Black Bass
The most popular game fish in North America
Advertisement
Black Bass Scientific Classification
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Black Bass Conservation Status
Black Bass Facts
- Prey
- Insects, crayfish, aquatic invertebrates, fish
- Main Prey
- Insects
- Name Of Young
- Fry
- Group Behavior
- Solitary
- Fun Fact
- The most popular game fish in North America
- Estimated Population Size
- Hundreds of millions or billions
- Biggest Threat
- Habitat loss
- Most Distinctive Feature
- Dark-colored lateral scales
- Distinctive Feature
- Spiny and soft dorsal fin
- Average Spawn Size
- 400-20,000
- Habitat
- Freshwater streams, rivers, lakes, and ponds
- Predators
- Fish and birds
- Diet
- Carnivore
- Lifestyle
- Crepuscular
- Number Of Species
- 13
- Location
- North America
- Nesting Location
- Shoals and sand, mud, or gravel beds
- Migratory
- 1
Black Bass Physical Characteristics
- Color
- Yellow
- Black
- Gold
- Green
- Skin Type
- Scales
- Lifespan
- Up to 15 years
- Weight
- Up to 22 pounds
- Length
- Up to 30 inches
- Age of Sexual Maturity
- 1-3 years
- Venomous
- No
- Aggression
- Medium
View all of the Black Bass images!
Summary
The term black bass is used to refer to 13 different species of fish in the genus Micropterus. This genus includes well-known species such as the largemouth bass, smallmouth bass, and spotted bass. All black bass species hail from freshwater waterways throughout North America. Anglers prize black bass as game fish due to their size and willingness to fight when hooked.
5 Black Bass Facts
- Scientists classify 13 species in the black bass genus Micropterus, including the largemouth and smallmouth bass.
- The largest black bass ever caught measured a whopping 22 pounds, 4 ounces.
- Black bass are considered invasive species in many countries where they have been introduced.
- Black bass rank as the most popular game fish in North America, as nearly 10 million anglers report catching black bass every year.
- Some rare black bass species include the Guadalupe bass and Suwanee bass.
Black Bass Classification and Scientific Name
Freshwater black bass belong to the ray-finned fish order Perciformes or “perch-like” fish. They are members of the family Centarchidae or sunfish, which includes eight different genera. Other members of the family include crappies, Sacramento perch, rock bass, mud sunfish, and banded sunfish. The name centrarchus derives from the Greek words kentron, meaning “sharp point,” and archos, meaning “rectum.”
Black bass belong to the genus Micropterus. The origin of the genus name stems from a case of mistaken identity. The word micropterus derives from the New Latin micro, meaning “small,” and ptero, meaning “feather” or “winged.” When it was first described, the identified black bass specimen had a mutilated fin. This led the researcher to incorrectly assume that all black bass possessed small fins.
Some species in the black bass genus get their specific or common name from a distinguishing physical feature. For example, the largemouth bass gets its name from its characteristic large lower lip. Similarly, the redeye bass features bright red eyes. Meanwhile, other species get their name from their physical location. For instance, the Florida bass is native to Florida, while the Guadalupe bass is native to parts of Texas, including the Guadalupe River.
Many people also incorrectly assume that black bass get their common name from the dark color on their sides. In reality, the term black bass stems from the color of juvenile smallmouth bass. Smallmouth bass fry turn “coal black” a few days after hatching. Over time, this term came to refer to all black bass species, not just juvenile smallmouth bass.
Here is a list of all 13 recognized species in the genus Micropterus:
- Micropterus cahabae – Cahaba bass
- Micropterus cataractae – Shoal bass
- Micropterus chattahoochae – Chattahoochee bass
- Micropterus coosae – Redeye bass
- Micropterus dolomieu – Smallmouth bass
- Micropterus floridanus – Florida bass
- Micropterus henshalli – Alabama bass
- Micropterus notius – Suwannee bass
- Micropterus punctulatus – Spotted bass
- Micropterus salmoides – Largemouth bass
- Micropterus tallapoosae – Tallapoosa bass
- Micropterus treculii – Guadalupe bass
- Micropterus warriorensis – Warrior bass
Black Bass Appearance
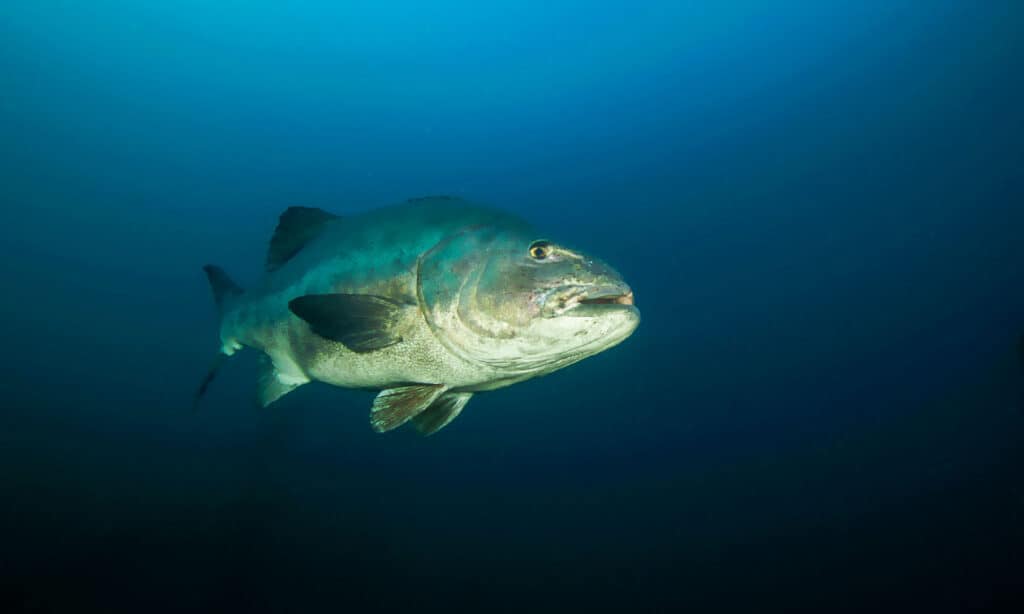

Black Sea Bass are hermaphroditic fish.
©iStock.com/KGrif
They vary in appearance depending on the species. That said, all 13 species share a number of similarities. All black bass appear primarily dull-green and sport dark-colored scales on their sides. They range in size but typically grow between 16 and 24 inches long. However, some species can grow up to a maximum of 30 inches. Females typically measure larger than males. Like other sunfishes, the dorsal fin contains both spiny and soft-rayed portions joined into a single fin.
From there, unique variations allow experienced anglers to distinguish one black bass from another. Here’s how you can identify a few of the most common black bass species.
The Alabama bass features blotches on its sides but not on its dorsal fin. The spiny and soft sections of its dorsal fin connect together with a shallow notch. It sports 10 spines in its dorsal fin and 3 spines in its anal fin. The number of lateral scales varies but typically ranges between 68 and 84.
The largemouth bass’s upper jaw extends past its eye, while the lower jaw juts notably past the upper jaw. Most largemouth bass sport dark lateral blotches down each side from the snout to the caudal fin. However, the presence of these blotches can vary depending on the environment where largemouth bass live. The number of lateral line scales varies between 59 and 72 in most specimens.
In terms of overall appearance, the Florida bass closely resembles the largemouth bass. As a result, some experts recognize the Florida bass as a largemouth bass subspecies. The main differences separating the two are size and growth rates. Northern largemouth bass grow more slowly and measure smaller than Florida bass. Florida bass frequently grow to weigh 20 pounds or more, as compared to the average of 10 pounds for northern largemouth bass.
The smallmouth bass sports 3 dark bars on each cheek and between 8 and 16 vertical lateral bars on each side. Unlike the largemouth bass, its upper jaw does not extend past the eye. It also features more lateral line scales, running from 67 to 81, depending on the specimen.
Black Bass Distribution, Population, and Habitat
Black bass are widely distributed throughout North America. Historically, they ranged mostly throughout the eastern half of the continent. In particular, you could find them east of the Rocky Mountains, from Hudson Bay in Canada to northeastern Mexico. Today, several black bass species live outside of their native range. In particular, you can now find largemouth and smallmouth bass throughout much of the world. Black bass live in a wide range of habitats, including rivers, streams, lakes, ponds, and reservoirs. However, different species prefer certain environments over others. For example, smallmouth bass typically inhabit clearer water than largemouth bass. Meanwhile, redeye bass enjoy calm water along banks or inlets, while Guadalupe bass prefer fast-flowing water.
That said, several black bass species live within a very narrow range. For instance, redeye bass are native to the Coosa River system of Georgia and Alabama. Similarly, the Suwannee bass and shoal bass are both native to the waters of Florida and Georgia. The spotted bass ranges throughout the Mississippi River basin and the southeast, while the Guadalupe bass is endemic to Texas, particularly the Guadalupe River.
Black Bass Predators and Prey
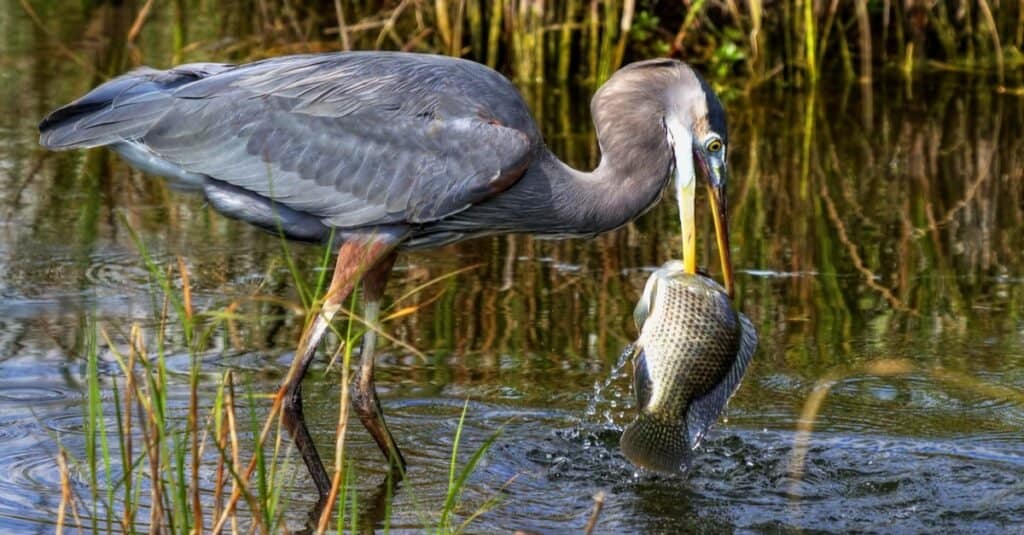

Predators of black bass include
great blue herons
.
©David Byron Keener/Shutterstock.com
Adults are often at the top or near the top of the food chain in their respective environment. This is especially true for larger species, such as largemouth bass or Florida bass. However, numerous large predatory fish prey on black bass, including northern pike, crappie, walleye, channel catfish, and common carp. Other predators of black bass include great blue herons, kingfishers, bitterns, hawks, and eagles. That said, humans likely rank among the greatest threats to most black bass.
Nearly all prey on aquatic invertebrates, insects, worms, crayfish, and fish. However, each species prefers certain prey over others. Shoal bass mainly feed on insects near the water surface. Juvenile smallmouth bass mostly eat plankton and insects, while the adults also prey on amphibians, crayfish, and fish. Suwannee bass primarily eat crayfish, although they will also eat fish and invertebrates. Meanwhile, largemouth bass and Florida bass start out eating copepods, shrimp, and insects. Once they mature, the adults’ diet expands dramatically to include frogs, snakes, salamanders, fish, and bats, as well as small turtles, alligators, and mammals.
Black Bass Reproduction and Lifespan
Most reach sexual maturity between 1 and 3 years old. Spawning typically takes place in spring between March and June as water temperatures start to warm. The optimal temperature varies depending on the species but typically ranges between 64 and 79 degrees Fahrenheit.
Males usually kickstart the spawning season by constructing a shallow nest near the banks of rivers or lakes. Nest sites vary by species, but are typically located on gravel, mud, or sand beds. The female then comes by and lays her eggs in the nest, which the male fertilizes externally with his sperm. The number of eggs can range anywhere from a few hundred to up to 20,000, depending on the species. Once the female lays her eggs, she leaves, and the male remains to guard the nest. The male will remain guard until the eggs hatch, and the fry leave the nest.
They generally live between 10 and 12 years in the wild. However, some specimens can live up to 15 years.
Black Bass in Food and Cooking
Many anglers catch and release them that they catch in the wild. However, many anglers keep and cook black bass. Most people would say that black bass has a somewhat “fishy” taste. However, the flavor of black bass varies depending on the species. Generally, the larger the fish, the more fishy it tastes. For example, smallmouth bass tends to taste more mild and clean than largemouth bass.
You can use multiple methods when preparing and cooking black bass. These include boiling, sauteing, baking, frying, and grilling. That said, most people prefer to fry or grill black bass filets. Grilling is more popular for larger filets, while frying is more popular for smaller filets. You can use a wide range of sauces, herbs, and spices to up the flavor of black bass even more.
Black Bass Population
Their populations vary depending on the species. Most species occur in large enough numbers that the IUCN lists them as Least Concern. Moreover, some species – such as largemouth bass and smallmouth bass – are now so widespread that experts classify them as cosmopolitan species. On the other hand, some black bass species live in a much more narrow range. For example, shoal bass appear to be decreasing in the Apalachicola and Chipola rivers due to a lack of spawning beds and competition with other species. Presently, the IUCN lists the shoal bass as a Near Threatened species. Similarly, the Suwannee bass lives in just two river systems in Georgia and Florida. Due to declining numbers, the IUCN classifies the Suwannee bass as Near Threatened.
Black Bass FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are they carnivores, herbivores, or omnivores?
Black bass are apex predators that prey on a wide variety of other animals. Their diet includes plankton, aquatic invertebrates, crayfish, and fish. Some larger species will also eat small amphibians, reptiles, and mammals.
What is the largest species?
The largemouth bass or Florida bass ranks as the largest black bass species. Some experts classify Florida bass as a subspecies of largemouth bass. Florida bass tend to grow larger than northern largemouth bass.
Do they migrate?
As the weather gets colder, some species will migrate in search of deeper pools. They seek out deeper water to help them enter a semi-hibernative state.
How do you catch them?
You can catch them using a wide variety of methods depending on the species. Some tend to stick close to shore, vegetated areas, or underwater objects. Meanwhile, others tend to prefer deep, open water.
Related Animals
View all 285 animals that start with BBlack Bass FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are black bass carnivores, herbivores, or omnivores?
Black bass are apex predators that prey on a wide variety of other animals. Their diet includes plankton, aquatic invertebrates, crayfish, and fish. Some larger species will also eat small amphibians, reptiles, and mammals.
What is the largest species of black bass?
The largemouth bass or Florida bass ranks as the largest black bass species. Some experts classify Florida bass as a subspecies of largemouth bass. Florida bass tend to grow larger than northern largemouth bass.
Do black bass migrate?
As the weather gets colder, some black bass species will migrate in search of deeper pools. They seek out deeper water to help them enter a semi-hibernative state.
How do you catch black bass?
You can catch black bass using a wide variety of methods depending on the species. Some bass tend to stick close to shore, vegetated areas, or underwater objects. Meanwhile, others tend to prefer deep, open water.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- , Available here: https://tpwd.texas.gov/regulations/outdoor-annual/fishing/freshwater-fishing/bass-identification
- , Available here: https://fws.gov/species/largemouth-bass-micropterus-salmoides
- , Available here: https://www.fws.gov/species/smallmouth-bass-micropterus-dolomieui