Dwarf Hamster
Cricetulus barabensis
dwarf hamsters love to explore at night.
Advertisement
Dwarf Hamster Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Mammalia
- Order
- Rodentia
- Family
- Cricetidae
- Genus
- Cricetulus
- Scientific Name
- Cricetulus barabensis
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Dwarf Hamster Conservation Status
Dwarf Hamster Facts
- Name Of Young
- pups
- Group Behavior
- Solitary
- Fun Fact
- dwarf hamsters love to explore at night.
- Estimated Population Size
- 57 million
- Biggest Threat
- Global warming, pollution, industrial development.
- Most Distinctive Feature
- Pouch-like cheeks
- Gestation Period
- 20-22 days
- Litter Size
- six
Dwarf Hamster Physical Characteristics
- Color
- Brown
- Grey
- White
- Tan
- Sandy
- Skin Type
- Fur
- Top Speed
- 5 mph
- Lifespan
- 2-3 years
- Weight
- 0.71 – 0.88 ounces
- Length
- 5.5 – 10.5 cm
- Age of Sexual Maturity
- four to five weeks old
- Age of Weaning
- three weeks
View all of the Dwarf Hamster images!

A dwarf hamster is a group of several subspecies, specifically dealing with hamsters that are smaller than four inches long.
They often have a lifespan of two to three years, though some live less than this. They are incredibly smart, and some subspecies hibernate through the winter months underground.
If you want to take a little extra time with this furry pet, you may even learn how to train them to do different tricks.
5 Incredible Dwarf Hamster Facts!
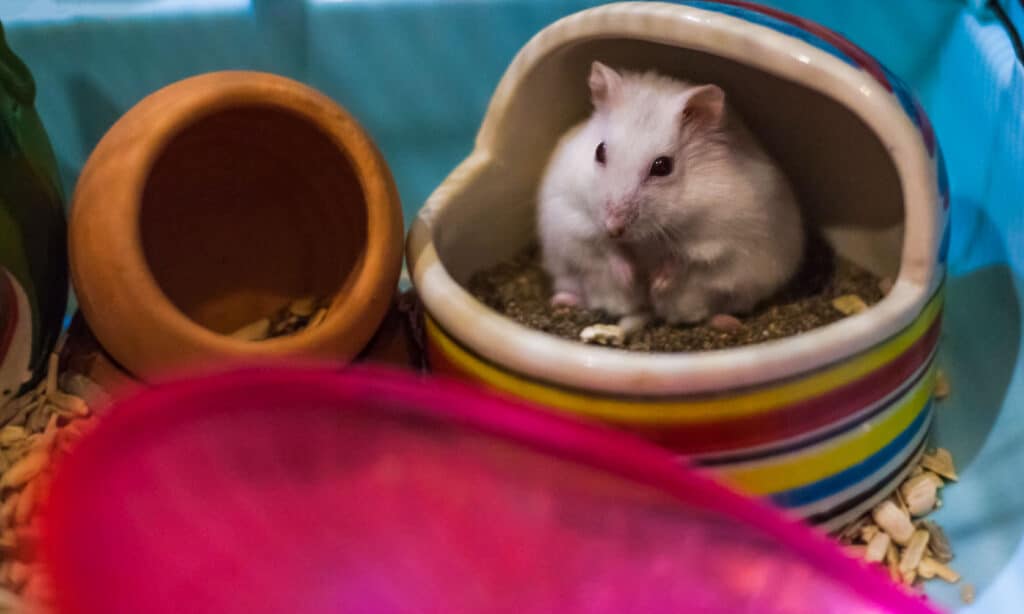

Similar to other hamster species, dwarf hamsters are active during the night and often engage in loud play with the various toys within their enclosure.
©iStock.com/Vichai Phububphapan
Here are a few fun hamster facts.
- Dwarf hamsters, like other types of hamsters, are nocturnal. They tend to play noisily at night with their many toys in their cage.
- When the dwarf hamster is stressed, he’ll squeal, squeak, or even scream instead of crying. They’ll also make these noises if they are hurt or afraid.
- Dwarf hamsters are born naked, blind, and deaf. Their fur doesn’t come in until they are about five days old, followed by their sight (14-18 days old) and finally their hearing (18+ days).
- Even though dwarf hamsters cannot burp, they can pass gas.
- Some dwarf hamsters lick and groom owners as a way to show affection.
Scientific Name
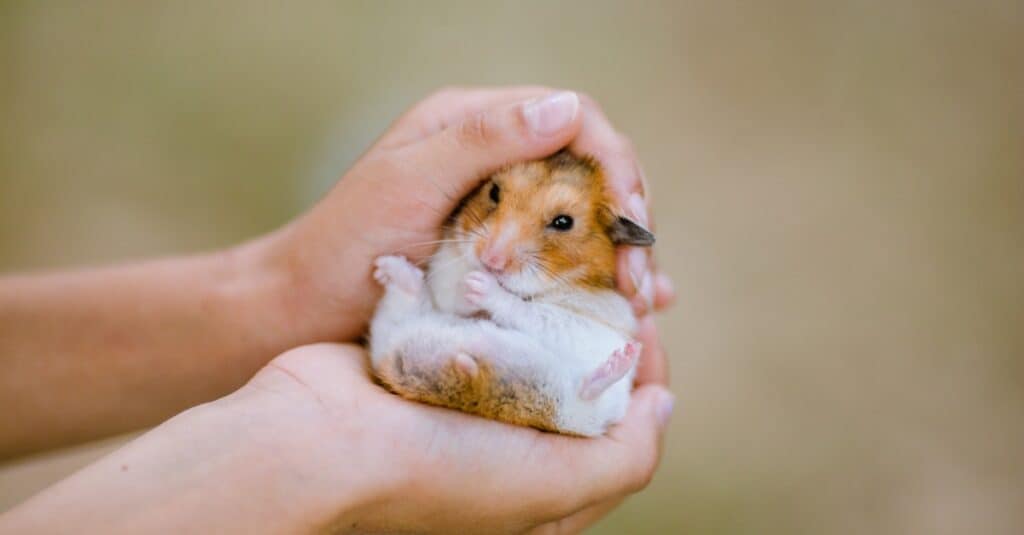

The Cricetulus barabensis, known as the dwarf hamster, belongs to the Cricetidae family within the Mammalia class, as designated by its scientific name.
©iStock.com/MajaArgakijeva
The dwarf hamster’s scientific name is Cricetulus barabensis, and it is part of the Cricetidae family of the Mammalia class. There are a total of seven subspecies, which include the Robo dwarf hamster, Chinese dwarf hamster, grey dwarf hamster, and Campbell’s dwarf hamster (among others). The grey dwarf hamster has much larger ears than other subspecies.
The name “barabensis” comes from the Greek word “Barabbas,” which comes from Aramaic “barabba,” which means “son of the father.”
Evolution and Origins
Winter White dwarf hamsters are native to Siberia, Mongolia, Kazakhstan, and Manchuria, where they resided in meadows, fields, and birch forests. Nonetheless, they also inhabit semi-arid regions in Central Asia.
The evolutionary past of dwarf hamsters is documented by 15 extinct fossil genera that date back to the Middle Miocene Epoch, which ranges from 11.2 million to 16.4 million years ago in Europe and North Africa, and 6 million to 11 million years ago in Asia. Four of the seven current genera comprise species that are now extinct.
Furthermore, during the late 1700s, naturalists documented the Syrian hamster, which is also referred to as Mesocricetus auratus or the golden hamster, and this marked the start of its domestication.
In 1930, Syrian hamster breeding stock was captured by medical researchers for animal experimentation, and additional domestication eventually resulted in its widespread popularity as a pet.
Appearance
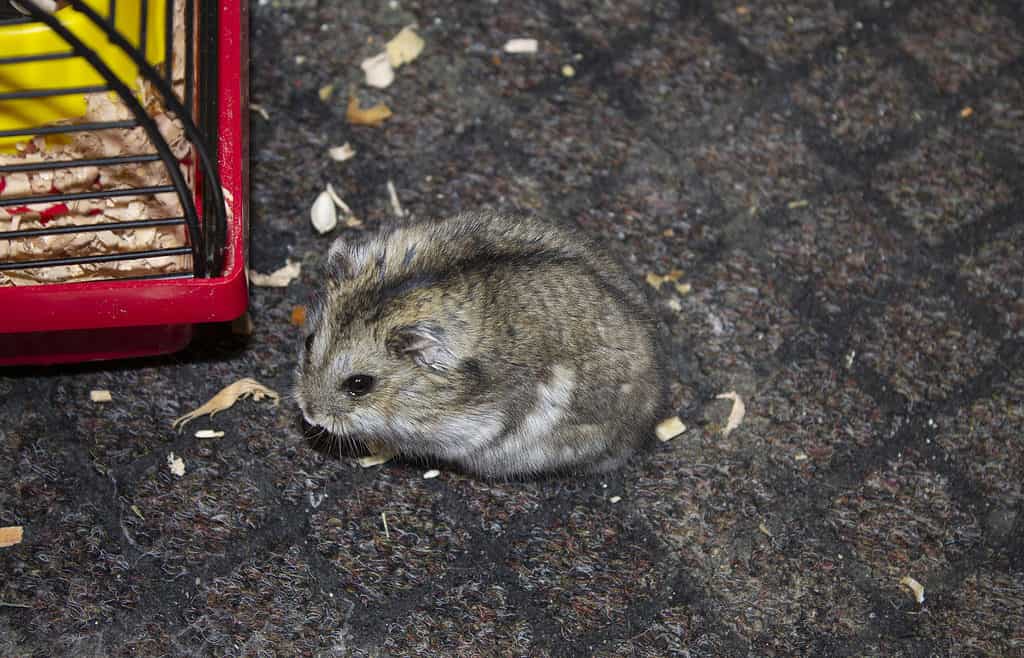

The dwarf hamster derives its name from its remarkably tiny dimensions, although its physical characteristics vary from one species to another.
©Tsesar Anna/Shutterstock.com
The dwarf hamster is named for its incredibly small size, though their overall appearance changes from one species to the next. They typically only grow to be two to four inches long, but the smallest of them all is the Roborovski dwarf hamster (or the robo dwarf hamster) at just 1.5 to two inches long. The largest subspecies is the Chinese dwarf hamster at four inches long, though he is technically not considered a true dwarf because he can grow larger.
The winter white dwarf hamsters go from gray and white to brown and white, based entirely on the season. It allows them to hide from potential predators. Campbell’s dwarf hamsters have incredibly small ears and are covered in grayish-brown hair. Grey dwarf hamsters look more like mice than hamsters, and they can be gray, grayish brown, or sandy gray.
Chinese dwarf hamsters have white bellies with a dark stripe against gray-brown fur on their back. The Roborovski dwarf hamster is fairly similar, though it looks like it has eyebrows with white spots above its eyes.
Different Types

Four pet Dwarf hamster types: Russian Campbell, Russian Winter White, Roborovski, and Chinese.
©Vinicius R. Souza/Shutterstock.com
Three distinct true Dwarf hamster species exist, with the Roborovski being the smallest among them. The four types of pet Dwarf hamsters are the Russian Campbell, the Russian Winter White, the Roborovski, and the Chinese Dwarf Hamster (although the Chinese dwarfs are not considered genuine Dwarf hamsters).
Behavior
Other than times of mating, dwarf hamsters are rather solitary creatures. They go long and far to find their resources, and they protect it at all costs from other rodents in the area. They are quite shy unless they are regularly exposed to human contact.
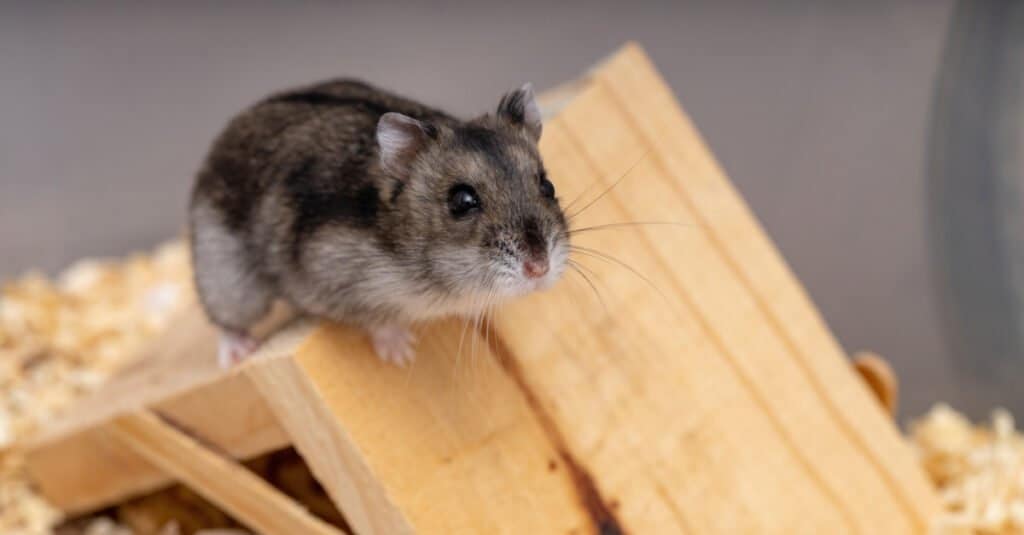
Habitat

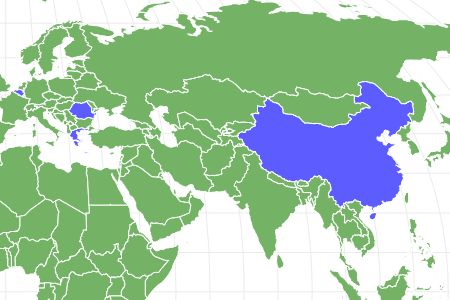
Dwarf hamsters are available for purchase as pets across the United States, although they are indigenous to Greece, Romania, Belgium, and the northern areas of China.
©iStock.com/krblokhin
Dwarf hamsters can be purchased as pets throughout the United States, but they exist naturally in the wild in Greece, Romania, Belgium, and northern regions in China. While they prefer to be in areas that are 68 to 72 degrees Fahrenheit, they can go a little higher or lower without much issue.
The easiest places for these animals to thrive are in dry environments, like deserts, scrubland, mountains, some forests, and desert edges. Each species of dwarf hamster has different adaptions to thrive in their local weather. For instance, the winter white dwarf hamster’s fur changes color during colder months to conceal itself from predators in the snow.
When temperatures get colder, Roborovski dwarf hamsters often stay in their underground habitat as part of hibernation. They stockpile food in warmer months to prepare for this hibernation period. Russian dwarf hamsters and other types of dwarf hamsters are more accustomed to cold weather, so hibernation is unnecessary.
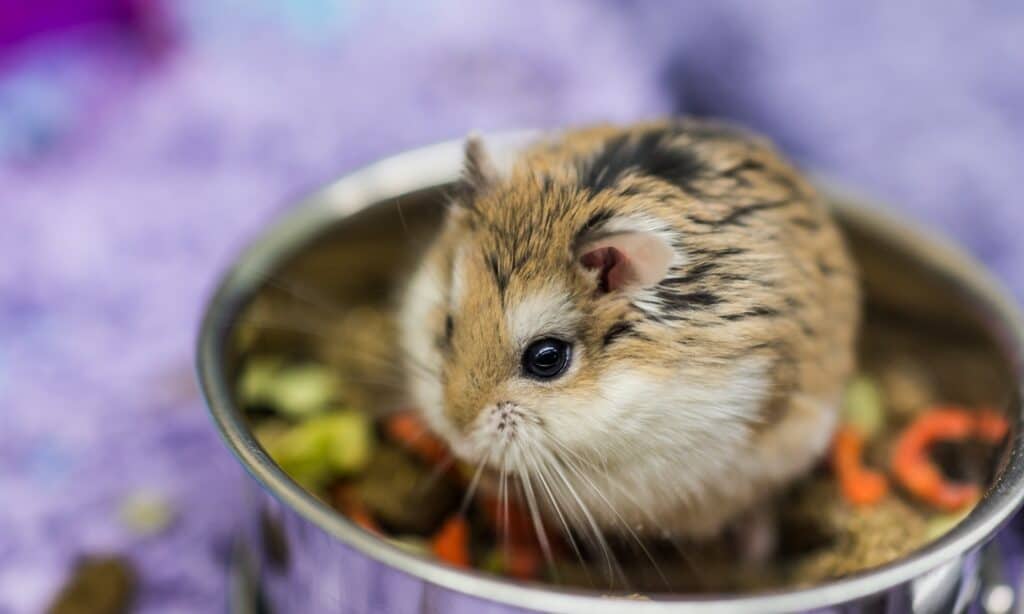
Diet
The typical diet of a dwarf hamster will largely consist of grains and pellets, which can be easily found in pet stores and grocery stores. It is safe to give them other nutrients like vegetables, fruits, grass hay, and grains, but the food offered in these pet stores is often all they need to be healthy.
Predators and Threats
Though the diet of a pet dwarf hamster primarily consists of pellets, seeds, and a few assorted vegetables, these animals may seek out insects in the wild. The eating habits are greatly varied because these hamsters have to be territorial to survive. However, avoid exposing your hamster to chocolate or caffeine as these substances are highly toxic.
To attack prey, the dwarf hamster simply grabs what they find in its environment. They don’t need much protein, so they are just as satisfied with their plant-based diet.
What Eats Dwarf Hamsters?
Due to their small size, the dwarf hamster’s natural predators include kestrels, falcons, foxes, owls, and eagles.
What Do Dwarf Hamsters Eat?
Though the dwarf hamster primarily relies on seeds and plant life, there are some occasions that present them with an opportunity for a little more sustenance. Crickets and mealworms are common parts of the wild dwarf hamster’s diet, but they only have these insects as treats.
Reproduction and Life Cycle
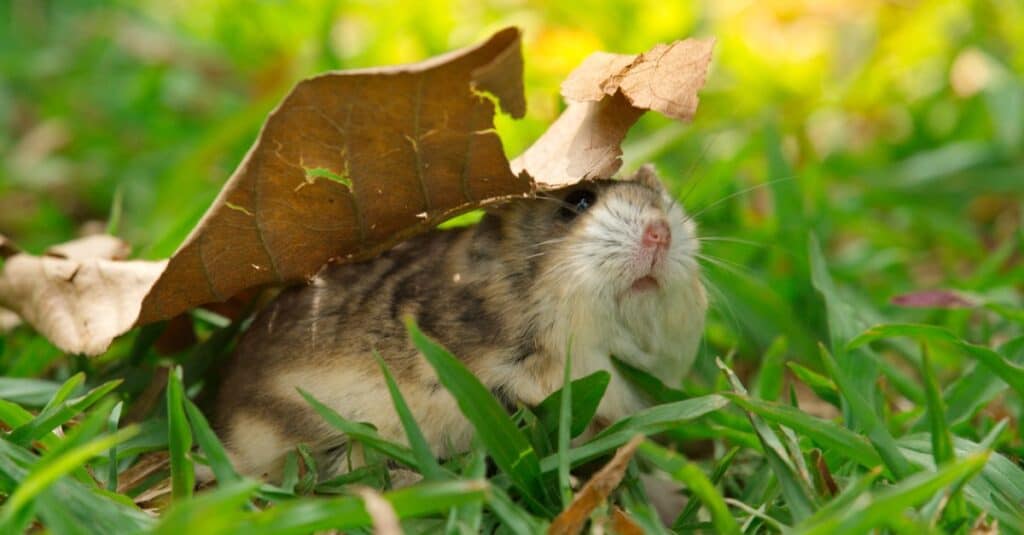

The lifespan of dwarf hamsters typically ranges from two to three years, but this may differ depending on the species.
©iStock.com/hikaru1222
In order for dwarf hamsters to mate, the female must be in heat, which means that she’s in her estrus cycle. All these hamsters need is an opportunity to mate by being placed with a male in their cage.
Through pregnancy, it is fairly safe to keep the mating pair together. Her pregnancy often results in about six babies. Throughout her life, it is safe for her to have babies with more than one male, though the pair might need to be separated after the live birth. In total, her pregnancy lasts between three and four weeks.
The babies of dwarf hamsters — which are called pups — must stay with their mother until they are weaned at three weeks. Their eyes won’t open until they are about two weeks old, and they are color-blind from birth. By their 18th day of life, you’ll be able to see their little ears pop up (as they’ve previously laid flat on the head). They are deaf and hairless when they are first born, though their fur will start to come in when they are about five years old.
However, unlike other species that might eat their young, the pups can stay with the mother for a little longer. Since the pups reach sexual maturity as early as four weeks old, they will need to be placed in separate cages by sex.
The average lifespan of dwarf hamsters is two to three years, though it will vary by species. The winter white dwarf hamster, for example, only lives about a year in the wild or as a pet, while the Campbell’s dwarf hamster only lives two years at the most.
The most common health issues that these rodents face include skin diseases (mites or ringworm), hair loss, digestive issues, diabetes, teeth issues, and respiratory infections. With the right care, they should be able to live to their projected old age. Proper identification of your hamster will give greater insight into its potential life span and health issues.
Population
Due to the frequent sale of dwarf hamsters as pets, experts believe that the total population is at least 57 million. Of that 57 million hamsters, approximately 11 million are kept as pets. The IUCN considers dwarf hamsters to generally be of least concern.
View all 110 animals that start with DDwarf Hamster FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are dwarf hamsters good pets?
Yes. They are relatively easy to care for and are rather small in size. They don’t need much space in their tank, and a few videos online can even show you how to train yours. Plus, it is rather easy to get them used to regular handling.
Do dwarf hamsters like to be held?
Initially, these types of hamsters are rather shy, which means that you will have to learn how to train them to get used to handling. Experts recommend spending about 5 minutes a few times a day to hold the hamster until he acclimates to this activity. Over time, regular handling leads to a tamer and easier to hold pet.
Do dwarf hamsters get lonely?
Not really. Even though they are often kept as pets with their human companion, they originally roamed the desert on their own as solitary animals. These mammals had to fight aggressively to maintain their territory so that other hamsters wouldn’t steal their resources.
Do dwarf hamsters bite?
Yes. All rodents can bite, but the only reason that hamsters tend to take a nibble is if they feel scared or threatened.
How do I take care of a dwarf hamster?
There are only a few things you need to make a dwarf hamster happy and healthy – the right cage, the right diet, and the right bedding. Their habitat should be as large as you can make it because they love to hide, play, burrow, and exercise throughout the day. Make sure to either find a metal habitat with good ventilation or a large tank. A cage with a metal wire top often offers the best ventilation to keep ammonia from accumulating in the cage between changing, which is a risk with a plastic or glass tank.
The bedding you choose is important. It allows them to chew and hide, but it also provides warmth. Some people choose to use wood shavings, but paper-based bedding is preferred because it is easy to digest if swallowed. The bottom of your hamster’s cage should be about 2 inches thick in bedding. Add other décor to the cage to give your hamster entertainment, like hiding places, an exercise wheel, and toys. No matter what you include, this habitat needs to be cleaned and disinfected weekly to keep the hamster from becoming sick.
Most hamster food from pet stores consists of seeds, dried fruits, and pellets. They also need constant access to clean water each day within a bowl or bottle. Though you can include vegetables, fruits, and grass hay, these additions are only needed in moderation.
How much is a dwarf hamster?
It entirely depends on where you shop for them. They can cost as little as $4 or as much as $20 in most pet stores.
What are the differences between a Dwarf hamster and a Syrian hamster?
The major difference between a Dwarf hamster and a Syrian hamster is size, and the Syrian is significantly larger. Other key differences include their appearance and behavior.
Apart from the fact that they are both hamsters, spotting the differences between the two breeds is relatively easy. Both can have long or short-haired coats, which come in various colorations and markings.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- ITIS / Accessed January 29, 2022
- Metro / Accessed January 29, 2022
- petco / Accessed January 29, 2022
- LiveScience / Accessed January 29, 2022
- Wikipedia / Accessed January 29, 2022
- Animals Network / Accessed January 29, 2022
- thesprucePets / Accessed January 29, 2022