Yellowfin Tuna
Thunnus albacares
The yellowfin forms schools with other tuna species
Advertisement
Yellowfin Tuna Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Actinopterygii
- Order
- Scombriformes
- Family
- Scombridae
- Genus
- Thunnus
- Scientific Name
- Thunnus albacares
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Yellowfin Tuna Conservation Status
Yellowfin Tuna Facts
- Main Prey
- Fish, crustaceans, cephalopods, and mollusks
- Group Behavior
- School
- Fun Fact
- The yellowfin forms schools with other tuna species
- Estimated Population Size
- Millions
- Biggest Threat
- Overfishing
- Most Distinctive Feature
- The long yellow-colored secondary fins
- Other Name(s)
- Ahi
- Gestation Period
- A few days
- Habitat
- Oceans
- Predators
- Sharks, whales, marlins, seabirds, humans, and other fish
- Diet
- Carnivore
- Type
- Ray-finned fish
- Common Name
- Yellowfin tuna
- Number Of Species
- 1
View all of the Yellowfin Tuna images!

The yellowfin is the second most commonly eaten tuna species in the world.
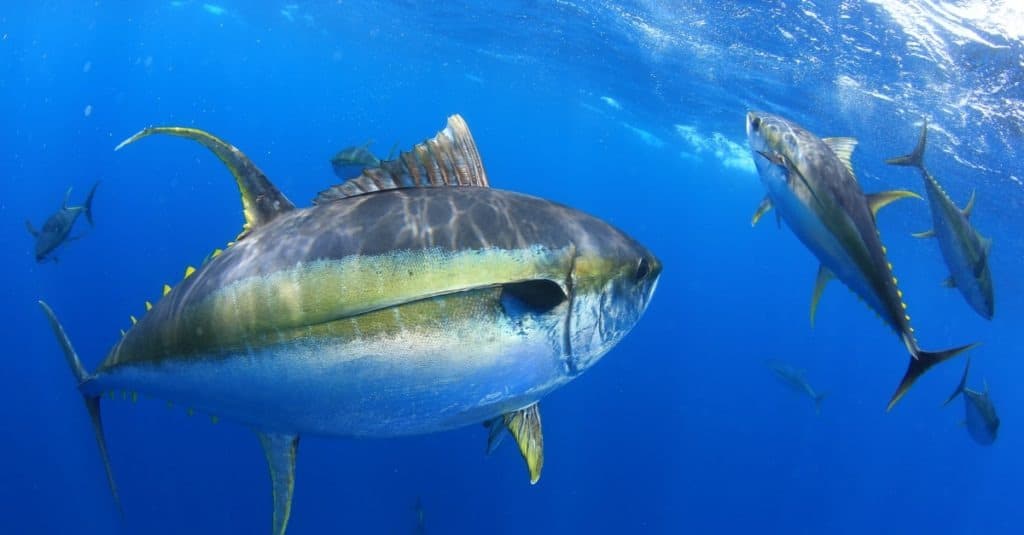
With its yellow coloring and huge secondary fins, this species is unmistakable and easy to recognize.
3 Incredible Yellowfin Tuna Facts!
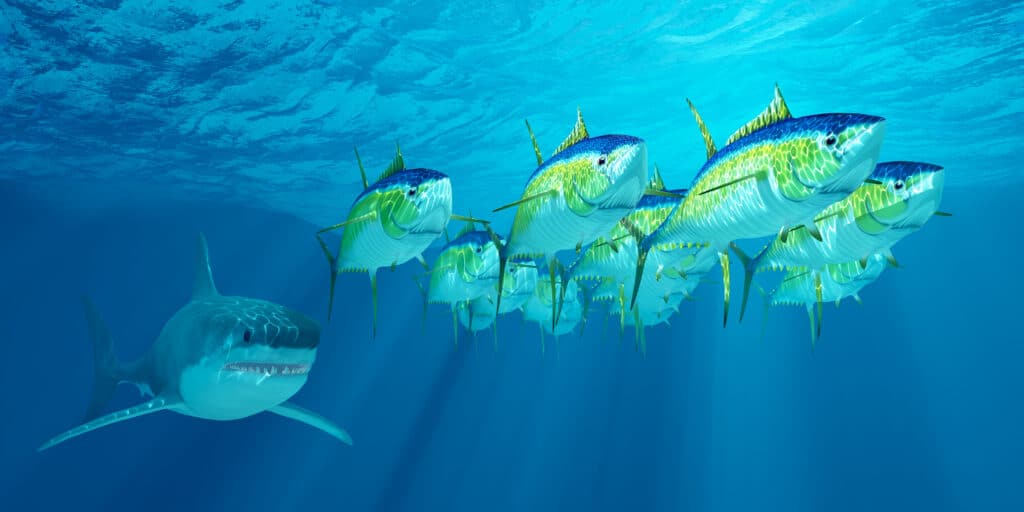

The yellowfin tuna fish forms extensive schools comprising of skipjack, bigeye, and even dolphins and whales as it travels across the world.
©Catmando/Shutterstock.com
- As it migrates around the globe, the yellowfin tuna fish forms large schools with skipjack, bigeye, and even dolphins and whales.
- This species can swim up to 50 miles per hour.
- Newly hatched fry are nearly microscopic in size.
Evolution and Origins
Yellowfin tuna likely caught the notice of sport anglers when they showed up at the tuna fishing spots in Catalina Island, California, shortly after the invention of sport fishing and the targeting of Pacific bluefin tuna.
Bluefin tuna can trace its origins back to an ancestor that was cold-blooded, with the earliest fossil records dating back to the late Paleocene or early Eocene epochs in deposits from the Tethys Sea in regions like the Middle East, southern Europe, and the London clay formation.
The tuna possesses various features that enable it to swim effectively such as a sleek, aerodynamic body resembling a torpedo, elongated pectoral fins that provide lift and facilitate turning, and a crescent-shaped tail fin that aids in speed and efficiency.
Classification and Scientific Name
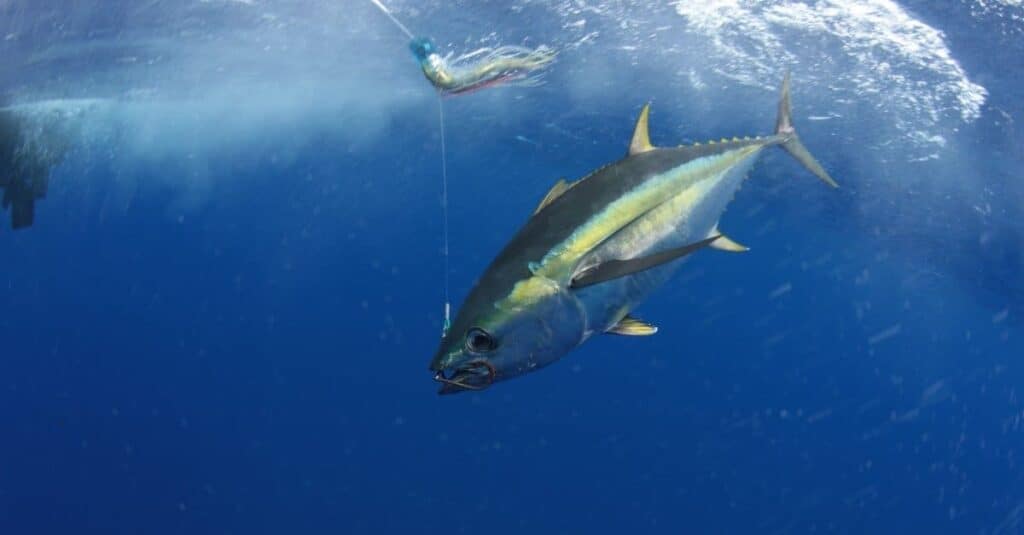

Thunnus albacares is the scientific name assigned to the yellowfin tuna fish.
©Al McGlashan/Shutterstock.com
The scientific name of the yellowfin is Thunnus albacares. This is a combination of two Latin words: albus, meaning white, and caro, meaning flesh. The yellowfin is also known by the alternative Hawaiian name of Ahi.
Appearance
The yellowfin tuna fish, or Ahi, is characterized by a dark blue back and yellow sides fading to silver around the belly. The most prominent characteristics are the two long, yellow fins jutting out from the back and stomach. Most specimens weigh up to 450 pounds.
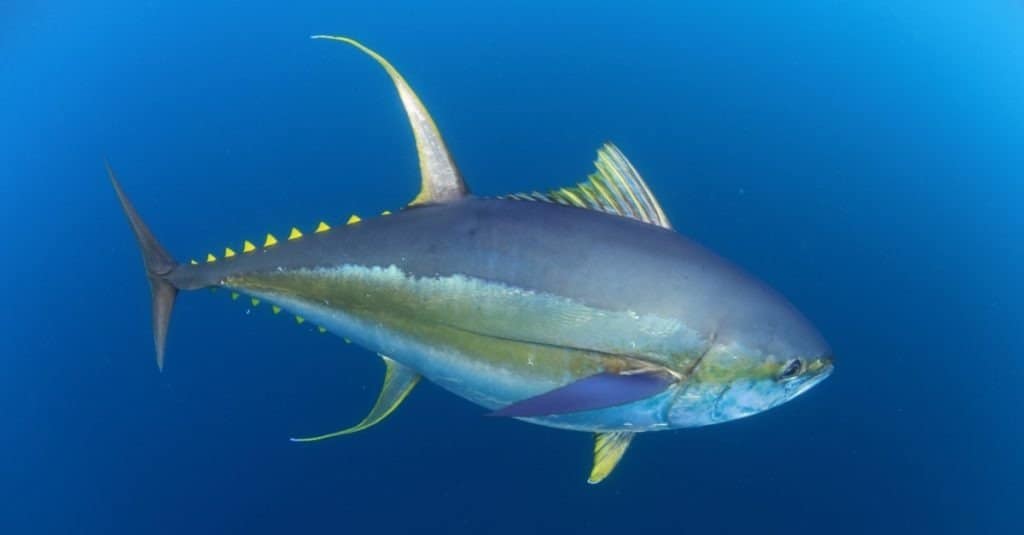

The yellowfin tuna, also known as Ahi, has a dark blue dorsal surface and yellow sides that gradually turn silver towards the underside.
©Al McGlashan/Shutterstock.com
Distribution, Population, and Habitat
The yellowfin tuna fish can be found throughout the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Oceans, but several stocks appear to be declining due to overfishing and bycatch. According to the IUCN Red List, this species is considered “least concern“.
Predators and Prey
The yellowfin is one of the fastest fish in the water, which enables it to evade predators and capture prey.
What does the yellowfin eat?
The yellowfin preys upon squid, crustaceans, and many types of perciform fish.
What eats the yellowfin?
Yellowfin are preyed upon by seabirds, sharks, billfish, false killer whales, and larger tuna. Only the largest predators can consume an adult yellowfin, however. The other predators target juveniles and eggs.
Reproduction and Lifespan

Cuba is an island country surrounded by ocean waters and many different types of fish.
©Al McGlashan/Shutterstock.com
The yellowfin breeds all year round (with peak spawning season in the summer) by releasing millions of sperm and eggs into the water. The few that survive this initial stage will mature in two to three years and live for about seven or eight years.
Fishing and Cooking
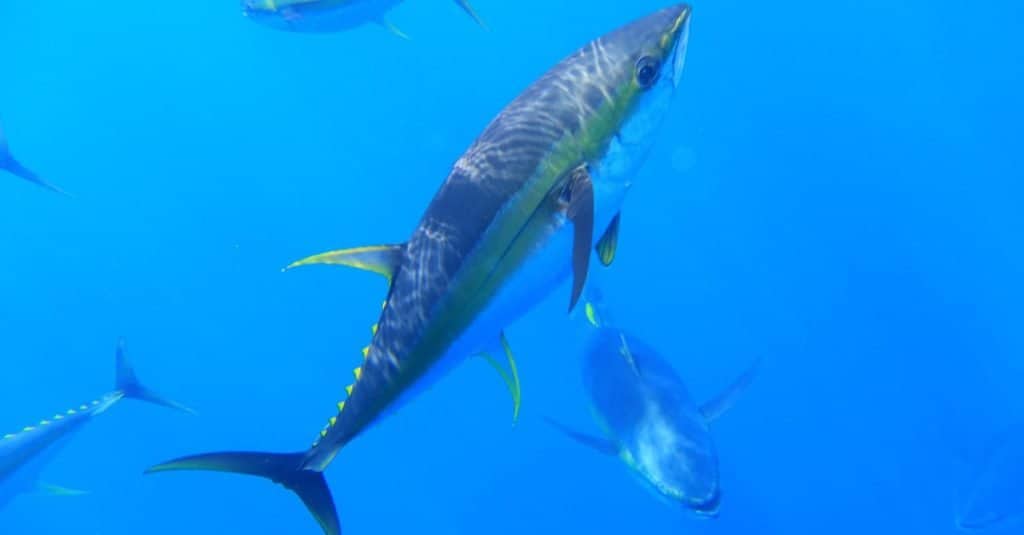

Yellowfin tuna spawns throughout the year, with maximum breeding season occurring in summer, by discharging millions of eggs and sperms into the water.
©Al McGlashan/Shutterstock.com
The yellowfin makes up 30% of the annual tuna stock, second only to the skipjack. They are often pole-caught for sustainability reasons. The yellowfin has a milder flavor and firm texture compared to skipjack, and it can be found for a reasonable price.
View all 32 animals that start with YYellowfin Tuna FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
How do you cook yellowfin tuna?
The yellowfin is frequently grilled or made into a steak or salad.
What is the yellowfin tuna?
The yellowfin is a member of the true tuna group. It can be distinguished from other species by the yellow coloration and the very long secondary dorsal and anal fins.
Can yellowfin tuna be eaten rare?
Yes, yellowfin can be eaten rare, but this has greater health risks compared to well-cooked meat.
Is yellowfin tuna good for you?
Yellowfin is a healthy meal high in good fats and other nutrients, but due to its mercury content, consumption should be limited to only a few servings a week.
How big is a yellowfin tuna?
The yellowfin can grow up to 4 feet long and weigh some 450 pounds.
What is the estimated population size of Yellowfin Tunas?
There are millions of Yellowfin Tunas.
What are some distinguishing features of the Yellowfin Tuna?
The Yellowfin Tuna has a long, yellow-colored secondary fin.
What is another name for the Yellowfin Tuna?
The Yellowfin Tuna is also called the ahi.
What is an interesting fact about the Yellowfin Tuna?
The yellowfin forms schools with other tuna species.
How fast is a Yellowfin Tuna?
A Yellowfin Tuna can travel at speeds of up to 50 miles per hour.
How do Yellowfin Tunas have babies?
Yellowfin Tunas lay eggs.
What are the differences between Bluefin tuna and Yellowfin tuna?
The main differences between bluefin and yellowfin tuna are that bluefin is significantly larger, fetch a higher price, and have a smaller global distribution than yellowfin.
Both bluefin and yellowfin tuna are top predators in the world’s oceans, but there are some definitive differences between them. Worldwide, there are three recognized bluefin species, and only one recognized yellowfin species. All three bluefin species are highly prized as sport and culinary fish, but the yellowfin is also seeing an increase in both markets as well. These large, powerful fish are easily identifiable and are clear apex predators in any habitat they frequent.
What are the key differences between a mahi and an ahi?
The key differences between a mahi and an ahi are origin of name, appearance, distribution, and culinary uses.
What are the main differences between Ahi Tuna and Bluefin Tuna?
Ahi tuna and the bluefin tuna differ in size, appearance, pectoral fins, and water depths.
What are the key differences between the yellowtail and yellowfin tuna?
The key differences between the yellowtail and yellowfin tuna include their size, appearance, habitat and distribution, lifespan, and conservation status.
What are the key differences between yellowfin tuna and albacore?
The key differences between yellowfin tuna and albacore are their size, body shape, color, and lifespan.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- WWF, Available here: https://www.worldwildlife.org/species/yellowfin-tuna
- Thought Co, Available here: https://www.thoughtco.com/yellowfin-tuna-facts-4589034