Flea Beetle
Flea beetles can jump like fleas when threatened.
Advertisement
Flea Beetle Scientific Classification
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Flea Beetle Conservation Status
Flea Beetle Facts
- Name Of Young
- larvae
- Group Behavior
- Infestation
- Fun Fact
- Flea beetles can jump like fleas when threatened.
- Most Distinctive Feature
- Enlarged femora that allow flea-like hopping
- Distinctive Feature
- Flea beetles eat tiny holes on the surface of the leaves they infest
- Habitat
- On the leaves and stem of various host plants
- Predators
- Braconid wasps and tachinid flies
- Diet
- Herbivore
- Lifestyle
- Diurnal
- Favorite Food
- The leaves of different plant species
- Type
- Leaf beetles
- Common Name
- Flea beetles
- Special Features
- Strong hind legs for jumping into the air
- Location
- Worldwide
View all of the Flea Beetle images!
Insects in the subfamily Alticinae are commonly referred to as flea beetles. They’re among the smallest beetles in the world and are found worldwide in various habitats. Insects in this group are characterized by their ability to jump like fleas. Despite their tiny sizes, they are considered major pests in gardens. Both adult and larvae forms of flea beetles can cause major damage to plants, with the adults feeding on leaves and the larvae feeding on plant roots.
Flea Beetles Species, Types, and Scientific Name
Flea beetle is the common name for insects in the subfamily Alticinae. Insects in this group are called this common name because they can jump like fleas when disturbed. They belong to the family Chrysomelidae. A family of beetles commonly known as leaf beetles. The group, which consists of herbivorous insects, is grouped into more than 2500 genera and more than 37,000 species. Leaf beetles are the most encountered beetles in the world.
The flea beetles are among the tiniest leaf beetles. The Alticini tribe contains over 500 genera and 8000 species of beetles. Historically, the family used to be a separate sub-family. However, experts now consider them a tribe for modern research purposes.
Some of the most common species of flea beetles include:
- Phyllotreta cruciferae- Crucifer flea beetle
- Phyllotreta striolata – Striped flea beetle
- Phyllotreta pusilla – Western black flea beetle
- Epitrix cucumeris – Potato flea beetle
- Disonycha xanthomelas – Spinach flea beetle
Appearance: How to Identify Flea Beetles
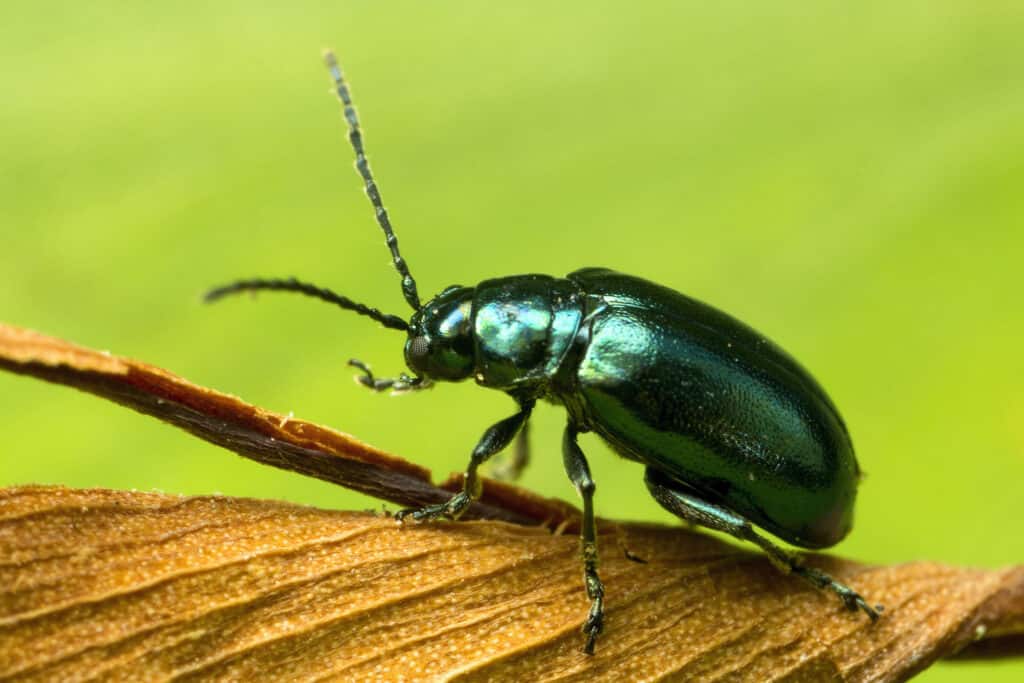

Flea beetles are similar in appearance to leaf beetle, albeit markedly smaller.
©InsectWorld/Shutterstock.com
Flea beetles look very similar to other leaf beetles. However, they’re typically smaller. In fact, they’re among the tiniest of all beetles. They’re also characterized by enlarged femora, which allows them to spring up in the air to escape when disturbed.
Most flea beetles are small, typically between 1/16 –1/8 inch long. The only exception to this rule is the spinach flea beetle which is slightly bigger. They can be up to 1/4 inch long. Appearance may vary from one species to the other. They can be black, brown, metallic gray, or bluish. Some species also have stripes on some parts of their body.
Insects in this family are often recognized based on the damage they leave on plants. Adults leave irregularly shaped holes on leaf surfaces. They may also attack the stems and petals of plants. In cases of a large infestation, the tiny holes can merge into larger ones.
Habitat: Where to Find Flea Beetles
Flea beetles are found worldwide and can live in a variety of habitats. They’re prolific pests and are often found in association with the specific plant they prefer. Adults usually live on the leaves of plants, but larvae can live in the soil and on other parts of a plant, such as the stems and petals.
Some species are known for their ability to seek shelter in the soil in cases of adverse weather. Many species will remain in their hideout during warm and dry seasons and stay hidden during rainy periods. The German name Erdflöhe which means “earth fleas,” refers to their ability to hide in the soil. Adults spend the winter in brush and wooded areas. They’ll only visit gardens during the early planting season.
Diet: What Do Flea Beetles Eat?
Like other leaf beetles, flea beetles are plant eaters. Therefore, they feed on different species of plants. However, most species have a preferred plant species they’re typically associated with. For instance, Altica chalybea (the grape flea beetle) is a pest of grape buds. On the other hand, Phyllotreta striolata (striped flea beetle) only infests cabbage and other similar plants. Similarly, the cucumber beetle feeds on cucumber vines, while E. hirtipennis infest tobacco plants.
Not all members of this group are pests. In fact, experts released Aphthona flava, a type of flea beetle, intentionally in Canada and the United States to control the leafy spurge weed.
What Eats Flea Beetles?
Braconid wasps and tachinid flies are major predators of flea beetles. The larvae of these insects feed on flea beetles as parasites. Ladybugs and other beneficial bugs can also eat flea beetles.
Prevention: How to Get Rid of Flea Beetles
Flea beetles are more active during the spring season, so efforts to prevent their proliferation should start around that period of the year. They typically emerge around the same time as seedlings emerge. Delaying planting for a few weeks is one of the common ways to prevent damage caused by this beetle. You can also start control measures earlier by tilling the garden during fall ahead of the following spring season. This helps to unearth the larvae in your garden.
Another form of control is planting repellent plants such as hyssop, basil, catnip, and sage. Conversely, you may plant trap crops like radishes to take the attention of the beetles from your valuable plants. You may introduce beneficial insects into your garden to keep flea beetle populations under control.
If an infestation is underway already, you can prepare a homemade spray from isopropyl alcohol, water, and liquid soap. Leave this mixture to sit overnight before spraying it on your plant. You can also dust the leaves with talcum flowers to repel the beetles.
Related Animals…
View all 91 animals that start with FFlea Beetle FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are flea beetles the same as fleas?
No. Flea beetles are different from fleas. In fact, both insects are not related. The common name of flea beetles merely refers to their ability to leap in the air using their hind legs like fleas when disturbed.
What eats flea beetles?
Flea beetles have a lot of natural predators. Some predatory wasps, ladybugs, and beneficial nematodes can eat flea-beetle adults and larvae.
Are flea beetles harmful?
Flea beetles are not harmful to humans since they cannot bite or sting. However, they can damage seedlings and small plants, especially in cases of a massive infestation.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- Almanac, Available here: https://www.almanac.com/pest/flea-beetles
- Britannica, Available here: https://www.britannica.com/animal/flea-beetle
- Wikipedia, Available here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Flea_beetle