Red Tail Boa (common boa)
Boa constrictor constrictor
Red tailed boas don’t suffocate their prey, they squeeze until the heart stops circulating blood to the brain.
Advertisement
Red Tail Boa (common boa) Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Reptilia
- Order
- Squamata
- Family
- Boidae
- Genus
- Boa
- Scientific Name
- Boa constrictor constrictor
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Red Tail Boa (common boa) Conservation Status
Red Tail Boa (common boa) Facts
- Name Of Young
- Neonates, snakelets
- Group Behavior
- Solitary except during mating season
- Fun Fact
- Red tailed boas don’t suffocate their prey, they squeeze until the heart stops circulating blood to the brain.
- Other Name(s)
- boa constrictor
View all of the Red Tail Boa (common boa) images!
The red tail boa is sometimes called the Suriname red tail boa, boa constrictor, or common boa.
Summary
The common boa can grow to be 13 feet long or greater when they reach their full-grown size. They are wonderful pets, though their reproductive habits and natural habitat range greatly. They don’t require much upkeep beyond a large enclosure and the right humidity, but they are also captured as a way to make snakeskin products.
5 Amazing Red Tail Boa Facts
- Due to the slow speed of the metabolism, one meal can fill up this snake for months before he becomes hungry again.
- The oldest boa constrictor on record lived to be 40 years, 3 months, and 14 days old. However, the expected lifespan is 20-30 years when in captivity.
- As big as this boa may be when full-grown, they are easy to care for and are great pets for beginners.
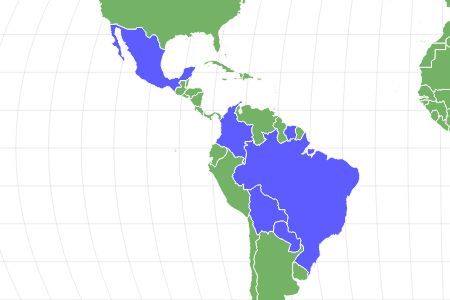
- The common boa primarily lives in Central America, though it is native to Colombia, Suriname, and other countries nearby.
- The typical price of a baby is $200, but more unique colors cost about $1,000 or more.
Where to Find Red Tail Boas
The preferred habitat of the boa constrictor has high levels of humidity and warmth, which is why they are often found in South and Central America. Woodlands, grasslands, tropical forests, and semi-deserts are all prime spots for these snakes to live. They are sometimes referred to as the Colombian red tail boas or Suriname red tail boas for their abundance in Colombia and Suriname. No matter where you look, they follow the food. Due to importation, they are an invasive species in Aruba, Mexico, Puerto Rico, Southeast Asia, and the United States.
If you’re looking to adopt one, that’s a different story. Due to the commercial demand for this boa as a pet, they can be found with private breeders or even major pet stores in both North and South America.
Types of Red Tail Boas
The boa constrictor consists of seven main subspecies. However, scientists have not separated them significantly in their descriptions. The primary difference between the subspecies appears to be the location, though some of them have biological differences too.
- Amaral’s boa (B. c. amarali) – This species lives in Brazil, Bolivia, and Paraguay. It was named for a Brazilian herpetologist named Afrânio Pompílio Gastos do Amaral.
- Red-tailed boa (B. c. constrictor) – This is the main name associated with the boa constrictor, and it primarily lives in South America.
- Peruvian long-tailed boa (B. c. longicauda) – This species lives in northern Peru.
- Ecuadorian boa (B. c. melanogaster) – This boa is specific to Ecuador.
- Orton’s boa (B. c. ortonii) – This subspecies was named for James Orton, an American naturalist. It primarily lives in South America.
- Pearl Islands boa (B. c. sabogae) – The species primarily lives off the coast of Panama in the Pearl Islands.
Even though there are other species that have been filed under the red tail boa subspecies, herpetologists and taxonomists have since separated them into their own species.
Red Tail Boa Scientific Name
The red tail boa, which is often referred to as the Suriname red tail boa, the common boa, or the boa constrictor, is a group of subspecies under the Boidae family of the Reptilia class. The scientific name is Boa constrictor, which is Latin in origin. Boa literally means “large snake.”
Red Tail Boa Population & Conservation Status
The biggest threat to the red tail boa is the over-collection of the species by humans, whether it be for the pet trade or for its skin in the fashion industry. They are not currently at risk of extinction because their numbers are steady, spreading them through Colombia, Suriname, Venezuela, and much of South America. While the exact population is unknown, they are classified as Not Extinct by the IUCN.
How to Identify Red Tail Boa: Appearance and Description
The large red tail boa can be quite a sight to see, especially because it can grow to be up to 13 feel long. Their size primarily depends on their diet and amount of space they have to grow, though the female is often the larger of the sexes. While the female is more likely to be 7-10 feet long as a full-grown adult, the males typically don’t grow any longer than 8 feet. Often, these snakes weigh about 60 lbs. when they reach adulthood, though there are some cases of these boas reaching 100 lbs. or more.
The color entirely depends on the subspecies. The red tail boa is primarily known for the saddle-like pattern of red or reddish-brown splotches along its brown, grey, or cream-colored body.
How to identify the red tail boa:
- Tan, gray, or cream color on body.
- Red or reddish-brown saddle pattern from head to tail.
- Ranges from 3 to 13 feet long.
- Weighs around 60 lbs. or greater.
Red Tail Boa Pictures
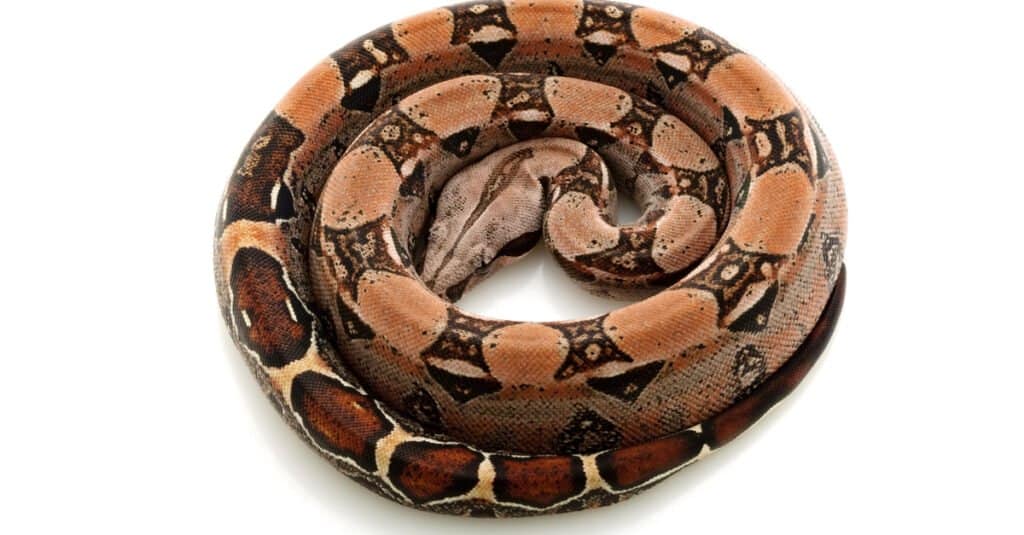

Red tail boas are common pets for those looking for a snake to love.
©fivespots/Shutterstock.com
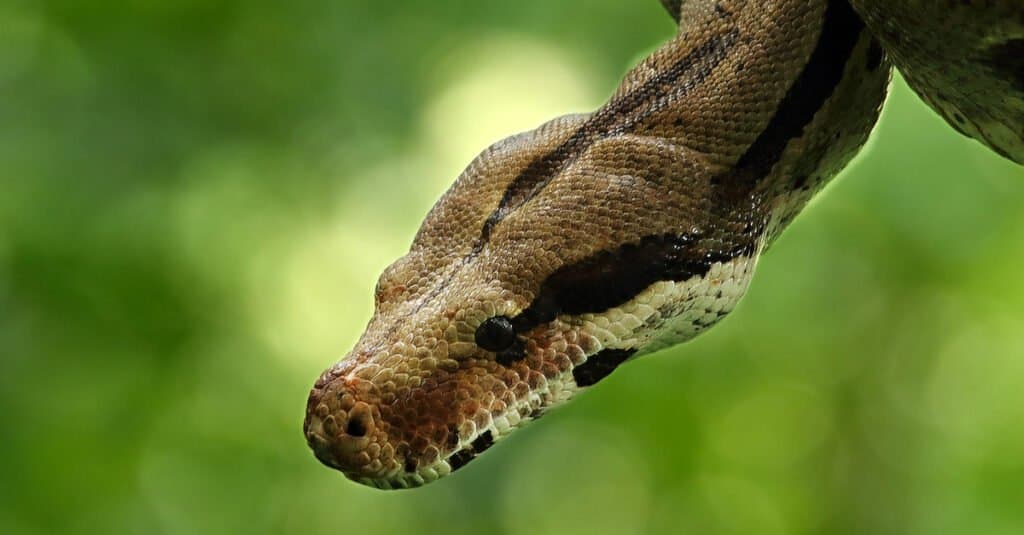

The red tail boa’s scientific name is the more commonly heard boa constrictor.
©Jan Hejda/Shutterstock.com
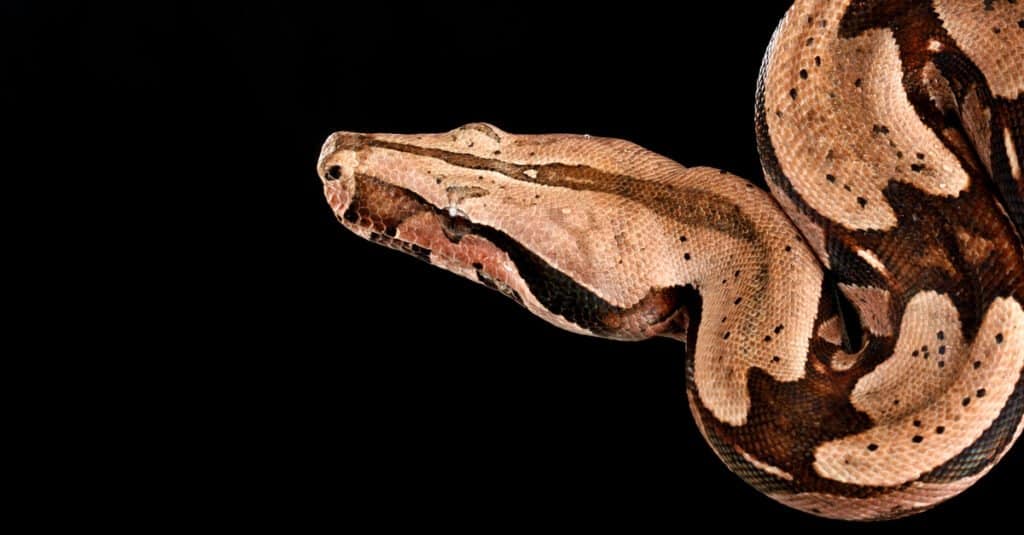

Red tail boas can measure up to 13 feet.
©Audrey Snider-Bell/Shutterstock.com
Red Tail Boa: How Dangerous Are They?
The level of danger you are in with a boa constrictor is primarily determined by whether they are kept in captivity or approached in the wild. In captivity, their behavior is fairly predictable. They are docile and calm, bonding well with their owner. In the wild, they are less familiar with humans, so they may seem timid.
If they bite you with their teeth, you don’t have to worry about any venom. In fact, they may simply let go as soon as they realize that you are not the prey that they want. You’ll need to wash the bite with soap and water. Medical treatment isn’t really necessary unless you keep bleeding, or if you were bitten on your eye.
Red Tail Boa Behavior and Humans
Considering that this snake is often kept as a pet, it is safe to say that boa constrictors have a great relationship with humans. As pets, they are easy to tame, taking on a docile personality. They aren’t venomous, and there are no worries about this type of snake becoming a pest. Their typical price is just $200 for a baby. However, much of the total price is due to the need for a large enclosure, which may cost $500 or more.
In the wild, if they want to catch prey or if they think your hand is food, they may use their teeth to bite. However, they quickly recognize the difference between the two.
What Do Red Tail Boas Eat?
Red tail boas eat largely smaller mammals using a unique method of constriction. Their favorite prey includes bats, squirrels, opossums, rodents, and rabbits. They’ll also snatch bats out of the air, eat bats, and other smaller animals such as lizards. Like all snakes, they’re strict carnivores that only eat meat.
For a complete analysis on their diets, make sure to read ‘What Do Boa Constrictors Eat? 12 Animals they Hunt.’
Similar Animals
View all 114 animals that start with RRed Tail Boa (common boa) FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are red tail boas aggressive?
Typically, these snakes aren’t aggressive, even though they can cause a lot of damage to anyone they consider to be a good meal.
Is a red tail boa a good pet?
Absolutely. This boa thrives in captivity, and most owners are able to get them quite tamed. They are bred often as pets, living for over 30 years with the right level of care. You’ll need to provide the right humidity for their enclosure, and they’ll need access to the right food.
Are red tail boas good beginner snakes?
If you want a bigger snake that doesn’t have complicated care, then the red tail boa is a great first choice. They are easy to accommodate with enough space for their enclosure, and they tend to be docile.
How big do red tail boa constrictors get?
The full-grown size of this boa species is quite a large range. While some only reach a size of 3 feet long, others can reach 13 feet or greater.
Why is called red tail boa?
This boa constrictor has a red tint on their scales.
Are red tail boas venomous?
No. The red tail boa is non-venomous. Instead, they use constriction to overwhelm their prey, leading them to fall unconscious and die.
How do red tail boas hunt?
These snakes ambush their prey, waiting patiently for their preferred meal to come along. They strike with their teeth, even though they have no venom. However, their bite allows their teeth to hold their prey in place as they wrap their body around it to cut off their circulation. Once the prey dies, they use their teeth to pull it down their throat. It takes about 4-6 days for red tail boas to digest large prey, though the teeth don’t serve much of a purpose beyond holding it in place. It is sometimes enough for the snake to not eat for months.
What do red tail boas eat?
As long as this snake can fit their prey into their mouth, they’ll eat it. Their diet ranges from small rodents to medium-size mammals. They need several days to digest, though it can take longer with larger game. They are primarily carnivores.
Where do red tail boas live?
Red tail boas are found around the world, though they primarily exist in South America.
Who would win a fight between a giant boa and an alligator?
An alligator would win a fight against a giant boa.
Most of the fights in the wild are decided by size or the presence of a particularly deadly attack, like venom. In this case, the boa is much smaller than the alligator and has to wrap its body around the reptile to kill it.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.