Spitting Cobra
Spitting cobras are types of cobras that can spit venom at predators and prey.
Advertisement
Spitting Cobra Scientific Classification
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Spitting Cobra Conservation Status
Spitting Cobra Facts
- Prey
- Small mammals, amphibians, reptiles, insects, eggs, birds. Some species scavenge.
- Group Behavior
- Solitary
- Fun Fact
- Spitting cobras are types of cobras that can spit venom at predators and prey.
- Diet
- Carnivore
Spitting Cobra Physical Characteristics
- Color
- Brown
- Grey
- Yellow
- Red
- Blue
- Black
- Green
- Pink
- Skin Type
- Scales
- Lifespan
- 20 year lifespan in captivity
- Length
- 2.29 to 8.9 feet
- Age of Sexual Maturity
- two or three years
View all of the Spitting Cobra images!
“The Spitting Cobra Evolved to Deter Humans”

When a spitting cobra spits it aims for the eyes and frequently hits the target. It makes you wonder how a snake knows where and what a human’s eyes are. Some biologists believe that the ability to accurately aim at the eyes evolved in cobras, who are much older than Homo sapiens, when humans first came on the scene and started harassing them. In other words, the reptile may not know where your eyes are and how much you value your sight, but nature does. Read on to learn more about these fascinating animals.
Amazing Facts
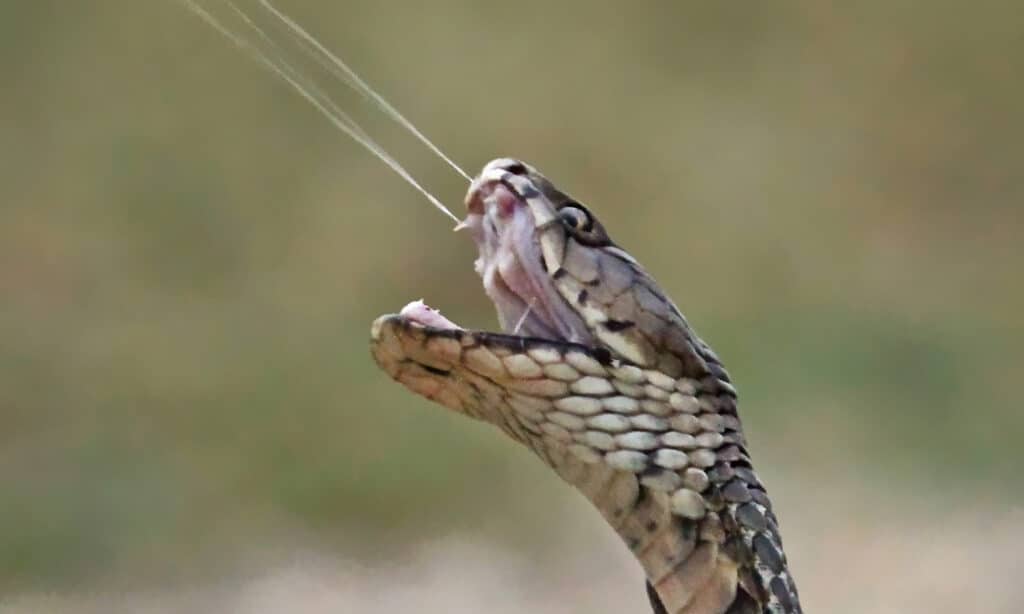

Spitting cobras are some of the deadliest reptiles on the planet.
©Eugene Troskie/Shutterstock.com
Here are five amazing facts about spitting cobras.
- Some spitting cobras can spit venom as far as 10 feet.
- Ashe’s spitting cobra is the largest spitting cobra and can grow over 8 feet in length.
- Their venom might cause some blistering if it lands on your skin but can blind you if it lands in your eyes.
- The Indochinese spitting cobra has the smallest spitting range of the other spitters at around 3.3 feet. It also sprays a mist as opposed to a stream.
- Identification of a spitting cobra can be done by examining the fangs. The opening in the fang of the spitting cobra is aimed toward the front of the mouth and is much smaller than the opening in the fang of a non-spitting cobra.
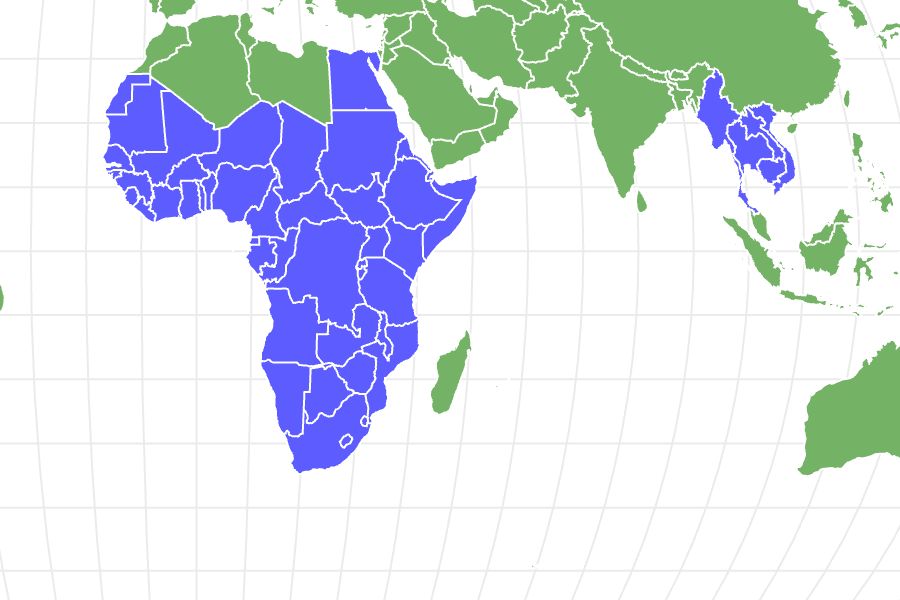
Where To Find Spitting Cobras
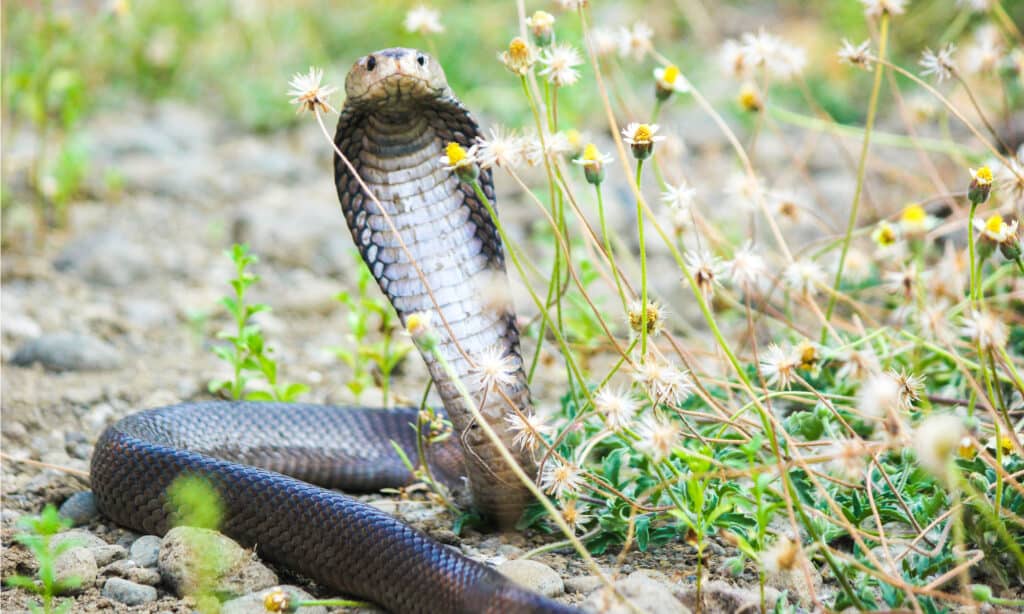

Spitting cobras have adapted to survive in a variety of environments.
©hermawanandik/Shutterstock.com
These venomous reptiles are found in Africa and Asia. Habitats range from the savannas, deserts, and tropical forests of Africa to the mangroves, swamps, and rice paddies of Asia. Habitats also include pastures, jungles, places where people live and work, and locations as high as 6600 feet.
Evolution
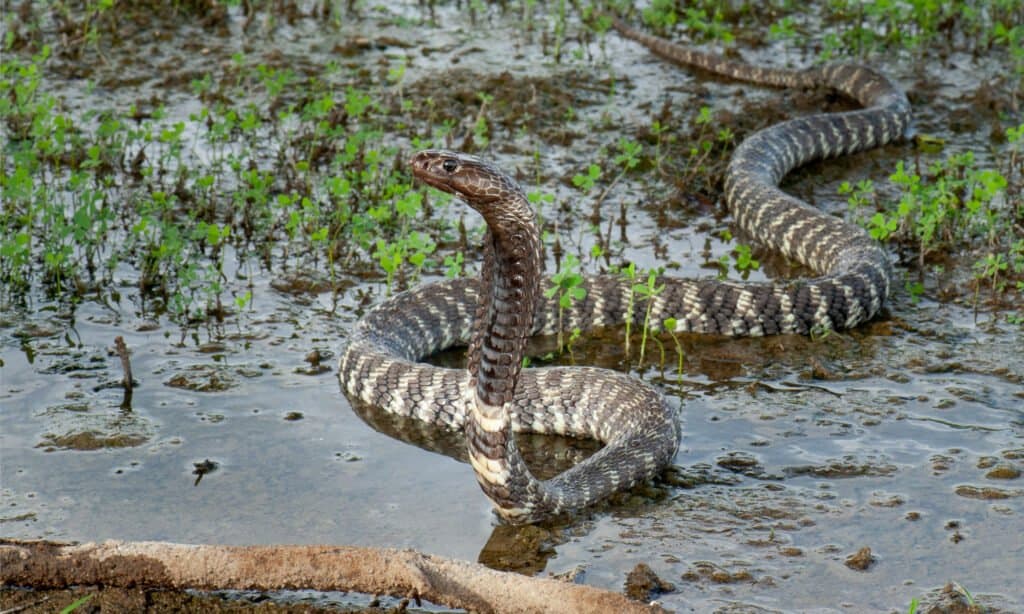

Spitting cobras may have evolved their venom-shooting ability as a defense against early human relatives.
©iStock.com/Shumba138
Spitting cobras are unique amongst venomous snakes by virtue of the fact that they use their venom primarily for defense, not predation. Scientists believe that this unusual trait may have arisen as a defense against some of humanity’s early ancestors, such as homo erectus. This theory comes from the fact that spitting cobras first developed their namesake trait at about the same time that hominids first began to evolve from ancient apes around 2 to 7 million years ago. Fossils of cobras have also been found in archaeological sites containing early human ancestors as well. Early hominids who had begun to use tools such as spears would require long-distance defenses in order to preemptively stop a projectile attack. This evidence is highly circumstantial, but it is the only theory science has to date as to why these snakes may have begun to spit.
Scientific Name
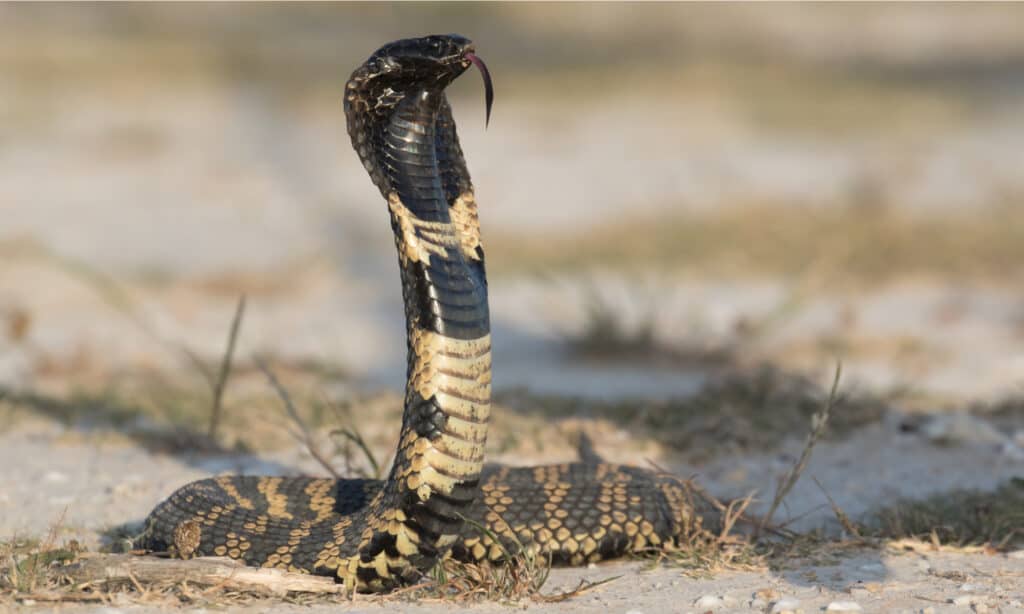

Rinkhals are the only spitting cobras that do not belong to the genus
Naja.
©Andre Coetzer/Shutterstock.com
Most spitting cobras belong to the Naja genus. The one exception is the rinkhals, which is the only member of the Hemachatus genus. It is different from the other spitting cobras in that its scales are somewhat keeled and ridged. Naja is derived from Naga, a Sanskrit word that simply means “snake.” Hemachatus comes from the Greek words haima, which means “blood” and achatēs, which means “agate,” so the name means blood-colored agate. Interestingly, the rinkhals is not considered a “true” cobra, though it is grouped with the spitting cobras.
The Different Types of Spitting Cobra
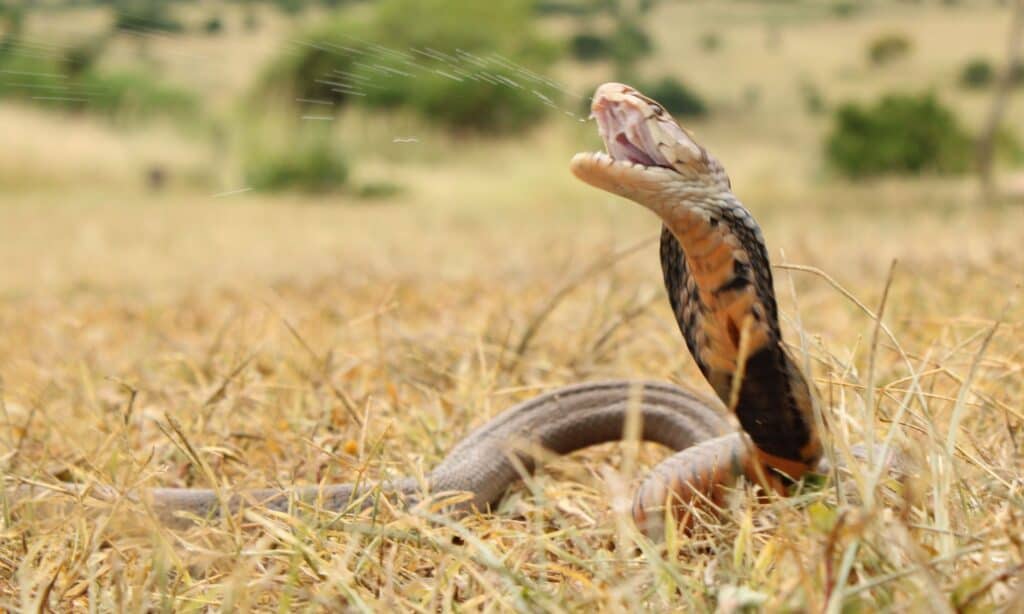

Mozambique spitting cobra is so named because it projects venom from its fangs into its attacker’s eyes, which can cause vision problems or blindness.
©Cormac Price/Shutterstock.com
There are about 18 species of spitting cobra. Some of them greatly resemble each other and identification can only be made through close inspection of the snake. For example, the Chinese and monocled cobras look very much alike but have different numbers of scales in their abdomens and beneath their tails.
Spitting cobras, with the exception of the rinkhals, are also considered true cobras though scientists aren’t quite sure what “true cobra” means. Many biologists claim that a true cobra can only belong to the Naja genus. These snakes can expand and flatten their ribs and their head to create a hood and rear up in a defensive posture. They spit by using muscles to squeeze their venom glands and force the venom out through small holes in their fangs.
Below you can find a list of all 18 species of spitting cobra:
| Rinkhals | Hemachatus haemachatus |
| Ashe’s Spitting Cobra | Naja ashei |
| Mali Cobra | Naja katiensis |
| Mozambique Spitting Cobra | Naja mossambica |
| Zebra Spitting Cobra | Naja nigricincta |
| Black Spitting Cobra | Naja nigricincta woodi |
| Black-necked Spitting Cobra | Naja nigricollis |
| Nubian Spitting Cobra | Naja nubiae |
| Red Spitting Cobra | Naja pallida |
| Mandalay Spitting Cobra | Naja mandalayensis |
| Philippine Cobra | Naja philippinensis |
| Samar Cobra | Naja samarensis |
| Indochinese Spitting Cobra | Naja siamensis |
| Javan Spitting Cobra | Naja sputatrix |
| Equatorial Spitting Cobra | Naja sumatrana |
| Chinese Cobra | Naja atra |
| Andaman Cobra | Naja sagittifera |
| Monocled Cobra | Naja kaouthia |
Population & Conservation Status
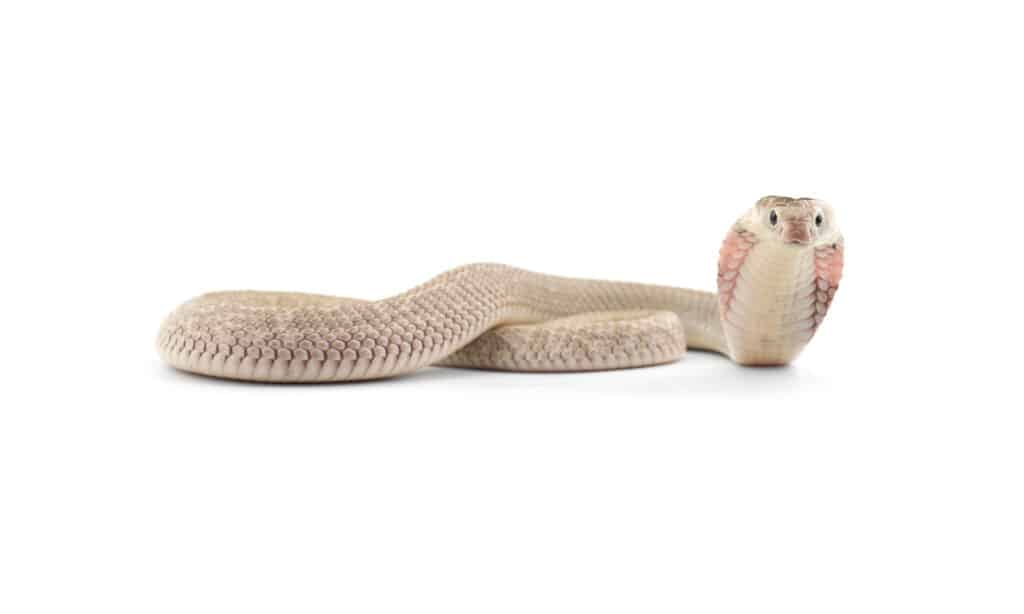

Chinese cobras are one of the most threatened species of spitting cobras.
©PetlinDmitry/Shutterstock.com
Though biologists don’t have the exact number of spitting cobras in the world, the conservation status of most is least concern. Exceptions are the Indonesian cobra and the Chinese cobra, whose status is vulnerable.
Appearance and Description
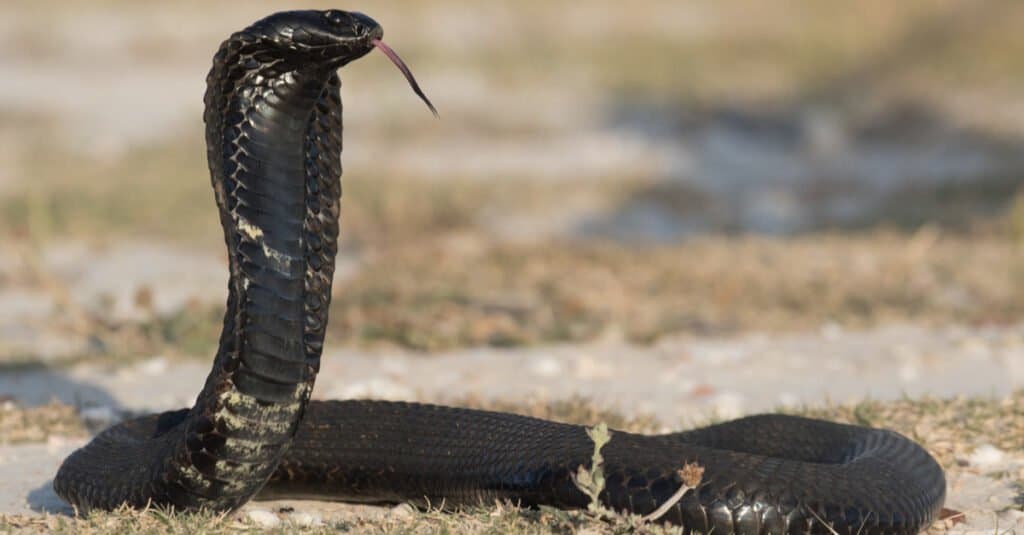

It is difficult to distinguish many spitting cobras from their counterparts without examining their fangs or witnessing their spit.
©Andre Coetzer/Shutterstock.com
Identification of a spitting cobra can be challenging, for they look like any other type of cobra, and some even crossbreed with other cobras who live in their area. Unless a person is a herpetologist who specializes in cobra species, the one way a person can know they have a spitter is if the snake actually spits. Some biologists believe that all members of Naja have at least the ability to spit.
Besides examination of the fangs, the venom of a spitter is more cytotoxic than the venom of other cobras. Cytotoxic means that the venom destroys cells, which is why skin sometimes blisters if a cobra spits on it. Scientists believe that the ability to spit evolved three times over the course of the cobra’s evolution. The venom that’s spat out rarely kills but causes enough damage to make would-be predators avoid the snake in the future.
Besides the ability to create a hood, most of these snakes have slender bodies, though N. ashei is a bit more robust. They are not the biggest snakes in size, and it is rare to find one over 10 feet. Their colors range from red to brown to gray to glossy indigo black, and they may have bands, monocles at the back of their hood, spots, or mottling. Besides spitting, all of them can still bite, and their bite can be fatal.
Spitting Cobra vs King Cobra
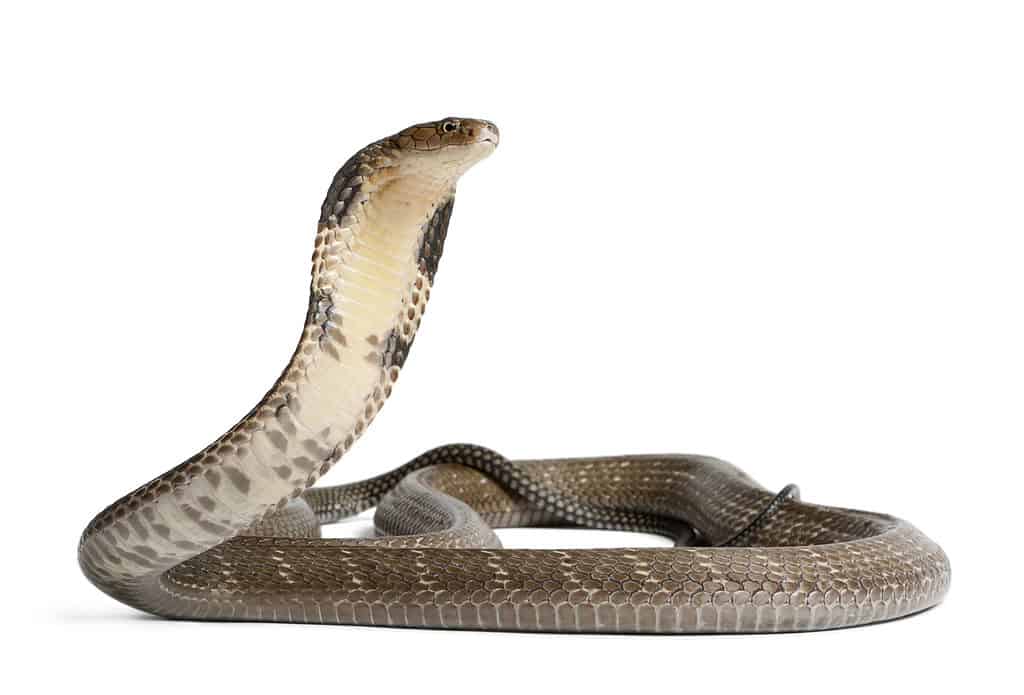

King cobras do not spit venom, nor are they considered to be true cobras.
©Eric Isselee/Shutterstock.com
Interestingly, the king cobra is not considered a “true cobra.” It is the only member of the Ophiophagus genus and gets its common name because it is much larger in size than other cobras and indeed preys upon them. The king cobra is found only in south and southeast Asia, can grow as long as 19 feet, and has what some describe as a growl as opposed to a hiss. A grown individual is not particularly aggressive and would rather avoid a fight. Yet it has been known to leap off the ground at an attacker, bite and hang on while pumping lots of venom into the wound.
Another thing that separates the king cobra from spitting cobras is that it makes a nest of dead leaves where it lays and incubates its eggs. No other snake does this. Unlike most spitting cobras, the king cobra is considered vulnerable because of habitat loss.
Spitting Cobra Venom: How Dangerous Are They?
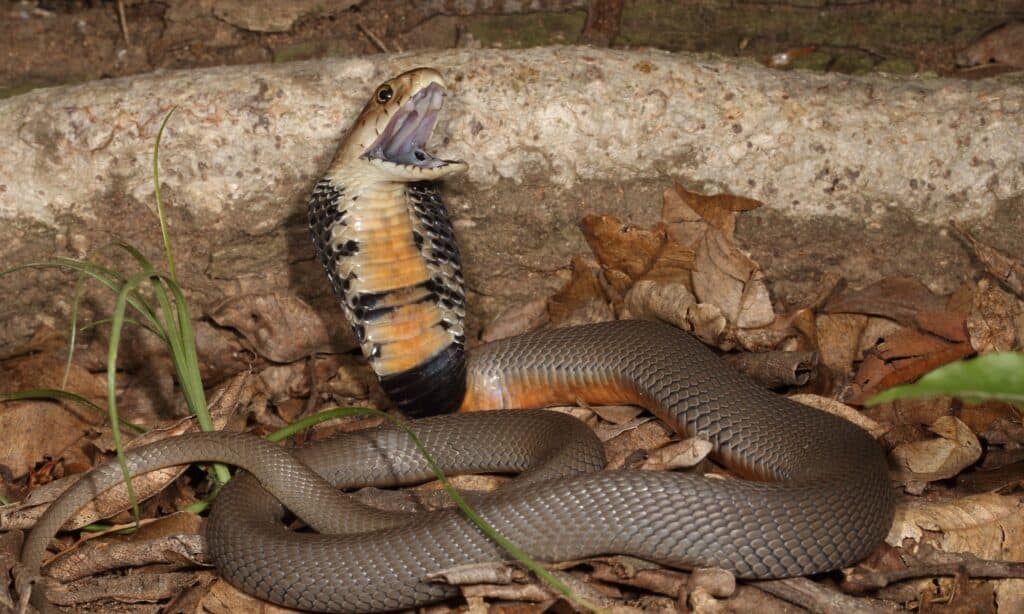

The venom from most spitting cobras is incredibly dangerous.
©NickEvansKZN/Shutterstock.com
Some of the most venomous members of the entire Naja genus are the Philippines, Indochinese, Samar, and Chinese spitting cobras. Like other cobras, the venom of spitters evolved to attack the nerves and cardiac cells, but it is good at disrupting cells in general. Because of this, the venom that enters the eyes can cause blindness if the eyes aren’t quickly treated.
If the cobra bites and envenomates its victim, it’s important that they get medical help as soon as possible. Venom can paralyze the person as it attacks the nerve cells, prevents blood from coagulating, and causes necrosis. This can all lead to death. It also needs to be said that baby cobras are venomous from birth.
Behavior and Interaction with Humans
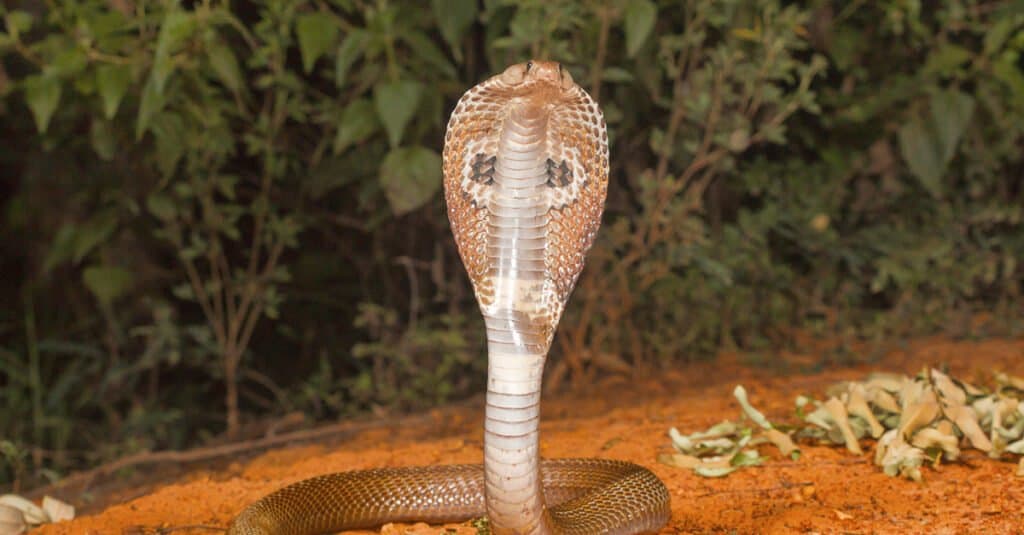

Many species of spitting cobra display complex mating rituals.
©RealityImages/Shutterstock.com
Spitting cobras are solitary animals. Many are nocturnal or crepuscular and are less aggressive if they are caught out during the day. Other cobras such as the Chinese cobra are active day and night. Many cobras choose to live in locations near water and can be said to be semi-aquatic, like N. kaouthia. The diet of juveniles is often frogs or toads, while adults have small mammals, fish, and even other snakes as prey. When they’re not hunting they hide in burrows or tree holes.
Cobras are often apex predators where they live, but some, like the Javan spitting cobra, are sometimes victims of even more robust predators such as the Komodo dragon. Mongooses and pigs also steal their eggs.
The snakes are ready to mate when they’re about two or three years old. The pair engages in a courtship ritual that involves swaying and dancing before they mate, which is often during the rainy season in the locations where they live. The females can lay anywhere from two to 23 eggs after being gravid for about three months. The eggs hatch after 48 to 120 days. Depending on the species, the female may or may not guard the eggs. The lifespan of one of these cobras is about 20 years.
These snakes are helpful to humans because they eat pests that might eat or damage crops, but their ability to both inject and spurt dangerous venom demands that they are treated with respect.
Similar Animals
- Mandarin rat snakes are native to Asia.
- Wolf snakes live in many of the same areas as cobras.
- Rinkhals aren’t true cobras but are often called cobras because they have a hood.
Spitting Cobra FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Why do spitting cobras spit venom?
Scientific research now believes that spitting cobras may have evolved to spit venom at eyes in response to the rise of humans! While venom that’s spit isn’t fatal, it’s particularly effective against humans. Spitting cobras spit venom as a defensive measure, but they still must bite and release venom when hunting for prey.
Are spitting cobras venomous?
Spitting cobras are extremely venomous.
How do spitting cobras hunt?
They hunt by picking up chemical signals of their prey. They do this by flicking their tongue, then transferring the molecules into a vomeronasal organ that then sends the information to the snake’s brain. They also hunt by sight, and though they are nearly deaf they pick up vibrations through their jaw.
Are spitting cobras aggressive?
Some species can be aggressive, especially when they’re babies. Since babies can also deliver venom it is best to be careful around them.
Where do spitting cobras live?
These snakes live in Africa and Asia.
What do spitting cobras eat?
Their diet is mostly small mammals, amphibians, eggs, insects, other reptiles, and birds, basically anything of a size they can subdue and swallow. Some spitting cobras even eat carrion.
What is a spitting cobra?
It is an elapsid snake with the ability to force venom some distance out of its fangs as a deterrent. Nearly all belong to the Naja genus.
What are some ways for the Mozambique spitting cobra to survive?
Besides spitting and striking, N. mossambica will enter the water, swim away from danger, and even play dead.
How far can a spitting cobra spit?
Some cobras can spit as far as 10 feet.
How does a spitting cobra use its spit to protect itself?
The cobra protects itself by spitting its venom into the eyes of a would-be attacker, causing intense pain and potentially blinding them.
How long is a spitting cobra?
They range in length from 2.29 to 8.9 feet.
What happens if a snake spits on you?
If the snake spits on you, you need to wash the venom off your skin right away. If the venom enters your eyes you must flush all of it out at once to avoid permanent blindness.
Are there any spitting cobras in the United States?
Venomous spitting cobras do not live in the US in the wild, however, a spitting cobra was caught on the loose by officials in Raleigh, North Carolina in 2021. The snake was a pet that had escaped.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- Britannica, Available here: https://www.britannica.com/animal/cobra-snake
- Wikipedia, Available here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spitting_cobra
- ITIS, Available here: https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=700221#null
- ITIS, Available here: https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=700233#null
- National Geographic, Available here: https://www.nationalgeographic.com/animals/article/news-cobras-venom-eyes-perfect-aim
- Live Science, Available here: https://www.livescience.com/43520-cobra-facts.html
- Discover, Available here: https://www.discovermagazine.com/the-sciences/spit-take-surprise-indian-monocled-cobras-can-spit-venom