
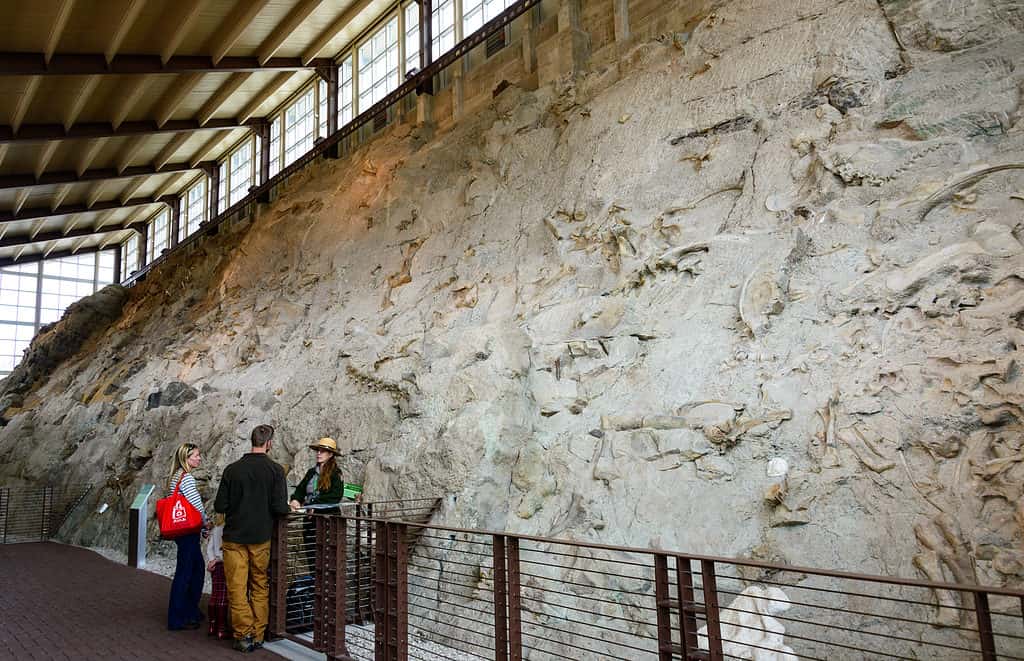

Dinosaur National Monument “Wall of Bones” was left intact to portray the number of fossils present in the Morrison Formation.
©Zack Frank/Shutterstock.com
Species
There is some debate in the scientific community over the number of Allosaurus species, but there are three that are included by all:
- Allosaurus fragilis, the youngest and most common, this species was better suited for hunting and tackling large prey than the older species. The skull shows that the animal had better binocular vision.
- Allosaurus jimmadseni, this species is older and occurs a few million years earlier than A. fragilis. The famous specimens, “Big Al” and “Big Al II” are both of this species. It has differently shaped skull openings and indications of poor binocular vision. This allosaurus had more crests on its head – near the eye and around the nasal area.
- Allosaurus europaeus, fossils of this species were found in Portugal. During the late Jurassic, the Atlantic Ocean was very narrow. Dinosaurs could easily have traveled between the continents. There are not enough remains of this species to determine if it is definitely an allosaurus species.
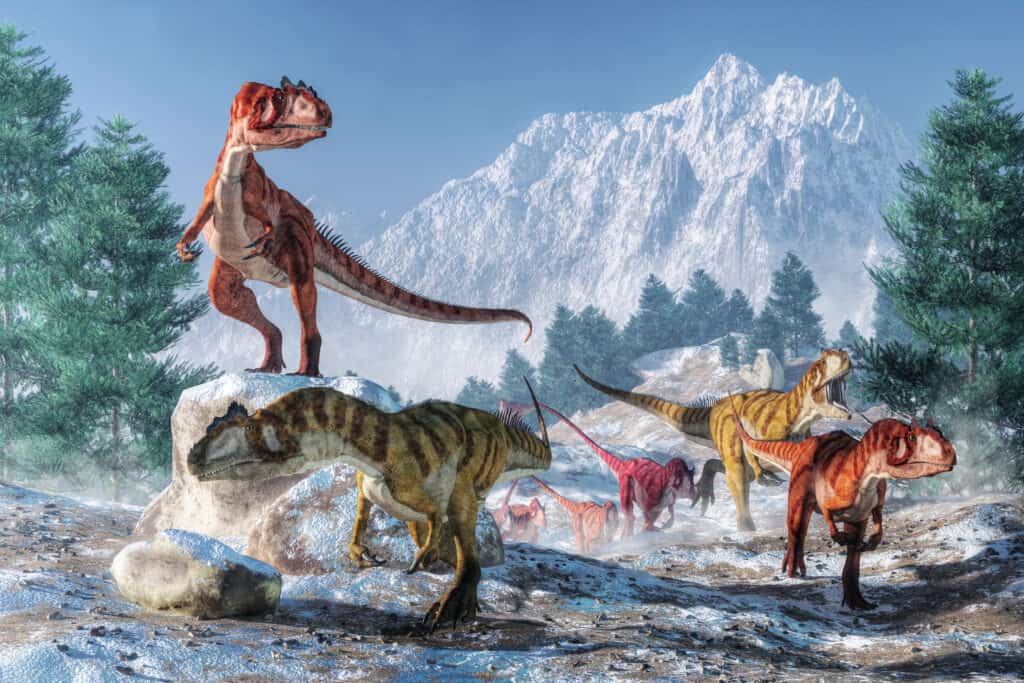

Many scientists believe that
Allosaurushunted in packs.
©Daniel Eskridge/Shutterstock.com
Diet – What Did Allosaurus Eat?
As is seen through its physical attributes, Allosaurus is a carnivore. It had a build designed for speed that suggests it used to hunt and prey. Along with the legs, its claw-shaped fingers can easily be used to grasp the prey. Although it did not have a strong bite due to smaller teeth, the Allosaurus is predicted to have used its skull and ridges to kill its hunt in the same manner as birds of prey do today.
The diet of Allosaurus mainly consisted of large herbivores like Ornithopods, Sauropods, Stegosaurus, or Apatosaurus. Many studies have even suggested that it used to eat animal carcasses and was a scavenger. Now, there may be a debate on whether or not it hunts dead animals, but one thing that every study agrees on is that they ate meat.
Habitat – When And Where It Lived?
Allosaurus existed in the late Jurrasic period and was quite prevalent till the Turonian period. Their fossils have been found from over 163 million years ago and even from over 89 million years ago. Most of the fossils are found in the USA and the first one was discovered in Colorado in the Morrison Formation.
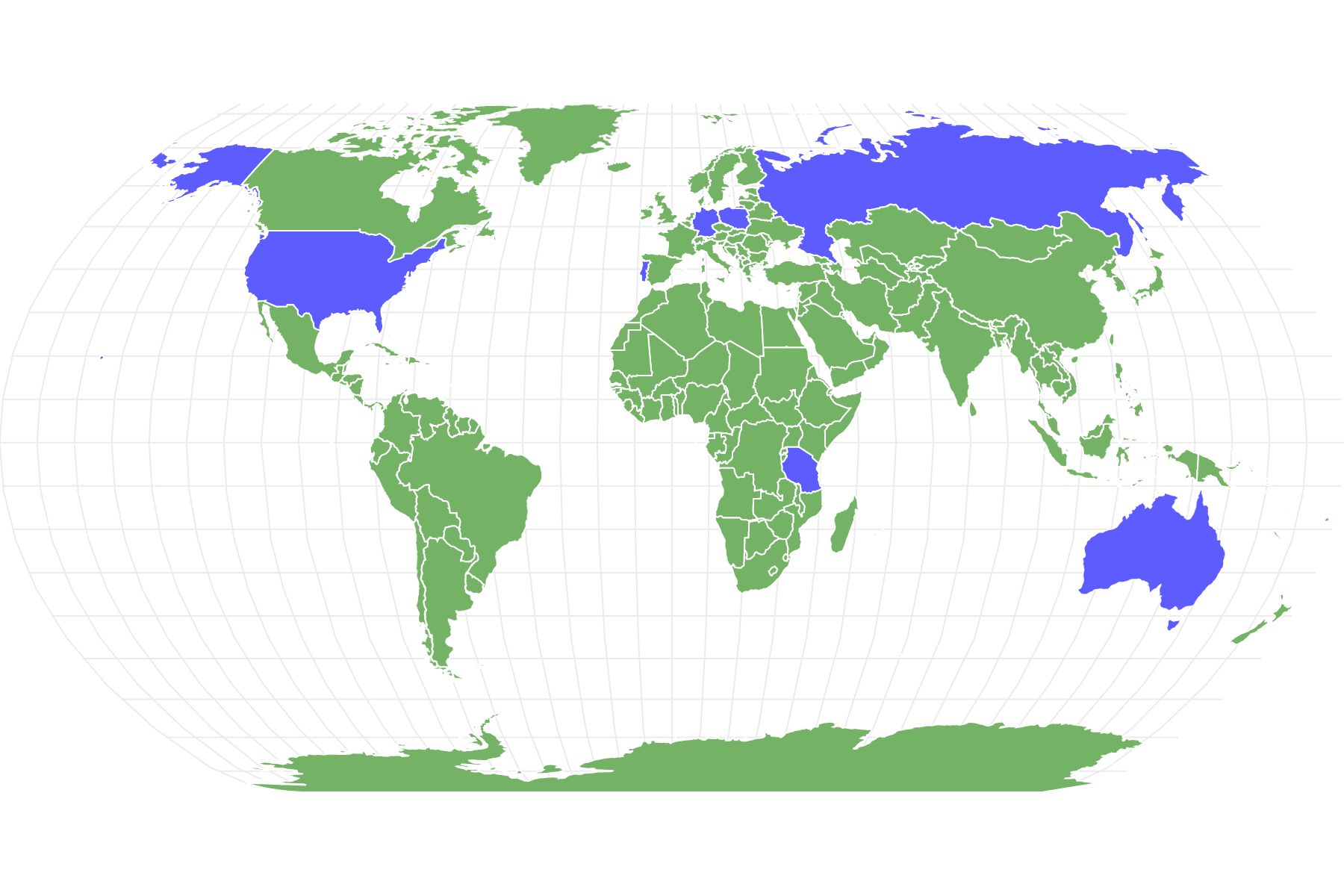
They were mainly spread across North America, Europe, and Africa. Their habitat was believed to be near plain lands and streams. Some of them even lived in forests with rivers flowing between them.
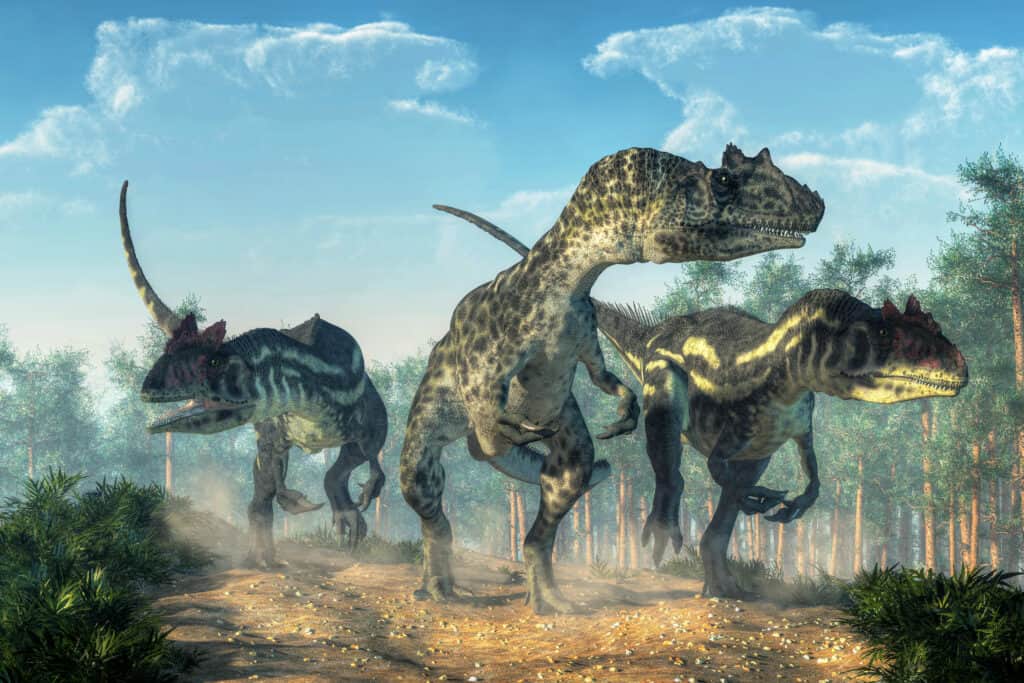

It is unclear if the Allosaurus hunted together or hunted each other. Cannibalism is probable.
©Daniel Eskridge/Shutterstock.com
Behavior
The Allosaurus mostly lived in groups and were rather sociable. They even hunted in the form of groups. But the studies have shown quite a disparity in their group behavior. Some suggest that they fought against each other while others seem to think that a group of Allosaurus hunted the same prey.
There are signs of injuries on their bones and fossils that seem to support this idea. However, thinking of carnivorous animals hunting the same prey seems quite out of the ordinary. Hence, it is very much possible that they depicted antagonistic and maybe even cannibalistic behavior.
Threats And Predators
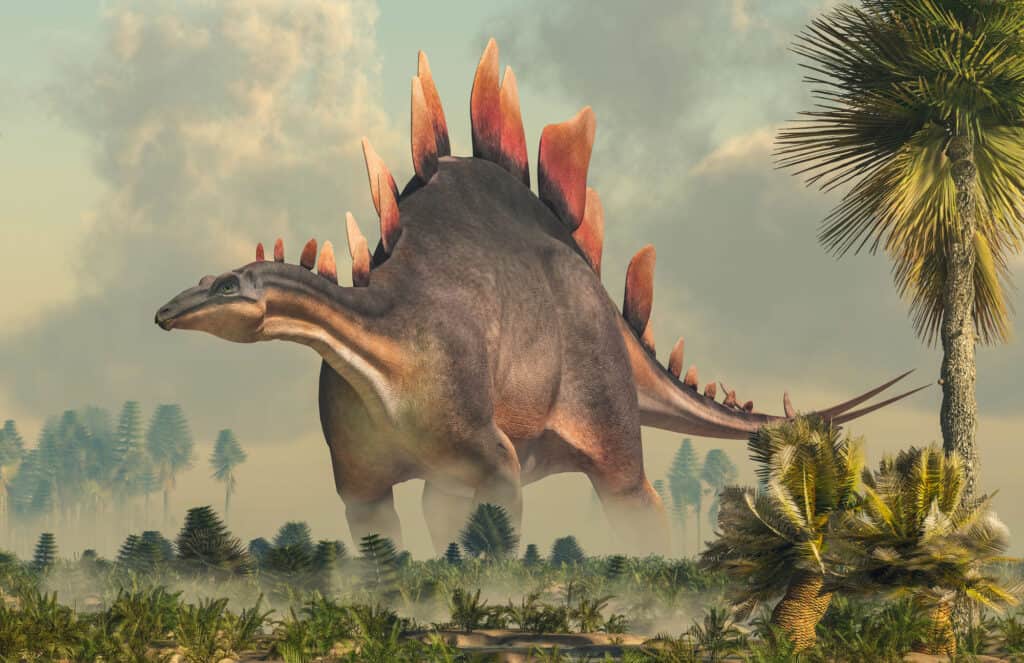

The Stegosaurus was a threat to the Allosaurus with fossils showing injuries the two dinosaurs inflicted on each other.
©Daniel Eskridge/Shutterstock.com
Many studies have shown that the Stegosaurus was a fierce threat to the Allosaurus. The Stegosaurus was a plant eater and had a spiky tail. Many fossils exist that show injuries on one dinosaur due to the other. So, it can be believed that there was a raging battle between the two.
Apart from that, the Torvosaurus and Ceratosaurus were known predators of Allosaurus. They were also carnivores but had similar or smaller sizes than the Allosaurus. But the battle was mostly on who gets to eat the prey.
However, one distinct quality of Allosaurus is its cannibalism. Being one of the biggest predators in the Late Jurassic era, they were a threat to themselves.
Discoveries and Fossils – Where It was Found
Allosaurus is one of the most abundant fossils found to date. Most of these fossils are found in the US but were also present in Europe and Africa.
The first fossil of an Allosaurus was found in the year 1869 in Colorado. It was believed to be soft horse hoofs by locals but then was later studied to be the vertebrae of an Allosaurus.
Many fragments were discovered later on by many scientists like its vertebrae, part of a rib, a tooth, and even a toe bone. But the biggest discovery was made in the year 1945. A minimum of 73 dinosaurs were found in Utah and out of 73, 46 were at least the specimens of an Allosaurus. The fossils were of both juvenile and adult dinosaurs.
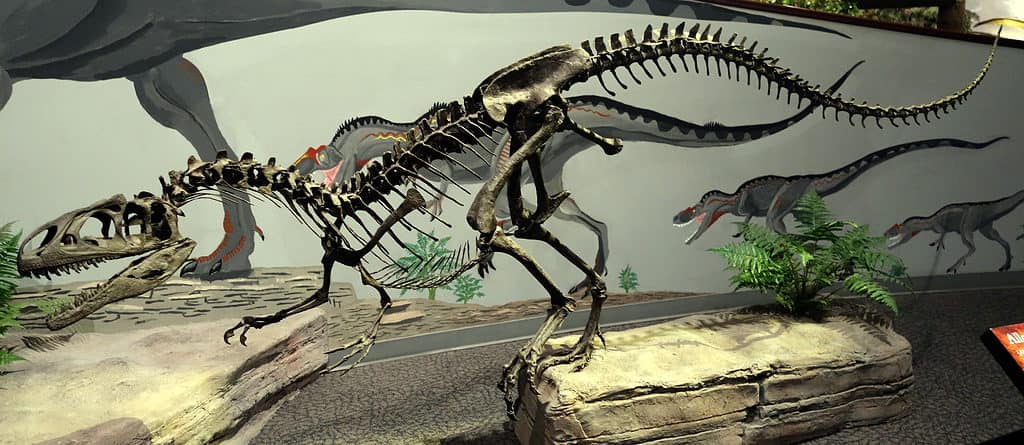

Allosaurus skeletons have been found in the Morrison Formation in Colorado.
©Etemenanki3, CC BY-SA 4.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0>, via Wikimedia Commons – Original / License
To this day, it remains a mystery how such a large resource of fossils was found in one place. But there are some basic assumptions.
Some scientists think there was a flood that carried the carcasses of the dead Allosaurus to one place while others think they got trapped in a mud slope. Even a drought could have brought them all into one place. So, it is only safe to assume and nothing concrete enough to make it a theory.
After that, many fossils of an Allosaurus have been found in Portugal and Poland. But another great discovery was in the year 1991 in Wyoming.
A fossil about 95% complete was found that contributed majorly to the Paleontological study. It was named “Big Al.” Then, another complete specimen was discovered in 1996 that was considered the biggest complete specimen to date. It was named “Big Al II.”
Extinction – When Did It Die Out?
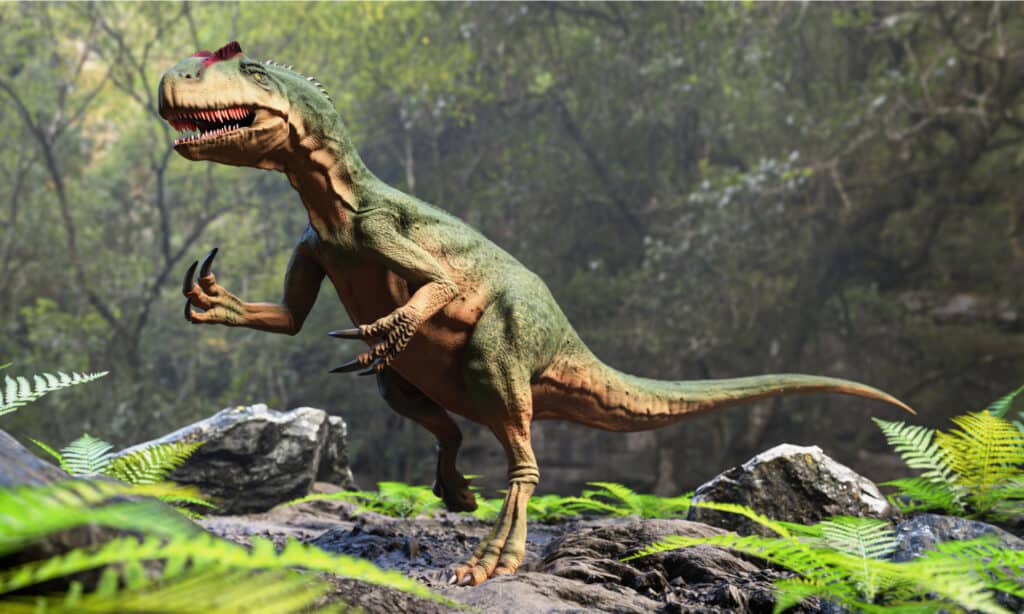

Allosaurus became extinct around 144 million years ago – the reasons are unknown but it could have been due to drought or disease.
©MattLphotography/Shutterstock.com
Data shows that Allosaurus went extinct around 144 million years ago. The cause is uncertain but there are certain theories about the species’ termination. Some suggest that a drought had befallen the then-era and a lot of dinosaurs along with Allosaurus died due to the cause. The biggest fossil found in Utah also supports this theory. But the latest fossil discovered, named Big Al II, was found to have pathological infections. Hence, it could be that there was an infection spreading but nothing can be confirmed.
Similar Animals to The Allosaurus
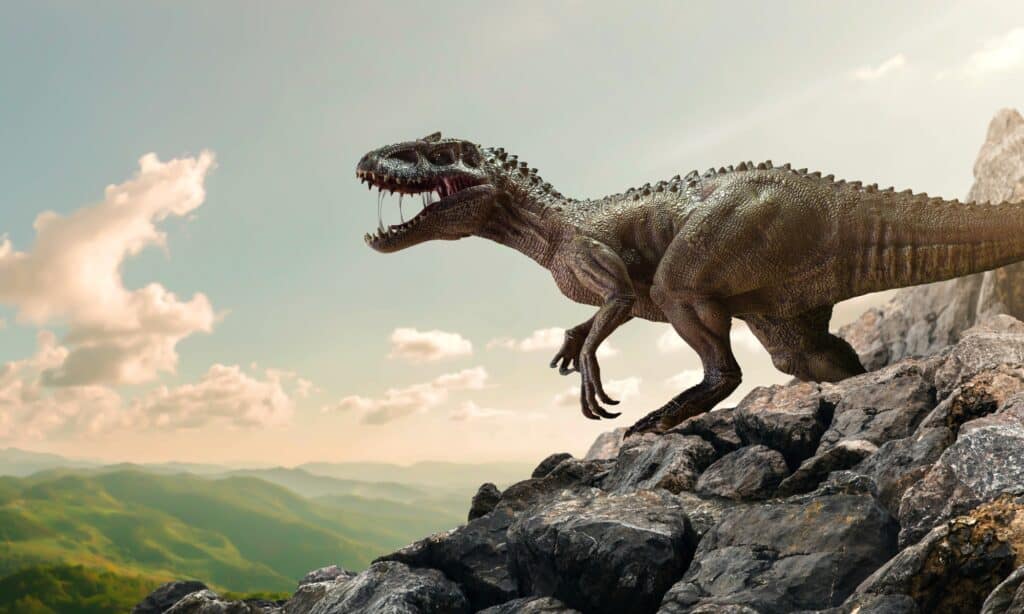

Dinosaur
Tyrannosaurus rexclosely resembled Allosaurus.
©iStock.com/chaiyapruek2520
- Tyrannosaurus rex (T-Rex) – a carnivorous dinosaur with sharp teeth, a long tail, small arms, and a heavier body. It resembled Allosaurus but it had two fingers on each of its hands rather than the three of an Allosaurus.
- Ceratosaurus – another carnivore from the same era as that of an Allosaurus, this animal weighed two tons too. It had a long tail and similar anatomy. However, it had a distinctive horn and four fingers instead of three.
Allosaurus FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Is An Allosaurus Bigger Than A T-Rex?
No. The T-Rex was significantly bigger than an Allosaurus as it carried a height of 12-15 meters. In contrast, the Allosaurus had a height of 8-12 meters.
Was Allosaurus A Top Predator?
In its time, Allosaurus was one of the biggest predators. Having the most abundant fossils in the Morrison formation, also suggests that they were on the top.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- Jurassic-pedia / Accessed June 9, 2022
- Kidadl / Accessed June 9, 2022
- Britannica / Accessed June 9, 2022
- Animals / Accessed June 9, 2022
- Wikipedia / Accessed June 9, 2022
- Fossilera / Accessed June 9, 2022