Considering that they both belong to the class Insecta and have similar shapes and sizes, it is understandable why people can’t distinguish between ladybugs and Japanese beetles. The truth, however, is that the ladybug and Japanese beetle have a plethora of differences, as we are about to see.
Comparing Ladybugs vs Japanese Beetle
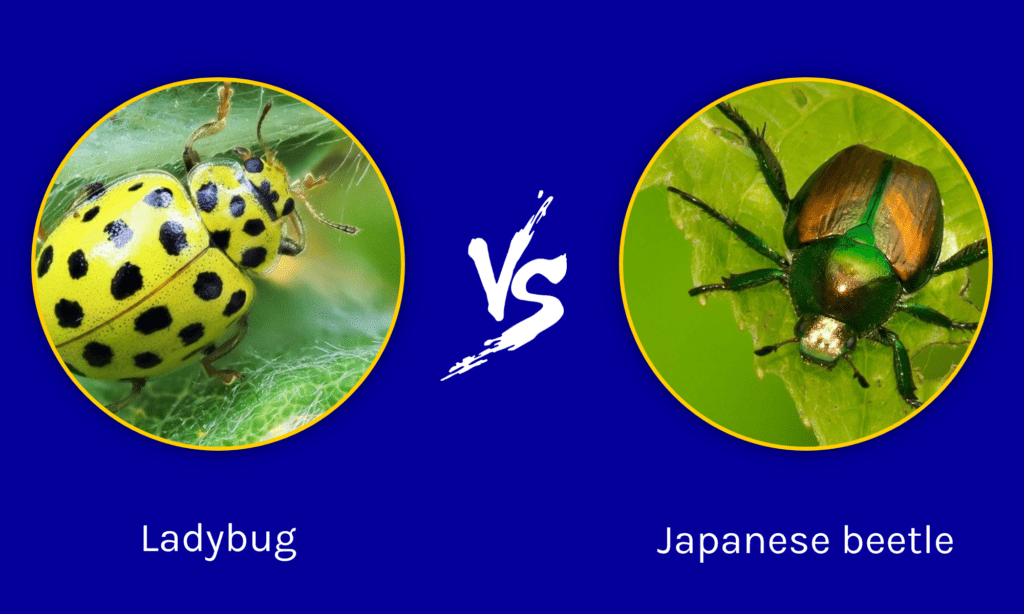
Like we mentioned before, there are a ton of differences between a ladybug and a Japanese Beetle and the table below them sums them all up.
| Ladybug | Japanese Beetle | |
|---|---|---|
| Location and Habitats | Worldwide (Africa, Asia, Central America, Eurasia, Europe, North America, Oceania, South America). Gardens, forests, hedgerows, meadows, pastures, and yards. | Native to Asia, but also found in Canada, the United States, and some parts of Europe. Found anywhere from forests to grasslands to farms. |
| Size | 0.08-0.4 of one inch 0.007 oz | 15 mm (0.591 inches) 0.0029 oz |
| Color | Brown, Yellow, Red, Black, Orange, Pink, and White. Distinct black, yellow, and reddish markings | Green and Golden; copper-brown wing covers (elytra) |
| Physical Appearance | Hemispherical and oval-shaped bodies, short legs and antennae. | Oval shape, clubbed antennae, five white hair tufts on either side of the abdomen. |
| DietMostly carnivorousHerbivorePreyInsects including aphids, beetle, spider mites, beetle larvae, thrips, caterpillars as well as other ladybugs. | Plants and plant life including grapes, peaches, cheery, hibiscus, dahlia, chestnut, soybean as well as sassafras. | |
| Predators | Birds, rodents, dragonflies, frogs, toads, wasps, assassin bugs, and stink bugs among others. | Raccoons, moles, spiders, wild birds, and other insects. |
The Main Differences Between Ladybugs And Japanese Beetles
Ladybugs and Japanese beetles have considerable differences in diet, location, color, and prey. For instance, while ladybugs are carnivorous through and through, Japanese beetles are predominantly herbivorous. How about we get into some more explicit details that will help us distinguish these two insects?
Ladybugs vs Japanese Beetle: Location And Habitat
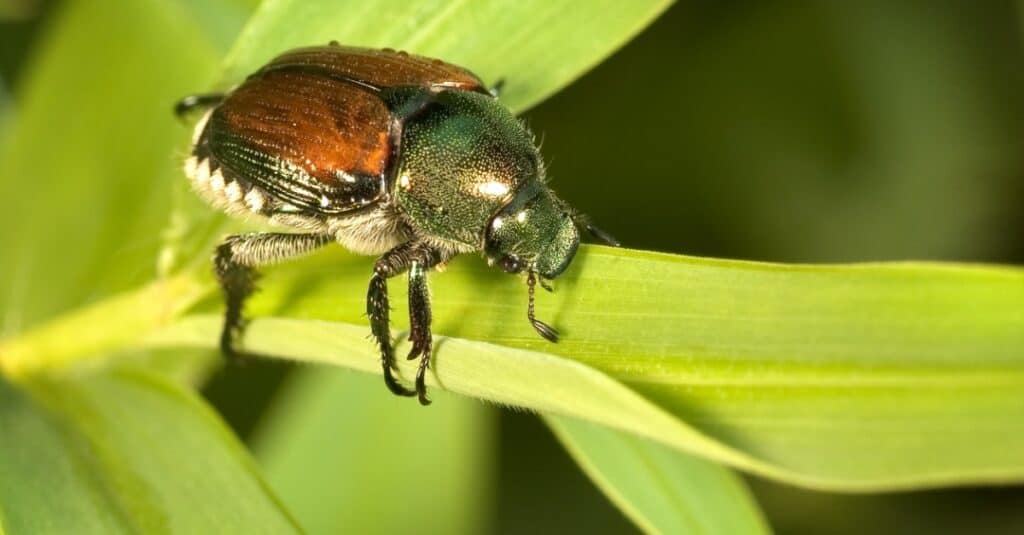

Japanese beetles are native to Southeast Asia.
©iStock.com/WebSubstance
While they are both insects, ladybugs and Japanese beetles have some variations in their location. Lady bugs have a global presence from Africa to Asia to North America to South America to Central America to Europe and Oceania.
Japanese beetles, on the other hand, as you can probably tell from the name, are native to Southeast Asia. They have also been found in Canada and the United States and some researchers believe their presence in North America can be traced to shipments of iris bulbs in the early 1900s.
Regarding habitats, ladybugs are comfortable in gardens, forests, meadows, hedgerows, yards, and pastures. Japanese beetles often dwell anywhere from forests to grasslands to farms and they can also dwell in the city as long as they can find gardens around to feed on.
Ladybugs vs Japanese Beetles: Diet
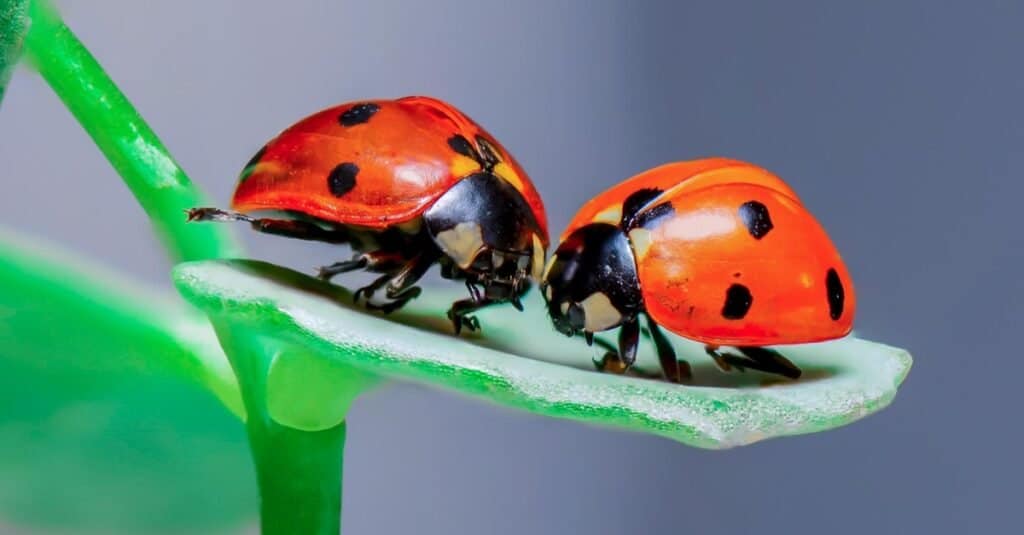

As carnivores, ladybugs eat aphids, spider mites, beetles, among others.
©Pixabay / CC0, Pexels – License
Ladybugs and Japanese beetles also differ in diets and prey. Ladybugs have a carnivorous diet comprising other insects such as aphids, spider mites, beetles, small insects, caterpillars, and thrips among others. They also explore cannibalism by feeding on other ladybugs, when occasion demands it.
Japanese beetles, on the other hand, are largely herbivorous and their diet consists of plants and plant life from grapes to peaches to dahlia to chestnut. Their larvae, however, restrict their diet to grass and other similar plants. Japanese beetles are considered very destructive to gardens and they can reportedly clear an entire fruit tree in just about 15 minutes. One could call them the gardener’s bane.
Ladybugs vs Japanese Beetles: Physical Appearance
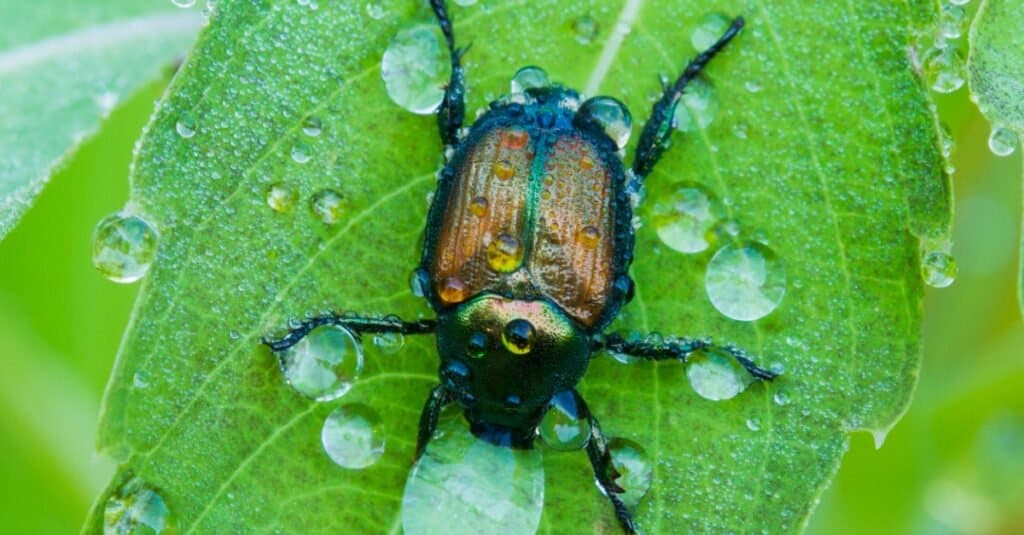

Japanese beetles have an oval-shaped, clubbed antennae, and five white hair tufts on each side of the abdomen.
©iStock.com/mirceax
Lady bugs have a shell skin type with hemispherical to oval-shaped bodies and six legs. They also have short legs, antennae, and colors including brown, yellow, red, black, orange, pink, and white. However, the most popular species have a red shell and distinct black, yellow, and reddish markings/spots, making them very recognizable. Ladybugs also have joints with special abilities to release a toxic fluid to scare off predators. They might even bite if it comes to it.
Japanese beetles also have an oval-shaped, clubbed antennae, and five white hair tufts on each side of the abdomen. They have a typically solid exoskeleton with a bronze/copper-brown wing cover(elytra) shielding the other strong wings.
Ladybugs vs Japanese Beetles: Size
Ladybugs and Japanese beetles are similar in that they are small in terms of length, weight, and dimensions.
Lady bugs measure 0.08-0.4 inches in length and they weigh about 0.007 ounces. Japanese beetles are a little longer with length reaching about 0.591- 1 inch, while also weighing 0.00291 ounces.
Ladybugs vs Japanese Beetles: Predators
Ladybugs and Japanese beetles have one thing in common with most other animals- predators. As much as they prey on other animals and plants, there are other species that also prey on them.
For ladybugs, their nemesis includes rodents, dragonflies, birds, frogs, wasps, assassin bugs, and stink bugs among others. Japanese beetles, on the other hand, are often hunted down by moles, raccoons, wild birds, spiders, and other insects.
Ladybugs vs Japanese Beetles: Number Of Species
It would interest one to know that there are over 5,000 species of ladybugs virtually across all the continents. The major and most popular categories include:
- The seven-spotted ladybug
- The thirteen-spotted ladybug
- The Asian ladybug
- The Coleomegilla maculate ladybug
- The Hippodamia convergens ladybug
Even more interesting is the fact that Japanese beetles only have one species; like they are a single species.
We have to admit; it’s quite rare to find a member of the Insecta class with just one species. These numbers show there is a world of difference between ladybugs and Japanese beetles, in terms of range of species.
Ladybugs vs Japanese Beetles: Conservation Status
For ladybugs, the International Union For The Conservation Of Nature’s Threatened Species classifies them as “Near threatened” which means they may be at risk of extinction in the future. The conservation status of the Japanese beetle is however classified as “least concern” meaning they face no impending threats that put them at risk of extinction.
Isn’t it rather interesting that the ladybug with over 5,000 species is at risk of extinction while the Japanese beetle with just one species faces no such risks?
The photo featured at the top of this post is © Sergey/Shutterstock.com
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.






