Locust
Each locust can eat its weight in plants each day.
Advertisement
Locust Scientific Classification
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Locust Conservation Status
Locust Facts
- Diet
- Herbivore
View all of the Locust images!
The word “locust” is given to certain types of grasshoppers with short horns.

Locusts are insects that are known for their swarming behavior, which occurs when environmental conditions are right. Locust plagues have affected crops and farmland since biblical times, attacking any growing green vegetation in their path.
Colloquially, the words “locust” and “locust bugs” refer to different creatures depending on where in the world you are. Sometimes, locust may also refer to the cicada, a different species of bug that emerges from the ground and is known for making loud sounds from the trees.
5 Incredible Facts!
- These insects are some of the oldest bugs, being relatively unchanged since the Triassic era.
- Migratory locusts have the largest range of any locust or grasshopper species.
- Swarms are nearly impossible to wipe out once they begin.
- The word locust means different things in different parts of the world.
- These insects have plagued humans for thousands of years, destroying large amounts of crops.
Species, Types, and Scientific Name
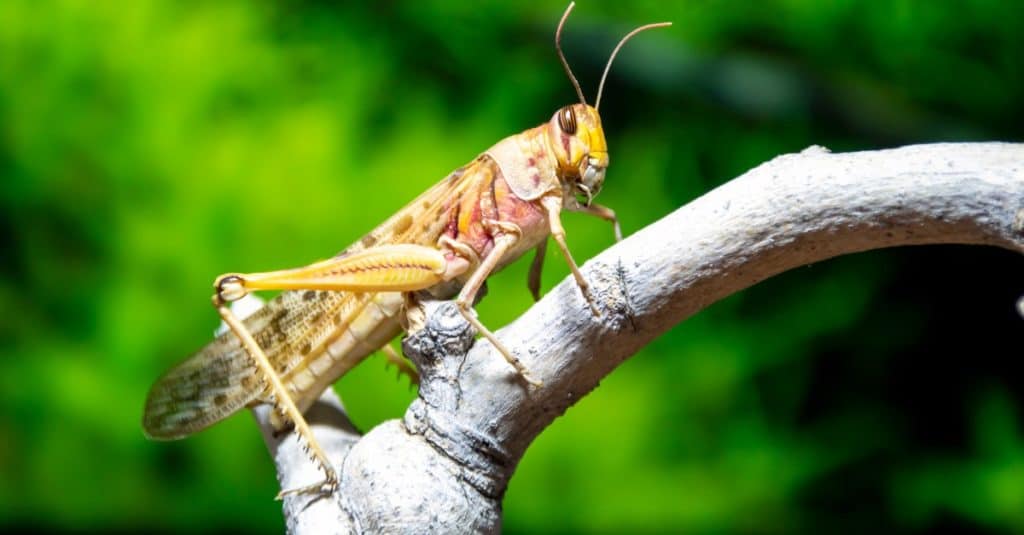

There are 27 species of locusts in the family Acrididae that can gather in swarms and destroy crops.
©SubAtomicScope/Shutterstock.com
Locusts belong to the family Acrididae. All locusts belong to Acrididae, but not every bug in the family Acrididae is considered to be a locust.
There are 27 species found worldwide. They are:
- Sudan plague – (Aiolopus simulatrix)
- Egyptian – (Anacridium aegyptium)
- Sahelian tree – (Anacridium melanorhodon)
- Sudan tree – (Anacridium wernerellum)
- Spur-throated locust (Austracris guttulosa)
- Small plague grasshopper (Austroicetes cruciata)
- Italian – (Calliptamus italicus)
- Yellow-spined bamboo – (Ceracris kiangsu)
- Australian plague – (Chortoicetes terminifera)
- High plains – (Dissosteira longipennis)
- Moroccan – (Dociostaurus maroccanus)
- Yellow-winged – (Gastrimargus musicus)
- Siberian – (Gomphocerus sibiricus)
- Migratory – (Locusta migratoria)
- Brown locust (Locustana pardalina)
- Differential grasshopper (Melanoplus differentialis)
- Migratory grasshopper (Melanoplus sanguinipes)
- Rocky Mountain – (Melanoplus spretus)
- Red – (Nomadacris septemfasciata)
- Bombay locust (Nomadacris succincta)
- Senegalese grasshopper (Oedaleus senegalensis)
- Mato Grosso – (Rhammatocerus schistocercoides)
- South American – (Schistocerca cancellata)
- Desert – (Schistocerca gregaria)
- Central American – (Schistocerca piceifrons)
- Peru Locusts (Schistocerca interrita)
- Pallid-winged grasshopper (Trimerotropis pallidipennis)
Historical records tell about plagues of locusts that devastated crops thousands of years ago. The ancient Egyptians, the Chinese, and the Bible all have references to them.
Locust vs. Grasshopper
Locusts are not a particular species. They are, in fact, a subset of grasshoppers that develop swarming behavior and gregarious growth when environmental conditions are right. Grasshoppers do not decimate crops and plague farmers like locust swarms do. They also cannot fly as far as locusts do.
Locust vs Cicada
Cicadas and locusts are not similar species. Cicadas suck sap from trees and are known to come out of the ground and sing. They also leave their shed shells all over the trunks of trees. Locusts do not possess the same burying behavior, and they tend to feed in large swarms on crops and other vegetation.
Appearance
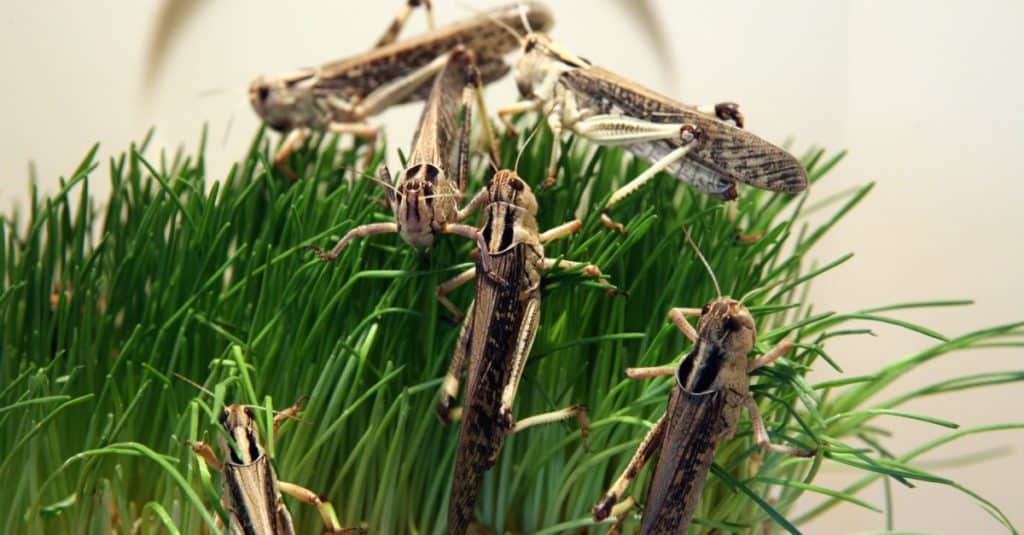

There are three stages in the locust life cycle: egg, nymphs or “hoppers,” and adults.
©Vladimir Wrangel/Shutterstock.com
These insects are usually about the size of a paper clip and have green or dusty brown shells. They have long back legs used for jumping and hopping, and they can rub the legs together to creates sounds.
There are three stages in the locust life cycle: egg, nymphs or “hoppers,” and adults. When they are in the nymph stage, the insect may experience an excess amount of serotonin, triggering their gregarious phase. This phase happens when the rain returns after a long dry spell. Then, nymphs and adults change in color, often becoming darker colors with bright markings. This is when the locusts begin to swarm together and attack crops, fields, and any place with fresh vegetation.
When in this phase, locusts also begin to mature more quickly and reproduce much more quickly. Their brains increase in size, and they develop more endurance so they can travel farther as a swarm.
The biggest swarm ever recorded was a swarm of Rocky Mountain Locusts in 1875 that is thought to have contained over 1.2 trillion insects. In a surprising turn of events, the Rocky Mountain Locust went extinct 25 years later, with the last insect being recorded in 1902.
Habitat
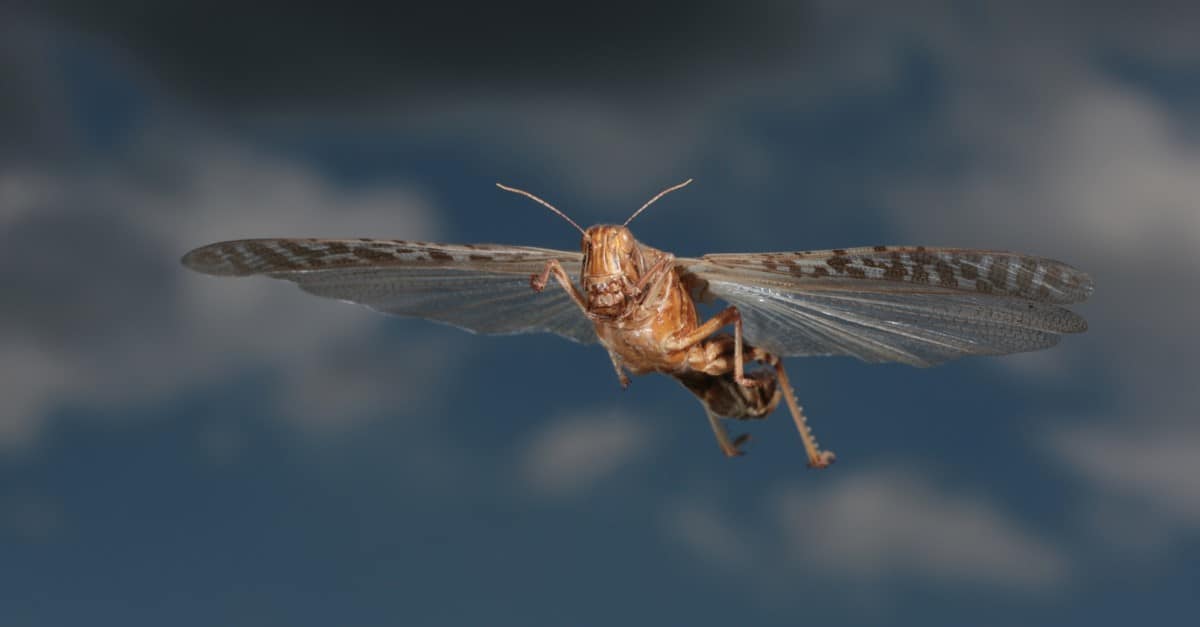

North America has not had any locusts since the last species went extinct in 1902.
©Holger Kirk/Shutterstock.com
These insects are found on nearly every continent in the world except for Antarctica and North America. The Rocky Mountain Locust was the only species found in North America until its extinction in 1902.
Their habitats include fields, wetlands, sparse woodlands, and places frequented by crops or domestic animals. They prefer open, sunny areas with many types of grass and flowers.
Diet
Locusts have been known to swarm in large groups consisting of billions of insects. These swarms attacked vegetation and farmland, resulting in human starvation and costly damage to the fields. These insects prefer to eat soft foliage, such as leaves and grasses. Different species will have different diets and different preferences as to which plants they like to consume.
When food is scarce, locusts will sometimes forage on dead grasshoppers, or even target weaker members of their own species.
While they do swarm and devastate crops, these insects play a huge role in stimulating plant growth in their habitats. Nymphs have a larger appetite than adults.
Prevention
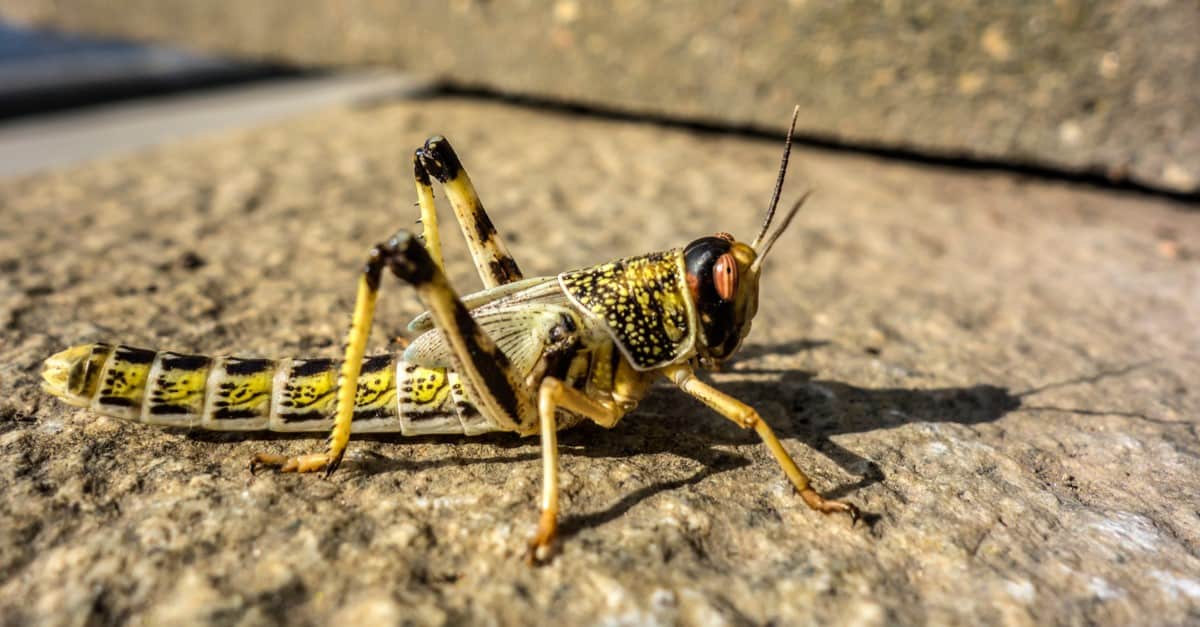

This Egyptian locust is famous for the plague of locusts recorded in the Bible.
©ivanoel/Shutterstock.com
In ancient times, people were unable to do much to protect their crops from a swarm of these insects. They were a serious threat and were rightly feared by the people of ancient times.
Modern solutions for these insects once involved massive amounts of pesticides to protect crops. These pesticides were sprayed over the fields using small planes.
In 1997, however, a safer method was found to control massive swarms. A biological pesticide was created that killed the insect via fungal growth. It spread from insect to insect, ultimately killing the swarm. The most ideal control methods are ones that do not greatly affect the environment.
Although they could do little to control the locust plagues, humans have been consuming these insects for many millennia. The Torah permits the consumption of certain species, and eating these insects is considered halal. They can be fried or smoked and are considered a delicacy in some cultures.
View all 98 animals that start with LLocust FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What is a locust?
A locust is a type of bug found in the same family as grasshoppers. All locusts are grasshoppers, but not all grasshoppers are locusts. Locusts are triggered by environmental conditions, causing them to release copious amounts of serotonin and swarm in overwhelming numbers.
What is the difference between a locust vs. a cicada?
Locusts swarm together in huge numbers to attack crops and vegetation. Cicadas bury in the ground and come out every few years, depending on the species. They make loud sounds and songs that often mark the season of summer. Cicadas also leave their shells behind on trees, while locusts do not shed their shells the same way.
Can a locust kill you?
Locusts will not attack humans and do not carry dangerous diseases. However, locust swarms that wipe out farmland can be detrimental to those who live off of the crops that the locusts feed on.
Are locusts dangerous?
Locusts are dangerous to those who live off of the land that they decimate. However, locusts do not bite or sting humans. They also do not tend to carry diseases that can be transmitted to humans.
Do locusts bite or sting?
Locusts will only attack and feed on plants. They do not bite or sting human beings.
Is locust a bad sign?
Locusts have a bad reputation because, when they begin to swarm in their gregarious phase, they demolish crops and farmland. Locust swarms can also be incredibly difficult to mitigate once they have started, so they could be a bad sign for farmers and anyone who lives and profits off of the land. When they are not in their gregarious phase, however, locusts are harmless and tend to remain by themselves.
What is the difference between a locust vs a grasshopper?
Locusts are a type of grasshopper. Grasshoppers live alone and do not plague crops and farmlands, while locusts will swarm together in huge numbers and devastate farmland.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- World Atlas / Accessed April 15, 2021
- The Bug Man / Accessed April 15, 2021
- Hindawi / Accessed April 15, 2021
- Orkin / Accessed April 15, 2021
- National Geographic / Accessed April 15, 2021
- Britannica / Accessed April 15, 2021
- Wikipedia / Accessed April 15, 2021