Vine Snake
A slender body and elongated snout give the vine snake a regal look.
Advertisement
Vine Snake Scientific Classification
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Vine Snake Conservation Status
Vine Snake Facts
- Prey
- Small amphibians and reptiles
- Fun Fact
- A slender body and elongated snout give the vine snake a regal look.
- Litter Size
- 6-10
Vine Snake Physical Characteristics
- Color
- Brown
- Yellow
- Green
- Skin Type
- Scales
- Lifespan
- Up to 15 years
- Venomous
- Yes
- Aggression
- Medium
View all of the Vine Snake images!
A slender body and elongated snout give the vine snake a regal look.
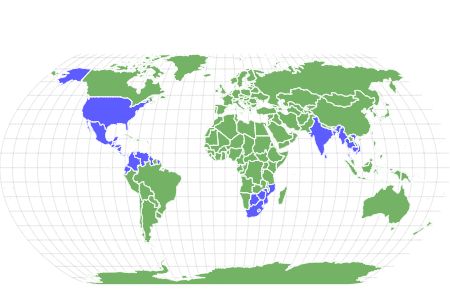
The vine snake is found in Asia, Africa, and the Americas. While all species of the vine snake have some form of venom they use on their prey, only the twig snake of Africa is harmful to humans. Bites from other species will, at most, cause irritation or, in some cases, an allergic reaction.
Despite the differences between the different species of vine snakes, they all rely on similar traits when hunting. They hunt by ambush and use their natural camouflage to their advantage. Venomous fangs allow them to take down frogs, lizards, and birds.

Three Amazing Facts About Vine Snakes!
- The Sri Lankan vine snake appears green, but when threatened, will expand, displaying a black-and-white scale pattern.
- The African vine snake, also known as the twig snake, has a deadly bite, but due to the construction of its mouth, it can only latch on to a few parts of the human body, such as the webbing between the thumb and fingers.
- The vine snake has unique fangs. Rather than the venom being dispersed through the fang itself, grooves along the outside of the fang allow the venom to drip down as the snake chews.
Where to Find Vine Snakes
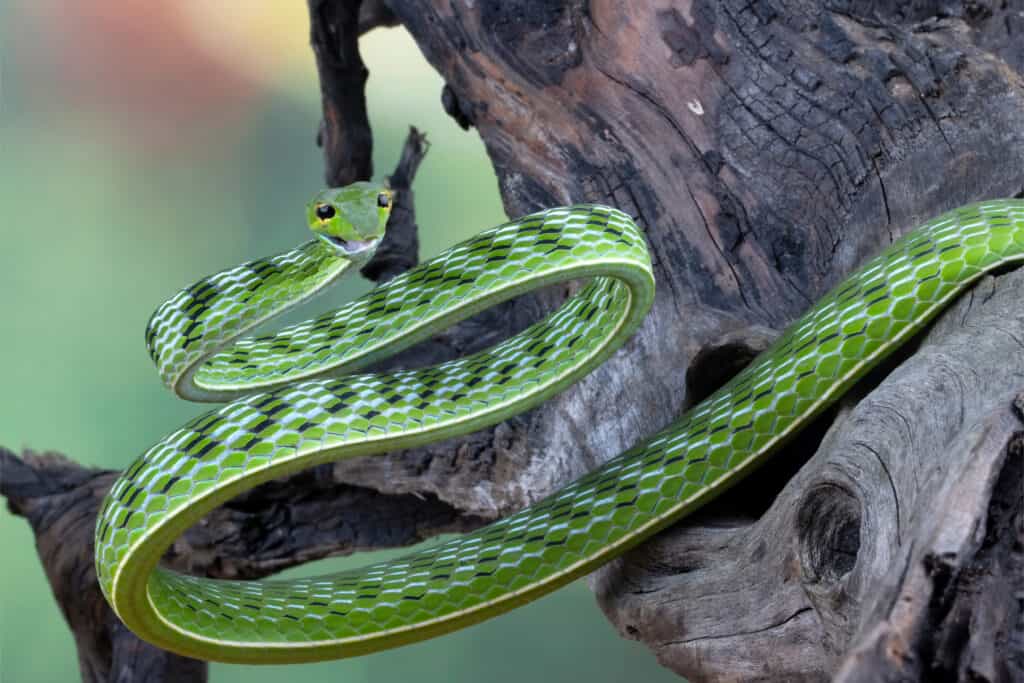

Asian vine snakes are green to match a rainforest habitat.
©Kurit afshen/Shutterstock.com
The vine snake can be found in many areas around the world. Different species are located in Africa, Asia, Mexico, Central America, Northern South America, and the Southwestern United States.
The brown species of vine snakes, such as the Savanna vine snake, typically live in dry forests and savannas. The green species, such as the Sri Lankan green vine snake, typically live in rainforest areas.
Scientific Name
The vine snake is the name given to any of the species of snakes in the family Colubridae. They include Ahaetulla which are Asiatic vine snakes, such as the Sri Lankan green vine snake, and Chironius, which has 23 species. Imantodes are recognizable by their blunt heads, and Oxybelis is a genus found in the Americas. Finally, Thelotornis is the genus that has a bite that is deadly to humans.
Evolution
Fossil records show that snakes first appeared during the Cretaceous period – although often retained their hind limbs. The earliest true snake fossils come from the marine simoliophiids, the oldest being Hassiophis terasanctus, dated between 112 and 94 million years ago.
Scientists believe that snakes descended from lizards. Pythons and boas, the most primitive snakes, have vestigial hind limbs and some have remnants of a pelvic girdle, appearing as horny projections.
Many modern snakes originated during the Paleocene, alongside the radiation of mammals that occurred after the extinction of non-avian dinosaurs. The expansion of grasslands in North America led to a major radiation of snakes. During the Miocene, the number of snake species increased with the first vipers and elapids and the diversification of Colubridae.
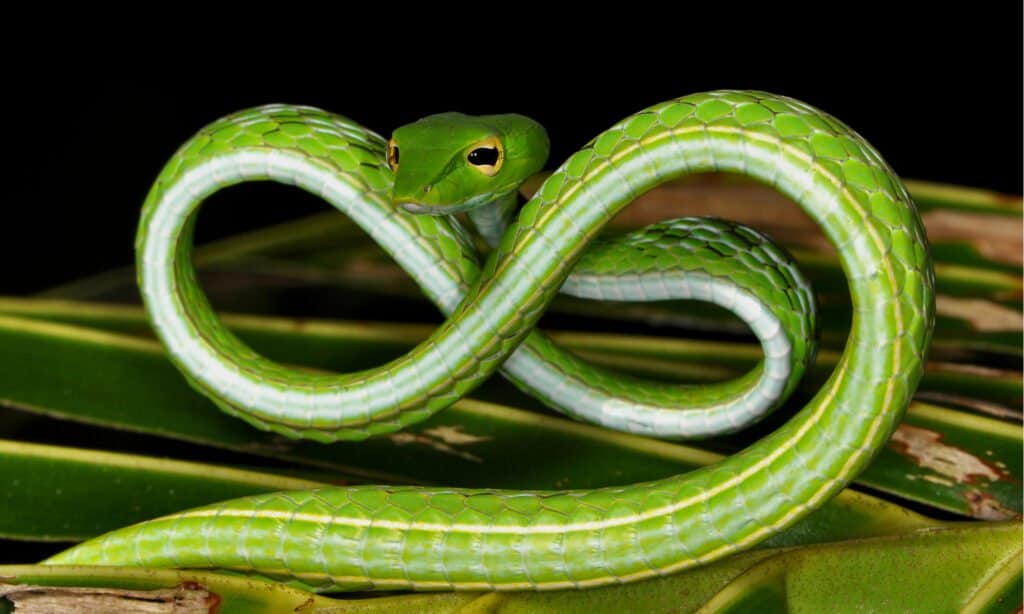

Asian vine snakes can be found throughout tropical Asia.
©Ferdy Timmerman/Shutterstock.com
Species
There are different species of vine snakes divided into four genera:
Asian vine snakes (Ahaetulla), are mildly venomous, rear-fanged vine snakes distributed throughout tropical Asia. This species contains four subspecies:
- Ahaetulla prasina medioxima
- Ahaetulla prasina procularis
- Ahaetulla prasina prasina
- Ahaetulla prasina suluensis
Sipos vine snake (Chironius), is a genus of new world vine snakes that contains 23 species including:
- Boettger’s sipo (Chironius flavolineatus), is a vine snake endemic to savannas and semi-arboreal areas in Brazil and much of South America.
- Brown sipo (Chironius fuscus), is a vine snake found throughout Central and South America.
- Machete savane or Amazon whipsnake, (Chironius carinatus), endemic to Columbia, Brazil, Costa Rica, Venezuela, Suriname, Guyana and Trinidad and Tobago.
- Saint Vincent blacksnake (Chironius vincenti), can only be found on the island of Saint Vincent in the Caribbean Lesser Antilles.
The green vine snake (Oxybelis), is a long, slender new world vine snake endemic to Central and South America.
The Twig snake (Thelotornis), native to Africa, the twig snake is a greyish-brown vine snake with faint markings. They are deadly with hemotoxic venom but bites on humans are rare because the snake can’t breach the skin anywhere except the webbing between the thumb and fingers. There are four species of twig snake.
- Savanna vine snake (Thelotornis capensis), can be found in southern Africa.
- Forest vine snake (Thelotornis Kirtlandii), can be found across the African continent.
- The eastern vine snake (Thelotornis mossambicanus), is native to Eastern Africa.
- Usambara vine snake (Thelotornis usambaricus), can be found in Tanzania, Kenya, and Mozambique.
Population & Conservation Status
The population size of the vine snake is unknown. It is well-established and it is considered a species of least concern. The exception to this is Chironius vinventi which is considered critically endangered.
Appearance and Description
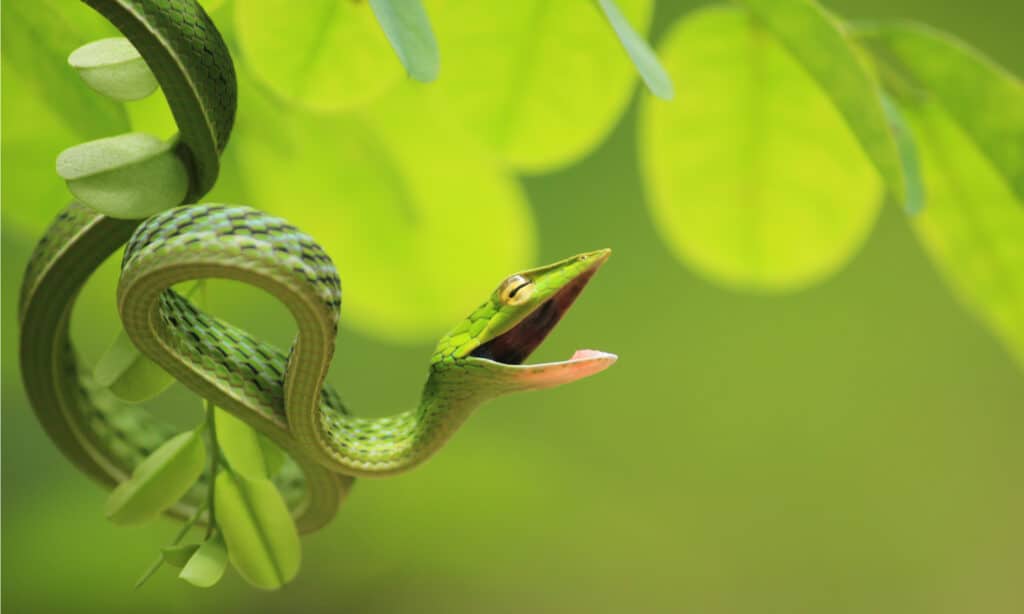

©Nikhil patil 0321/Shutterstock.com
There are many common vine snakes, and their coloring can be bright green, brown, or something in between. The easiest way to distinguish these snakes is by their narrow heads with an elongated, pointed snouts. They also have very slender bodies. Regardless of length, they are rarely wider than a penny.
Their narrow bodies mean that, when kept as a pet, they must be handled cautiously. They are delicate, and, if they escape, can easily become injured when recaptured.
Read about the largest vine snake ever found.
Venom: How Dangerous Are They?
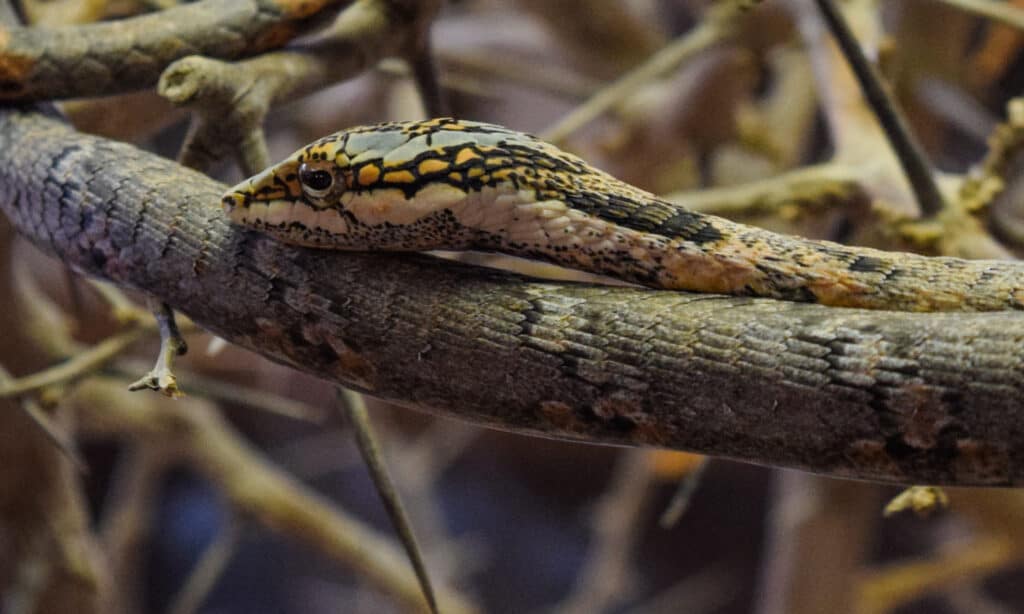

Twig snakes are greyish-brown with faint light and dark markings and are venomous.
©Authentic travel/Shutterstock.com
The twig snake, an African genus of vine snake, is very dangerous. Its venom creates clotting problems in the blood. Someone bitten by one of these snakes may bleed to death.
There are four species of the genus Thelotornis. They are all African snakes and can be found in the savanna (Savanna vine snake), the jungle (forest vine snake), Eastern Africa (Eastern vine snake), and along the coast (Usambara vine snake).
Behavior and Humans
Most of the common vine snakes are not aggressive, however, they are solitary. If they are cornered or feel threatened, they may strike. The design of their fangs, toward the back of the mouth, and with grooves that allow the venom to drip down, mean that the snake needs to chew, rather than just bite, to inject venom.

Vine Snake FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Is the vine snake poisonous?
Bites from most species of the vine snake are not deadly. Some may cause a mild reaction. The bites of the Thelotornis, or twig snakes, have caused fatalities in humans.
A few of the other genera of vine snakes, such as Ahaetulla are mildly poisonous to humans. The placement of the vine snake’s fangs makes venomous bites rare, even from the dangerous twig snake. Located in the back of the upper jaw, the fangs are designed to inject venom as the snake chews, rather than when striking.
How do vine snakes hunt?
They are ambush predators. They lay perfectly still until prey gets within range, then strike with lightning-quick speed.
Are vine snakes aggressive?
Not typically, although they don’t generally like being handled. If they are feeling threatened, they will puff out their neck and hold their body in the shape of an “S”.
Where do vine snakes live?
Africa, Asia, Mexico, Central America, Northern South America, and the Southwestern United States.
What do vine snakes eat?
Small reptiles and amphibians.
What happens when a vine snake bites you?
The bite of the twig snake, the most poisonous vine snake, is hemotoxic. This means that it affects the body’s ability to control bleeding. Illness and death may result from internal hemorrhaging and uncontrolled breathing.
Can a vine snake be a pet?
The Asian vine snake is often kept as a pet by experienced snake owners. They have some very specific needs to remain healthy, such as a humidity of between 75 and 90 percent and finicky diet needs.
Is the Philippine vine snake venomous?
It is venomous, but the venom is weak and generally doesn’t cause issues for humans.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- Loveland Living Planet Aquarium / Accessed April 26, 2022
- Britannica / Accessed April 26, 2022
- Animalia / Accessed April 26, 2022