Ichthyosaurus
Ichthyosaurus communis
Gave birth to live young instead of laying eggs like other reptiles
Advertisement
Ichthyosaurus Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Reptilia
- Order
- Ichthyosauria
- Family
- Ichthyosauridae
- Genus
- Ichthyosaurus
- Scientific Name
- Ichthyosaurus communis
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Ichthyosaurus Conservation Status
Ichthyosaurus Facts
- Main Prey
- Fish and squid
- Fun Fact
- Gave birth to live young instead of laying eggs like other reptiles
- Most Distinctive Feature
- Giant eyes that helped it see well in dark and deep ocean areas
Ichthyosaurus Physical Characteristics
- Length
- 11 feet
View all of the Ichthyosaurus images!

There are already some fearsome predators swimming around our oceans. Now, imagine a dolphin-like creature with giant eyes that could swim down to the ocean’s darkest depths to hunt fearsome creatures like the giant squid. That describes the extinct ichthyosaurus.
The name ichthyosaurus means fish and lizard, which is a pretty good description of what a whispichthyosaurus was. Despite having the suffix “Saurus” this extinct reptile is not technically a dinosaur. Ichthyosaurus is the most well-known of a family of sea-dwelling reptiles with a similar sounding name – ichthyosauridae, also called, ichthyosaurs.
Strangely, all ichthyosaurs, including ichtyosauruses, were descended from land-dwelling reptiles that were themselves descended from fish. Scientists have some theories as to why the ichthyosaurs returned to the oceans, but they are not sure exactly why that happened. One theory is that there was less competition for resources in the water than on land.
Description and Size
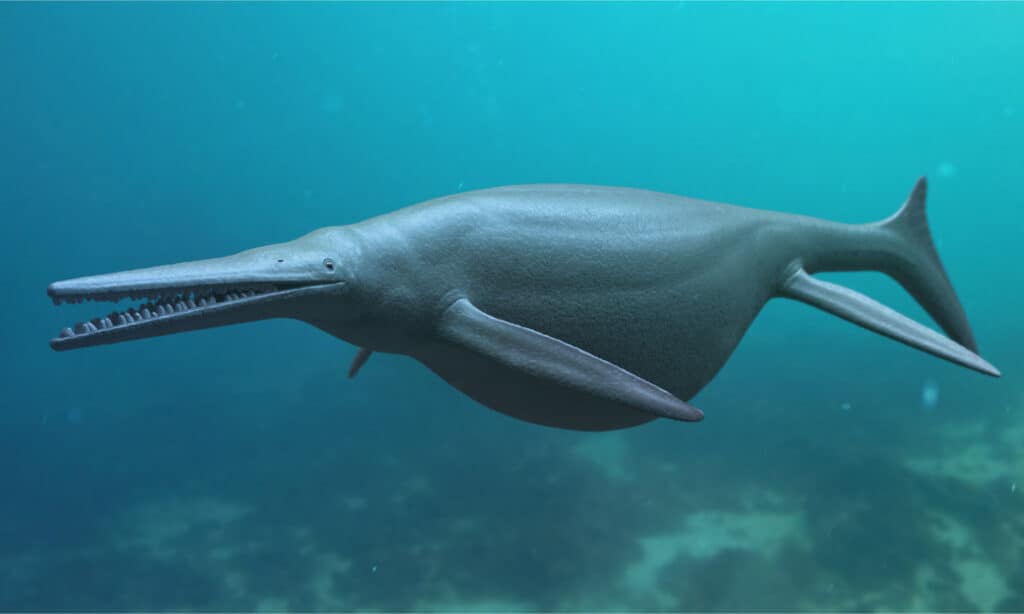
Ichthyosaurus is often compared to a dolphin or a shark though it is related to neither species.
©Giant Ichthyosaurus Aquatic Dinosaur 3D Rendered/Shutterstock.com
Some ichthyosaur species were absolutely huge. Some estimates put the largest species at 26 meters long, which is the same size as a blue whale. The ichthyosaurus was pretty small in comparison. It only measured about 11 feet long.
The ichthyosaurus is often compared to a dolphin or a shark. When you see the shape of the body, it’s easy to see why. They have a pointed nose like a bottle-nose dolphin and a vertical tail-fin like a shark. However, they are not related to either.
Dolphins are mammals and sharks are fish. So, why do all three species have some similar features? Experts believe it is caused by something called convergent evolution. This theory explains why some unrelated creatures living in the same environment develop similar features—they just work really well.
The ichthyosaurus also had two sets of fins in addition to the tail-fin. This particular species had 5 or more “fingers” within the front fin. Other ichthyosaur species had more than 30! Unlike sharks or dolphins, ichthyosaurus had rear fins too.
Another thing that makes ichthyosauruses different than other reptiles is that they gave birth to live babies instead of laying eggs.
Evolution and Origins
The origins of ichthyosaurs can be traced back to the Triassic Period in Asia, where they initially existed as long-bodied, undulating swimmers without the distinctive adaptations observed in later species.
However, by the Late Triassic, certain lineages of ichthyosaurs had evolved to reach impressive sizes.
According to Valentin Fischer, a vertebrate paleontologist at the University of Liège in Belgium, who was not involved in the study, lenticarpus is considered the most closely related terrestrial ancestor to ichthyosaurs.
Fischer came across reports of these fossils a few years ago during a paleontologists’ conference.
What Did Ichthyosaurus Eat?

Ichthyosaurus is often compared to a dolphin or a shark though it is related to neither species.
©3dsam79/Shutterstock.com
The ichthyosaurus was a carnivore. They ate squid, fish, and perhaps even smaller ichthyosaur species. In rare cases, birds and turtles have been found fossilized in ichthyosaur stomachs.
The ichthyosaurs had a really good advantage for hunting. They had giant eyes which allowed them to hunt in dark places in the ocean where other carnivores probably couldn’t see as well. They likely dove deep to find snacks like the giant squid. Some experts believe the ichthyosaurs may have been warm-blooded, meaning their internal temperature generally stayed stable despite the outside conditions. This could have been a further advantage during their deep dives.
Their earbones were solid, meaning they relied on vibrations from the water to hear. Their primary sense for hunting and safety would have been a vision.
The Oceanic Reptile
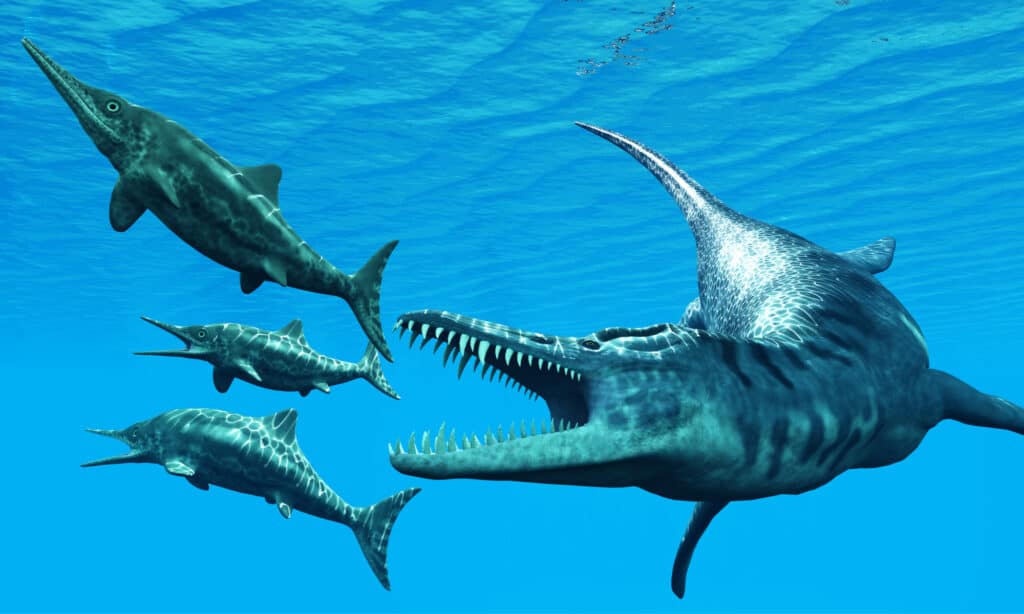

Ichthyosaurus was near the top of the food chain, but they were attacked by larger carnivores like Liopleurodon.
©Catmando/Shutterstock.com
Ichthyosauruses lived in the ocean during the late Triassic and early Jurassic periods. Their fossils have been found in many places all over the world. However, not much is known about their exact location. Because they gave birth to live young instead of laying eggs, ichthyosauruses never had to come on land. And, that’s a good thing. Unlike some other species of ocean-dwelling reptiles, their fins were only good for swimming, not walking.
Threats and Predators
Ichthyosaurus may have been near the top of the food chain, with only larger ichthyosaur species to worry about in terms of attack. However, that doesn’t mean they were without worries.
The greatest threat may have simply been the competition for resources as more carnivorous fish species like sharks developed and became more abundant. Climate change may have been another concern for them. Some experts wonder if a warming ocean is a part of what led to their demise either by changing the availability of resources or creating an unlivable environment for the ichthyosaurus.
Discoveries and Fossils
Mary Anning discovered the first ichthyosaurus fossils in the early 1800s. She discovered the fossils in England with her brother. Her discoveries were so important to paleontology that she has a species of ichthyosaur named after her—the ichthyosaurus anningae. Ichthyosaurus fossils are pretty plentiful. They are so common that it is pretty easy to find some for sale online in our modern era.
Why Did Ichthyosaurus Go Extinct?
Many experts believe that their extinction may have been due to a lack of resources. However, new evidence suggests that a warming ocean may have been to blame. However, experts believe it was probably a combination of several factors since other large ocean-dwelling reptiles survived this period. Some dedicated scientists and paleontologists are researching this topic today.
The ichthyosarus went extinct in the early Jurassic period. However, other ichthyosaur species were around until the late Cretaceous period, which ended about 65 million years ago. The ichthyosaur family mysteriously died out about 30 million years before the large extinction that killed all the dinosaurs.
View all 39 animals that start with IThank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- Wikipedia, Available here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ichthyosaurus
- Wikipedia, Available here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mary_Anning#Ichthyosaurs
- Beta Capeia, Available here: https://beta.capeia.com/paleobiology/2017/09/25/the-evolutionary-history-of-ichthyosaurs
- Fossil Age Minerals, Available here: https://www.fossilageminerals.com/collections/ichthyosaurus-fossils-for-sale
- Britannica, Available here: https://www.britannica.com/animal/ichthyosaur
- Wikipedia, Available here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ichthyosaurus