Darkling Beetle
Darkling Beetles have segmented antennae. Each one is divided into eleven segments.
Advertisement
Darkling Beetle Scientific Classification
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Darkling Beetle Conservation Status
Darkling Beetle Facts
- Name Of Young
- Larvae
- Fun Fact
- Darkling Beetles have segmented antennae. Each one is divided into eleven segments.
- Biggest Threat
- Predators eating larvae
- Habitat
- Prefer dry and dark climates
- Diet
- Herbivore
- Lifestyle
- Nocturnal
- Favorite Food
- Decomposing plant matter
- Number Of Species
- 20000
- Location
- Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Europe, Australia
Darkling Beetle Physical Characteristics
- Color
- Brown
- Black
- Dark Brown
- Skin Type
- Shell
- Length
- 0.5 - 1.5 inches
- Venomous
- No
- Aggression
- Low
View all of the Darkling Beetle images!
The Darkling Beetle family has over 20,000 members!
That’s right, the Darkling Beetle family is vast but they all share a few physical characteristics. They can be found on almost every continent and in environments from humid to dry, although most do favor dark and dry places. Called Darkling Beetles because they are most active at night, these beetles can pose a threat to farmers that keep livestock, especially poultry.
Darkling Beetle Facts
- Darkling Beetles have segmented antennae that they use to gather data about their environment.
- These beetles can live in extremely dry climates by collecting water on their hard front wings, or elytra.
- The larvae form of these beetles, called mealworms, are popular to use in feed for pets.
- Darkling Beetles are attracted to areas rich in food, including manure piles and compost. Because of this, they are common pests on farms that can carry diseases.
- Scientists discovered the remains of Darkling Beetle larvae in ancient Egyptian pottery that probably held grain.
Darkling Beetle Species, Type, and Scientific Name
These beetles are an entire scientific family, known as Tenebrionidae. This family includes over 20,000 species and is represented in habitats all over the world. With so many members, you might think that the Darkling Beetle family doesn’t have much in common. While the various species do differ in appearance, they all share a few similar characteristics. These include segmented antennae, notched eyes, segmented legs, and a front sternite that is not divided by a leg.
The name Darkling comes from the tendency of some species within the family to stay in dark places. Tenebrionidae is based on the Latin word Tenebrio, which means “seeker of dark places.” This behavior is not shared by all members of the family, however.
They are part of the Tenebrionoidea superfamily of beetles. They are the largest family within the superfamily, which includes 28 other families in addition to Tenebrionidae. These beetles belong to the Coleoptera order. This includes all beetles, which are characterized by hard front wings called elytra. Darkling Beetles are part of the Insecta class, Arthropoda phylum, and Animalia kingdom.
Appearance: How to Identify Darkling Beetles
Color, size, and many other features vary among the species of Darkling Beetles. After all, there are over 20,000 of them. Size ranges from 0.5 inches to 1.5 inches. Most are dark brown or black, either all through their body or the majority of their hard wings, called elytra. They all do share a few characteristics that classify them as Darkling Beetles.
Every Darkling Beetle species has segmented antennae. Their antennae each have eleven sections or segments. You can see this clearly in some of the larger species and it is even obvious in the smaller varieties as well. They can present a uniform appearance or look like small beads that make up the entire antennae. Beetles, including the Darkling Beetle, use these to sense and gather data about their environment.
They have a visible frontal ridge over their eyes. This can actually notch their eyes. In smaller species, this is less pronounced just due to their smaller size. It can be a distinguishing feature that is easy to identify, especially in the larger members of the family.
Darkling Beetles have segmented legs as well. While this is common in Arthropods, all of these beetles have a specific number of segments: four in the pair of hind legs, five in the pair of mid legs, and five in the pair of front legs. Their sternum is also segmented, although the front sternite is not divided by a pair of legs like in some other Arthropods.
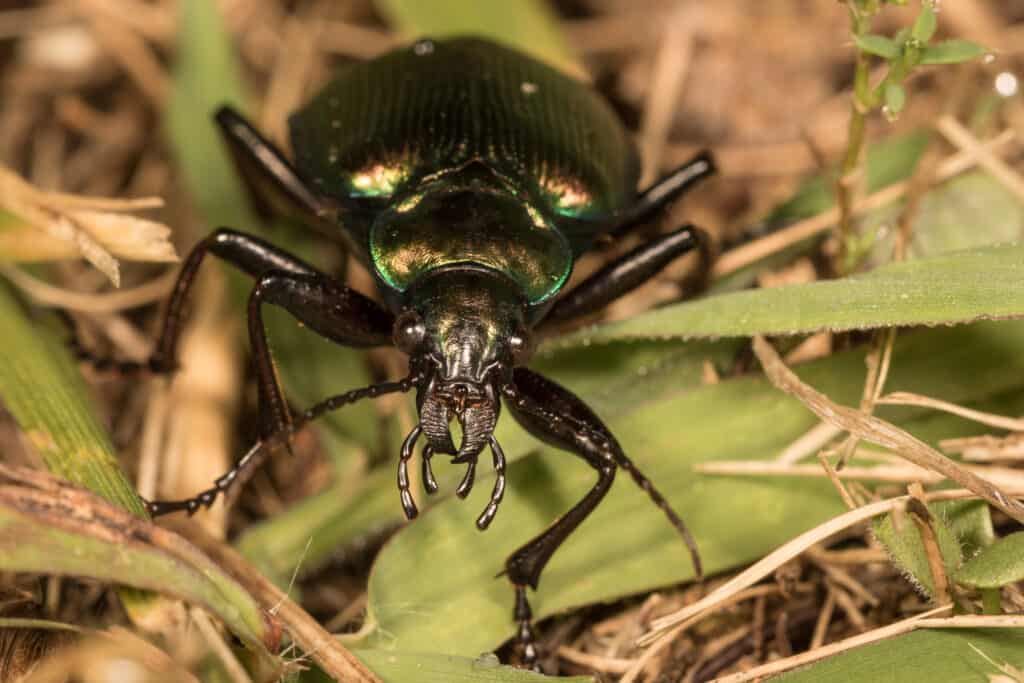

The Darkling Beetle is primarily nocturnal, so you may not even realize it if you are infested!
©Katarina Christenson/Shutterstock.com
Habitat: Where to Find Darkling Beetles
With over 20,000 species in the Darkling Beetle family, it is probably no surprise that these beetles are found on continents and in habitats all over the world. Many do favor dark places and come out at night, giving them the common name Darkling Beetle.
These beetles are common and found on every continent except Antarctica. This beetle lives in North America, South America, Asia, Africa, Europe, and Australia. They can be found everywhere from dense forests to hot deserts.
Darkling Beetles are most common in dry climates. They often eat decomposing plants and insects and are considered cleaners within their ecosystems. Because of this, they often live where these food sources are plentiful.
Diet: What Do Darkling Beetles Eat?
Darkling Beetles are not picky and will often eat whatever is in their environment. The various species do differ slightly in their preferred diet, although this is usually based on what they have at hand. Most often, these beetles eat decaying and decomposed plant matter.
A few species eat wood while others eat larvae of other insects. Some species eat fungi and spores. Many can survive on different types of food, depending on what they have available. They do not typically require a specialized or highly selective diet to thrive.
Species that live in dry climates where food and water are scarce can collect water on their elytra from fog and moisture in the air. When these droplets form, they roll down to the beetle’s mouth. This is often the only source of water that they get in these extremely dry and arid habitats.
Darkling Beetle larvae burrow and eat many of the same things as their parents. They are called mealworms and are often prey for other insects, birds, reptiles, and small animals. They are also common in mealworm feed for pets.
Prevention: How to Get Rid of Darkling Beetles
The larvae form of Darkling Beetles is often more of a pest than its adult counterpart. Larvae burrow into grain storage, including rice and flour. They have even been found in ancient Egyptian pottery that was used to store grain.
Darkling Beetles can become a health hazard on homes and farms. Because they favor environments with plenty of food, such as grain or decomposing plant matter, they are common on farms and where animals are kept. They can also chew through insulation. Most species are nocturnal, making it hard to realize that they are a lot of Darkling Beetles around until their numbers are extremely high.
They can carry diseases, such as parasites, that pose a particular threat to poultry. Commercial poultry farms need to take special care to monitor for Darkling Beetles. Even hobby farmers or homeowners who keep chickens should watch for these pests.
If you do have a Darkling Beetle infestation, the first step is to find out where they are located. They likely have a central location that is abundant in food, such as compost or manure piles. They also need water, so look around water sources for an unusually large number of beetles. Keep in mind that they will be most active at night and you may need to get out your flashlight to track them down in the dark.
Prevention is all about reducing the potential food and water sources for Darkling Beetles. Keep the areas clear of manure and clean up any soiled or wet areas right away. This will keep Darkling Beetles from thinking that it is rich in sustenance and keep them from coming in the first place. If you already have an infestation, work with a professional to determine which insecticide is safe for your other animals, pets, and family while also being effective at getting rid of the beetles and their larvae.
Related Animals
View all 110 animals that start with DDarkling Beetle FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What do Darkling Beetles need to survive?
Like most animals, Darkling Beetles need adequate food, water, and a climate that is conducive to their wellbeing. They can adapt to many conditions, however, including scavenging food from available decomposing matter and getting water from the air or their food. They can live in hot or cold climates, although they cannot survive in extreme freezing temperatures.
Do Darkling Beetles prefer the dark?
Many species of Darkling Beetles are nocturnal, which means that they are most active at night. Keep in mind that with over 20,000 species within the Darkling Beetle family, there are always exceptions and some species are active during the day.
What attracts Darkling Beetles?
Food sources are the most common things that attract Darkling Beetles. These include decomposing plant and animal matter. Farms commonly see Darkling Beetles due to the presence of animal manure, bedding, grain, and other food sources.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- Britannica / Accessed October 1, 2022
- Solutions Pest & Lawn / Accessed October 1, 2022
- Gardening Know How / Accessed October 1, 2022