Hercules Beetle
Dynastes hercules
This dynastine scarab beetle makes a weird huffing sound when it’s disturbed.
Advertisement
Hercules Beetle Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Arthropoda
- Class
- Insecta
- Order
- Coleoptera
- Family
- Scarabaeidae
- Genus
- Dynastes
- Scientific Name
- Dynastes hercules
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Hercules Beetle Conservation Status
Hercules Beetle Facts
- Name Of Young
- Larva or grub
- Group Behavior
- Mainly solitary
- Fun Fact
- This dynastine scarab beetle makes a weird huffing sound when it’s disturbed.
- Estimated Population Size
- Unknown, but the beetle does not have special conservation status.
- Biggest Threat
- Habitat destruction and pollution
- Distinctive Feature
- Hard, armoured shell and horn-like pincers
- Gestation Period
- 30 days
- Litter Size
- 100
- Habitat
- Rainforests of the mountains and lowlands
- Predators
- Bats, Rats, Birds
- Diet
- Herbivore
- Average Litter Size
- 100
- Favorite Food
- Decaying wood
- Type
- Insect
- Common Name
- Hercules Beetle
- Number Of Species
- 10
- Location
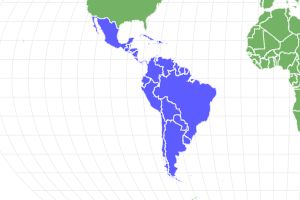
- South and Central America and the Lesser Antilles
Hercules Beetle Physical Characteristics
- Color
- Yellow
- Black
- Green
- Skin Type
- Exoskeleton
- Top Speed
- 8.9 mph
- Lifespan
- Two and a half years, in total
- Weight
- 1.2 ounces for male, 0.57 ounces for female
- Length
- Average 2.43 inches for females, 3 inches for male plus horns longer than body. There have been rumors of a male that was 7.09 inches long.
- Age of Sexual Maturity
- 15 to 22 months
View all of the Hercules Beetle images!

“The Hercules Beetle is the world’s longest beetle!”
The Hercules beetle is one of the world’s largest insects, and it is not just large. The males have long horns that grow from their heads and the middle of their bodies. They come together to resemble pincers or a claw.
The larva, which is curved, white, or yellow with a black head, may even be bigger than the adult, but they lose some weight during the ordeal of pupation. The Hercules beetle also flies, though clumsily. It’s one of the biggest flying insects as well.
5 Incredible Hercules Beetle Facts!
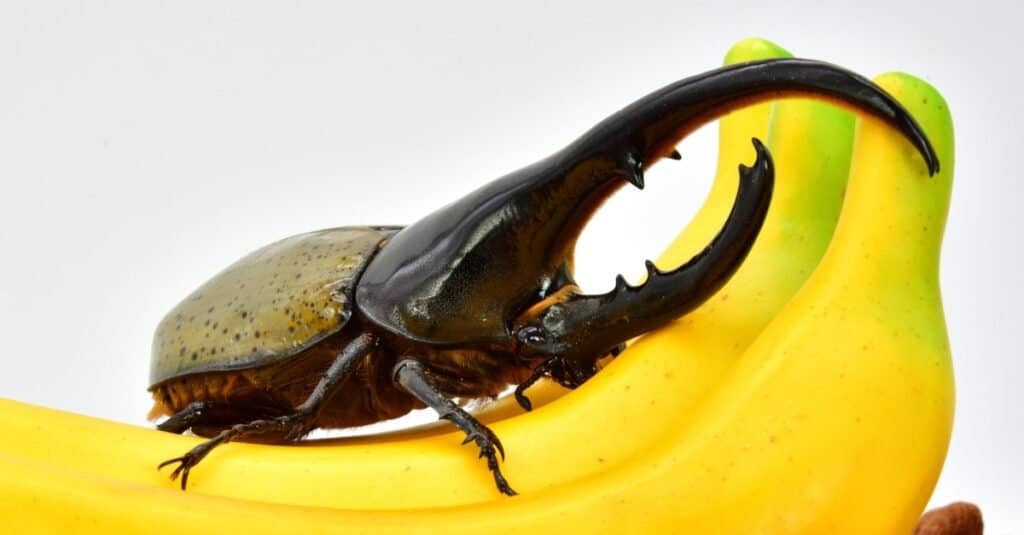

Hercules beetle sitting on bananas.
©fukushima_insectarium/Shutterstock.com
Here are some more facts about this amazing insect:
- The Hercules beetle spends most of its life as a larva. It can take a larva, or grub two years to turn into an adult, while a captive adult only has a lifespan of three to six months. However, some people claim that a well-cared-for Hercules beetle can have a lifespan of as much as a year.
- Only the males have trademark horns. They use them to fight other males during the breeding season.
- The larva of a Hercules beetle can grow 4.5 inches long and weigh over 3.5 ounces. They are good sources of protein and are often eaten. People season them, wrap them in banana leaves then roast them over a fire.
- The beetle is a type of dynasty scarab, which means it is big and has a robust body, clubbed antennae, and horns. The colors of their carapaces can have a metallic glint to them. Relatives of the Hercules beetle include the eastern Hercules beetle, which is not a subspecies but an entirely different species found in the eastern United States. The eastern Hercules beetle, Dynastes tityus is smaller than Dynastes hercules, and its horns are not as spectacular.
- The color of the hard front wings of the beetle, or the elytra changes color with the humidity. If it’s dry, the elytra are yellow or green, but when humidity is high they turn black.
Species, Types, and Scientific Names
The Hercules beetle is a type of scarab beetle, and its scientific name is Dynastes hercules. Dynastes is Greek for “master, lord or ruler,” and hercules comes from the Greek demigod of the same name who was known for his immense strength. There are at least 10 subspecies, though biologists don’t agree on all of them. They are:
- Dynastes hercules hercules
- D. hercules ecuatorianus
- D. hercules lichyi
- D. hercules morishimai
- D. hercules occidentalis
- D. hercules paschoali
- D. hercules reidi
- D. hercules septentrionalis
- D. hercules takakuwai
- D. hercules trinidadensis
Because of its horns, the Hercules beetle is also classified as a type of rhinoceros beetle.
Evolution and Origins
The process of evolution involves a number of unavoidable changes that lead to the emergence of new species (populations of various creatures), their environmental adaptation, and eventual extinction. Every species or organism has its roots in the biological evolution process.
The Hercules Beetle’s huge horns most likely evolved as a result of sexual selection, which is such a powerful driving factor. Females selectively bred for larger and larger horns over time because they gave sexual preference to males that could push aside rival males!
The Lesser Antilles, Central America, and South America are home to the Hercules beetle (Dynastes hercules), a species of rhinoceros beetle. It is one of the biggest flying insects on the planet and the longest type of beetle that is still alive.
Appearance
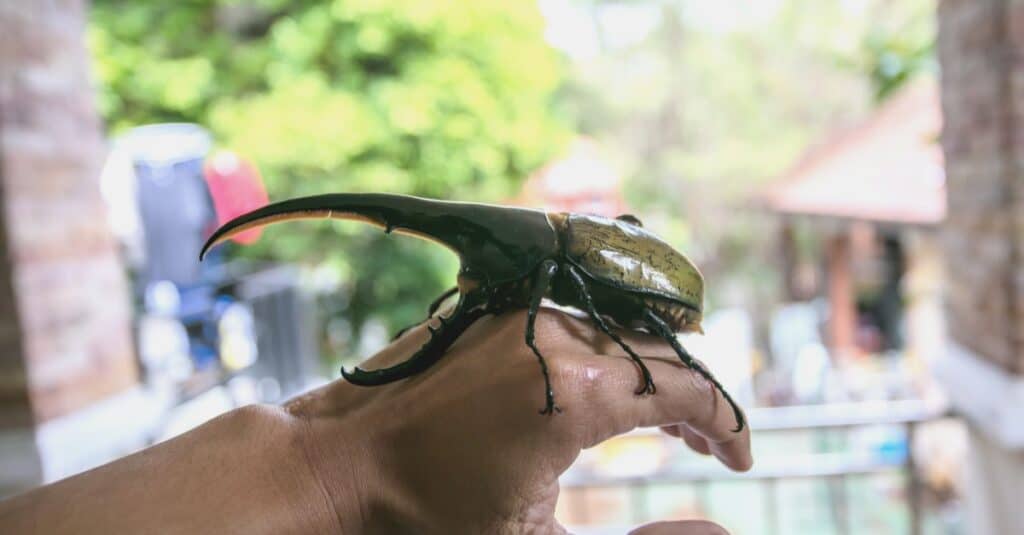

The claw-like horns on the male beetle, which may be as long as its body, give off an identifiable appearance.
©Tanawat Palee/Shutterstock.com
The appearance of the male beetle is unmistakable, with its claw-like horns that may be as long as its body. The horn that comes from the animal’s body is longer ta the one that comes from its head and both have teeth. The hornless female looks like a regular scarab beetle, with a heavy body. Her elytra are mostly brown or black and the rest of her body is black. Sometimes the elytra have a metallic sheen that is a distinguishing trait of scarab beetles.
Hercules beetles mate in the rainy season of their native country, which is in midsummer to early winter. Males famously fight to mate with females using their horns and can not only damage each other but damage the female they are fighting over. In the wild, the winner probably simply pushes the loser off of a tree limb.
The female is gravid for about a month before she lays as many as 100 eggs. She’ll deposit them either on the ground or in rotting wood. It takes around 27 days for the eggs to hatch. When they do, the larvae eat rotting wood and molt three times until they are of tremendous size. Then, they pupate and stay in that stage for around 32 days before the adult ecloses.
Though this dynasty scarab is native to Central America, South America, and islands in the Caribbean such as Trinidad and Tobago it is sold around the world as a pet, often for very high prices. It is especially popular for terraria in Japan and is considered a good luck charm.
The Hercules beetle can fly, though not very efficiently. It is sometimes seen flying around street lights, as it is nocturnal. The beetle makes a huffing sound if it’s picked up or bothered and also emits a bad-smelling odor.

©feathercollector/Shutterstock.com
Habitat
These beetles are naturally found in rainforests, whether they are in the mountains or in the lowlands. The huge grubs of these rhinoceros-type beetles live in the rotting wood that they eat, while the adults hide under leaf litter and inside logs.
Life Cycle

The Five-horned rhinoceros beetle (Eupatorus graciliconis) is known as the Hercules beetle, Unicorn, or Horn beetle, in tropical forests.
©Mark Brandon/Shutterstock.com
Although there is not much-documented information about the life cycle of a Hercules beetle in the world. A lot of knowledge has been gained through observations of captive-bred populations of these interesting creatures.
The mating season for adult beetles occurs during the rainy seasons (July through December). Females have an average gestation period of about 30 days from copulation to egg-laying. These beetles may lay up to 100 eggs on the ground or within deadwood. The eggs have an incubation period of about 27 days before they begin to hatch.
Once hatched, the larva may last up to two years! They will also go through three different stages of metamorphosis known as instars. The larvae are yellow with a back head and they can grow up to 11 cm in size. After the third stage, the pupal stage begins and lasts about 30 to 32 days. The Hercules beetle will then transition into adulthood and will live for three to six months in captivity.
Diet
Like other rhinoceros beetles, Hercules beetles eat fruit, especially fruit that has fallen from the tree and rotted a bit, which makes it easier for the insect’s chewing mouthparts to handle. Where they live, the fruits are often mangos and other tropical fruit. They’ll also eat rotting wood like their larvae and other rotting plant material. In captivity, Hercules beetles are often fed fresh fruit such as grapes as well as high-protein beetle jelly.
View all 104 animals that start with HHercules Beetle FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are Hercules Beetles herbivores, carnivores, or omnivores?
Hercules Beetles are Omnivores, meaning they eat both plants and other animals.
What Kingdom do Hercules Beetles belong to?
Hercules Beetles belong to the Kingdom Animalia.
What phylum to Hercules Beetles belong to?
Hercules Beetles belong to the phylum Arthropoda.
What family do Hercules Beetles belong to?
Hercules Beetles belong to the family Scarabaeidae.
What order do Hercules Beetles belong to?
Hercules Beetles belong to the order Coleoptera.
What genus do Hercules Beetles belong to?
Hercules Beetles belong to the genus Dynastes.
What type of covering do Hercules Beetles have?
Hercules Beetles are covered in shells.
Where do Hercules Beetles live?
Hercules Beetles live in Central and South America.
In what type of habitat do Hercules Beetles live?
Hercules Beetles live in tropical rainforests.
What is the main prey for Hercules Beetles?
Hercules Beetles eat decaying wood, fruit, and leaves.
What are some predators of Hercules Beetles?
Predators of Hercules Beetles include bats, rats, and birds.
What are some distinguishing features of Hercules Beetles?
Hercules Beetles have hard, armored shells and horn-like pincers.
How many babies do Hercules Beetles have?
The average number of babies a Hercules Beetle has is 100.
What is an interesting fact about Hercules Beetles?
Hercules Beetles can grow up to 7 inches long!
How many species of Hercules Beetle are there?
There are 13 species of Hercules Beetle.
Can a Hercules beetle hurt you?
Hercules beetles can’t seriously damage humans, though a pinch from its horns can hurt. Indeed, they make interesting if short-lived pets. Another of the Hercules beetle facts is that people pay surprisingly high prices for these beetles and often keep them in terraria. The price of a male Hercules beetle, sought after for its pincer-like horns, can range between $470 and $938.
How strong is a Hercules beetle?
A Hercules beetle comes by its name honestly. Its astonishing strength allows it to pick up an object that is 850 times its weight. If a 150-pound person had the strength of a Hercules beetle, they would be able to lift a fully loaded mack truck and then some. Hercules beetles have been known to flip the top off of their terraria and escape.
What kills Hercules beetles?
Though Hercules beetles can be killed by humans, they do not seem to have natural predators. The grub, however, is preyed upon by birds, mammals, bats, humans, and other animals.
What do Hercules beetles eat?
Hercules beetles eat fruit and decaying plant matter.
Are Hercules beetles endangered?
Hercules beetles are possibly endangered as their habitat is being destroyed and polluted, though they don’t have special status on the conservation list.
Are Hercules beetles herbivores, carnivores, or omnivores?
Hercules beetles are herbivores. Specifically, they eat fruit, and the larvae eat rotting wood.
Are Hercules beetles dangerous?
Hercules beetles are not dangerous to humans, pets, or crops.
How many legs does the Hercules beetle have?
The Hercules beetle has six legs, like most other insects.
How do you identify a Hercules beetle?
A male Hercules beetle can be told easily by its two horns, one projecting from his thorax and the other from his head. They form a structure that looks much like a lobster claw. The female lacks these horns and is a bit harder to tell from other scarab beetles, but she has black elytra that may fade to yellow or olive green at the back. Her elytra also have tiny punctures.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- Star Advertiser, Available here: https://www.staradvertiser.com/2020/10/22/news/collectors-pay-high-prices-for-big-bugs/
- Animal Diversity Web, Available here: https://animaldiversity.org/accounts/Dynastes_hercules/
- Wikipedia, Available here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hercules_beetle