Supersaurus
Supersaurus vivianae
Advertisement
Supersaurus Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Reptilia
- Order
- Dinosauria
- Family
- Diplodocidae
- Genus
- Supersaurus
- Scientific Name
- Supersaurus vivianae
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Supersaurus Conservation Status
Supersaurus Facts
- Group Behavior
- Herd
- Diet
- Omnivore
Supersaurus Physical Characteristics
- Venomous
- No
- Aggression
- Low
View all of the Supersaurus images!
“The supersaurus was one of the largest dinosaurs to ever exist. Its neck alone could be as long as 50 feet!“
Scientific Name
The official scientific name of the supersaurus is Supersaurus vivianae. The history of the supersaurus is quite complicated, and several aspects of it are still untapped. Its name was given by paleontologist Brian Curtice after he analyzed the bones from a specimen in Colorado. The name “supersaurus” literally means “super lizard,” referencing the elongated shape of their bodies. They were very similar in shape and size to other massive sauropods of their time, such as the apatosaurus and the brachiosaurus. They belong to a genus of diplodocid sauropod dinosaurs.
Supersaurus Summary
The supersaurus was a giant herbivore with an elongated tail and neck. The animal lived between 145 to 155 million years ago during the late Jurassic period. This giant inhabited several regions of North America, and its fossils were found in areas of Wyoming, Colorado, and Portugal. While these animals are known to feed on plants, they had no known predators due to their enormous size.
Description & Size
The supersaurus was a gigantic animal with front legs longer than its back ones. Its legs were like those of an elephant, broad with five-toed feet. One toe on each of their feet had a thumb claw, most likely to protect them from predators or other aggressive sauropods. The animal had a tiny skull and head compared to its overall body size. It also had an extremely long neck, reaching up to 39-50 feet, allowing it to reach the leaves of very tall trees. Its elongated body was almost five stories tall (50 ft) and 14 car lengths long (120-140 ft). While this creature was enormous, it was not the largest or heaviest animal of all time. This title belongs to the blue whale. A large part of its body was just its neck and tail. Its body proportions are as follows:
| Overall Body Length | 128 – 137 ft |
| Weight | 70000 – 80000 lbs |
| Height | 50-60 ft |
| Neck Length | 39-50 ft |
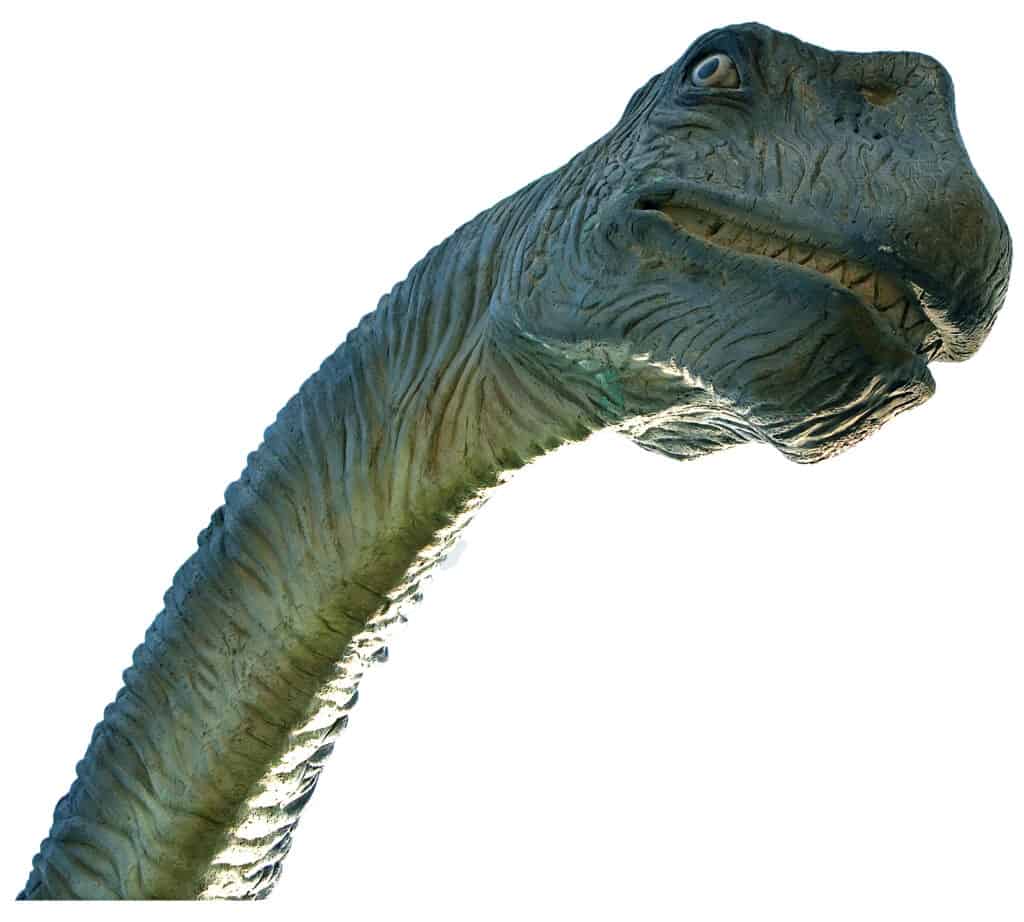

The supersaurus had a tiny skull and head compared to its overall body size. It also had an extremely long neck.
©iStock.com/SValeriia
Diet – What Did the Supersaurus Eat?
The supersaurus had a diet comprised of only plants, making it an herbivore. Considering its size, it’s likely that the dinosaur consumed a large number of plants every day. Based on fossil remains, we know the animal had blunt teeth, suitable for stripping foliage. Thus, it was very prone to stomach ulcers or gastroliths. Another possible food source for the supersaurus was conifers that grew abundantly during the Jurassic period. They also could have fed on gingkos, seed ferns, cycads, bennettitaleans, ferns, club mosses, and horsetails. It must be noted, however, that all of this information is based on assumptions, which are based on the information we have about the Jurassic period.
Habitat – When and Where It Lived
A humongous, herbivorous creature living during the late Jurassic period, the supersaurus is likely to have lived in extensive grasslands and lush forest habitats.
The herds of the supersaurus likely migrated to richer feeding grounds once the areas they inhabited became barren from overfeeding. Their long necks enabled them to reach the foliage on treetops, giving them the ability to reach more food than most other animals living at the time. Scientists discovered the supersaurus’ fossils primarily in North America.
Threats and Predators
Based on the overall body structure of these animals, paleontologists have concluded that these animals were probably slow movers, which might’ve made them susceptible to predation. However, many scientists also believe that the supersaurus had no predators due to its immense size. While predators of the Jurassic period were large, they were still much smaller compared to the supersaurus. It would have been very difficult for animals such as the Allosaurus to take down a full-grown supersaurus.
Juveniles would have been more susceptible to predation. Still, since these animals likely traveled in large packs, it is unlikely that predators commonly hunted these large sauropods.
Discoveries and Fossils – Where It Was Found
The first fossils of this dinosaur were found in the US, in western Colorado. These were found by paleontologist James A. Jensen in 1972 and were named 13 years later. This fossil specimen mainly consisted of two shoulder blades, ribs, neck vertebrae, and a pelvis, giving a rough idea of what the animal might’ve looked like.
Many other similar species of sauropods also lived during the Jurassic era. So, fossils of the Supersaurus were often mistaken for other enormous dinosaurs, including Camarasaurus, Apatosaurus, and Brachiosaurus. In fact, paleontologists used the bones of other dinosaurs to create a model of what the Supersaurus might have looked like before enough fossils were collected to recreate the creature in its entirety.
Extinction – When Did It Die Out?
The Supersaurus went extinct during the Triassic-Jurassic extinction. Several factors contributed to this, including slowly developing sea-level changes, oceanic acidification, and climate change. One theory is that an asteroid or comet might’ve hit the earth during this mass extinction event. This event killed an estimated 70 percent of all animals, including every dinosaur species.
Similar Animals to the Supersaurus
Similar animals to the Supersaurus include:
- Apatosaurus: One of the largest land animals to have existed, the apatosaurus had a height of 75 ft and weighed about 50,000 lbs. Similar to the supersaurus, it had a very long neck.
- Diplodocus: A long-necked, four-legged animal, the diplodocushad had a whip-like tail.
- Brachiosaurus: The brachiosaurus had four legs, a long neck, a small skull, and a long muscular tail, which was quite similar in structure to that of the supersaurus.
Supersaurus FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
When was the Supersaurus alive?
This dinosaur lived about 155-145 million years ago, during the late Jurassic period.
How big was the Supersaurus?
The Supersaurus was one of the largest land animals to ever exist. It was 128 to 137 ft in length and weighed between 70,000 – 80,000 lbs.
Was the Supersaurus bigger than the Argentinosaurus?
Although Supersaurus is the longest dinosaur ever discovered, it is not the heaviest. That honor is likely to go to the superheavy titanosaur Argentinosaurus, which weighed up to 200,000 lbs and was nearly twice as big as the Supersaurus.
Where did the Supersaurus live?
The Supersaurus lived in North America during the Jurassic period. Its fossils have been discovered in Wyoming, Colorado, and Lisbon, Portugal.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- Dino Fandom, Available here: https://dino.fandom.com/wiki/Supersaurus
- Enchanted Learning, Available here: https://www.enchantedlearning.com/subjects/dinosaurs/dinos/Supersaurus.shtml
- Dinosaur pictures, Available here: https://dinosaurpictures.org/Supersaurus-pictures