Gulper Catfish
Asterophysus batrachus
Gulper catfish can consume prey twice its size
Advertisement
Gulper Catfish Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Actinopterygii
- Order
- silfuriformes
- Family
- Auchenipteridae
- Genus
- Aterophysus
- Scientific Name
- Asterophysus batrachus
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Gulper Catfish Conservation Status
Gulper Catfish Facts
- Prey
- Fish
- Name Of Young
- Fry
- Group Behavior
- Solitary/Pairs
- Fun Fact
- Gulper catfish can consume prey twice its size
- Other Name(s)
- Ogre catfish
Gulper Catfish Physical Characteristics
- Color
- Brown
- Grey
- Black
- Light Grey
- Lifespan
- 10-20 years
- Venomous
- No
- Aggression
- Medium
View all of the Gulper Catfish images!
Gulper Catfish Summary
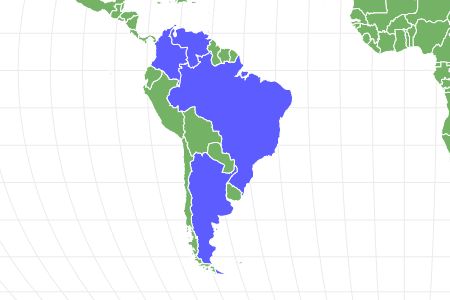
The gulper catfish (Asterophysus batrachus), also known as the ogre catfish, is a species that is native to the Orinoco and Rio Negro basins located in Colombia, Brazil, and Venezuela in South America. These predatory fish inhabit blackwater tributaries and actively hunt at night. Their thick and rounded body distinguishes them from other species of catfish, and they are capable of catching and consuming prey that is twice their size. These catfish can be found both in the aquarium hobby and in the wild.
3 Facts About Gulper Catfish
- Instead of scales, gulper catfish have an elastic skin that stretches over their bellies.
- They grow to a maximum size of 12 inches (30 cm) and can consume prey twice their size.
- They swallow their prey whole.
Gulper Catfish Appearance
Gulper catfish have thick-set bodies, and their coloration can range from black, white, brown, and even orange. The belly of the gulper is grey or white and matches their long barbels. Their belly often appears distended after meals, and their large jaw opens widely to swallow prey.
The elastic skin that covers their scaleless body allows their stomach to stretch to accommodate their meal. Incredibly, their jaw stretches to the back of their head when catching prey. They have anterior dorsal fins and three pairs of barbels around their mouths. The average adult size of a gulper catfish is between 10 and 12 inches (25-30 cm), but some can reach 14 inches (35 cm) in length.
The flathead catfish, pictured above, does not have the unique ability to unhinge its jaw like the gulper catfish.
©iStock.com/stammphoto
Gulper Catfish Distribution, Population, and Habitat
Distribution
The gulper catfish is native to South America where it can be found in the Orinoco drainage systems in Venezuela and the river basins in Rio Negro. They are spotted in southern parts of South America, like Argentina. Additionally, the gulper catfish is distributed throughout river basins and drainage systems in Brazil and Colombia.
Population
These fish belong to the family order Auchenipteridae. The earliest species populated rivers in southern Central America. After a while, the population extended to the southern regions of Argentina and Brazil.
Their conservation status is not threatened, and it does not appear on the IUCN redlist, but they are quite uncommon in the wild and are primarily found in the aquarium trade industry.
Habitat
Gulper catfish are not accustomed to high currents, preferring to inhabit slow-moving, murky waters, like blackwater tributaries. They hunt in shallow water during the night, since they are nocturnal creatures. In fact, these bottom-dwelling fish spend the majority of the day hiding.
When kept in aquariums, their natural habitat should be replicated so that they can grow to their full adult size and exhibit natural behaviors. This means keeping them in a large aquarium with a soft substrate, excellent filtration, aquatic vegetation, and driftwood.
Gulper Predators and Prey
Gulper catfish are ferocious predatory fish that consume prey larger than themselves. They accomplish this by extending their large jaws and swallowing their prey whole. However, without scales to protect them, gulper catfish are vulnerable to attacks from predators.
These fish are strictly carnivores and eat a protein-rich diet that consists of fish. However, in aquariums, they may eat pellets and feeder fish. Because they can extract nutrients from plants, they may also incorporate vegetable matter into their diet.
Gulper Catfish Reproduction and Lifespan
Sexually mature male gulper fish have thickened anal fins that become elongated and fuse together to form an intromittent organ. This forms a genital pore at the tip of their modified rays. Males are smaller and narrower than females. The females’ larger body allows them to carry eggs in their stomachs.
When males want to mate, they will chase a female and rub her body to indicate their desire. Reproduction takes place through spawning, but there is not much documentation on gulper catfish mating and reproduction because it is uncommon for this species to reproduce in captivity.
The average lifespan of a gulper catfish in the wild is between 10 and 20 years, but their life expectancy in an aquarium is shorter, at eight to 15 years.
Related Animals
View all 170 animals that start with GGulper Catfish FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Where are gulper catfish found?
Gulper catfish are found throughout South America, in water systems in Brazil, Argentina, Venezuela, and Colombia where they inhabit blackwaters with slow-moving currents. They can be found in the Rio Negro water systems and the Orinoco river basin.
What do gulper catfish eat?
Gulper catfish are predatory fish that eat prey of various sizes, even ones larger than themselves. They can extend their jaw to swallow large prey whole, which includes bigger fish. They can also eat a variety of pellets and vegetable matter when kept in aquariums even though they are carnivores.
How big do gulper catfish get?
Gulper catfish can reach adult sizes between 10 to 12 inches (25-30 cm), however, some wild specimens have been found to reach 14 inches (35 cm) in size. In aquariums, gulper catfish will rarely grow more than 11 inches (28 cm) depending on their conditions and tank size.
Can you keep gulper catfish in aquariums?
Gulper can be kept in aquariums if the tank is large enough and they are fed a balanced diet and the aquarium has good water conditions. Most gulper catfish will live comfortably in an aquarium over 100 gallons so that they have space to grow properly and move around comfortably.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- The aquarium wiki, Available here: https://assets.theaquariumwiki.com/wiki/Asterophysus_batrachus
- Seriously fish, Available here: https://www.seriouslyfish.com/species/asterophysus-batrachus/
- Fishroma , Available here: https://fisharoma.com/gulper-catfish-2/#
- Wikipedia , Available here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Asterophysus_batrachus#