Rainbow Boa
Epicrates cenchria
The rainbow boa is named for its iridescent skin that refracts light and creates a rainbow-colored effect.
Advertisement
Rainbow Boa Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Reptilia
- Order
- Squamata
- Family
- Boidae
- Genus
- Epicrates
- Scientific Name
- Epicrates cenchria
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Rainbow Boa Conservation Status
Rainbow Boa Facts
- Prey
- Rodents, small birds, small lizards, some aquatic animals.
- Fun Fact
- The rainbow boa is named for its iridescent skin that refracts light and creates a rainbow-colored effect.
- Litter Size
- 12-25 babies
View all of the Rainbow Boa images!
The rainbow boa is a brown-patterned reptile that primarily seeks out rodents and small birds in its diet.
A rainbow boa prefers warm temperatures with high humidity for the most part, and it is endemic to Central and South America. Instead of determining sexual maturity by age, the males must be at least four feet long to mate. Temperature plays a big role when their eggs hatch, which is why they often choose warmer locations to live.
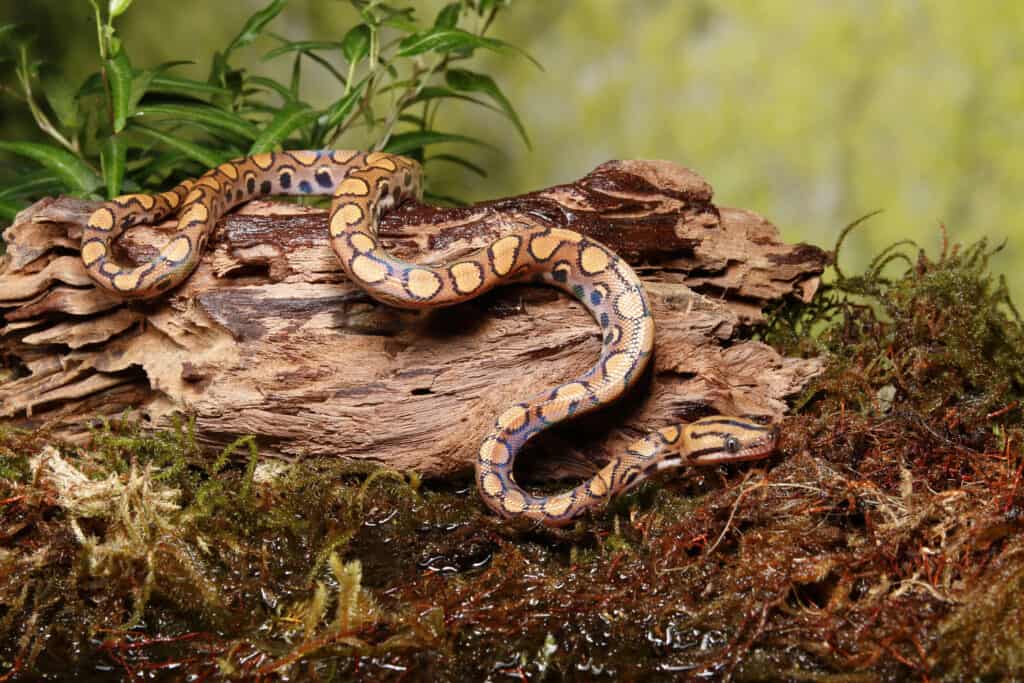

Rainbow Boas are a highly popular choice amongst pet enthusiasts
©iStock.com/David Kenny
5 Amazing Rainbow Boa Facts
- The gestation period of the rainbow boa is approximately 5 months.
- Evolution hasn’t completely changed them! These reptiles are still considered to be primitive because they have two vestigial hind limbs.
- To sense the body heat of prey, these snakes have specialized pits along their lips to locate their next meal.
- The rainbow boa is endemic to Central America and South America, but their numbers have declined as a result of being captured for the pet trade.
- While the name “rainbow” boa would suggest that this snake is colorful, it only reflects these colors in an iridescent shimmer. The actual body is an assortment of brown hues.

Native Habitat
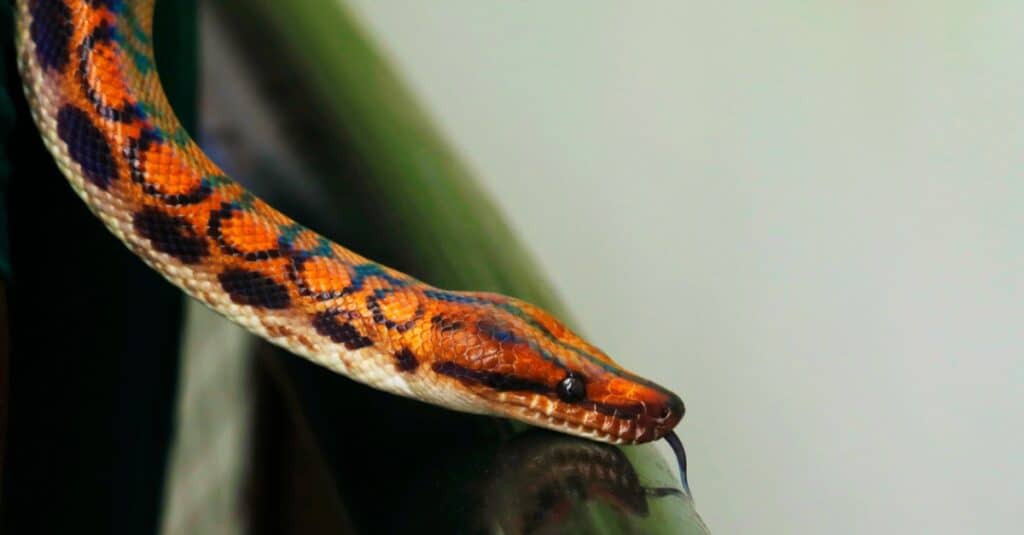

Rainbow boa head. It can reflect sunlight into a rainbow.
©iStock.com/libin jose
The main location to find this boa is broad because the different types are spread throughout Central and South America. They prefer land, often living in humid weather conditions with high temperatures. These predators primarily hunt on the floor of the forest, but they will climb up trees and bushes to rest.
If you want to buy boas as pet snakes, you can visit a local pet store that sells exotic reptiles. They’d direct you to the proper enclosure and tank size needed to support this hefty pet. Generally, their cost is difficult to determine because the pet trade is so regulated. Some cost over $400 for intermediate pet owners but finding a range of prices is difficult. Furthermore, the cost of the right tank size is high, which is why it is best to seek out these boas at zoos or in nature instead.
Scientific Name
The rainbow boa, sometimes called the slender boa, has the scientific name of Epicrates cenchria. The name comes from a combination of tributes to scientists and researchers who were pivotal in the discovery of multiple snake species. It comes from the Reptilia class as part of the Boidae family.
Evolution
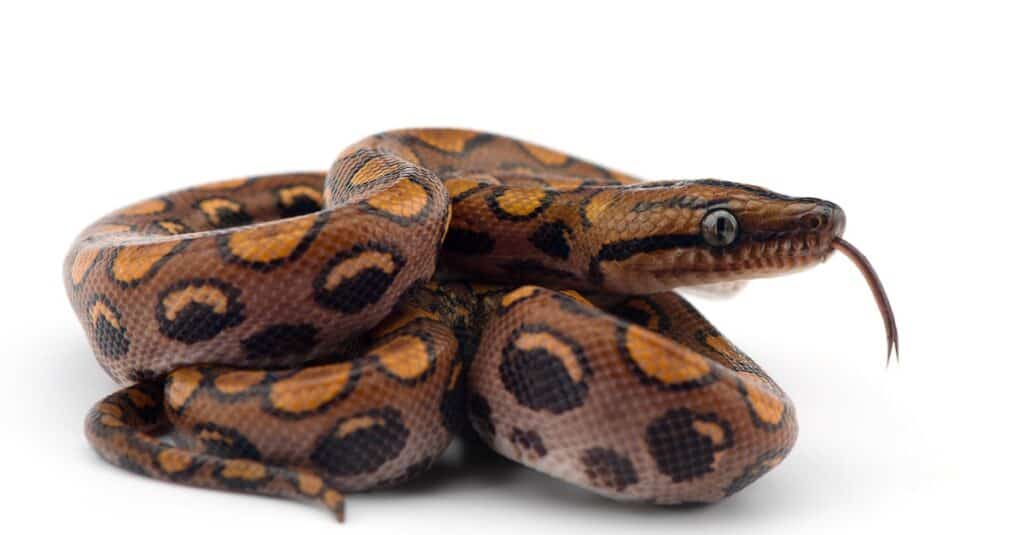

Rainbow boas are considered true boas
©iStock.com/PetlinDmitry
As members of the family Boinae, Rainbow Boas are considered true boas, along with 34 other species which can be found in the Caribbean, Central America, and South America. Because they come under the larger family Boidae, they are also related to the following:
- Bevel-nosed boas: Found in Oceania, they consist of five species belonging to the Candoiinae subfamily.
- Old world sand boas: Found in Africa, Asia, Canada, Europe, Mexico, the Middle East, and the United States, they belong to the Erycinae subfamily.
- Malagasy boas: Found on the island nation of Madagascar, they belong to the Sanziniinae subfamily.
- Neotropical dwarf boas: these small-sized constrictors can be found from southern Mexico to Colombia and belong to the Ungaliophiinae subfamily.
The 9 Different Types of Rainbow Boas
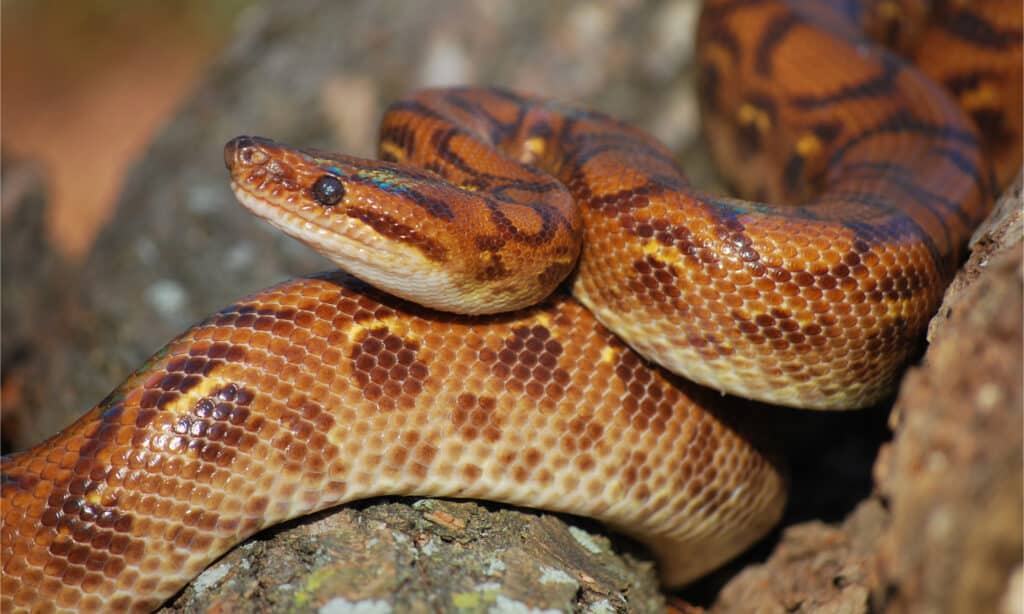

Brazilian rainbow boas are considered to be easy to care for
©Kassia Marie Ott/Shutterstock.com
There are five main subspecies of rainbow boas, though only one of them seems to be at risk of becoming endangered. With proper identification, you’ll see how a few differences can completely change how you look at them.
- Brazilian rainbow boa (Epicrates cenchria cencria): They make great pet snakes with very little care. You need to keep their enclosure moist, though their care is already minimal. They require high temperatures with high humidity, and they can be aggressive. They need no smaller than 30 gallons of space for their tank size.
- Peruvian rainbow boa (Epicrates cenchria gaigeae): This boa primarily lives in Peru and Bolivia, preferring humid and tropical forests. Despite being incredibly slender, their identification shows that they are the biggest rainbow boa subspecies. Females tend to be longer.
- Columbian rainbow boa (Epicrates maurus): The Columbian rainbow boa lives in northern South America. However, as the name suggests, the Columbian rainbow boa primarily lives in Columbia. Very seldom do they grow longer than 5 feet in size. It is also known as the brown rainbow boa.
- Argentine rainbow boa (Epicrates alvarezi): This species is only found in Argentina and boasts a 20-year lifespan with proper care.
- Paraguayan rainbow boa (Epicrates crassus): The typical locations of this snake are Paraguay, Brazil, and Argentina. For proper identification, check out their length as they only reach about 4 feet long.
- Caatinga rainbow boa (Epicrates assisi): This snake is found in Brazil, and they are not often found in the US pet trade. They are extremely hard to find and do not make good pet snakes.
- The Marajo Island, central highland, and Espirito Santo rainbow boas are all subspecies of the Brazilian rainbow boa. The two latter subspecies were discovered in 1935, while the Marajo Island boa was found in 1938.
Size
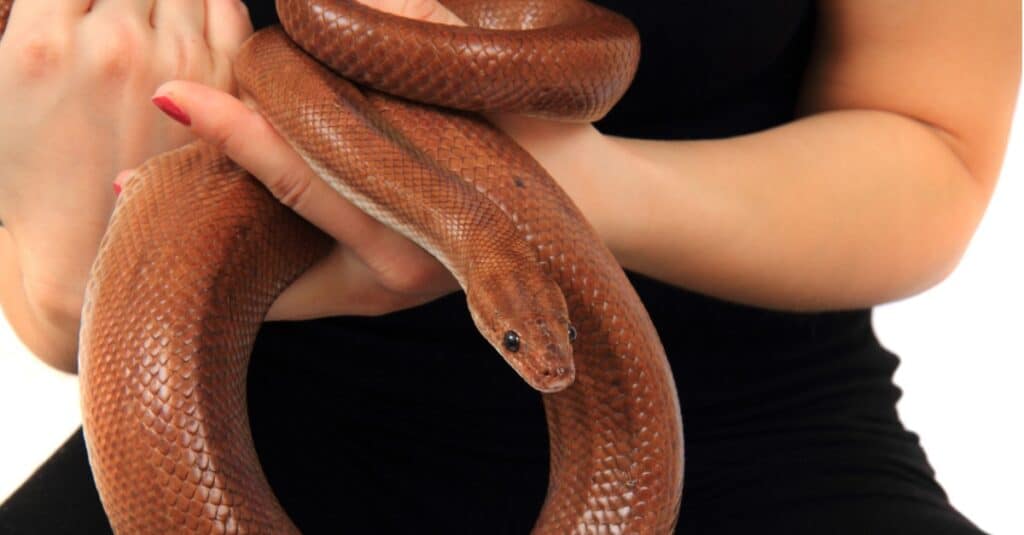

The Peruvian rainbow boa is the largest subspecies of rainbow boa and is capable of reaching 8 feet
©iStock.com/jonnysek
The different types of rainbow boas come in different sizes.
- Brazilian rainbow boa is from 4 to 6 feet in length
- Peruvian rainbow boa is between 7 to 8 feet long. Peruvian rainbow boas are the largest of the rainbow boas.
- Columbian rainbow boas are four feet long, rarely exceeding five feet long.
- Argentine Rainbow boas can grow up to about 4.5 – 6ft in length. They have the most slender bodies of all rainbow boas.
- Paraguayan Rainbow boas usually reach about 3.5 – 4 ft.
- Caatinga Rainbow Boas reach 4 feet in length.
Diet
In captivity, pet owners feed their rainbow boas mice and rats. In the wild, rainbow boas eat many types of rodents, birds, and lizards. They capture their prey by ambushing them and encircling them to constrict their dinner.
Lifespan
In the wild, rainbow boas live for 7-12 years. In captivity, rainbow boas live for 20 years. The oldest recorded rainbow boa was a Columbian rainbow boa that lived for 42 years!
Reproduction and Development
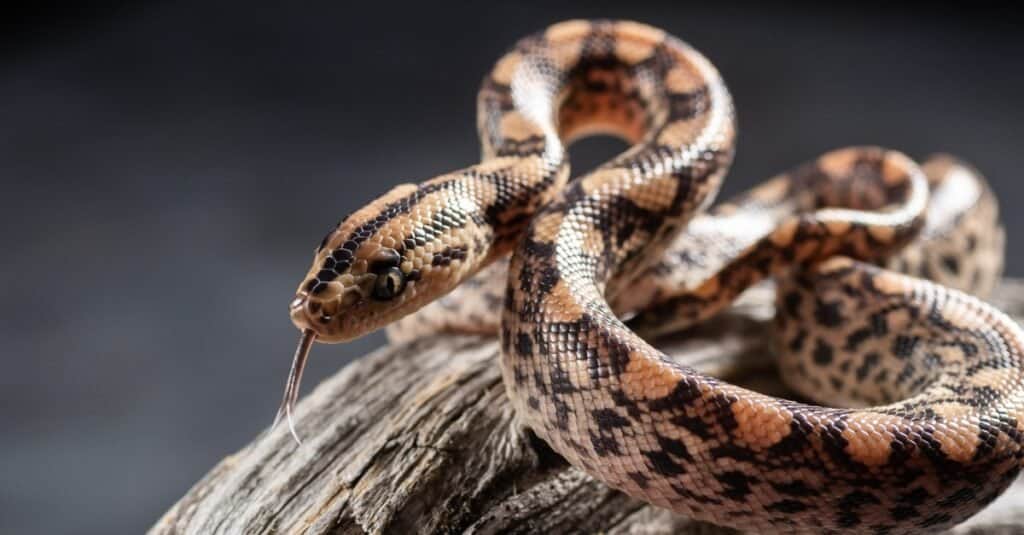

Rainbow boas have a gestation period of five months and can have a maximum of 25 babies at once
©iStock.com/Evgenyi_Eg
You can tell the sexual maturity of a rainbow boa by its length, rather than its age. Females breed when they are 4.5 feet long on average. Male rainbow boas breed when they are 4 feet long. They usually reach this size around age three or four years old.
A Rainbow boa is pregnant for five months. They have between 12 to 25 baby snakes at a time, although some litters have been as high as 35! Each baby snake is between 15 to 20 inches long and grows to 40 inches long in its first year. Female snakes are almost always larger than male snakes and eat more food.
Population & Conservation Status
As they are endemic to Central and South America, the identification of a global population is hard to pinpoint. One of the biggest threats to these predators is the pet trade since their beautiful patterns and colors make them ideal for pet sales. They also constantly deal with damage to their natural habitat, which is used for ranching, agriculture, and commercial development, despite their ability to control small mammal populations. When left alone, their average lifespan can reach well over 20 years with a 5-month gestation period.
According to the IUCN, the conservation status of this boa constrictor family is “least concern,” though it hasn’t been assessed since 2013. The Argentinian rainbow boa seems to be the only species at risk as it is “near threatened” (as of 2020).
How to Identify a Rainbow Boa: Physical Description
Though it is named for one of the most natural assortments of colors in the world, the Brazilian rainbow boa isn’t actually bright and bold. Instead, the majority of their bodies are brown or reddish-brown colors, featuring three solid black stripes behind the head. With their natural ridges along with the scales, it looks as though they reflect bold colors as if through a prism, even though the real colors are neutral tones. Along their back, you’ll see black rings that look almost like blotches. Still, this species has many variations in color, and they range from 4-6 feet long with a head that exceeds the width of their neck, making it easy to discern from the tail.
How to identify these snakes:
- Brown or reddish-brown bodies.
- Three black stripes behind the head.
- Large black rings along the back.
- Up to 6 feet long.
- Wider head than neck.
Pictures

©iStock.com/libin jose

©iStock.com/Evgenyi_Eg
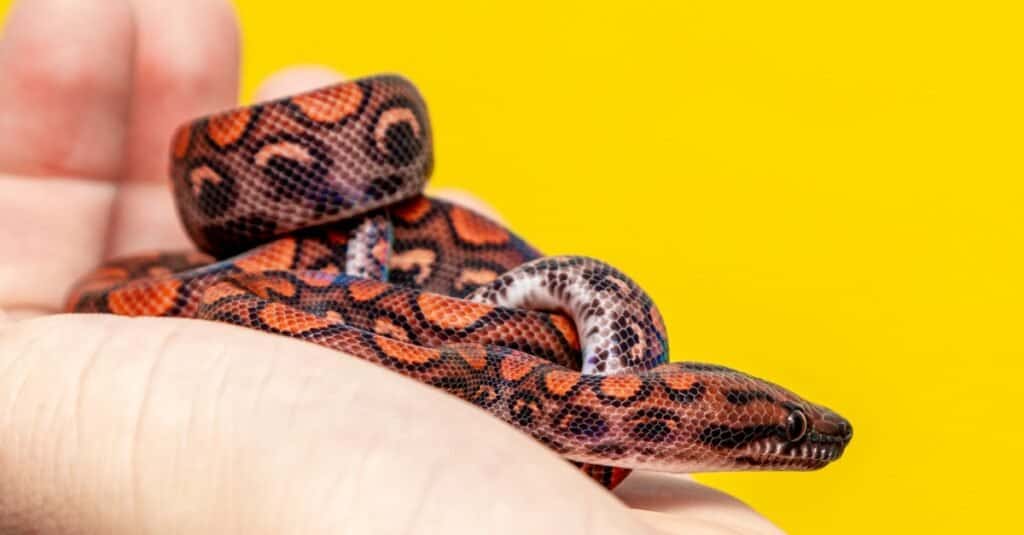

©iStock.com/Murilo Gualda
How Dangerous Are They?
Though these snakes look intimidating, take a breath of relief because they are non-venomous. Even if they attempt to bite you, they cause anything more than a scratch like a cat would. Whether the snake is your pet or in the wild, the best thing that you can do is to remain calm. If nothing else, the bite is meant as a way to defend itself, not actually do any damage. Relaxing will allow the boa to let go and go back to its enclosure or natural surroundings without much injury.
Behavior and Humans

Rainbow boas are especially popular owing to their laidback nature
©iStock.com/Murilo Gualda
These boas are a common pet amongst intermediate owners for their docile nature and beautiful appearance. Since they don’t have venom, they are a much less risky option, though they require access to a balanced diet and plenty of space in their habitat.
Even in the wild, the rainbow boa is not known to be a pest. They can be shy yet defensive if disturbed, and they typically go after small prey. Basically, if you leave them alone, they won’t bite.
If you choose to adopt these pet snakes, you need to research proper care and tank size for your particular area. Even baby boas need plenty of space to hide and move in their enclosure to prevent boredom and aggression. When you first bring them home, don’t be surprised if the baby boa attempts to nip at you until they are comfortable.
Similar Animals
View all 114 animals that start with RRainbow Boa FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are rainbow boas aggressive?
Yes. Since this type of snake tends to be rather shy, they become aggressive if they do not want to be handled or if they feel threatened.
Do rainbow boas make good pets?
Due to how aggressive and timid they can be the rainbow boa is not a good pet for any beginner. Individuals who have some experience with snakes are better suited to this particular species.
How big do rainbow boas get?
The average size of a rainbow boa is 4-6 feet long, giving them a medium-sized body. When they are born after the five-month gestation period, the typical size of a baby boa is 15-20 inches long, growing up to nearly 40 inches in the first year.
Do rainbow boas like to be handled?
Though they can be quite shy, this reptile tends to be rather calm when handled regularly. The babies are a little nippier when they are young, which is due to their natural instincts to protect themselves. Once they have acclimated to their surroundings, they become much easier to handle. Generally, Brazilian rainbow boas prefer only 10 minutes of handling at a time until they are used to their habitat.
Are rainbow boas good for beginners?
No. This type of snake is best for intermediate pet owners.
Are rainbow boas venomous?
No. In fact, most boas are not venomous at all, choosing to constrict their prey before devouring it.
How do rainbow boas hunt?
These boas have heat-sensing pits along their jaw, which they use to look for prey on rocky terrain or on the ground. Though they can swim, they often choose not to hunt in the water unless necessary.
Where do rainbow boas live?
Brazilian rainbow boas primarily live near the Amazon River, the coasts of Guyana, the southern region of Venezuela, Suriname, and French Guiana. Their location entirely depends on their access to humid weather, though they also can live comfortably in savannas with open space to hunt.
What do rainbow boas eat?
These predators are carnivores. When found in the wild, the typical diet includes rodents and birds, though they will also digest lizards and some aquatic animals as their prey. Once they’ve captured their prey, they constrict it to kill it before eating it. Most pet owners feed their rainbow boas live rats.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- Smithsonian's National Zoo & Conservation Biology Institute, Available here: https://nationalzoo.si.edu/animals/brazilian-rainbow-boa
- Animalia, Available here: https://animalia.bio/rainbow-boa
- Reptiles Magazine, Available here: https://reptilesmagazine.com/rainbow-boa-care-sheet/
- Everything Reptiles, Available here: https://www.everythingreptiles.com/brazilian-rainbow-boa/
- ITIS, Available here: https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=209561#null