Leaf-Tailed Gecko
Only found on Madagascar!
Advertisement
Leaf-Tailed Gecko Scientific Classification
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Leaf-Tailed Gecko Conservation Status
Leaf-Tailed Gecko Facts
View all of the Leaf-Tailed Gecko images!
The leaf-tailed gecko, a lengthy lizard, has quite a unique physique. With a broad and triangular head, their name comes from the leaf-like resemblance of their tail.
The texture helps leaf tailed geckos to be camouflaged within their surroundings to conceal themselves against the natural foliage in their surroundings. They tend to blend in with the bark of trees and with leaves, which is made even easier with their coloring. However, there are several species of this type of gecko, including the mossy, satanic, and giant leaf-tailed gecko.
This gecko has a unique vocal trick – it can emit a loud noise that sounds just like the scream of a child.
5 Incredible Leaf-Tailed Gecko Facts!
Here are some interesting facts about these geckos
- They have large eyes without eyelids. To keep their eyeballs moist, they lick them periodically.
- If dirt gets on or in the eye of the gecko, the reptile removes it in the same way that they moisten the surface – with their tongue.
- The size of this lizard can vary drastically, growing 4 to 12 inches at its adult length. The giant leaf-tailed gecko is already 2 inches long when it is initially born.
- The skin of the leaf-tailed gecko resembles the rough bark of a tree, allowing them to hide from predators.
- Each of the toes of these lizards contains millions of microscopically small plates that allow them to move effortlessly on smooth surfaces.

Scientific Name
Leaf-tailed geckos are classified in the kingdom Animalia and Phylum Chordata. Their class is called Reptilia and the order is called Squamata. Their family is called Gekkonidae while the genus is called Uroplatus.
Uroplatus is derived from Latin, combining two words – οὐρά (“tail”) and πλατύς (“flat”). Phantasticus is also rooted in Latin, which means “imaginary.” The unique body of the leaf-tailed gecko led George Albert Boulenger, a naturalist from Belgium, to say that it is “mythical,” which is part of the reason for the name.
Evolution And Origin
After the split of the two supercontinents, Laurasia and Gondwanaland, around 200 million years ago, geckos began to diverge from other lizards. It is believed that the earliest known fossil record of an extinct genus of gecko, Yantarogekko from the Eocene era, was found in Baltic amber, although as there are not much left of its remains, it is unable to be more definitive in its assignation and is left in the more widely categorized genus of Gekkonidae.
Types Of
There are 14 extant species of the leaf-tailed gecko. Here are just a few of the different species of the leaf-tailed gecko:
- Spearpoint leaf-tailed gecko (Uroplatus ebenaui)
- Satanic leaf-tailed gecko (Uroplatus phantasticus)
- Common leaf-tailed gecko (Uroplatus fimbriatus)
- Southern leaf-tailed gecko (Uroplatus sameiti)
- Lined leaf-tailed gecko (Uroplatus lineatus)
Appearance
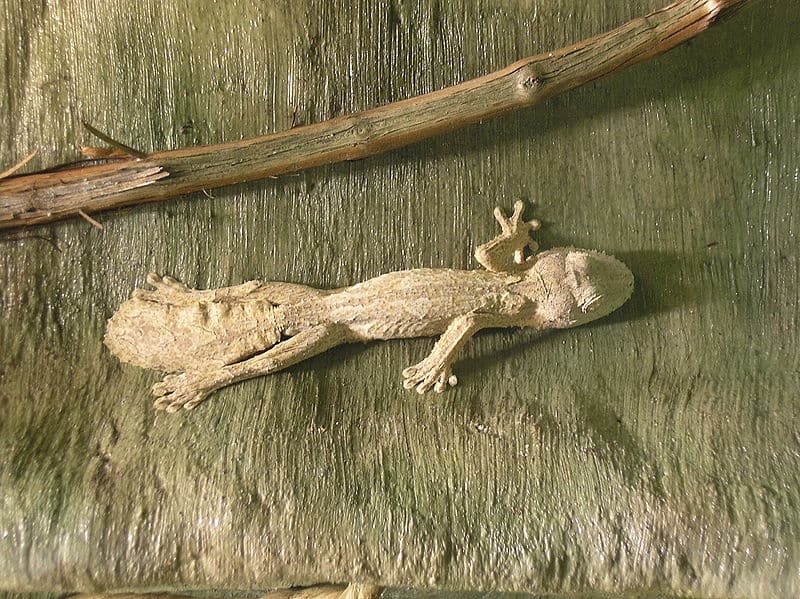

Leaf-Tailed Geckos have long bodies that can grow up to 12 inches in size.
©deror avi – Public Domain
One of the facts that distinguish the leaf-tailed gecko is that they have long bodies that can grow 4 to 12 inches in size. Their heads are broad, taking on a triangular shape like that of the angles in their tail. The size of giant leaf-tailed geckos is usually 2.5 inches long as babies, growing to be 10-12 inches long as adults with larger eyes than other variations.
The eyes of these lizards are big and marbled, but the red center of the eye stands out significantly against their body which typically features green, tan, brown, and grey. The natural colors allow them to easily camouflage within their surroundings – especially because their texture is rough like the leaves and branches of the trees. The mossy leaf-tailed geckos can even camouflage with the moss on trees.
Along the lower jaw, these geckos have fringed flaps, matching their sides. When they lay on a surface, they can flatten their body to keep the illusion that they are merely a leaf in nature.
Behavior
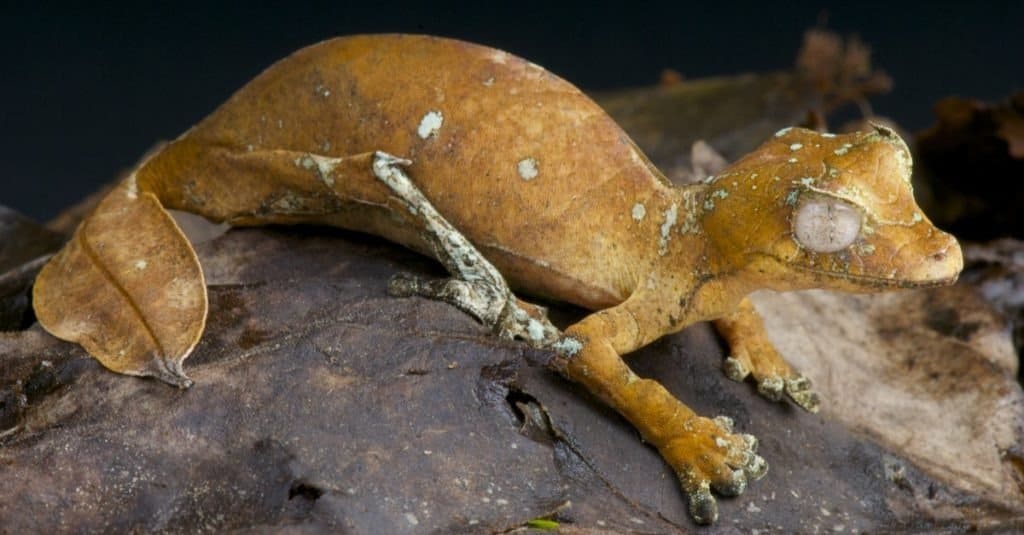

As nocturnal reptiles, these geckos rest during the day and are active at night.
©reptiles4all/Shutterstock.com
These geckos are nocturnal animals, meaning that they rest during the day and are active during the night. During most days, you can find the geckos basking in the sun until they are ready to hunt for their prey.
Being carnivorous reptiles, the gecko is an active hunter at night. The darkness and shadows allow them to stay hidden from their prey as they seek out a meal without being noticed.
When they are resting, these lizards face downward, but that doesn’t mean that they are unprepared for danger. At the moment that the gecko is disturbed by anything in their surroundings, it will let out a loud distress call that sounds much like a child screaming. They also become aggressive towards the disturbance, showing their bright red mouth as they open them widely. The satanic leaf-tailed geckos especially do not like to have their resting time interrupted, primarily spending time alone.
The camouflage capabilities of these lizards are a determining factor in the way that they sleep since their physique can vary. Reptiles that look like bamboo will stretch out while they sleep, while the ones that look like leaves may curl up in knots to keep themselves out of the view of predators.
The movement of the geckos is usually slow – much like that of a chameleon. They do not like the limelight, moving little by little. If a gecko is moving slowly, it is a good sign that it is happy. However, if a gecko is stressed, it would be in constant motion, jumping around with a sense of panic as it attempts to escape the situation.
When they are out hunting, the geckos usually possess what is called a bug stare. When they expose this stare, the eyes usually widen as their pupils are revealed, giving a sense that they are now hunting more.
Even though the geckos bite, their jaws and claws are not strong enough. They are not dangerous especially to humans as their bites or claw grip are not enough to break any human skin but following proper safety procedures is still important.
Habitat
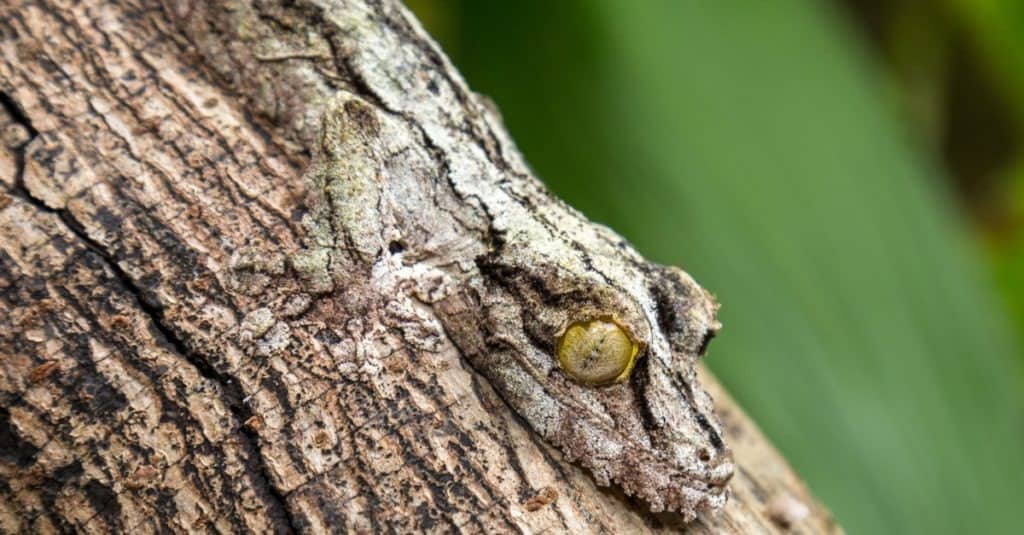

These geckos prefer the humid forests and will rest on leaves and branches of the trees.
©Anna Veselova/Shutterstock.com
These geckos often prefer to make their habitat within humid forests, particularly staying in lowlands. However, they will also live at elevations of up to 2,625 feet. During the day, they rest on the leaves and branches of the trees, allowing their bodies to be easily camouflaged without the worry that a predator will find them.
One of the most common habitats for this gecko is the Nosy Mangabe Island. With the right amount of searching, you may even be able to see them in the rainforests found along the eastern coast of Madagascar.
These geckos are carnivorous, though they do not rank very high on the food chain. Rather than seeking out other reptiles, birds, or mammals, they look for insects and invertebrates that are easy to capture within their habitat. Land snails and insects are often their food of choice, though the satanic leaf tailed gecko will indulge in a variety of spiders, worms, and flies.
Predators And Threats
Even though these geckos have excellent camouflage capabilities that help the gecko in hiding from predators, they still serve as food for some birds and animals.
These reptiles face the threat from human activities like deforestation that have been clearing their natural habitats and in turn affecting their lives and posing as a threat to them.
What Eats Leaf-Tailed Geckos?
Leaf tailed geckos are eaten by a variety of birds and animals. Some of them include owls, eagles, rats, and snakes.
What Do Lead-Tailed Geckos Eat?
The leaf-tailed gecko prefers a steady diet of insects, including flies and spiders. They’ll also consume invertebrates that are much smaller than them, like worms or snails. However, these animals are not picky, and they will ultimately eat anything that they can overpower.
Reproduction, Babies, And Lifespan
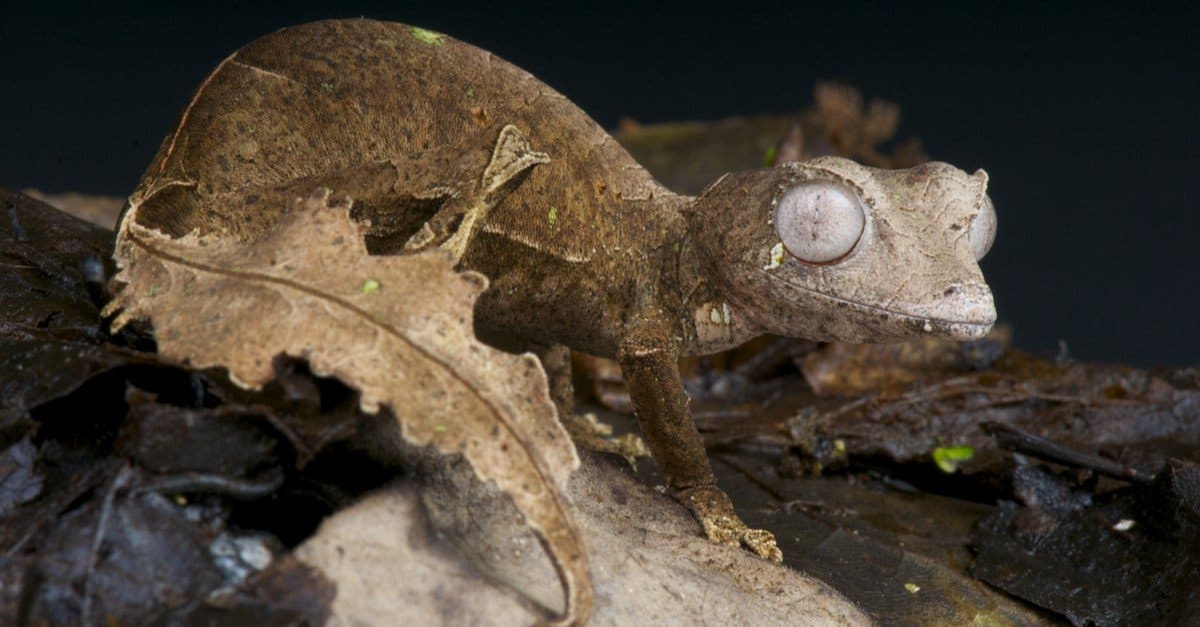

Leaf-tailed geckos only unite to mate, which is usually during the rainy season.
©reptiles4all/Shutterstock.com
The leaf-tailed geckos are usually considered to be solitary creatures and come together only to mate. Their mating season starts when their environment reaches a rainy time of year.
Interestingly, there is very little detail regarding the reproduction process of the leaf-tailed geckos. When ready to reproduce, the female leaf-tailed gecko usually lays two to four spherical eggs. The eggs are usually laid under the leaves or the insides of the dead plants to protect them.
The cluster of leaf-tailed gecko eggs is called clutches, and the females lay up to three clutches every year. The eggs can also be laid on the forest floor, taking about 95 days to hatch. The leaf-tailed gecko will usually have a 5-year lifespan.
Population
While the exact population of the leaf-tailed gecko is unknown, the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) has classified the animal as “vulnerable.” The status is not worrisome at the moment, making it one of the least concerning populations of animals in the world right now. The only variation that seems to have steadily decreased numbers is the population of the mossy leaf-tailed geckos.
In the Zoo
Leaf-tailed geckos can be kept in the zoo in captivity. Single geckos can be kept in about 12 inches-long cages, while the pairs can be kept in about 18 inches-long cages. While in captivity, they have to be fed a variety of insects, flies, worms, and spiders for their appropriate diet and growth.
View all 98 animals that start with LLeaf-Tailed Gecko FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are Leaf-Tailed Geckos herbivores, carnivores, or omnivores?
Leaf-tailed geckos are carnivores in nature. They are known to feed on a vast variety of invertebrates. Some of the creatures that the leaf-tailed geckos eat include land snails and a lot of insects. Apart from that, they also feed on several spiders, worms, and flies.
What Kingdom do Leaf-Tailed Geckos belong to?
Leaf-Tailed Geckos belong to the Kingdom Animalia.
What phylum to Leaf-Tailed Geckos belong to?
Leaf-Tailed Geckos belong to the phylum Chordata.
What family do Leaf-Tailed Geckos belong to?
Leaf-Tailed Geckos belong to the family Gekkonidae.
What order do Leaf-Tailed Geckos belong to?
Leaf-Tailed Geckos belong to the order Squamata.
What genus do Leaf-Tailed Geckos belong to?
Leaf-Tailed Geckos belong to the genus Uroplatus.
What type of covering do Leaf-Tailed Geckos have?
Leaf-Tailed Geckos are covered in Scales.
In what type of habitat do Leaf-Tailed Geckos live?
Leaf-Tailed Geckos live in dense tropical jungles.
What is the main prey for Leaf-Tailed Geckos?
Leaf-Tailed Geckos prey on spiders, insects, and worms.
What are some predators of Leaf-Tailed Geckos?
Predators of Leaf-Tailed Geckos include owls, rats, and snakes.
What are some distinguishing features of Leaf-Tailed Geckos?
Leaf-Tailed Geckos have sticky toes and broad, flattened tails.
How many eggs do Leaf-Tailed Geckos lay?
Leaf-Tailed Geckos typically lay 3 eggs.
What is an interesting fact about Leaf-Tailed Geckos?
Leaf-Tailed Geckos are only found on Madagascar!
What is the scientific name for the Leaf-Tailed Gecko?
The scientific name for the Leaf-Tailed Gecko is Uroplatus.
What is the lifespan of a Leaf-Tailed Gecko?
Leaf-Tailed Geckos can live for 2 to 9 years.
How big is a leaf-tailed gecko?
Leaf-tailed geckos can get up to 4 to 12 inches long.
What makes the leaf-tailed gecko unique?
The uniqueness of the leaf-tailed geckos come from their tails that also give them their names. The tails are leaf-shaped. Besides that, their eyes are marbled, and they make loud noises that resemble a child’s scream.
Are leaf-tailed geckos good pets?
Having a pet requires taking care of it. Not everyone can be considered equipped enough to keep and take care of the leaf-tailed geckos as pets as they have certain care needs that can only be fulfilled by advanced reptile owners. The satanic leaf-tailed gecko, however, is a popular pet worldwide and they are one of the most sought after reptiles in the world.
What do leaf-tailed geckos eat?
Leaf-tailed geckos eat a vast variety of invertebrates. Some of the creatures that the leaf-tailed geckos eat include land snails and a lot of insects. They also feed on several spiders, worms, and flies.
How fast is a Leaf-Tailed Gecko?
A Leaf-Tailed Gecko can travel at speeds of up to 30 miles per hour.
How do Leaf-Tailed Geckos have babies?
Leaf-Tailed Geckos lay eggs.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- Smithsonian's National Zoo & Conservation Biology Institute, Available here: https://nationalzoo.si.edu/animals/giant-leaf-tailed-gecko
- Soft Schools, Available here: https://www.softschools.com/facts/animals/leaf_tailed_gecko_facts/2601/
- Hogle Zoo, Available here: https://www.hoglezoo.org/meet_our_animals/animal_finder/mossy_leaf-tail_gecko/
- Wikipedia, Available here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Uroplatus_phantasticus
- Cleveland Metroparks Zoo, Available here: https://resourcelibrary.clemetzoo.com/Animal/1323