Fulvous Whistling Duck
Dendrocygna bicolor
They build a ramp from their nest, which leads to a nearby water source
Advertisement
Fulvous Whistling Duck Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Aves
- Order
- Anseriformes
- Family
- Anatidae
- Genus
- Dendrocygna
- Scientific Name
- Dendrocygna bicolor
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Fulvous Whistling Duck Conservation Status
Fulvous Whistling Duck Facts
- Prey
- Seeds, bulbs, stems, grasses, and insects
- Main Prey
- Aquatic plants
- Name Of Young
- Ducklings
- Group Behavior
- Social
- Fun Fact
- They build a ramp from their nest, which leads to a nearby water source
- Estimated Population Size
- 1.3 to 1.5 million
- Biggest Threat
- hunting, trapping, pesticide ingestion, collisions
- Most Distinctive Feature
- Reddish-yellow coloring, odd proportions
- Distinctive Feature
- Long legs, long neck
- Wingspan
- 33 to 40 inches
- Incubation Period
- 24 to 26 days
- Age Of Fledgling
- 2 months
- Habitat
- Lowland marshes and swamps
- Diet
- Omnivore
- Lifestyle
- Diurnal
- Type
- Bird
- Common Name
- Fulvous whistling duck
- Number Of Species
- 1
- Location
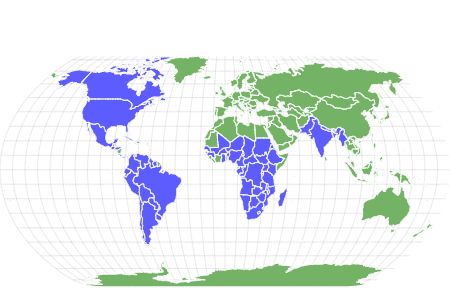
- North America, South America, Africa, Asia
- Nesting Location
- Floating vegetation in weedy rice fields
- Migratory
- 1
View all of the Fulvous Whistling Duck images!
“These noisy birds give a clear whistling call, “Kee-wee-ooo,” on the ground or while in flight.”
Summary
The fulvous whistling duck (Dendrocygna bicolor) is a large, oddly-shaped duck from the whistling subfamily. It lives across the tropical regions of four continents, inhabiting lowland marshes and swamps in rice fields. This species spends its days walking and swimming through water, searching for aquatic plants. Often, you will find them in small family groups or larger mixed-species flocks. Learn more about this whistling duck, including where it lives, what it eats, and how it behaves.
5 Amazing Fulvous Whistling Duck Facts
- You can find the fulvous whistling duck along the Gulf Coast and Southern Florida in the United States.
- They avoid wooded and mountainous areas, preferring flat, open country in flooded rice fields.
- They build a ramp from their nest, which leads to a nearby water source.
- Fulvous means “reddish-yellow,” which describes the duck’s coloring.
- Whistling duck parents will defend their nests by flapping their wings, biting, and kicking.
Where to Find the Fulvous Whistling Duck
Fulvous whistling ducks inhabit parts of North America, South America, Africa, and Asia, living in over 70 countries, including the United States, Mexico, Brazil, India, and Kenya. This species breeds in tropical regions of the world like the Southern United States, South America, sub-Saharan Africa, and India. In the United States, you will primarily find them along the Gulf Coast in Texas, Louisiana, and Southern Florida. Their habitats include lowland marshes and swamps in rice fields. They prefer flat, open country as opposed to wooded or mountain areas.
Fulvous Whistling Duck Nest
Males and females choose the nesting site, typically in weedy rice fields amongst weeds and grasses or on floating vegetation. They construct a platform using stalks and dead marsh grasses, forming a bowl shape and building a ramp that leads to a water source. They add more material as the original begins to sink or decay.
Scientific Name
The fulvous whistling duck (Dendrocygna bicolor) belongs to the Anseriformes order in the Anatidae family, encompassing water birds like ducks, geese, and swans. The Dendrocygna genus comprises the whistling ducks or tree ducks. Dendron is Ancient Greek for “tree,” and Cygnus is Latin for “swan.” The specific name, bicolor, is Latin for “two-colored.” The common name, fulvous, is reddish-yellow, which describes the duck’s coloring. The fulvous whistling duck has no recognized subspecies.
Size, Appearance, & Behavior
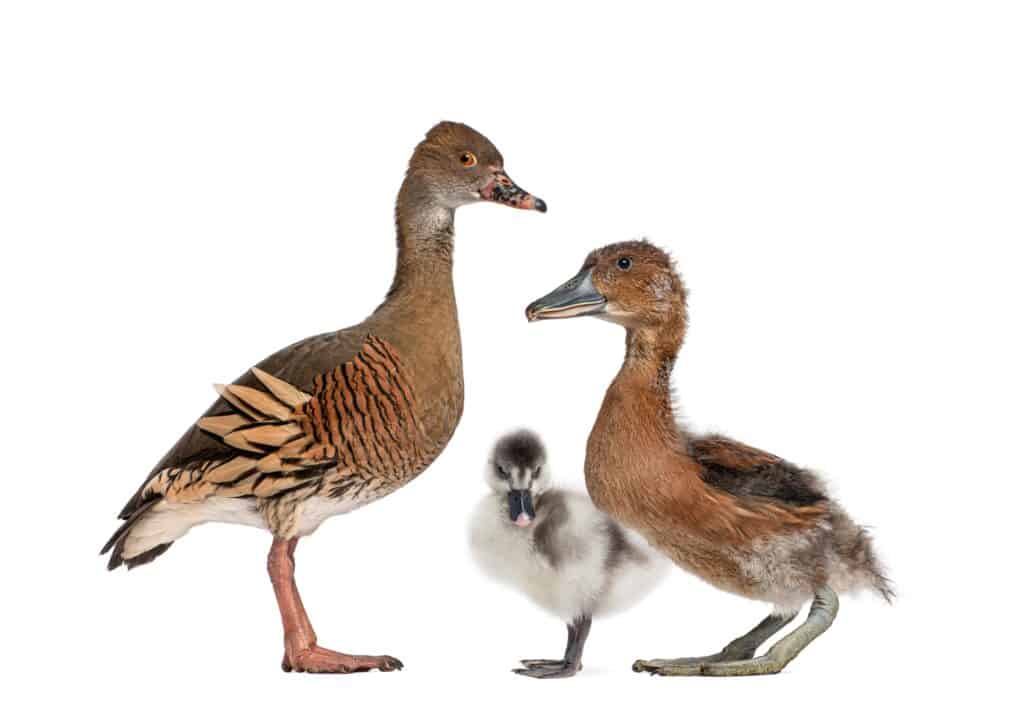

Fulvous Whistling Duck young are relatively independent shortly after hatching and can dive, swim, and find food.
©Eric Isselee/Shutterstock.com
The fulvous whistling duck is a large, long-legged tree duck with odd proportions. This bird measures 18 to 21 inches long and weighs 25 to 37 ounces, with a 33 to 40-inch wingspan. It’s similar in size to a mallard, except it has a longer neck and legs, with a relatively long bill. This species is varying shades of brown, with a rich buff or fulvous-colored head, neck, and breast. Their wings and backs have broad black bars, and their flanks have long white stripes. A dark brown or black line runs from the crown to the base of the mantle. Females have similar colors, except they feature duller plumage.
These noisy birds give a clear whistling call, “Kee-wee-ooo,” on the ground or while in flight. They are social birds who often flock together in small family groups and nest with other duck pairs. The fulvous duck will also mix with other whistling species outside the breeding season. The subfamily of whistling ducks is often distinguishable in flight due to their large feet and long legs, which trail behind them. They are strong fliers and readily take flight, traveling relatively fast. However, their speed is unknown.
Migration Pattern and Timing
The fulvous whistling duck is a short-distance migrant or year-round resident in its environment. They breed in Southern California, along the Gulf Coast, and West Indies in North America. They also live year-round in Mexico, the Bahamas, and parts of Central America. It moves seasonally in its South American, African, and Asian ranges in response to wet seasons.
Diet
The fulvous whistling duck is an omnivore who forages day or night with mixed-species flocks.
What Does the Fulvous Whistling Duck Eat?
Their diet consists primarily of aquatic plants and grass seeds but they will also eat bulbs, stems, and grasses. During breeding, females include aquatic insects, worms, and mollusks to prepare for egg-laying. They forage by picking through plant items while walking, swimming, and diving underwater. You will likely find them searching for food in damp rice fields.
Predators, Threats, and Conservation Status
The IUCN lists the fulvous whistling duck as LC or “least concern.” Due to its extensive range and large population, this species does not meet the “threatened” status criteria. The biggest threats to this duck include hunting, trapping, pesticide ingestion, collisions with power lines, and habitat loss and degradation from damming and invasive freshwater plants.
What Eats the Fulvous Whistling Duck?
Their primary predators include red foxes, northern harriers, raccoons, and bobcats. Skunks and raccoons are common nest predators of fulvous whistling ducks. But these duck parents defend their young by beating their wings, biting, and kicking.
Reproduction, Young, and Molting
Fulvous whistling ducks form monogamous pair bonds and many mate with one partner for life. Their courtship involves aerial displays and paired swimming. Females lay an average of 12 to 14 white eggs, which they occasionally drop in other bird’s nests from different species. Both sexes take turns incubating for 24 to 26 days but may leave the eggs unattended on warm days. Their young are relatively independent shortly after hatching and can dive, swim, and find food. They fledge the nest around two months and become sexually mature after one year. These ducks live an average of 5 years but can survive up to 11 years.
Population
The global fulvous whistling duck population is estimated to number 1.3 to 1.5 million mature individuals. Most global populations are decreasing, but North America shows an increasing trend. The decline doesn’t appear rapid enough to change their status to “threatened.”
Related Animals:
View all 91 animals that start with FFulvous Whistling Duck FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Where are fulvous whistling ducks found?
This species lives in North America, South America, Africa, and Asia across 70 countries. They inhabit lowland marshes and swamps, particularly flooded rice fields.
Are fulvous whistling ducks endangered?
The IUCN lists the fulvous whistling duck as LC or “least concern.” Due to its extensive range and large population, this species does not meet the “threatened” status criteria.
What does a fulvous whistling duck look like?
The fulvous whistling duck is a large, long-legged tree duck with odd proportions. This species is varying shades of brown, with a rich buff or fulvous-colored head, neck, and breast. A dark brown or black line runs from the crown to the base of the mantle
Why are they called whistling ducks?
They have distinct whistling calls, sounding like “Kee-wee-ooo.”
Do fulvous whistling ducks migrate?
The fulvous whistling duck is a short-distance migrant or year-round resident in its environment. They breed in tropical climates and move seasonally in response to wet seasons.
What do fulvous whistling ducks eat?
Their diet consists primarily of aquatic plants and grass seeds but they will also eat bulbs, stems, and grasses.
Can fulvous whistling ducks fly?
They are strong fliers and readily take flight, traveling relatively fast. However, their speed is unknown.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- Red List / BirdLife International, Available here: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/22679746/92827620
- JSTOR / The Wilson Bulletin / William L. Hohman, Timothy M. Stark and Joseph L. Moore, Available here: https://www.jstor.org/stable/4163646
- JSTOR / The Journal of Wildlife Management / Richard E. Turnbull, Fred A. Johnson, Maria de los A. Hernandez, Willis B. Wheeler and John P. Toth, Available here: https://www.jstor.org/stable/3809608
- Maryland Zoo, Available here: https://www.marylandzoo.org/animal/fulvous-whistling-duck