Below you can find a complete list of Madagascar animals. We currently track 200,000 species of animals in Madagascar and are adding more every day!
The island of Madagascar harbors one of the most unique ecosystems on the planet. Anchored off the eastern coast of Africa, it is the world’s fourth-largest island – nearly reaching the same size as Texas – with about 3,000 miles of coastline. The island is home to abundant rainforests, dry forests, deserts, and coastal reefs, which incubate a rich diversity of wildlife. Isolated from the mainland, about 90% of the island’s plant and animal species are native to the island and found nowhere else in the world. This has earned it the designation of a biodiversity hotspot. However, much of this rich biodiversity is being lost to human activity. Let’s have a closer look at some of these famous Madagascar animals below!
The Official National Animals of Madagascar
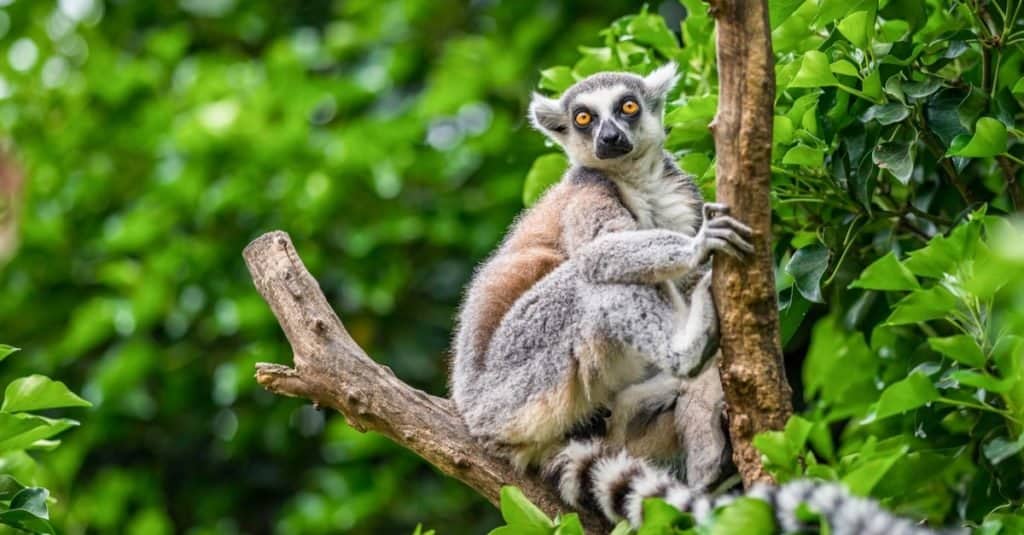

The ring-tailed lemur is one of Madagascar’s national animals
©Ondrej_Novotny_92/Shutterstock.com
The two national animals of Madagascar are the zebu and the ring-tailed lemur. The lemur is a type of long-limbed arboreal primate found exclusively on the island, while the zebu is a subspecies of cattle originating from India and specifically adapted to endure hotter and drier climates. Just like a camel, its hump can store nutrients for when food is scarce. The zebu basically fulfills the same role as the taurine cattle elsewhere in the world. As a source of meat and milk, it has been a lynchpin of the local economy for thousands of years. This has given the zebu an important status in Madagascar society.
Where to Find the Top Wild Animals in Madagascar

Madagascar’s natural fauna can be discovered in its national parks and protected areas all over the country
The best place to discover Madagascar’s rich natural wildlife is the many national parks and protected areas spread across the country. The largest destination is the Masoala National Park in the northeast. It contains more than 900 square miles of rainforests, marshes, mangroves, and flooded forests, where you can find a variety of different lemurs, geckos, frogs, and birds.
Other important parks include the Andasibe-Mantadia National Park in the east, the sandstone landscape of Isalo National Park in the southwest, and the Amber Mountain Reserve near the northern tip.
The Most Dangerous Animals in Madagascar Today
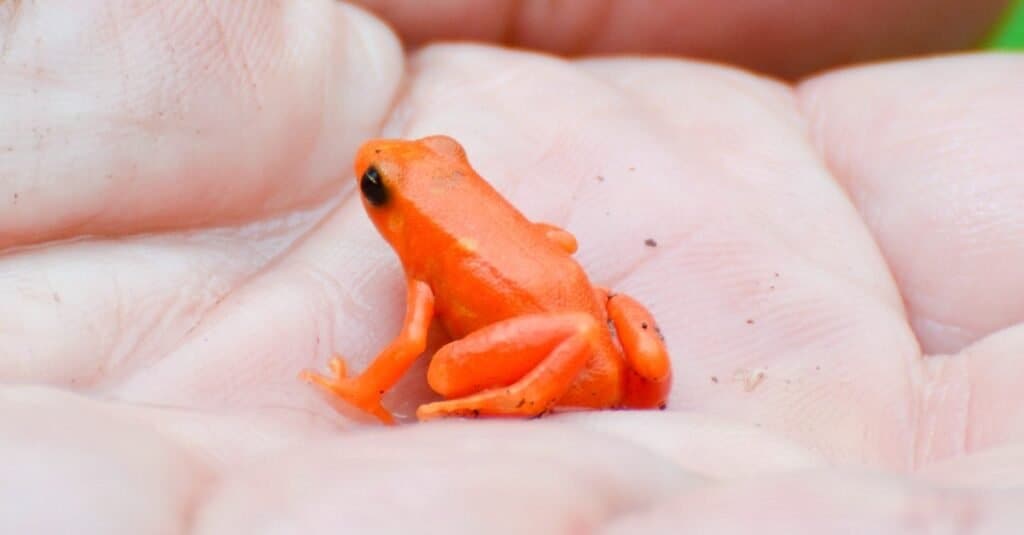

Golden Mantella frogs are known to produce toxins when attacked by predators
©iStock.com/dr322
Madagascar is home to many unique species, but surprisingly few of them are dangerous to humans. The island has almost no big carnivorous, aggressive snakes, or other highly toxic animals. Some species like the Malagasy tree boa may look intimidating but actually pose little threat to people. Here are a few you should look out for, however.
- Nile Crocodile – This species actually isn’t unique to Madagascar at all. It is found all over sub-Saharan Africa. But Madagascar does seem to have its own unique variation that lives in freshwater habitats and caves. Unfortunately, years of hunting have diminished the number of crocodiles on the island.
- Black Widow – Madagascar is home to its own unique species of black widow spider, whose venom may cause muscle pain, cramping, and sometimes seizures. Death is relatively rare though.
- Scorpions – Southwest Madagascar harbors a genus of large scorpions with a painful sting. Fortunately, it’s not often encountered by people.
- Golden Frogs – This is a genus of around 16 brightly colored poisonous frog species that goes by the name of Mantella. The golden frog isn’t really dangerous at all until a predator tries to eat it. Then it produces a toxin that can cause nausea and sickness, although it is not yet known to cause deaths.
The Largest Animal in Madagascar
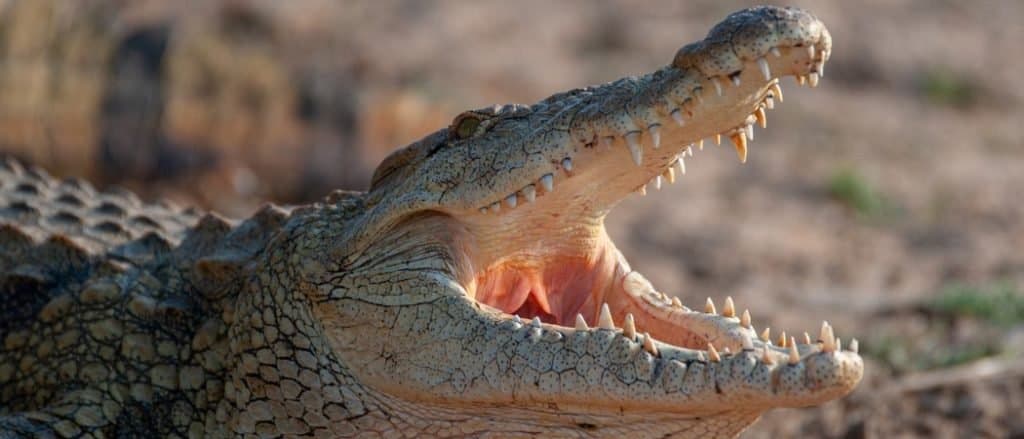

Nile crocodiles are impressively adaptable and are capable of settling down nicely in a wide range of habitats
©Rudi Hulshof/Shutterstock.com
The largest animal in Madagascar is the Nile crocodile (Crocodylus niloticus). The smaller, but no less imposing cousin of the saltwater crocodile whose range extends throughout central, eastern, southern, western Africa and western Madagascar, is capable of growing to 2,400 lbs and over 20 feet.
The highly adaptable reptile is capable of making itself feel at home in a wide range of habitats ranging from dams, to estuaries, to rivers, and swamps. Although its numbers were once teeming, they have since plummeted owing to these reptiles being hunted for their skins. They can be foound in locations such as the Ankarana Nature Reserve where they live in caves.
The Rarest Animal in Madagascar
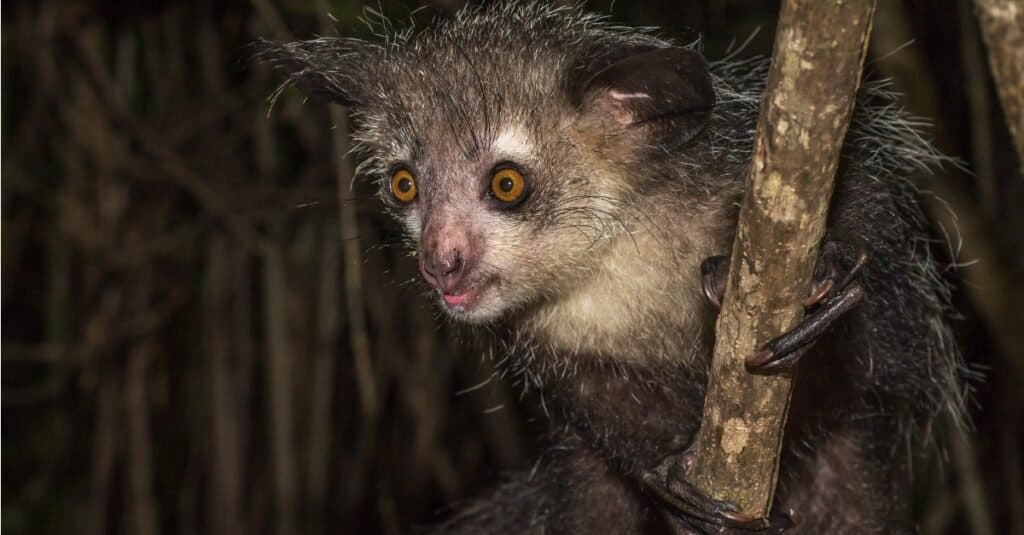

The Aye-aye, is nocturnal by nature and enjoys grubs, fruit, and honey
©javarman/Shutterstock.com
The aye aye, known for its trademark stare and its habit of using rather long digits to extract nourishing grubs from wood, is one of the rarest animals in Madagascar. As a matter of fact, the mammal which is 12-16 inches long with a 22-inch tail, was once believed to be extinct until a chance discovered almost 70 years ago.
The arboreal omnivore which is found on the island’s east coast, prefers to go searching for food by night. It generally spends it daylight hours ensconced in a spherical nest woven from twigs and leaves and carefully placed in the fork of tree branches. In addition to grubs, the primate also enjoys coconut flesh and various types of fruit. It is also partial to honey.
However, this primate with a rather disconcerting scarlet-eyed stare and a wide triangular face, and an untidy dark coat, has a few strikes against it, survival-wise. One is the belief in its being a harbinger of evil in certain customs, another is deforestation. It has adjusted to the latter challenge by making itself at home in cultivated areas. The former challenge has become a thing of the past since they are legally protected.
Endangered Animals in Madagascar
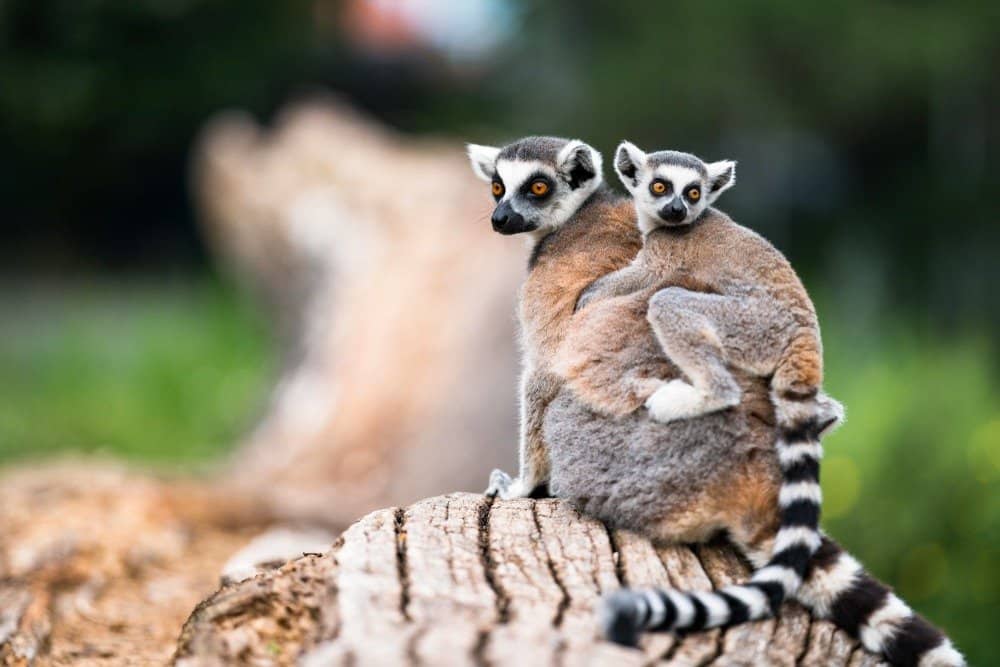

Ring-tailed lemurs have seen their numbers plummet drastically to about 2,000 in the wild
©Ondrej_Novotny_92/Shutterstock.com
The Madagascar ecosystem is in a perilous state. A great deal of the animal species, including many of the primates, are now threatened by human activity from slash and burn agricultural techniques, deforestation, and even illegal hunting. Here are a few of biodiversity jewels that are in danger of being lost:
- Ring-Tailed Lemur – The iconic ring-tailed lemur is perhaps the most well-known species native to Madagascar. It spends most of its life navigating the trees with its limbs, but unlike many other arboreal primates, the tail is not prehensile and merely provides balance and communication. As of 2017, it was estimated that only about 2,000 remain in the wild.
- Indri – Native to the island’s eastern rainforests, the Indri is one of the largest lemurs in the world. It is characterized by a short, rudimentary tail, big fuzzy ears, and black and white fur. Like other species of lemur, the Indri congregates together in a complex society. Its group vocalizations, which travel more than a mile in the air, sound something like an air horn.
- Aye-aye – This unusually named lemur has a unique arboreal hunting strategy. In order to search for food at night, the aye-aye will patiently tap on the barks of trees. Once it has found a hollow space, it will gnaw a hole in the wood with its forward-facing incisors and then pull out the grub with its long, spindly middle finger. The aye-age was thought to be extinct by the 1930s but was rediscovered a few decades later.
- Silky Sifaka – Also known as the angel of the forest for its white, silky fur, this lemur is one of the rarest mammals on the planet. Less than a thousand individuals remain in the wild.
- Ploughshare Tortoise – Home to a small stretch of territory in the northwest, the ploughshare tortoise can be identified by the unique growth rings projecting from the shell. Numbers have diminished quickly due to habitat loss and poaching (a single turtle can fetch around $200,000 on the exotic pet market). Only about a thousand of these animals remain.
- Humblot’s Heron – Named after the French naturalist Leon Humblot, this species of large, long-legged waterbirds are found along the north and west coasts of Madagascar. The loss of wetlands has caused this species to decline.
Incredible Native Plants in Madagascar
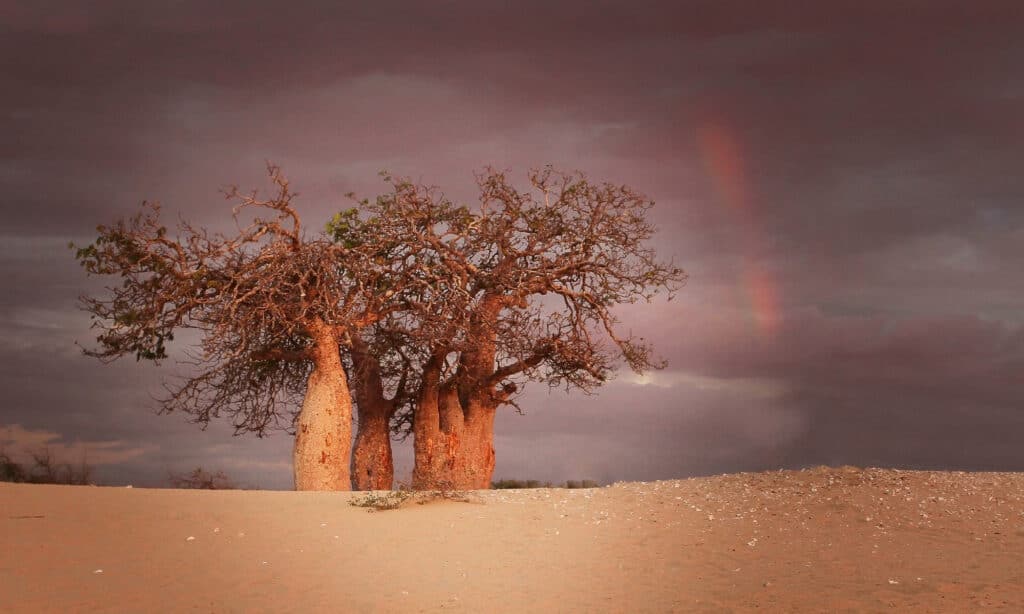

Six out of nine of the world’s baobab species are found in Madagascar
©iStock.com/gydyt0jas
Madagascar has a vibrant and diverse flora, with over 75% of species being endemic to the island. From fascinating octopus trees, wild banana trees, and palms pollinated by nosy lemurs, there’s something for everyone to admire. While many of these trees are now classified as endangered due to deforestation and other human activities, Madagascar is still a top destination for those interested in exploring the island’s beautiful landscape.
Madagascar is home to six of the world’s nine baobab subspecies and the Madagascan periwinkle also used to treat cancer. It is also home to the traveler’s palm, recognizable by its beautiful fan-like foliage, its ability to hold rainwater, and its habit of growing on an east-west axis.
Fish Found in Madagascar
Located off the coast of southeast Africa, Madagascar sits in the Indian Ocean just across the Mozambique Channel from the mainland of Africa. As an island, it has beautiful fauna, including unique-looking fish such as reef stonefishes, coelacanths, and many more.
Madagascar is also known for its orange-backed angel fish with its colors of orange and deep blue and the white-spotted bamboo shark, a slender carpet shark with alternating bands of black with white spots, and gray. It is also home to the melon butterfly fish which is covered in blue bands that fade to yellow, alternating with pale blue, as well as slashes of black, yellow, and orange.
Malagasy Animals

Aardwolf
The aardwolf has five toes on its front paws

Achrioptera Manga
Unlike other species of stick insects, the Achrioptera manga's mating season is year-round and mating occurs regularly.

American Cockroach
Despite its name, actually originated from Africa and the Middle East

Ant
First evolved 100 million years ago!

Antelope
Renew their horns every year!

Archaeoindris
Archaeoindris was the largest primate to evolve in Madagascar

Armyworm
They are so named because they "march" in armies of worms from one crop to another in search of food

Aye-aye
Thought to be extinct until 1957!

Banana Spider
People spin clothing and fishing nets out of these spiders’ silk.

Barb
There are over 1768 known species!

Barn Owl
Found everywhere around the world!

Barn Swallow
Older offspring help care for new hatchlings.

Bat
Detects prey using echolocation!

Bed Bugs
Bed bugs feed for 4-12 minutes.

Bee
Rock paintings of bees date back 15,000 years

Beetle
There are more than 350,000 different species

Beewolf wasp
They hunt bees

Bird
Not all birds are able to fly!

Biscuit Beetle
The biscuit beetle form a symbiotic relationship with yeast

Black Widow Spider
They typically prey on insects!

Blind Snake
The blind snake is often mistaken for a worm.

Boas
Boas are considered primitive snakes and still have vestigial legs, called spurs.

Brahminy Blindsnake
These snakes have been introduced to all continents, except Antarctica!

Brookesia Micra
Brookesia micra can curl up and pretend to be a dead leaf if it’s threatened.

Brown Dog Tick
Can live its entire life indoors

Bumblebee
The most common species of bee!

Butterfly
There are thought to be up 17,500 species!

Caecilian
Some species' babies use their hooked or scraper-like teeth to peel off and eat their mother's skin

Carpenter Ant
Carpenter ants can lift up to seven times their own weight with their teeth!

Cat
May have been domesticated up to 10,000 years ago.

Caterpillar
The larvae of a moth or butterfly!

Catfish
There are nearly 3,000 different species!

Centipede
There are about 3,000 documented species!

Chameleon
There are more than 160 different species!

Chicken
First domesticated more than 10,000 years ago!

Cicada
Cicadas have one of the longest insect lifespans

Cichlid
There are more than 2 000 known species!

Cockroach
Dated to be around 300 million years old!

Codling Moth
Pupae are able to undergo diapause to survive poor fruit yield years and winter.

Comet Moth
Adult comet moths do not feed at all till they die less than 12 days later.

Common Buzzard
The most common raptor in the UK!

Common Furniture Beetle
The common furniture beetle feeds exclusively on wood

Common House Spider
House spiders have the ability to eat most insects in a home.

Coton de Tulear
The soft coat of the Coton de Tulear is the result of a singular genetic mutation early in the breed's development.

Cow
There are nearly 1.5 billion worldwide!

Crab
There are 93 different crab groups

Crab Spider
Crab Spiders can mimic ants or bird droppings

Crane
Many are critically endangered species!

Cricket
Male crickets can produce sounds by rubbing their wings together

Crocodile
Have changed little in 200 million years!

Crocodylomorph
Crocodylomorphs include extinct ancient species as well as 26 living species today.

Crow
A group of these birds is called a Murder.

Dog
First domesticated in South-East Asia!

Dog Tick
Dog ticks feed on dogs and other mammals

Donkey
First domesticated 5,000 years ago!

Dragonfly
It's larvae are carnivorous!

Duck
Rows of tiny plates line their teeth!

Dumeril’s Boa
Some tribes believe that the snake's skin holds the souls of their ancestors.

Dung Beetle
The dung beetle can push objects many times its own weight

Dusky Shark
The Dusky Shark sometimes eats trash discarded by humans.

Earthworm
They are hermaphrodites, which means they have male and female organs

Earwig
There are nearly 2,000 different species!

Eel
Eels can be a mere few inches long to 13 feet!

Elephant
Spends around 22 hours a day eating!

Elephant Bird
Vorombe titan, a type of elephant bird, is the largest bird that ever lived

Elephant Shrew
Found exclusively on the African continent!

Falcon
The fastest creatures on the planet!

False Widow Spider
False spiders actually prey on black widow spiders and other hazardous spiders

Fiddler Crab
The fiddler crab gets its name from the motion the males make with their over-sized claw during the mating ritual.

Firefly
The firefly produces some of the most efficient light in the world

Flea
Adult fleas can jump up to 7 inches in the air

Fly
There are more than 240,000 different species!
Fossa
Most closely related to the Mongoose!

Fox
Only 12 species are considered "true foxes"

Frog
There are around 7,000 different species!

Fruit Bat
Among the largest bats in the world

Fruit Fly
Fruit flies are among the most common research animals in the world

Fulvous Whistling Duck
They build a ramp from their nest, which leads to a nearby water source

Galapagos Shark
Galapagos sharks are cannibalistic and sometimes eat their young, so the pups stay away from the adults in shallow water.

Gazelle
Named for the Arabic word for love poems

Gecko
There are thought to be over 2,000 species!

Gerbil
Originally known as the Desert Rat!

German Cockroach
The most common type of urban roach

Giant Trevally
The largest fish in its genus

Glass Lizard
Can grow up to 4ft long!

Glowworm
Found inhabiting dense woodland and caves!

Gnat
Males form large mating swarms at dusk

Goat
Most closely related to the Sheep!

Golden Oriole
Migrates between Europe and Asia!

Grasshopper
There are 11,000 known species!

Green Bee-Eater
Mainly eats honeybees!

Grey Heron
Male grey herons are picky about their mates. They'll reject a female that they don't fancy.

Grey Mouse Lemur
The largest species of mouse lemur!

Guinea Fowl
Found in a vairety of African habitats!

Gypsy Moth
One of the most invasive species in the world

Hamster
Able to run as quickly backwards as forwards!

Hare
Can reach speeds of over 50 mph!

Hawk Moth Caterpillar
Many hawk moth caterpillars eat toxins from plants, but don’t sequester them the way milkweed butterflies do. Most toxins are excreted.

Hedgehog
Thought to be one of the oldest mammals on Earth!

Heron
Inhabits wetlands around the world!

Hognose snake
Prima Donnas of the Snake World

Honey Bee
There are only 8 recognized species!

Hoopoe
Stunning bird with a stinky way to deter predators!

Horse
Has evolved over 50 million years!

Horsefly
Horseflies have been seen performing Immelmann turns, much like fighter jets.

Housefly
The fly has no teeth
Human
Thought to have orignated 200,000 years ago!

Huntsman Spider
Some huntsman spiders have an interesting way of moving around. Some cartwheel while others do handsprings or backflips.

Ibis
Found in swamps, marshes and wetlands!

Insects
There are an estimated 30 million species!

Jacana
The jacana has the ability to swim underwater

Jumping Spider
Some can jump 50 times the length of their bodies

Kingfisher
Inhabits wetlands and woodlands worldwide!

Ladybug
There are more than 5,000 species worldwide!

Leaf-Tailed Gecko
Only found on Madagascar!

Leech
Has 10 pairs of eyes!

Lemur
Natively found on the island of Madagascar!

Lizard
There are around 5,000 different species!

Locust
Each locust can eat its weight in plants each day.

Long-Winged Kite Spider
The long-winged kite spider sets itself apart from other spiny orb-weavers by its elongated spiked protrusions from its sides, giving it the appearance of a pointed kite (its namesake).

Madagascar Hissing Cockroach
One of the largest types of cockroach

Madagascar Jacana
The Madagascar jacana is endangered due to habitat loss and illegal hunting.

Maggot
Will only live in wet areas

Magpie
They are found across Europe, Asia and Africa!

Mantella Frog
Some of the smallest and most brightly colored frogs in the world

Masiakasaurus
Masiakasaurus had dentition adapted to catching fast-moving prey.

Mayfly
There are 2,500 known species worldwide!

Mealybug
They have a symbiotic relationship with ants.

Millipede
Some species have a poisonous bite!

Mole
Primarily hunts and feeds on Earthworms!

Mongoose
Range in size from just 1 to 3 foot!

Mongrel
Has characteristics of two or more breeds!

Monitor Lizard
Some species are thought to carry a weak venom!

Monkey
There are around 260 known species!

Moorhen
Feeds on aquatic insects and water-spiders!

Mosquito
Only the female mosquito actually sucks blood

Moth
There are 250,000 different species!

Mouse
Found on every continent on Earth!

Mule
The offspring of a horse and donkey parents!

Myna Bird
Many people believe the hill myna bird is better at mimicking humans than a parrot!

Night Heron
When they feel threatened juvenile night herons vomit their stomach contents.

Nightingale
Named more than 1,000 years ago!

Nile Crocodile
Unlike other reptiles, the male Nile crocodile will stay with a female to guard their nest of eggs.

No See Ums
There are more than 5,000 species.

Olive Baboon
Olive baboons will sometimes form strong friendships with each other

Orb Weaver
Females are about four times the size of males

Otter
There are 13 different species worldwide

Owl
The owl can rotate its head some 270 degrees

Parrot
Can live for up to 100 years!

Peregrine Falcon
Fastest animal on Earth

Pheasant
Females lay between 8 and 12 eggs per clutch!

Pigeon
They can find their way back to their nests from up to 1300 miles away.

Pompano Fish
They are bottom-feeders

Praying Mantis
The mantis can turn its head 180 degrees.

Puff Adder
This large snake is so-named because it will puff up its body to appear bigger than it is when directly threatened by a predator or person.

Quail
Inhabits woodland and forest areas worldwide!

Rabbit
There are more than 300 different species!

Radiated Tortoise
The most protected tortoise in the world!

Rat
Omnivores that eat anything!

Rhinoceros
It's horns are made from keratin!

River Turtle
Inhabits freshwater habitats around the world!

Robin
There are more than 45 species in Australia alone!

Rock Python
Rock pythons may have crossbred with the escaped Burmese pythons in Florida.

Rodents
The capybara, the world’s largest rodent, likes to be in and around bodies of water. Because of this, the Catholic Church in South America decided that it was a fish, and people were allowed to eat it during Lent and First Fridays.

Rooster
Will mate with the entire flock!

Sable Ferret
Ferrets were used during the Revolutionary War to keep down the rat population.

Sand Crab
The sand crab burrows beneath the sand with its tail

Satanic Leaf-Tailed Gecko
They are called “phants” or “satanics” in the pet trade.

Scorpion
There are around 2,000 known species!

Sea Eagle
The sea eagle tends to mate for life with a single partner

Seahorse
Males give birth to up to 1,000 offspring!

Sheep
Around 35 million in the English countryside!

Shrew
The spinal column of the shrew Scutisorex somereni is so strong and reinforced that it can support the weight of an adult human.

Shrimp
There are 2,000 different species worldwide!

Skink Lizard
Some skinks lay eggs in some habitats while giving birth to skinklets in other habitats.

Slug
They glide around on one foot, which is aided by the slime they produce

Smokybrown Cockroach
Has up to 45 eggs per egg case

Snail
There are nearly 1,000 different species!

Snake
There are around 4,000 known species worldwide

Sparrow
There are 140 different species!

Spider Wasp
They prey on spiders to feed their larvae or they parasitize other spider wasps.

Spotted Garden Eel
Males battle each other over females and territory

Squirrel
Small rodents found in woodlands worldwide!

Stick Insect
There are more than 3,000 different species!

Strawberry Hermit Crab
When strawberry hermit crabs find shells that are larger than their own, they gather in a line from biggest to smallest. Once the biggest one sheds its shell, the next one in line will claim it, which is repeated down the line.

Swan
Populations have been affected by pollution!

Tarantula Hawk
Tarantula hawks are excellent pollinators, especially for milkweed.

Tenrec
Hedgeho-like nocturnal insectivore

Termite
Their mounds can be up to 9 meters tall!

Thornback Ray
The skate with the biggest spines!

Thrush
The American robin is called the robin because its red breast reminded European settlers of the robin back in the old country.

Tick
They inject hosts with a chemical that stops them from feeling the pain of the bite

Tiger Beetle
The adult tiger beetle is one of the fastest land insects in the world

Tortoise
Can live until they are more than 150 years old!

Tree Frog
Found in warmer jungles and forests!

Turaco
Their name means “banana-eater,” but they rarely ever eat bananas.

Turtles
Some species of aquatic turtles can get up to 70 percent of their oxygen through their butt.

Vinegaroon
Vinegaroons can spray 19 times before the glands are depleted

Viper
Vipers are one of the most widespread groups of snakes and inhabit most

Vulture
There are 30 different species worldwide!

Warthog
Has two sets of tusks on it's face!

Wasp
There are around 75,000 recognised species!

Water Buffalo
Has been domesticated for thousands of years!

White Ferret / Albino Ferrets
There are two different types of white ferrets!

Wolf Spider
Carnivorous arachnid that hunts its prey.

Woodlouse
This animal can roll up into a ball

Worm
Doesn’t have eyes.

Yellow Crazy Ant
One of the top 100 worst invasive species!

Zebu
There are around 75 different species!
Malagasy Animals List
- Aardwolf
- Achrioptera Manga
- American Cockroach
- Ant
- Antelope
- Archaeoindris
- Armyworm
- Aye-aye
- Banana Spider
- Barb
- Barn Owl
- Barn Swallow
- Bat
- Bed Bugs
- Bee
- Beetle
- Beewolf wasp
- Bird
- Biscuit Beetle
- Black Widow Spider
- Blind Snake
- Boas
- Brahminy Blindsnake
- Brookesia Micra
- Brown Dog Tick
- Bumblebee
- Butterfly
- Caecilian
- Carpenter Ant
- Cat
- Caterpillar
- Catfish
- Centipede
- Chameleon
- Chicken
- Cicada
- Cichlid
- Cockroach
- Codling Moth
- Comet Moth
- Common Buzzard
- Common Furniture Beetle
- Common House Spider
- Coton de Tulear
- Cow
- Crab
- Crab Spider
- Crane
- Cricket
- Crocodile
- Crocodylomorph
- Crow
- Cuckoo
- Dog
- Dog Tick
- Donkey
- Dormouse
- Dragonfly
- Duck
- Dumeril’s Boa
- Dung Beetle
- Dusky Shark
- Earthworm
- Earwig
- Eel
- Elephant
- Elephant Bird
- Elephant Shrew
- Falcon
- False Widow Spider
- Fiddler Crab
- Firefly
- Flea
- Fly
- Fossa
- Fox
- Frog
- Fruit Bat
- Fruit Fly
- Fulvous Whistling Duck
- Galapagos Shark
- Gazelle
- Gecko
- Gerbil
- German Cockroach
- Giant Trevally
- Glass Lizard
- Glowworm
- Gnat
- Goat
- Golden Oriole
- Grasshopper
- Green Bee-Eater
- Grey Heron
- Grey Mouse Lemur
- Guinea Fowl
- Gypsy Moth
- Hamster
- Hare
- Hawk Moth Caterpillar
- Hedgehog
- Heron
- Hognose snake
- Honey Bee
- Hoopoe
- Horse
- Horsefly
- Housefly
- Hovasaurus
- Human
- Huntsman Spider
- Ibis
- Indri
- Insects
- Jacana
- Jumping Spider
- Kingfisher
- Ladybug
- Leaf-Tailed Gecko
- Leech
- Lemur
- Lizard
- Locust
- Long-Winged Kite Spider
- Madagascar Hissing Cockroach
- Madagascar Jacana
- Madagascar Tree Boa
- Maggot
- Magpie
- Mantella Frog
- Masiakasaurus
- Mayfly
- Mealybug
- Millipede
- Mole
- Mongoose
- Mongrel
- Monitor Lizard
- Monkey
- Moorhen
- Mosquito
- Moth
- Mouse
- Mule
- Myna Bird
- Night Heron
- Nightingale
- Nile Crocodile
- No See Ums
- Olive Baboon
- Orb Weaver
- Otter
- Owl
- Parrot
- Peregrine Falcon
- Pheasant
- Pigeon
- Pompano Fish
- Praying Mantis
- Puff Adder
- Quail
- Rabbit
- Radiated Tortoise
- Rat
- Rhinoceros
- River Turtle
- Robin
- Rock Python
- Rodents
- Rooster
- Sable Ferret
- Sand Crab
- Satanic Leaf-Tailed Gecko
- Scorpion
- Sea Eagle
- Seahorse
- Sheep
- Shrew
- Shrimp
- Skink Lizard
- Slug
- Smokybrown Cockroach
- Snail
- Snake
- Sparrow
- Spider Wasp
- Spotted Garden Eel
- Squirrel
- Stick Insect
- Strawberry Hermit Crab
- Swallowtail Butterfly
- Swan
- Tarantula Hawk
- Tenrec
- Termite
- Thornback Ray
- Thrush
- Tick
- Tiger Beetle
- Tortoise
- Tree Frog
- Turaco
- Turtles
- Vinegaroon
- Viper
- Vulture
- Warthog
- Wasp
- Water Buffalo
- White Ferret / Albino Ferrets
- Wolf Spider
- Woodlouse
- Worm
- Yellow Crazy Ant
- Zebu
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What are the most common types of animals in Madagascar?
Madagascar is home to some 200 types of mammals, about a quarter of which are some species of lemur. There are also about 300 species of birds and more than 200 species of reptiles and amphibians each. The island is particularly rich in insects, however, with perhaps more than 100,000 known species.
Why is Madagascar’s wildlife so unique?
The island of Madagascar is a highly isolated, insular ecosystem. It was last attached to the African mainland some 150 million years ago. This isolation has allowed the wildlife to evolve semi-independently from the mainland. Some species have flown or swam across, but the harsh currents and long distances make it difficult.
What kinds of extinct species have been found in Madagascar?
From the fossil record, we know that Madagascar was once home to giant lemurs, pygmy hippos, giant tortoises, and elephant birds (essentially, large flightless birds that resemble an ostrich). Many of these species have gone extinct in the past 2,000 years with the arrival of people.
What kind of animals are in Madagascar?
The island has nearly 25,000 species of wildlife, many of which are unique to the country. Madagascar is home to over 40 types of Lemur, many of which are vulnerable or endangered. There are also bats, mongoose, crocodiles, monitor lizards, in addition to hundreds of other species of reptiles, mammals, and insects.
What can kill you in Madagascar?
Very little of the wildlife in Madagascar is dangerous to humans. Nile Crocodiles and Madagascan Black Widows pose the greatest threat of death.
What dangerous animals live in Madagascar?
Of all the animal species found in Madagascar, very little of its wildlife is actually dangerous. Madagascan Black Widows, Nile Crocodiles, and Scorpions are the main animals to look out for.










