Chipmunk
There are 25 different species!
Advertisement
Chipmunk Scientific Classification
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Chipmunk Conservation Status
Chipmunk Facts
- Average Litter Size
- 5
- Lifestyle
- Solitary
- Favorite Food
- Nuts
- Type
- Mammal
- Slogan
- There are 25 different species!
View all of the Chipmunk images!
“One chipmunk can collect 165 acorns per day.”
Chipmunks are small mammals that live in burrows, fallen logs, or holes under houses. This rodent is the tiniest member of the squirrel family!
They are omnivores eating a variety of plants and small animals. Chipmunks have a collection of chirps and other sounds they use to communicate with one another. They have a lifespan of two to three years.
5 Incredible Chipmunk Facts!
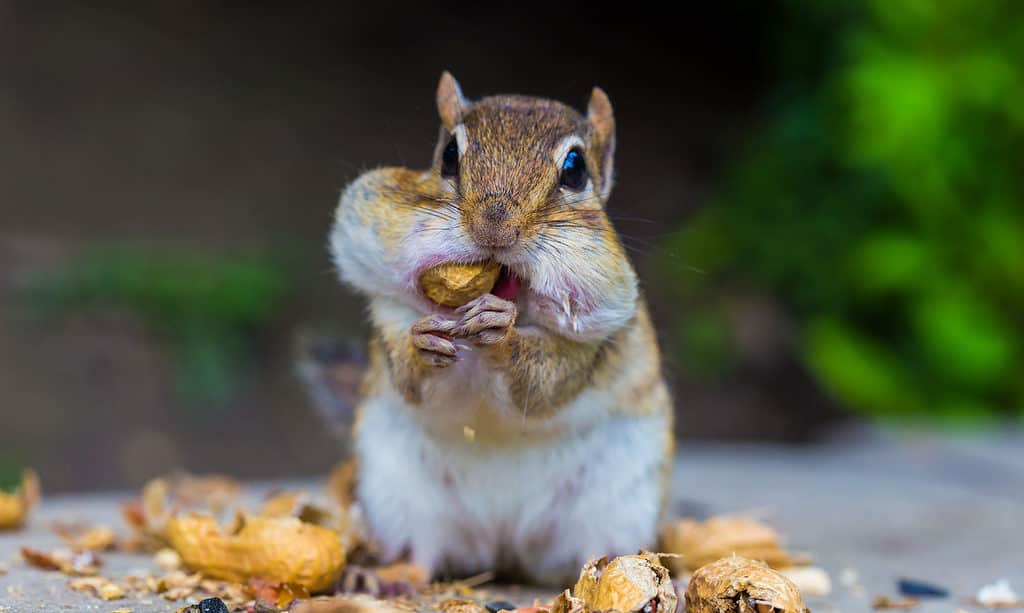

Chipmunks live in tunnel systems measuring up to 30 feet in length.
©colacat/Shutterstock.com
- There are 25 species or types
- While foraging during the day, this rodent stuffs food into pouches in its cheeks
- This animal remains in its burrow over the winter
- A chipmunk baby is the size of a jellybean
- They live in tunnel systems measuring up to 30 feet in length
Evolution and Origins
Chipmunks are a part of the squirrel family and actually split off from rats and mice close to 70 million years ago. Scientists think they probably evolved their stripes independently from rats and mice. The only species of Chipmunks that isn’t native to North America is the Siberian chipmunk as indicated by its name.
The name Chipmunk is derived from their behavior to wake up to eat stored food. They get their name from the “chip chip” sound they make while eating.
Different Types of Chipmunks
Here is a full list of Chipmunks:
- Eastern chipmunk
- Siberian chipmunk
- Least chipmunk
- Red-tailed Chipmunk
- Yellow-pine chipmunk
- Colorado chipmunk
- Lodgepole chipmunk
- Hopi chipmunk
- Townsend’s Chipmunk
- California chipmunk
- Buller’s Chipmunk
- Panamint chipmunk
- Long-eared chipmunk
- Gray-collared chipmunk
- Alpine chipmunk
- Cliff chipmunk
- Uinta chipmunk
- Merriam’s Chipmunk
- Allen’s Chipmunk
- Palmer’s chipmunk
- Sonoma chipmunk
- Yellow-cheeked chipmunk
- Gray-footed chipmunk
- Durango Chipmunk
- Siskiyou chipmunk
Scientific Name
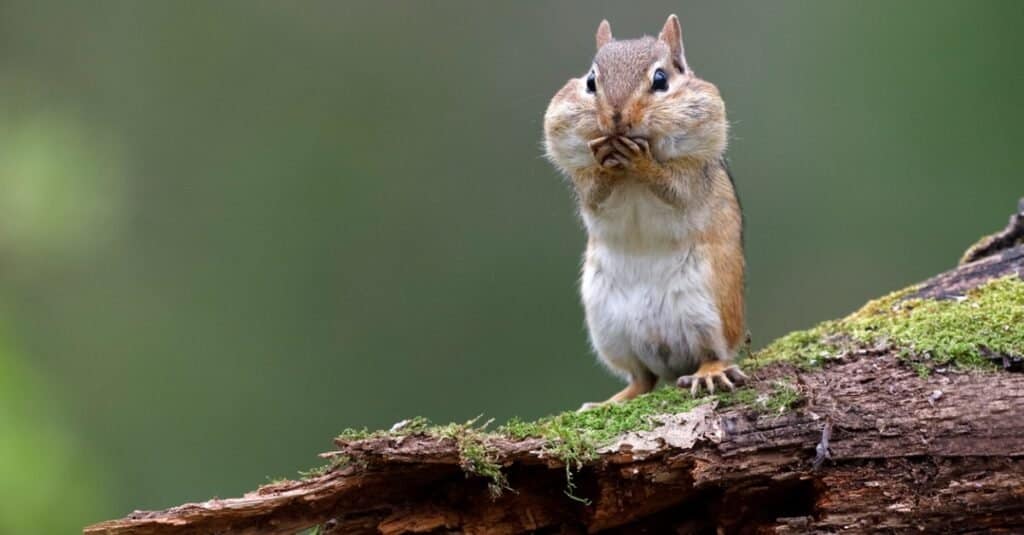

The scientific name for an Eastern chipmunk is
Tamias striatus.
©iStock.com/BrianLasenby
The scientific name for an Eastern chipmunk is Tamias striatus. The Latin word striatus means streaks. This refers to the stripes on an Eastern chipmunk’s back. Chipmunks can also be classed into three different genera: the eastern chipmunk, the Siberian chipmunk, and the neotamias. This last genus contains 23 different species that live in the western US. Because all chipmunks are so similar, there is disagreement about whether they should be classified as different genera or just refer to all of them as the same.
Chipmunks are sometimes called striped squirrels or timber tigers. They belong to the Sciuridae family and the Mammalia class.
There are 25 species or types. Some of these include:
- Eastern chipmunk
- Siberian chipmunk
- Townsend’s chipmunk
- Uinta chipmunk
- Red-tailed chipmunk
- Colorado chipmunk
Appearance and Behavior
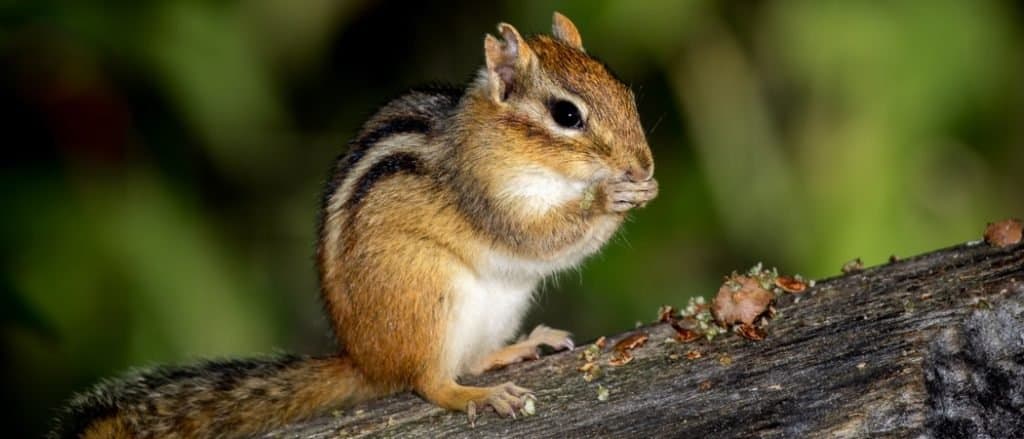

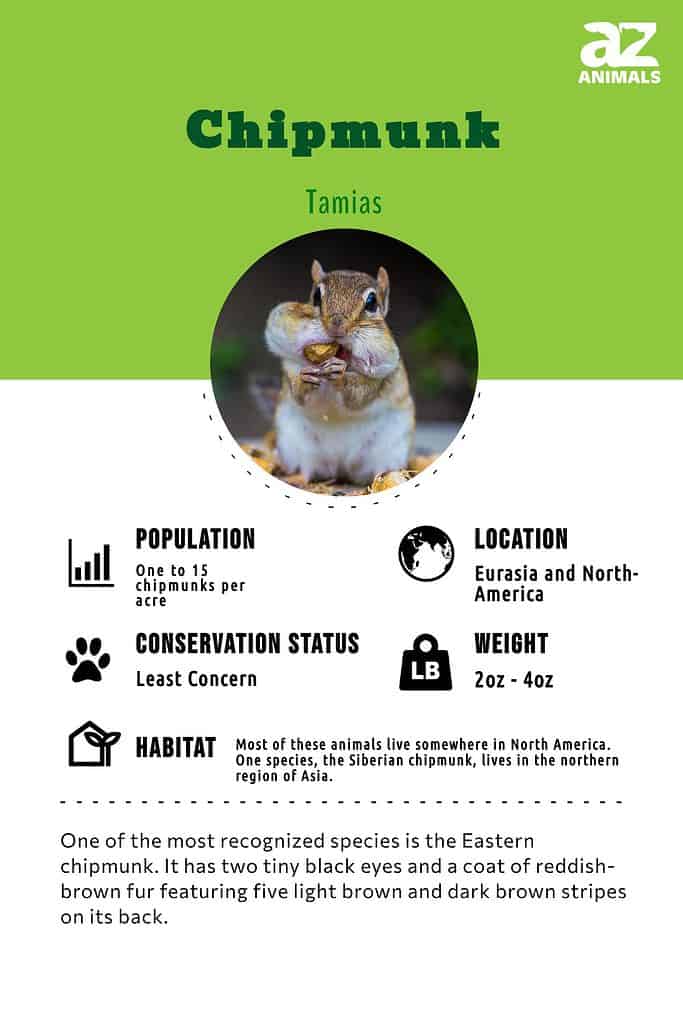
One of the most recognized species is the Eastern chipmunk.
©RT Images/Shutterstock.com
One of the most recognized species is the Eastern chipmunk. It has two tiny black eyes and a coat of reddish-brown fur featuring five light brown and dark brown stripes on its back. Also, this species has a light brown stripe near each ear and a dark tail. This animal’s fur can be brown, reddish-brown, or gray depending on what type it is.
This rodent uses its delicate claws to dig holes and climb trees. In addition, these animals have pouches in their cheeks that they fill up with nuts, fruit, seeds, and more. These pouches allow them to take a large supply of food back to their home after spending time foraging in the open.
Understandably, the less time the animal spends out in the open, the less vulnerable they are to predators. These animals can sometimes become quite a pest in the home and need to be removed then.
A grown chipmunk measures from four to seven inches in length with a tail that adds another three to five inches. They weigh anywhere from one to five ounces. A five-ounce animal weighs the same as a baseball used in the major leagues.
An average-sized chipmunk measuring four inches in length is almost as long as two golf tees lined up end to end. The biggest species is the Eastern chipmunk. An adult Eastern chipmunk measures about 11 inches long, from the tip of its nose to the tip of its bristly tail.
When it comes to defensive features, the dark coat of these animals allows them to blend in with their woodland habitat. Also, its speed can help this rodent to outrun some predators and find a hole to hide in.
Though chipmunks may not live right next to one another, they communicate with others in the same territory. These animals have a variety of calls or sounds that mean different things. Some chirping sounds let other chipmunks know a predator is in the area.
Other chirping sounds are made by males as they compete with each other for a female. In other words, they have their own rodent language!
These rodents are solitary animals. They are only together during the breeding season. They are shy rodents that want to stay out of sight most of the time. When chipmunks do form a group, it is called a scurry.
Learn how to get rid of chipmunks by reading this article. Also, read here to find out if keeping chipmunks as pets is a good idea.
Chipmunk vs. Squirrel

A chipmunk is a type of squirrel so there are a lot of similarities between these two rodents. Of course, there are some differences as well.
Both chipmunks and squirrels, aka tree squirrels, are omnivores with a diet that includes seeds, fruit, bird eggs, nuts, and insects. Also, both rodents climb trees and have a forest habitat.
One of the main differences between them is their size. Tree squirrels are larger measuring up to 20 inches long from their nose to the tip of their tail. Another difference is while chipmunks have stripes down their back, tree squirrels have solid gray or brown fur.
As a note, there’s another rodent called a ground squirrel that looks a lot like these animals! But they are not the same animal.
One easy way to tell them apart is a chipmunk’s small ears stand up on its head, while a ground squirrel’s small ears lay flat. Also, ground squirrels live in grassy areas and fields while chipmunks are found in woodland areas.
Habitat
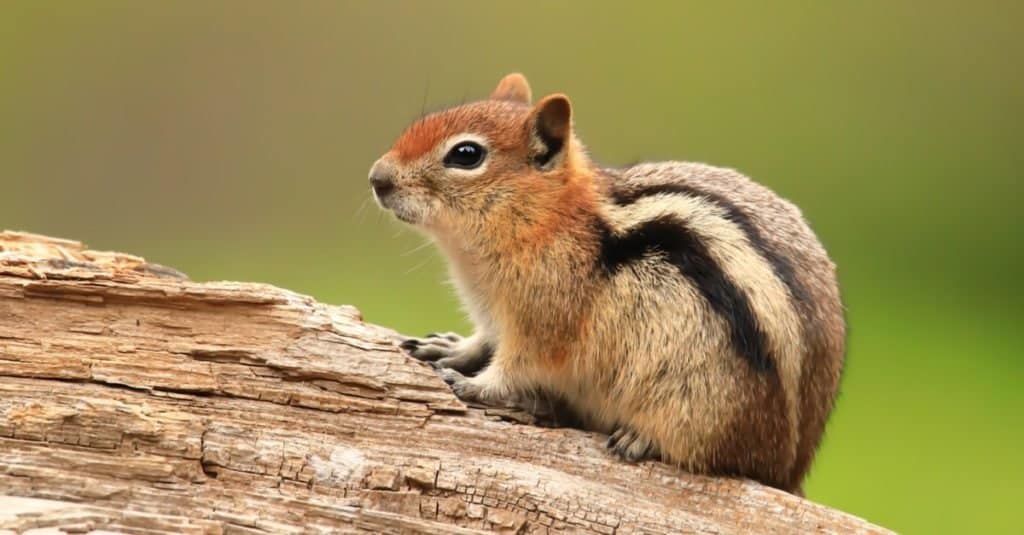

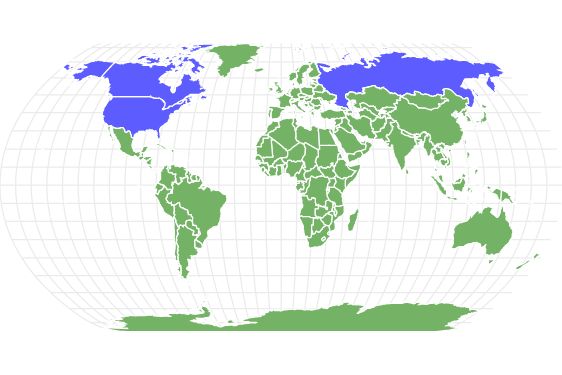
Most of these animals live somewhere in North America. One species, the Siberian chipmunk, lives in the northern region of Asia.
©AmberLouise/Shutterstock.com
Most of these animals live somewhere in North America. One species, the Siberian chipmunk, lives in the northern region of Asia. Specifically, wherever you find trees in North America, you’re likely to find animals! They can also live in fallen logs and in holes under houses. Many species live in tunnels located three feet beneath the ground.
These animals are found in a temperate climate. If they live in an area with really cold winters they will go into hibernation. However, these rodents don’t go to sleep in the wintertime as bears do. Instead, they sleep on and off while surviving on the nuts and seeds they collected throughout the warm weather months.
Seeing the animal out of its shelter in the wintertime is a rare occurrence. They go into hibernation in late October and come out in March or April. Learn more about other animals that hibernate here.
These animals sometimes migrate when they need to find a place with better access to water.
Diet

These animals are omnivores. They eat whatever is most plentiful in their habitat.
What eats chipmunks?
Not surprisingly, These animals have a lot of predators. These include hawks, snakes, raccoons, rats, weasels, coyotes, and owls.
What do chipmunks eat?
They eat fruit, nuts, seeds, insects, snails, birds’ eggs, and frogs. It’s not uncommon to see an Eastern chipmunk and other types of chipmunks in North America chowing down at a backyard birdfeeder.
Items not eaten by the animal are stuffed into its cheek pouches and taken back to the nest to store for winter.
Predators and Threats

Predators of Chipmunks include: include hawks, snakes, raccoons, rats, weasels, coyotes, and owls.
©Bildagentur Zoonar GmbH/Shutterstock.com
These animals are an important food source for many animals. So, it has a long list of predators. Some examples include hawks, snakes, raccoons, rats, weasels, coyotes, and owls. Of course, they also fall prey to housecats from time to time.
Many of these rodents’ predators are fast and live in the same type of environment. For example, a coyote may stalk a chipmunk and sneak up on it while it’s foraging in the open.
A hawk can easily see the animal foraging for food on the ground and swoop down to grab it. A snake can pursue the rodent by following it into its tunnel as the rodent tries to escape.
It’s not uncommon to see these animals dead on the road. They live in the same areas as many humans, so they are vulnerable to passing cars.
Some humans think of them as pests. A pest control technician may be called in to set a trap to catch one or more chipmunks that are living in a hole beneath a home or beneath a home’s roof. The presence of chipmunk poop in the area is a sure sign that a chipmunk is occupying the space.
A pest control professional may use a trap that kills the rodent. Alternatively, some pest professionals use humane methods and trap them alive so they can be moved to another location away from the residential area.
The conservation status of the Eastern chipmunk is Least Concern. Its population is stable.
Reproduction, Babies, and Lifespan
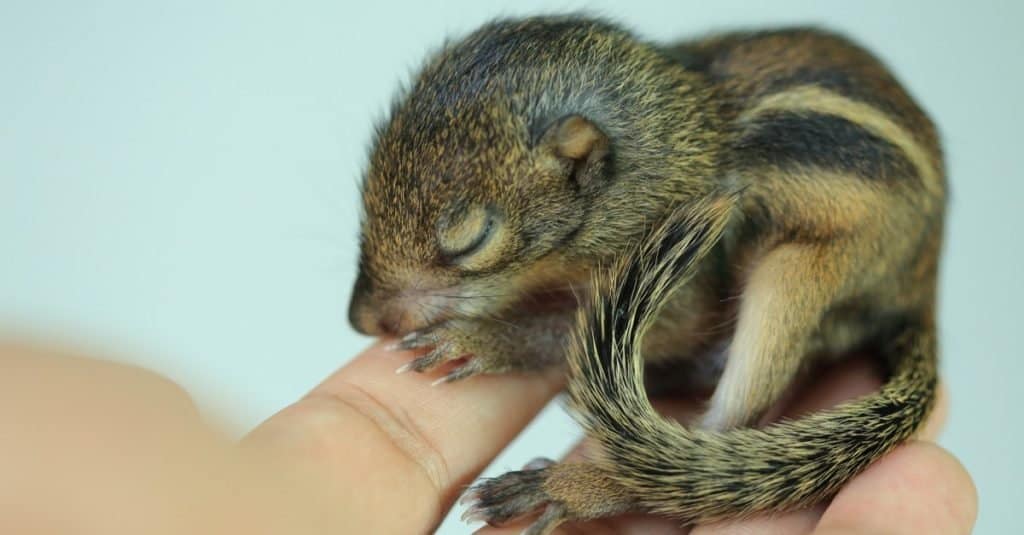

A baby chipmunk or pup weighs less than an ounce. The size of a newborn animal is about the same as one jellybean!
©wanpapha sichana-in/Shutterstock.com
The breeding season of an Eastern chipmunk takes place twice a year. They breed from February to April and from June to August. Females release a scent when they are ready to mate.
Sometimes males fight over females during this active season. One male may mate with several females. The gestation period is 31 days. As a comparison, the gestation period of the Eastern gray squirrel is a little longer at 44 days.
Most of these animals give birth to two to six live babies, also called pups. However, it’s possible for them to have up to nine pups in a litter!
A baby chipmunk or pup weighs less than an ounce. The size of a newborn animal is about the same as one jellybean! They are born blind and without any hair. The pups stay out of sight in the burrow for the first six weeks of life. They nurse their mother during that time. The father doesn’t play a part in the care of the pups.
At about six weeks old, the pups venture out of the burrow with their mother to learn how to forage for food. The pups have a full coat of fur and can live independently at around 8 weeks old.
Chipmunks can carry fleas and ticks. These rodents can also carry diseases such as leptospirosis, salmonella, and even rabies. Chipmunks have a lifespan of two to three years.
Population
The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species describes the population of Eastern chipmunks as, ‘abundant.’ Also, it’s estimated that there are from one to 15 chipmunks per acre depending on the area.
The conservation status of the Eastern chipmunk is Least Concern with a stable population.
Similar Articles about These Animals…
- Chipmunk Sounds: How To Identify A Chipmunk By Sound These feisty little guys make a wide variety of chirps, cheeps, and squeaks. Click here to learn how to identify them.
- Chipmunk Holes: How To Identify & Fill Chipmunk Burrows Chipmunks dig extensive burrows, learn more about them here.
- Chipmunk Repellent: The Best Way To Get Rid of Chipmunks Chipmunks are cute and fun to watch, but they are also very destructive if they get in a car or building. Check out this article to find out how to keep them out of your home.
Chipmunk FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are Chipmunks herbivores, carnivores, or omnivores?
Chipmunks are Omnivores, meaning they eat both plants and other animals.
What Kingdom do Chipmunks belong to?
Chipmunks belong to the Kingdom Animalia.
What class do Chipmunks belong to?
Chipmunks belong to the class Mammalia.
What phylum to Chipmunks belong to?
Chipmunks belong to the phylum Chordata.
What family do Chipmunks belong to?
Chipmunks belong to the family Sciuridae.
What order do Chipmunks belong to?
Chipmunks belong to the order Rodentia.
What type of covering do Chipmunks have?
Chipmunks are covered in fur.
In what type of habitat do Chipmunks live?
Chipmunks live in forests and thick woodlands.
What is the main prey for Chipmunks?
Chipmunks eat nuts, fruit, seeds, and berries.
What are some predators of Chipmunks?
Predators of Chipmunks include humans, hawks, and raccoons.
What are some distinguishing features of Chipmunks?
Chipmunks have stripes on their fur and have large front teeth.
How many babies do Chipmunks have?
The average number of babies a Chipmunk has is 5.
What is an interesting fact about Chipmunks?
There are 25 different species of Chipmunk!
What is the lifespan of a Chipmunk?
Chipmunks can live for 4 to 8 years.
How fast is a Chipmunk?
A Chipmunk can travel at speeds of up to 21 miles per hour.
What does a chipmunk’s poop look like?
Chipmunk poop and mouse droppings look a lot alike. They are similar to black grains of rice. Yuck! But, looking for chipmunk poop is one way to find out whether a chipmunk is living under a house or roof.
Be sure to avoid touching a chipmunk’s poop because it can carry bacteria.
Are chipmunks bad for your yard?
The answer is: Sometimes. Chipmunks can dig up flower bulbs and chew on plants in a garden. Also, they can dig holes and tunnels in a yard. But, on the other hand, they are super fun to watch!
Are chipmunks friendly?
No, wild chipmunks want to stay away from humans. Because of their tiny size, they are afraid of almost everything.
Alternatively, someone who finds an abandoned baby chipmunk may raise it as a pet. A chipmunk that’s been raised in a household is likely going to be friendly to humans. Raising a baby chipmunk is tricky and anyone who tries it should get the advice of a wildlife expert.
Are chipmunks bad to have around your house?
Sometimes. If a chipmunk burrows a hole under a home, there’s a chance it can chew electrical wires, and this can certainly create damage. Also, chipmunks may try to build a nest in a home’s gutters and drain pipes. The leaves, sticks, and debris of a chipmunk’s nest can clog a gutter or pipe.
However, it can be very interesting to watch them climb trees and run around your yard.
Are chipmunks omnivores?
Yes, they eat both plants and animals.
What do chipmunks eat?
Chipmunks eat seeds, fruit, nuts, birds’ eggs, small frogs, snails, and insects.
Can you have a chipmunk as a pet?
It’s possible to have a chipmunk as a pet. If a baby chipmunk is raised in a household, it can become a pet. A chipmunk that’s raised in a household is domesticated. In other words, it wouldn’t be able to survive in the wild because it wasn’t raised there.
One thing to keep in mind. A baby chipmunk may be carrying a disease. So, it’s best to consult a veterinarian or wildlife expert on how to handle this tiny animal.
What's the difference between chipmunks and ground squirrels?
Ground squirrels differ from chipmunks in their size, markings, and habitats. Read more about their differences here!
What is the difference between a chipmunk and a gopher?
The main differences between a chipmunk and a gopher include their appearance, mounds, diet, times of activity, and behavior. While it’s important to distinguish the two, chipmunks and gophers are prevalent yard pests for many homes. Both are garden pests that steal food and burrow holes in the ground. Their burrowing can undermine infrastructures like patios, stairs, and housing foundations.
What are the differences between the red squirrel and the chipmunk?
The main differences between red squirrels and chipmunks are that red squirrels are larger, are granivores, and mostly live in Canada and the Rocky Mountains. Chipmunks are smaller, are omnivores, and live across North America and Asia.
How to say Chipmunk in ...
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- Wikipedia / Accessed March 14, 2021
- Connecticut Department of Energy and Environmental Protection / Accessed March 14, 2021
- National Wildlife Federation / Accessed March 14, 2021