African Fish Eagle
Haliaeetus Vocifer
African fish eagles belong to the genus of sea eagles
Advertisement
African Fish Eagle Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Aves
- Order
- Accipitriformes
- Family
- Accipitridae
- Genus
- Haliaeetus
- Scientific Name
- Haliaeetus Vocifer
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
African Fish Eagle Conservation Status
African Fish Eagle Facts
- Prey
- Fish, small mammals, amphibians, reptiles, and birds
- Main Prey
- Fish
- Name Of Young
- Eaglets
- Group Behavior
- Pair
- Fun Fact
- African fish eagles belong to the genus of sea eagles
- Estimated Population Size
- 300,000
- Biggest Threat
- Pollution
- Wingspan
- 6.6 to 8 feet
- Incubation Period
- 42 to 45 days
- Age Of Fledgling
- 70 to 75 days
- Habitat
- Large bodies of water in Sub-Saharan Africa
- Diet
- Carnivore
- Lifestyle
- Diurnal
- Favorite Food
- Fish
- Special Features
- Hooked bill, rough soles, and long talons
- Location
- Sub-Saharan Africa
- Average Clutch Size
- 3
- Nesting Location
- Tall trees
View all of the African Fish Eagle images!
It is nicknamed the voice of Africa.
Nicknamed “the voice of Africa,” African fish eagles have loud distinctive calls that reverberate over the freshwater lakes of sub-Saharan Africa. This large eagle inhabits areas near significant bodies of water with plenty of food. Its reach is far and wide throughout the continent; it is the national bird for three countries: Zambia, Zimbabwe, and South Sudan. Find out everything there is to know about the African fish eagle, including its habitat, appearance, diet, and predators.
4 Amazing Bird Facts
- African fish eagles are monogamous and mate for life.
- They are descendants of an ancient sea eagle lineage.
- Their feet have rough soles, so slippery fish don’t get away.
- Snakes and monkeys like to steal their eggs.

Where to Find the African Fish Eagle
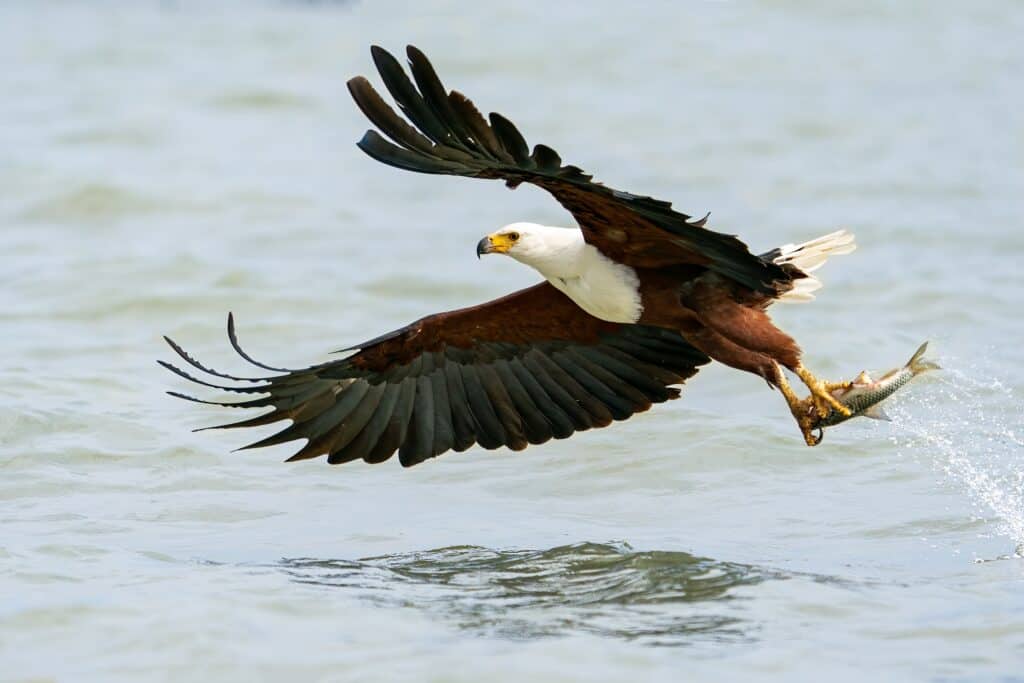

African fish eagles prefer to live around large lakes and are somewhat sedentary
©Tomas Drahos/Shutterstock.com
The African fish eagle ranges over most of the African continent, South of the Sahara desert. While this eagle occurs in many areas around large lakes, you can specifically find them in large populations around Lake Victoria, any of the Rift Valley lakes, Lake Malawi, the Orange River, and the Okavango Delta. You can find diverse habitats within the tropical savanna biome, especially those acquainted with water. Look for these birds soaring in the sky or perched on a comfortable branch near rivers, lakes, reservoirs, lagoons, swamps, rain forests, marshes, and deserts bordering coastlines. This eagle stays in its habitat year-round and leads a relatively sedentary lifestyle. They are diurnal, meaning they are most active during the day.
African Fish Eagles can be found in more than 30 countries around the world, including, Uganda, South Africa, Rwanda, Zimbabwe, and Zambia.
Nest
Eagle pairs build and maintain their nests using twigs and other pieces of wood, which they construct on tall trees. The nests can grow large, reaching six feet across and almost four feet deep. Nest building is a gradual process and typically takes several breeding seasons to get that large.
Scientific Name
In New Latin, the name Haliaeetus (genus) means “sea eagle.” The African fish eagle and its species pair, the critically endangered Madagascar fish eagle, are descendants of an ancient sea eagle lineage, giving them their dark beaks, talons, and eyes. The French naturalist François Levaillant called the African fish eagle “the vociferous one,” hence the name vocifer.
Evolution and Classification
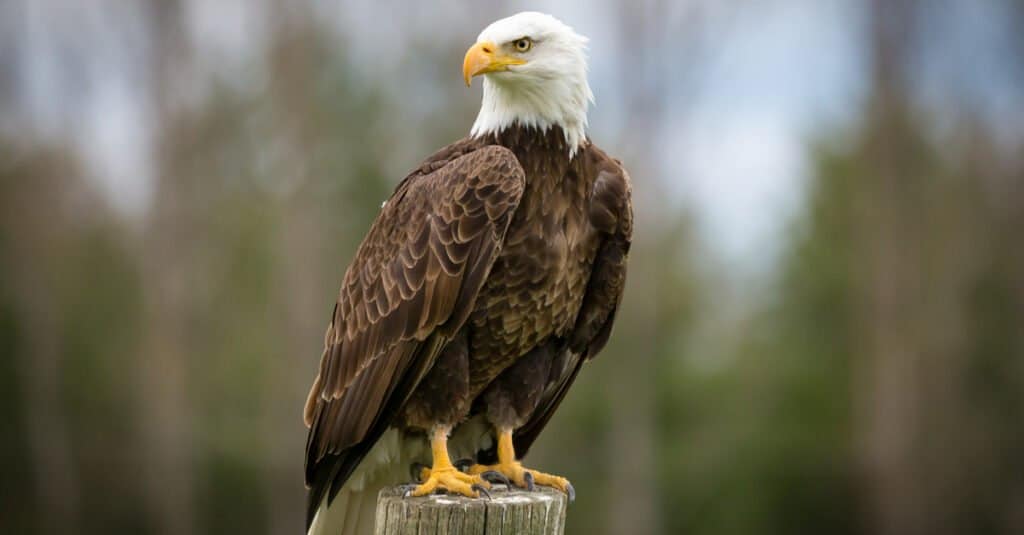

African fish eagles and bald eagles both belong to the genus Haliaeetus
©iStock.com/emranashraf
The African fish eagle belongs to the genus Haliaeetus considered to be one of the oldest avian species on the planet. Its membership of this group of mainly piscivorous raptors means it is also the cousin of the bald eagle (Haliaeetus leucocephalus), the white-bellied sea eagle (Haliaeetus leucogaster), and the Steller’s Fish Eagle (Haliaeetus pelagicus). Like other members of its family, it shares a significantly arched beak and bare legs and feet.
And like them, its history begins with the genus which scientists agree was an established presence about 12 – 16 million years ago, during the Miocene. They also assert that the ancestor of the modern-day Haliaeetus lived in an extensive, shallow body of water which corresponded to the present-day Bay of Bengal. The history of this avian family might go even further back to the Oligocene in North Africa, where fossil evidence has been discovered of an even earlier form which experts believe was somewhat similar to its descendants today.
Size, Appearance, and Behavior
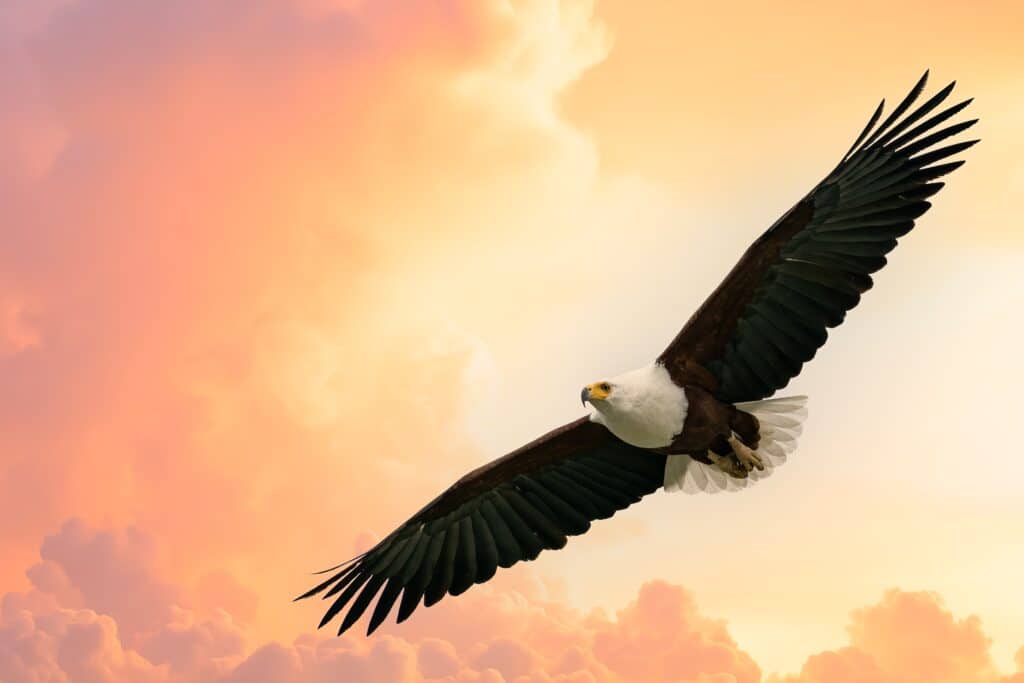

Female African fish eagles have a wingspan of almost 8 feet, males have a wingspan of almost 7 feet.
©Tomas Drahos/Shutterstock.com
Adults have a distinct appearance with brown bodies, white heads, and black wings. Its breast and tail are also snow white, with a featherless yellow face and dark brown eyes. This species is considered large and features sexual dimorphism. The females are more prominent, weighing between 7.1 and 7.9 pounds, with a wingspan of 7.9 feet. The males weigh 4.4 to 5.5 pounds, with a 6.6-foot wingspan.
It has a hook-shaped beak to catch and kill its prey, which is helpful for birds of prey. Their feet have powerful talons and rough soles, perfect for picking up and holding onto slippery fish. Their calls are distinctive; they throw their heads back and exclaim, “weeah kyow kow kow.”
These sedentary birds live in pairs and wait for their prey perched atop trees, then swoop down and swiftly grab their catch before returning to their branch. They also participate in kleptoparasitism, the practice of stealing food from other bird species; they often steal food from goliath herons.
Diet
Its diet includes fish, amphibians, reptiles, mammals, and other birds.

What Does an African Fish Eagle Eat?
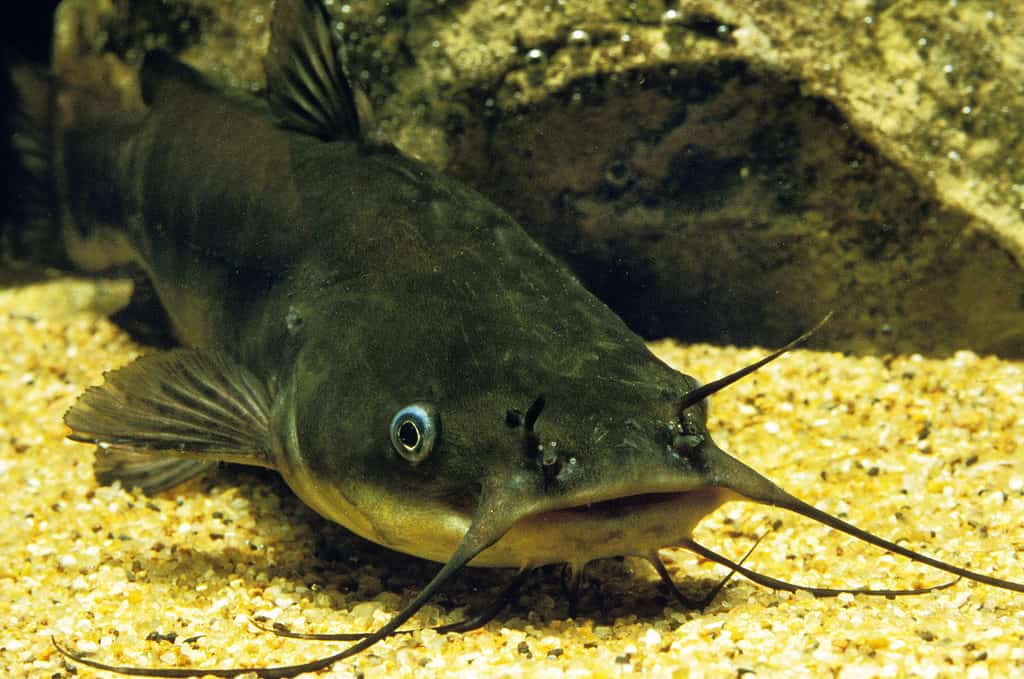

Catfish are one of African fish eagles’ favorite foods
©Slowmotiongli/Shutterstock.com
The African Eagle is a carnivore and primarily eats fish, especially mullets and catfish. But they will also eat cichlids, tilapia, characins, and African tiger fish. However, it also feeds on birds, particularly waterfowl like ducks and flamingoes. Its other prey includes reptiles, amphibians, carrion, and small mammals like monkeys and hares. If given the opportunity, the African fish eagle may steal domestic chickens.
Predators, Threats, and Conservation Status
The IUCN lists the African fish eagle as “least concern” and considers its population stable. Presently, there are no significant threats facing this species; it’s not particularly persecuted by humans or affected by habitat loss. In some regions, there is a build-up of pesticides which results in its prey being contaminated, which could potentially thin their eggshells. Other potential threats include the degradation of water quality, the development of shoreline habitats, and the entanglements of non-biodegradable gill nets.
What Eats the African Fish Eagle?

Nile Monitors are rather fond of eating African fish eagle chicks
©Dave Montreuil/Shutterstock.com
These birds of prey have very few predators, including humans, who don’t affect them much. But their eggs are vulnerable to being stolen and eaten. Snakes, Nile monitors, and monkeys are known for stealing and consuming their young. They also compete for food with the tawny eagle.
Reproduction, Young, and Molting
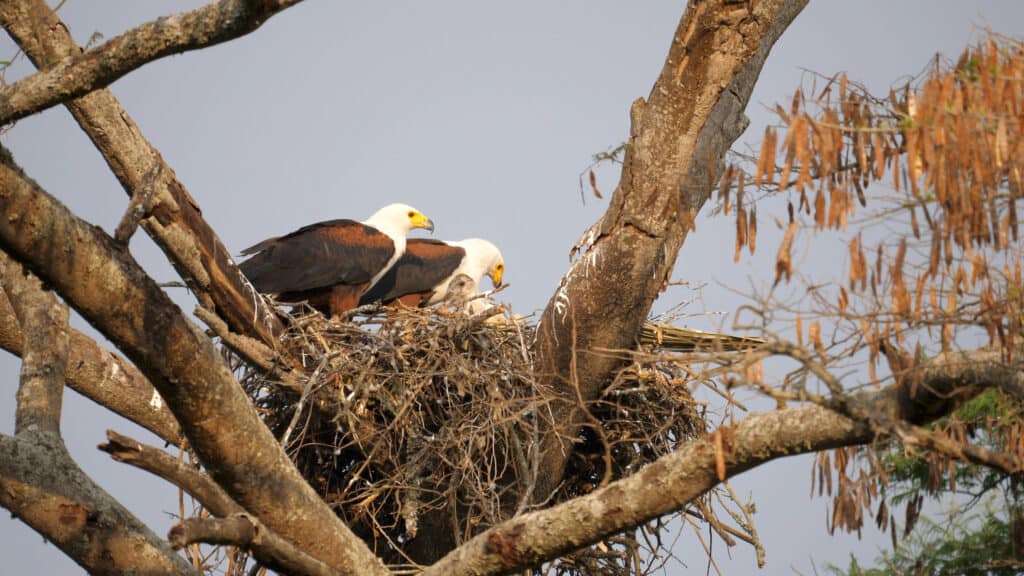

Both genders of African fish eagles care for their young
©Kiki Dohmeier/Shutterstock.com
Reproduction occur during the dry season when the water levels are low, which can vary by region. Females lay one to three eggs, and the couple takes turns incubating while the other hunts. The incubation period is 42 to 45 days, after which the chicks hatch and fledge around 70 to 75 days later. The parents will care for their young for three months after they leave the nest, but when they become nomadic, they congregate in groups away from adult eagles. Their life expectancy is between 12 and 24 years.
Population
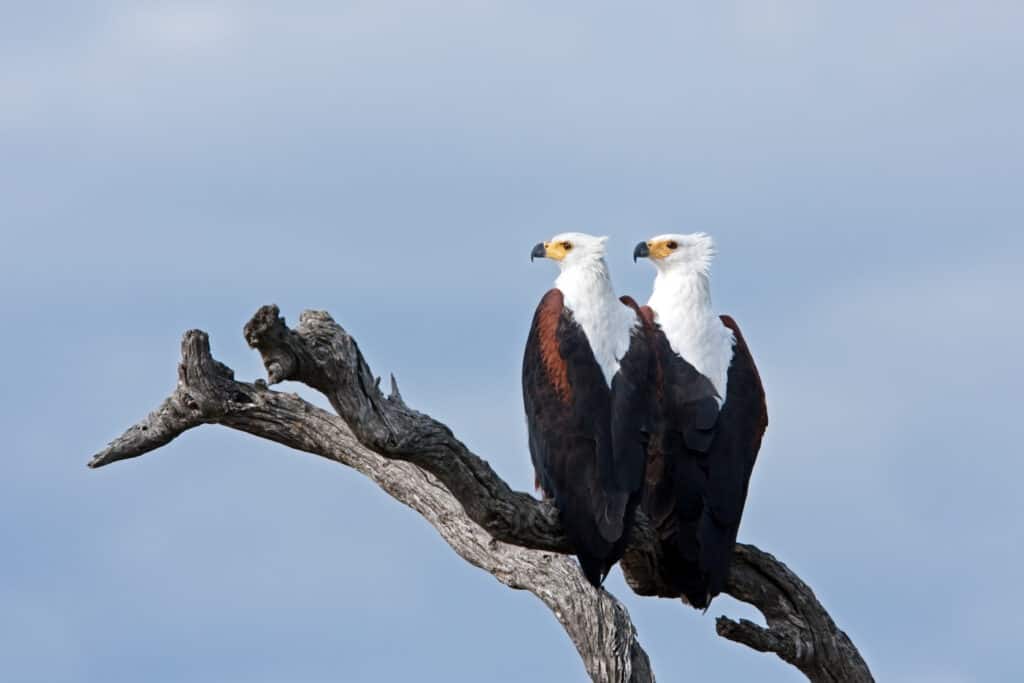

African fish eagles are doing rather well population-wise and are considered to be “Least Concern” in terms of conservation status
©Martin Prochazkacz/Shutterstock.com
Their population size is 300,000 individuals with steady numbers. The conservation status is “least concern” due to their extremely large range and population size. There is also no evidence of any declines and substantial threats.
A study from 1987 to 1999 witnessed the African fish eagle population decline by half at Lake Naivasha in Kenya due to food shortage. There was just enough food to keep them alive but not enough to breed. Researchers concluded there is a direct link between seasonality changes and lake health, which has the potential to harm the wildlife in that habitat.
Up Next:
View all 194 animals that start with AAfrican Fish Eagle FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Does the African fish eagle migrate?
No, this species lives year-round in its habitat.
How many eggs does the African fish eagle lay?
They lay between one and three eggs.
How fast does the African fish eagle fly?
They can fly up to 20 Mph!
What is the African fish eagle's wingspan?
Females have wingspans of 7.9 feet and males have a 6.6-foot wingspan.
When do African fish eagles leave the nest?
Eaglets fledge the nest around 70 to 75 days old.
What does the African fish eagle symbolize?
The African fish eagle symbolizes strength and power.
What do African fish eagles eat?
They have a wide-ranging diet but mainly consume fish, some reptiles, amphibians, and small mammals.
Is the fish eagle a real eagle?
The African fish eagle is not a “true” eagle. It belongs to the genus of sea eagles.
Do fish eagles eat ducks?
Yes! African fish eagles eat a variety of water fowl, including ducks and flamingoes.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- IUCN Red List / Accessed September 1, 2022
- Link Springer / Accessed September 1, 2022
- Science Direct / Accessed September 1, 2022