Earwig
There are nearly 2,000 different species!
Advertisement
Earwig Scientific Classification
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Earwig Conservation Status
Earwig Facts
- Average Litter Size
- 50
- Favorite Food
- Plants
- Common Name
- Earwig
- Number Of Species
- 1800
- Location
- Worldwide
- Slogan
- There are nearly 2,000 different species!
View all of the Earwig images!

“No in-ear problems with the Earwig!”
Earwigs are nocturnal insects that can be identified by the large pair of pincers at the end of their bodies. Outside, they’re found under rocks, in rotted tree bark, and in other moist places.
Inside, they can be found in the pantry, where they do eat foods that haven’t been well secured. The earwig also eats crops and garden plants, but it is also a very efficient killer of other garden pests such as thrips, aphids, and snails.
The meaning of the earwig’s name probably doesn’t come from the old wives’ tale that it will enter someone’s ear and lay eggs in their brain while they sleep, but from the unique shape of its hindwing.
It’s possible that an earwig may be found in the ear once in a blue moon but probably no more frequently than any other bug. Female earwigs certainly don’t lay their eggs in people’s brains.
5 Incredible Earwig Facts!
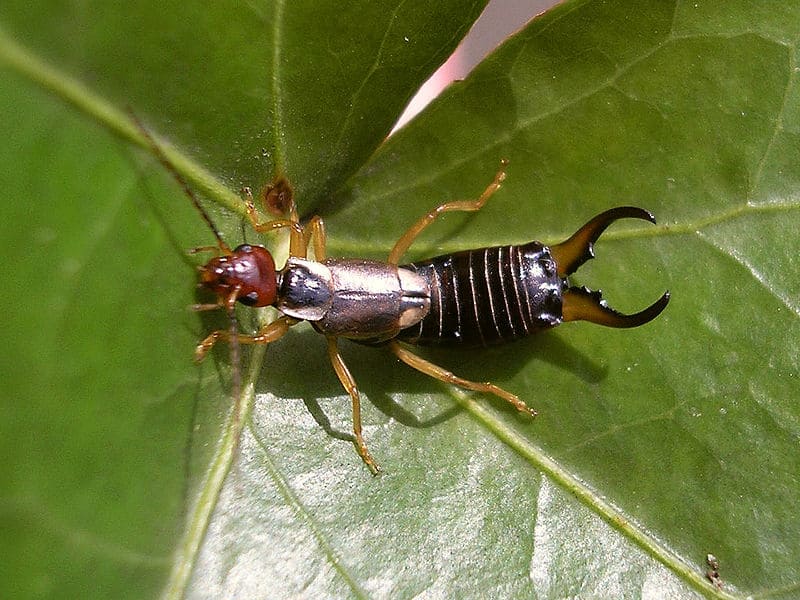

Male Earwig of species Forficula auricularia
©Pudding4brains – Public Domain
- Earwigs are omnivores, which means they eat both plant and animal material. They prefer scavenging over hunting, however.
- The earwig can be a pantry-raiding pest or useful in controlling such pests as aphids.
- The sex of an earwig can be told by the shape of the pincers. Those of the male is large and curved while those of the female are smaller and straighter.
- Earwigs have wings that are developed enough to allow them to fly, but they rarely fly. They prefer to hitch rides on clothing, plants brought in from the garden center, or lumber.
- A baby earwig is taken care of by its mother, which is unusual for insects. A baby earwig is called a nymph.
Evolution and Origins
Originally hailing from Europe, this particular species has successfully established itself in the North American region, where it currently thrives. It is distinguishable by its striking dark-red coloration and features distinctive pincer-like appendages known as cerci located at the end of its abdomen.
Furthermore, earwigs, which are classified as insects, have proven to be a highly successful group of creatures as they have managed to survive and thrive for an extensive period of time. Earwigs are believed to have first emerged during the late Triassic era, approximately 208 million years ago, and have continued to exist and evolve up to the present day.
Although earwigs have a reputation for being nocturnal scavengers with a frightening appearance and a tendency to avoid social interaction, they play an essential ecological role as beneficial insects. Earwigs are often referred to as “environmental janitors” as they feed on decaying plant and insect matter, which helps keep gardens clean and preserves the natural beauty and health of green spaces.
Different Types
Here are a few different types of earwigs:
- European earwig
- Forficulidae
- Archidermaptera
- Anisolabididae
- Neodermaptera
Species, Types, and Scientific Names
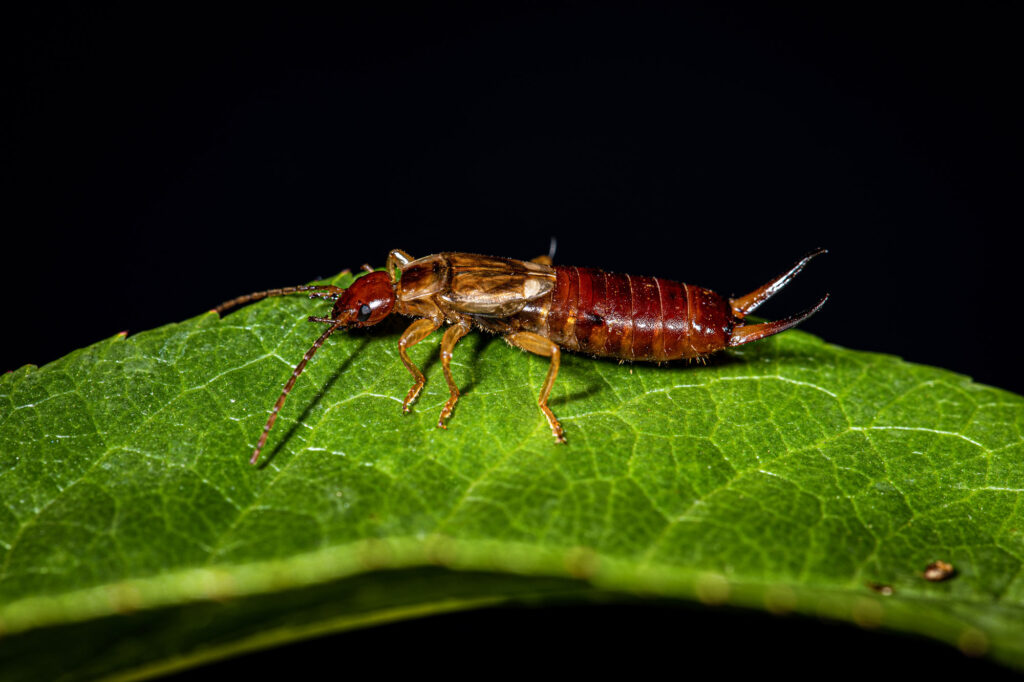

Beautiful Earwig Insect Close Up
©iStock.com/Huseyin Selcuk KIRAY
The earwig is a member of the Dermoptera order. There are a dozen families and 2000 species in this order, which is Greek for “skin wing.” Earwig itself derives from an Old English word meaning “ear insect” or “beetle” and refers to the shape of its wings. Despite the thousands of species, Dermoptera is considered a small order when compared to other insect orders.
The scientific name of the common earwig is Forficula auricularia. Forficula derives from a Latin word for “little shears” or “scissors,” which describes the insect’s pincers. Auricularia describes the human ear shape of the insect’s hind wings when they unfold. This earwig is native to Europe but has spread all around the world in temperate areas. There are 71 genera just in the Forficulidae family.
One earwig that is native to the United States is the spine-tailed earwig, which is found outdoors and drawn to porch lights. Its scientific name is Doru aculeatum. Doru is Greek for “spear” and the meaning of aculeatum is “prickly” in Latin.
Appearance
The earwig is about half an inch long when it is mature, though the giant Australian earwig can grow to 2 inches long. Its body is flat, long, hard, and shiny and comes in shades of yellow or brown.
Its upper wings are short and have a leathery texture, and they protect the hindwings, which are delicate and gauzy. The antennae are long, delicate, and beaded. Like most other insects, the earwig has six legs. Its abdomen is segmented, and its mouthparts evolved to bite and chew.
What distinguishes these insects is the forceps or pincer at the end of their body. The scientific name for these pincers is cerci. Those of the male are not only longer than those of the female, but they are curved and have teeth.
The insect uses its cerci while it feeds, and they also come into play when it mates and defends itself. It also uses the cerci to fold its hindwings up and hide them beneath the forewings. A third instar baby earwig, or nymph, can grow part of its cerci back if they lose it, but it will be straight.

©Peter Yeeles/Shutterstock.com
Habitat

©SIMON SHIM/Shutterstock.com
Earwigs are found just about everywhere on Earth save Antarctica, which is too cold and dry for them. Their ideal habitat is a moist, dark place that’s around 75 degrees Fahrenheit.
They are active at night, and some species are drawn to outdoor lights. During the day, they hide in crevices, trash, under rocks, or in rotting logs. They’re also found in garbage cans, in bathrooms, and on lawn furniture. Some earwigs are blind and live in caves.
A gardener who suspects earwigs is eating their plants can go out at night with a flashlight, and look for them. Earwigs in the home are often seen on the walls or on the ceiling. If they feel threatened, they’ll drop to the floor and scramble away.
Diet
Earwigs are omnivores, which means they eat both plants and animals, living or dead. They prefer to scavenge though others are predators of other insects such as plant lice, maggots, aphids, and flies. Because of this, earwigs may be beneficial to garden plants and crops. There are suborders of earwigs that are mammal parasites. Many of these earwigs feed on the secretions and even the guano of bats. Others are found on rats.
Prevention
These insects are harmless to humans, they don’t spread diseases, and they’re not even as destructive as other insects such as Japanese beetles. Still, an infestation of them can wreak havoc on the pantry or the garden.
Even if they weren’t household or garden pests, their appearance is off-putting to many people, and they smell bad on top of everything else. There are several ways to get rid of an infestation. One way is to expose them to their own predators. These include types of ground beetles, birds, snakes, and toads.
Another way of getting rid of these insects is to trap them. One type of trap is an oil pit trap. Just put 50 percent soy sauce and 50 percent cooking oil in a plastic container, put a lid on, and punch holes in the top near the lid that is big enough for the earwigs to enter. Then, bury the container up to the holes.
Another trap is to put one-foot pieces of garden hose or bamboo between garden plants. The insects enter these pieces, and all the gardener needs to do is collect them every morning and shake out the bugs into a container of soapy water. They also don’t like to walk on petroleum jelly, and a sprinkling of boric acid around a woodpile is also an effective killer of these insects.
Another way to get rid of them is to spray them with pure rubbing or grain alcohol. Mix the alcohol with some water, and spritz the bugs. The alcohol strips off the protective coat on their bodies and kills them.
View all 117 animals that start with EEarwig FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are Earwigs herbivores, carnivores, or omnivores?
Earwigs are Omnivores, meaning they eat both plants and other animals.
What Kingdom do Earwigs belong to?
Earwigs belong to the Kingdom Animalia.
What class do Earwigs belong to?
Earwigs belong to the class Insecta.
What phylum to Earwigs belong to?
Earwigs belong to the phylum Arthropoda.
What order do Earwigs belong to?
Earwigs belong to the order Dermaptera.
What type of covering do Earwigs have?
Earwigs are covered in shells.
Where do Earwigs live?
Earwigs are found worldwide.
In what type of habitat do Earwigs live?
Earwigs live in grass and woodlands.
What is the main prey for Earwigs?
Earwigs eat plants, flowers, and insects.
What are some predators of Earwigs?
Predators of Earwigs include toads, birds, and beetles.
What are some distinguishing features of Earwigs?
Earwigs have sharp pincers and delicate wings.
How many babies do Earwigs have?
The average number of babies an Earwig has is 50.
What is an interesting fact about Earwigs?
There are nearly 2,000 different species of Earwig!
How many species of Earwig are there?
There are 1,800 species of Earwig.
What is an earwig?
An earwig is an insect that can be told from other insects by the cerci at the end of its body.
What eats earwigs?
Efficient killers and eaters of earwigs are birds, toads, snakes, and beetles.
Why are earwigs called earwigs?
Their called earwigs either because of the myth of them crawling into people’s ears or because their hindwings are ear-shaped.
What do earwigs do?
Earwigs do what other insects do. They eat, they hide from predators, and they reproduce. Because they often eat pantry items, flowers, and crops, they are problematic for humans.
What do earwigs eat?
Earwigs are omnivores, so they eat plants, animals, and fungi.
How do you get rid of earwigs?
An infestation of earwigs can be gotten rid of by spraying them with insecticides including diluted alcohol and by luring them into traps. They can also just be vacuumed up if they’re seen.
Are earwigs harmful to humans?
Earwigs are not directly harmful to humans. They can bite and pinch, but these are more annoying than harmful.
Do earwigs go in your ears?
Earwigs do not go into people’s ears and lay eggs.
What attracts earwigs in your house?
Earwigs are attracted to places that are moist and warm, so it is difficult to completely house-proof against earwigs. The best thing to do is to make sure they are not brought into the house in the first place and to eliminate them right away if they are seen.
Are earwigs dangerous?
Earwigs aren’t dangerous. Even the bite and pinch from the toothed pincers of a male won’t do much harm to a human.
How many legs does an earwig have?
An earwig has six legs like other insects.
How do you identify an earwig?
An earwig can be identified by its brown, flattened body, its long antennae, and, especially, its pincers. Without the pincers, it would look very much like a cockroach.
What is the difference between a starfish and an earwig?
The key differences between an earwig and a silverfish are their size, physical features, diet, and lifespan.
The earwig and the silverfish are two small insects that normally dwell outside but can get into your house if you’re not careful. If they grow into an infestation, they can cause harm to your goods. However, their diet, lifespan, and outward appearance are each unique.
What is the difference between earwigs and termites?
The key differences between an earwig and a termite are size, color, diet, lifespan, key features, and infestation.
Earwigs and termites are not related in any way at all. They don’t look alike or eat the same things; they also have varied preferences for living arrangements.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- The Old Farmer's Almanac, Available here: https://www.almanac.com/pest/earwigs
- Wikipedia, Available here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Earwig
- Animal Diversity Web, Available here: https://animaldiversity.org/accounts/Forficula_auricularia/