Mudskipper
Mudskippers can walk on land using their pectoral fins!
Advertisement
Mudskipper Scientific Classification
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Mudskipper Conservation Status
Mudskipper Facts
- Name Of Young
- Fry
- Group Behavior
- Solitary/Group
- Fun Fact
- Mudskippers can walk on land using their pectoral fins!
- Biggest Threat
- Habitat loss
- Most Distinctive Feature
- Ability to breathe out of water
- Average Spawn Size
- Hundreds of eggs
- Predators
- Mammals, snakes, shorebirds, larger predatory fish, water snakes
- Number Of Species
- 43
- Slogan
- They walk on land
- Group
- School
- Nesting Location
- Burrows in mud or sand
Mudskipper Physical Characteristics
- Color
- Brown
- Green
- Dark Brown
- Light-Brown
- Skin Type
- Skin
- Venomous
- No
- Aggression
- High
View all of the Mudskipper images!
Mudskipper Summary
A mudskipper is any of numerous species of amphibious fish belonging to the subfamily Oxudercinae. These fish derive their name from their habit of “skipping” across mudflats and burrowing into soft sediment. Their remarkable ability to walk and breathe on land distinguishes them from most other species of fish. In fact, they find it easier to hunt on land than in water. They range throughout the tropical, subtropical, and temperate waters of the Atlantic and Indo-Pacific Oceans.
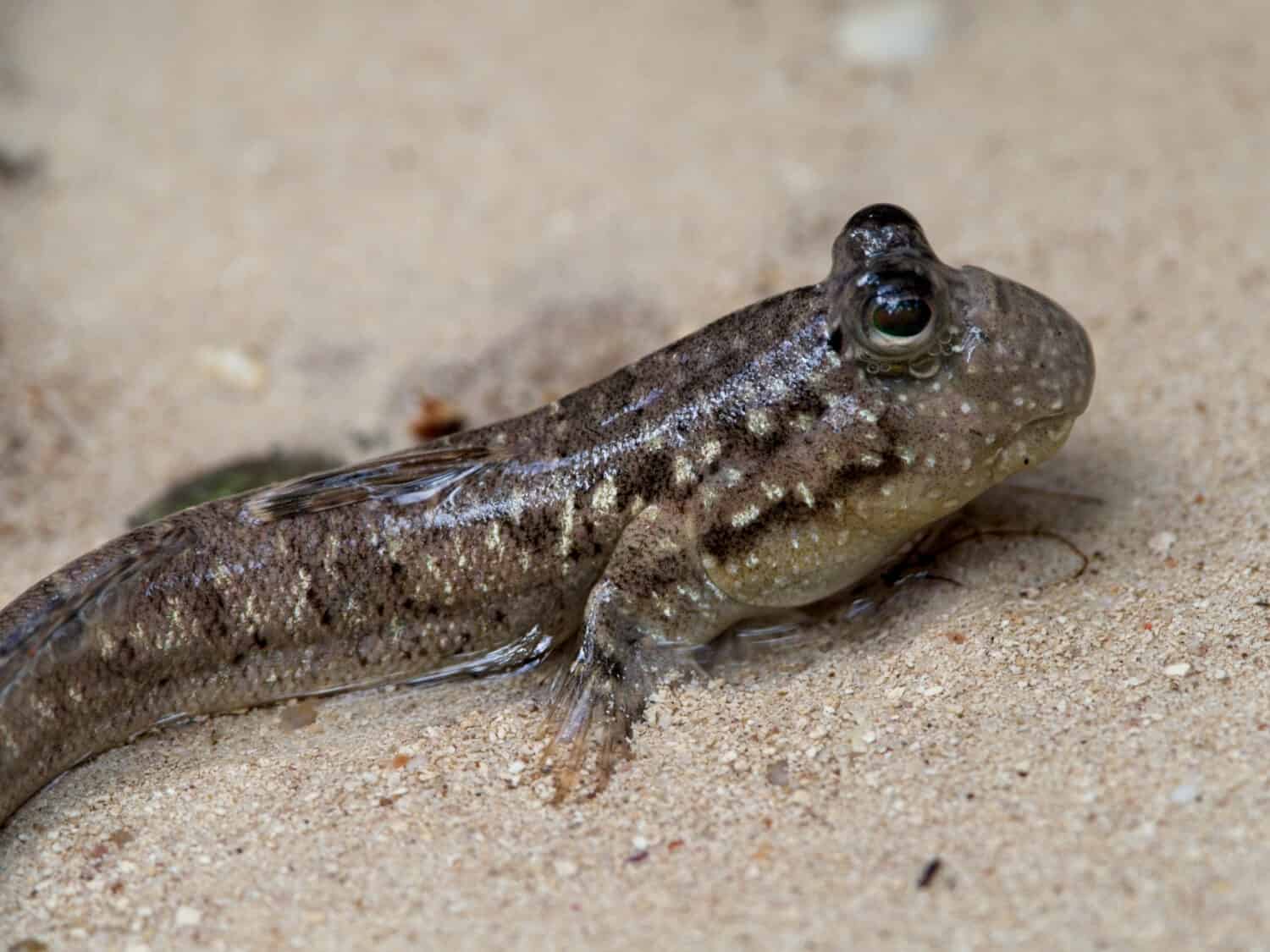

Mudskippers use their pectoral fins to walk on land.
©Tristan Barrington/Shutterstock.com
5 Mudskipper Facts
- Able to “walk” on land: These fish use their pectoral fins like feet to walk on land. They also use them to skip and climb.
- They spend more time out of the water than in it: Strangely enough, these fish spend a larger portion of their lives on land than in the water. They hold water inside their gill chambers, which helps them breathe out of water.
- They burrow in mud: These unusual fish survive in part by burrowing into the soft sediment of intertidal zones. These burrows provide protection, shelter, and a place to lay their eggs.
- Bulging eyes: One of the most unique features of the mudskipper is its bulging eyes, which perch on top of its head.
- They blink: Unlike most other fish, mudskippers blink. They do this to keep their eyeballs moist when out of water.
Mudskipper Classification and Scientific Name
Mudskippers belong to the subfamily Oxudercinae within the goby family Oxudercidae (alternately Gobiidae). This subfamily divides into 10 genera. It further belongs to the order Gobiiformes (gobies and their relatives) and the class Actinopterygii (ray-finned fishes). See the following section for a list of mudskipper species.
Mudskipper Species
Mudskippers are any of 43 recognized species. They include the following (grouped by genera):
- Genus Apocryptes
- Apocryptes bato
- Genus Apocryptodon
- Apocryptodon madurensis
- Apocryptodon punctatus
- Apocryptodon wirzi
- Genus Boleophthalmus
- Boleophthalmus birdsongi
- Boleophthalmus boddarti
- Boleophthalmus caeruleomaculatus
- Boleophthalmus dussumieri
- Boleophthalmus pectinirostris
- Boleophthalmus poti
- Genus Oxuderces
- Oxuderces dentatus
- Oxuderces nexipinnis
- Genus Parapocryptes
- Parapocryptes rictuosus
- Parapocryptes serperaster
- Genus Periophthalmodon
- Periophthalmodon freycineti
- Periophthalmodon schlosseri
- Periophthalmodon septemradiatus
- Genus Periophthalmus
- Periophthalmus argentilineatus
- Periophthalmus barbarus
- Periophthalmus chrysospilos
- Periophthalmus darwini
- Periophthalmus gracilis
- Periophthalmus kalolo
- Periophthalmus magnuspinnatus
- Periophthalmus malaccensis
- Periophthalmus minutus
- Periophthalmus modestus
- Periophthalmus novaeguineaensis
- Periophthalmus novemradiatus
- Periophthalmus pusing
- Periophthalmus spilotus
- Periophthalmus takita
- Periophthalmus variabilis
- Periophthalmus walailakae
- Periophthalmus waltoni
- Periophthalmus weberi
- Genus Pseudapocryptes
- Pseudapocryptes borneensis
- Pseudapocryptes elongatus
- Genus Scartelaos
- Scartelaos cantoris
- Scartelaos gigas
- Scartelaos histophorus
- Scartelaos tenuis
- Genus Zappa
- Zappa confluentus
Mudskipper Appearance
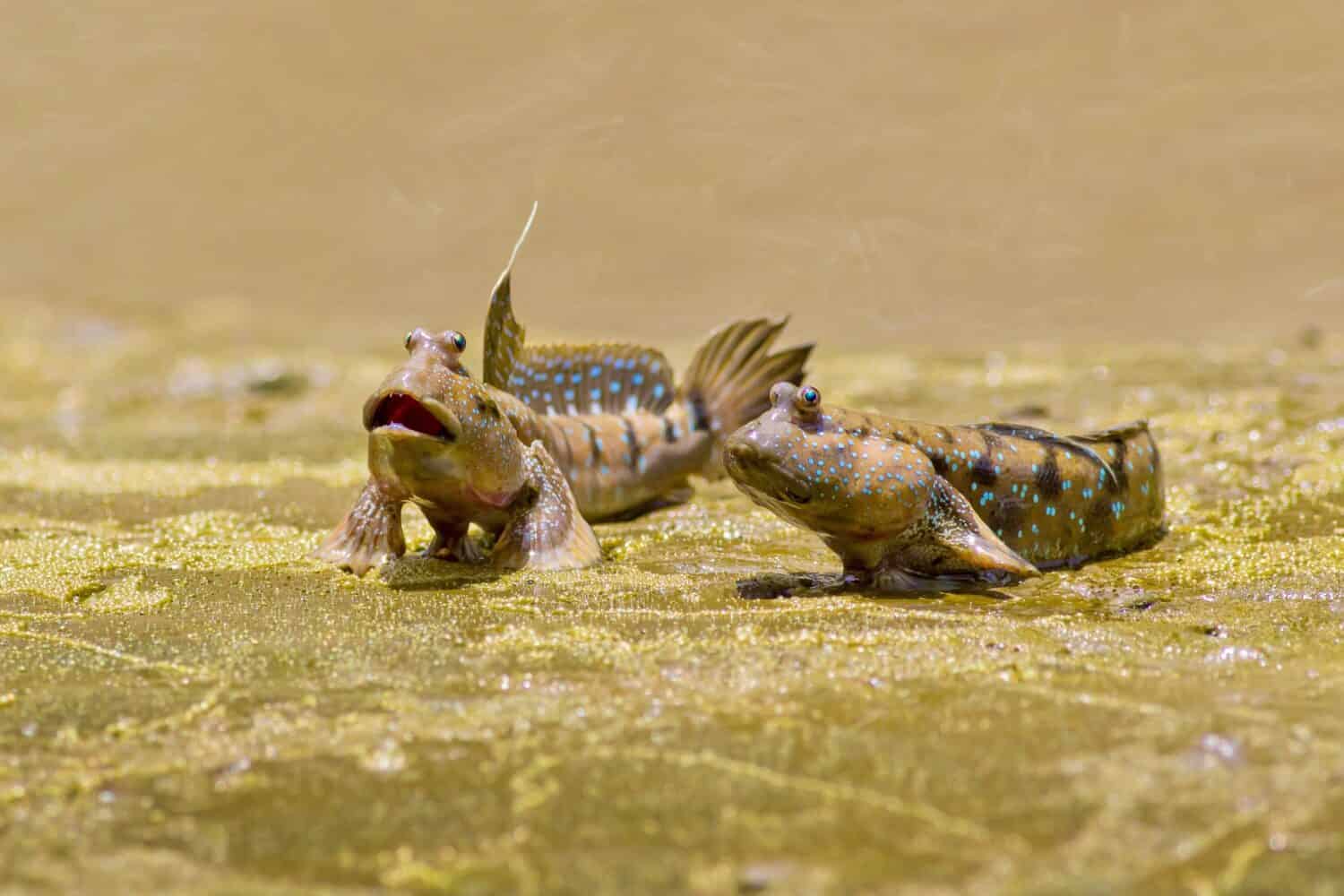

Mudskippers are famous for their odd appearance, including their bulging eyes and elongated bodies.
©aDam Wildlife/Shutterstock.com
Mudskippers are unique-looking fish with elongated bodies, protruding eyes on the tops of their flat heads, and prominent pectoral fins located far forward on their bodies. They use these fins to “walk” on land, “skip” across muddy flats, and even climb low vegetation. In color, they tend to be either dark or light brownish-green. Their specialized gills enable them to breathe air as long as they retain water inside their gill chambers. The lining of their mouths and throats also enables them to absorb oxygen. In size, these fish grow up to 11 inches in length with the giant mudskipper (Periophthalmodon schlosseri) being the largest species.
Mudskipper Distribution, Population, and Habitat
Mudskippers range throughout the Indo-Pacific region including areas of Africa, Asia, and Oceania. In addition to this, they also live along Africa’s Atlantic coast. Depending on the species, mudskippers can survive in marine, brackish, and freshwater environments. They inhabit a variety of habitats including oceans, estuaries, swamps, and mudflats. They dig burrows in intertidal zones to thermoregulate, hide from predators, and lay their eggs.
The IUCN includes several species of mudskippers on its Red List of Threatened Species including the giant mudskipper, the slender mudskipper, and the kalolo mudskipper. It currently assigns them the status of Least Concern.
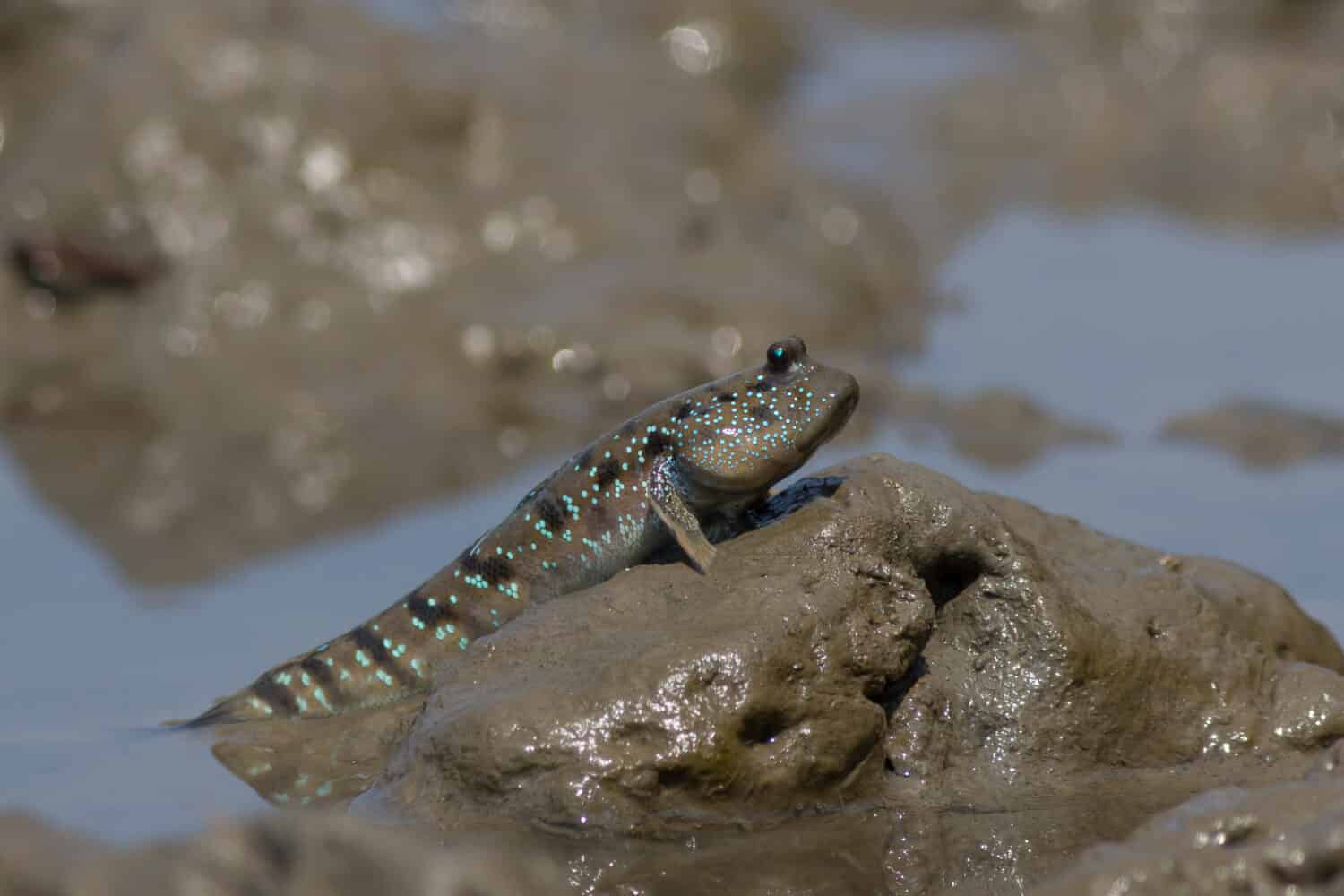

Mudskippers are amphibious, able to survive both in water and on land.
©aDam Wildlife/Shutterstock.com
Mudskipper Evolution and History
The first tetrapods (land-dwelling vertebrates) appear to have evolved about 395 million years ago between the Devonian and Carboniferous Periods. Scientists believe the unusual amphibious adaptations of mudskippers may offer clues to this crucial period of evolution. However, the fossil record from this time is extremely sparse.
One of the mudskipper’s notable adaptations is its lack of a fleshy tongue. To swallow, it uses mouthfuls of water both to suck in its prey and guide it to the back of its throat. This allows it to eat on land. Some scientists speculate that this adaptation played a role in allowing water-dwelling animals to transition to land hundreds of millions of years ago.
Mudskipper Predators and Prey
Mudskippers are carnivorous fish that come up on land to feed. This is due to their difficulty in catching prey while in water. Before moving onto dry land, each individual mudskipper takes in a mouthful of water to use as a “hydrodynamic tongue.” On land, it pounces on its prey, expelling some of the water in its mouth. After the water surrounds its prey, it sucks the water back in, drawing the animal in with it. The water also acts as a tongue that enables the swallowing mechanism by guiding the prey to the back of the mudskipper’s mouth.
What Do Mudskippers Eat?
Fish within this subfamily consume small crustaceans like crabs as well as snails, worms, and various insects. Some reports also describe them as occasionally cannibalistic.
What Eats Mudskippers?
These fish have a number of predators both on land and in the water. On land, these include various mammals, snakes, and shorebirds like herons and kingfishers. In the water, their predators include larger predatory fish and water snakes.
Mudskipper Reproduction and Lifespan
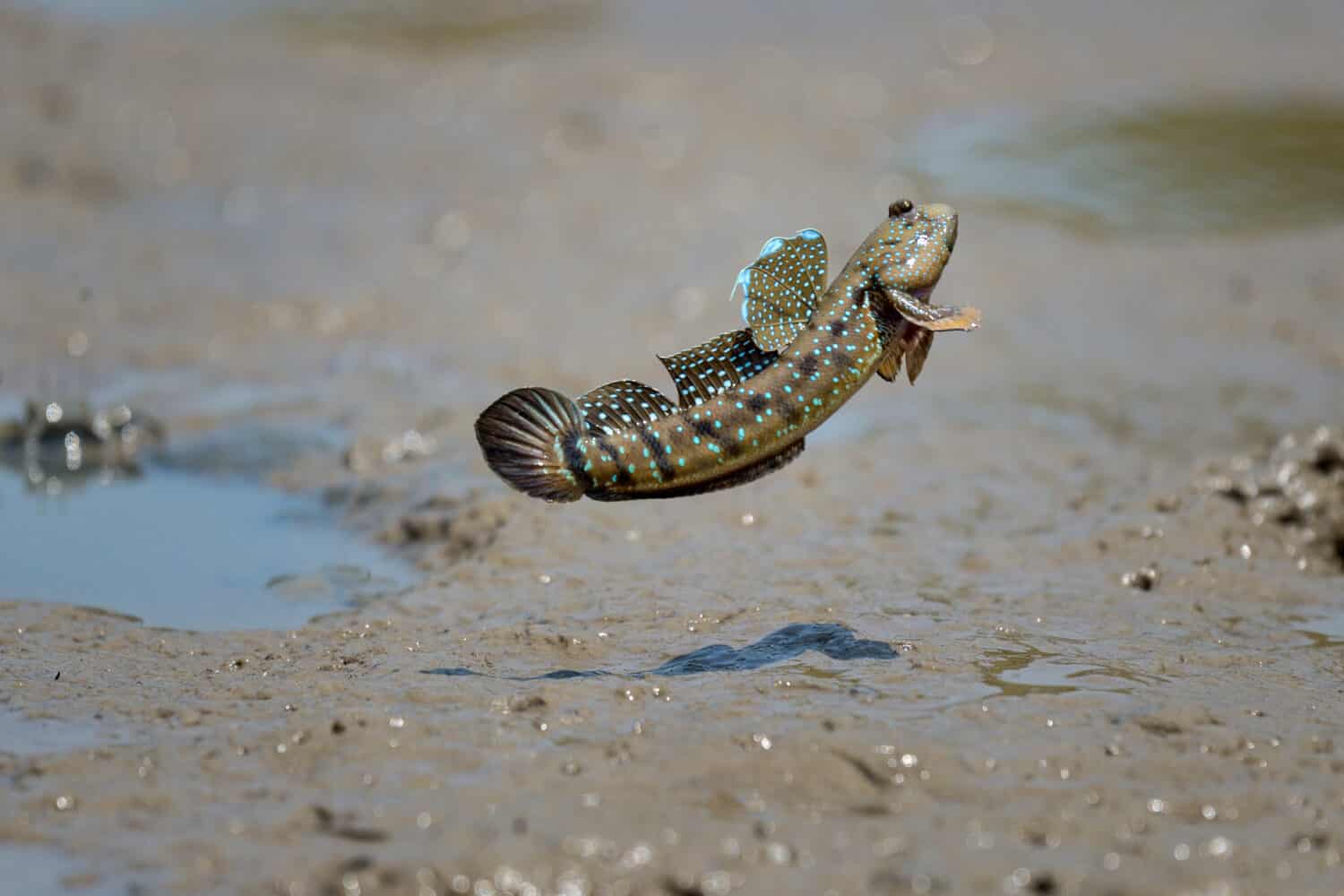

Male mudskippers leap in the air during spawning season to attract a mate.
©Anake Seenadee/Shutterstock.com
During spawning season, male mudskippers compete for females by leaping as much as two feet in the air and posturing. The successful male accompanies the female into her burrow, which she digs by scooping up mud in her mouth and flinging it away. Once the female lays her eggs, potentially hundreds at a time, the male fertilizes them. Shortly thereafter, the female leaves the male alone to guard the eggs.
During low tide, the parental guardian transports mouthfuls of air into the burrow to aid embryonic development. When the embryos have completed their development, the guardian then removes the air from the burrow to facilitate the entry of water during a nocturnal rising tide. The incoming water induces hatching.
Mudskippers in Fishing and Cooking
Mudskippers are perfectly edible, though they may taste muddy due to their burrowing habits. Some authorities recommend soaking them in water for a few days to remove or lessen this taste. They are a delicacy in parts of Asia including China, Japan, and Vietnam. Although grilling and frying are two of the most popular cooking methods, these fish can be eaten in a variety of ways. To get started, check out this recipe for fried mudskippers.
Related Animals:
View all 164 animals that start with MMudskipper FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Where are mudskippers found?
Mudskippers are found throughout tropical, subtropical, and temperate regions of the Atlantic and Indo-Pacific Oceans.
Can mudskippers walk?
Although mudskippers lack legs, they are able to “walk” using their pectoral fins.
How long can mudskippers live out of water?
Mudskippers can survive out of water for days at a time by trapping water in their gill chambers. They also absorb oxygen through the lining of their mouth and throat.
Are mudskippers endangered?
The IUCN assigns the status of Least Concern to several species of mudskippers.
Do mudskippers scream?
Mudskippers often scream to intimidate each other in a territorial dispute.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- Ocean Conservancy, Available here: https://oceanconservancy.org/blog/2022/05/12/5-facts-mudskippers/
- Britannica, Available here: https://www.britannica.com/animal/mudskipper
- FishBase, Available here: https://www.fishbase.se/summary/FamilySummary.php?ID=789
- Eschmeyer's Catalog of Fishes, Available here: https://researcharchive.calacademy.org/research/ichthyology/catalog/SpeciesByFamily.asp#Oxudercidae
- Mudskipper Species List, Available here: http://www.mudskipper.it/SpeciesList.html
- Encyclopedia of Life, Available here: https://eol.org/pages/52568894
- Fishes Out of Water, Available here: https://repository.si.edu/bitstream/handle/10088/57124/Parenti_Lynne_R_-20161021-C2_Parenti_and_Jaafar.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
- Phys.org, Available here: https://phys.org/news/2015-03-mudskipper-fish-clues-tongue-animals.html
- Integrative and Comparative Biology, Available here: https://academic.oup.com/icb/article/51/1/38/638172
- Abby's Plate, Available here: https://abbysplate.com/how-to-fry-mudskippers/
- Popular Science, Available here: https://www.popsci.com/environment/mudskippers-blink-evolution/
- Molecular Phylogentics and Evolution, Available here: https://www.bio.fsu.edu/steppanlab/assets/files/2022-Steppan-Mudskippers.pdf
- Badman's Tropical Fish, Available here: https://badmanstropicalfish.com/mudskipper-care/