Crucian Carp
Carassius carassius
Can survive drought by burying itself in mud.
Advertisement
Crucian Carp Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Actinopterygii
- Order
- Cypriniformes
- Family
- Cyprinidae
- Genus
- Carassius
- Scientific Name
- Carassius carassius
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Crucian Carp Conservation Status
Crucian Carp Facts
- Prey
- water fleas, organic detritus, algae, zooplankton, aquatic weeds, small crustaceans, insects, larvae, fish eggs, small fish and small animals living in the lake, pond or river mud
- Group Behavior
- School
- Fun Fact
- Can survive drought by burying itself in mud.
- Estimated Population Size
- Abundant
- Biggest Threat
- genetic invasion by Prussian carp and goldfish
- Distinctive Feature
- Looks like a big, golden-green goldfish
- Other Name(s)
- English carp, golden carp, gibele and Prussian carp
- Gestation Period
- 2-3 days
- Optimum pH Level
- 6.5-9.0
- Habitat
- lakes, ponds, slow-moving rivers
- Predators
- Bass, European catfish, European smelt, blue tilapia, snakes, northern pike, Little egret
- Diet
- Omnivore
- Type
- Cyprinidae - carp
- Common Name
- Crucian carp
- Number Of Species
- 1
- Migratory
- 1
View all of the Crucian Carp images!
The crucian carp, native to England and now living in almost the entirety of Europe and parts of Asia, is a hearty freshwater fish that thrives in lakes, ponds and slow-current rivers. Also called the English carp, golden carp, gibele and Prussian carp, the species is a cousin to the domesticated goldfish. They are able to live for hours outside of water and even several days after freezing of their thick outer skin, according to historical reports. In Britain and some other countries, the crucian carp is a common target for rod and tackle fishing competitions.
5 Crucian Carp Facts
- The crucian carp is able to survive being outside of water for several hours
- When the external layer of the fish’s body is frozen, the crucian carp may still survive for several days
- Many people consider this fish the “wild goldfish” since the domesticated goldfish and crucian carp share many characteristics
- Most live 10 years in the wild but can live up to 30 years in captivity
- Spawning takes place in several batches for a total of about 250,000 eggs per season
Crucian Carp Classification and Scientific Name
The crucian carp, classified as Carassius carassius, is a member of the family Cyprinidae and genus Carassius. Other names by which the fish is known include English carp, golden carp, gibele and Prussian carp. Because of their resemblance to the domestic goldfish, many people also call them wild goldfish. Their family Cyprinidae, the carp and minnow family, includes about 3,000 species of fish. The family name is from the Greek “kyprînos,” meaning carp. The genus name Carassius comes from the Low German term karusse or Medieval Latin coracinus, meaning a type of river fish.
Crucian Carp Appearance
The crucian carp is a medium-sized carp fish averaging about 6 inches in length, although some have grown as large as 25 inches long. Most adult fishes of this species weigh about 4.4lbs. But the record for the heaviest caught crucian carp is 6.6lbs. Young fishes are golden bronze in color and transition to a more golden green in adulthood with reddish-orange fins. It is a scaly fish with an average of 33 scales along its lateral line. While a goldfish has a concave dorsal fin, the crucian carp’s dorsal fin is convex.
The crucian carp’s coloring helps it blend in well in its freshwater habitat. This bland coloring is why it is not as popular as goldfish, koi or orfe, other carp, in domestic fish ponds or freshwater aquariums. But you can still sometimes find the fish living in these manmade habitats on display.
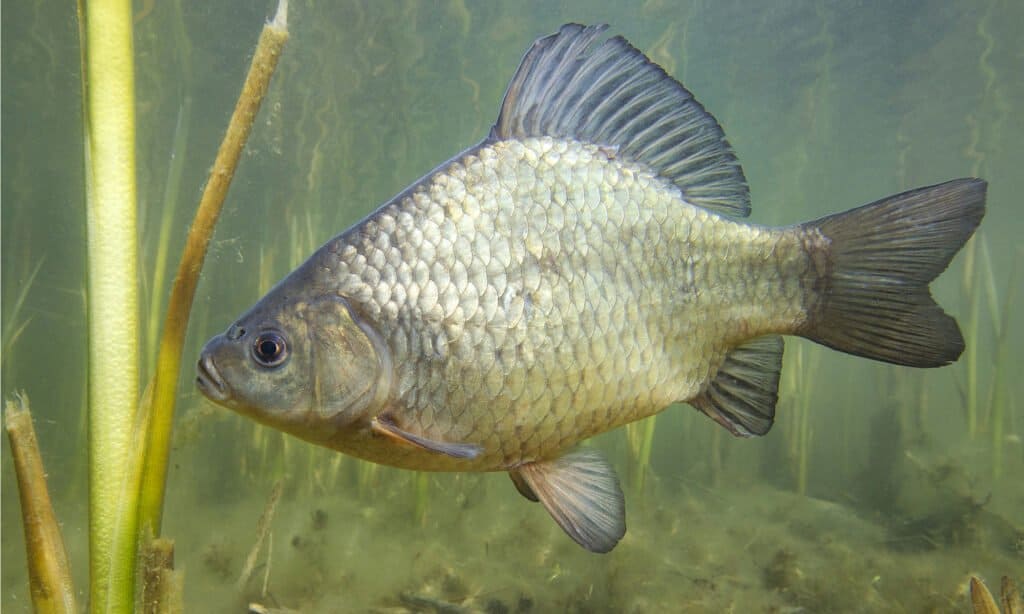

Crucian carp can live 10 years in the wild but can live up to 30 years in captivity.
©Rostislav Stefanek/Shutterstock.com
Distribution, Population, and Habitat
According to the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, the crucian carp’s conservation status is of Least Concern and abundant but decreasing in population.
One of the species’ biggest threats is introduction of the non-native Carassius gibelio, also called the Prussian carp, into the crucian carp’s waters. These two carp can reproduce with the hybrid young proving more able to find food and avoid predators. This makes the crucian carp more vulnerable to starvation and predation. The same is true with goldfish introduced to the crucian carp’s habitat. While offspring of the two fish are sterile and cannot reproduce, they prove more hearty and able to survive than the native species.
Where to Find Crucian Carp and How to Catch Them
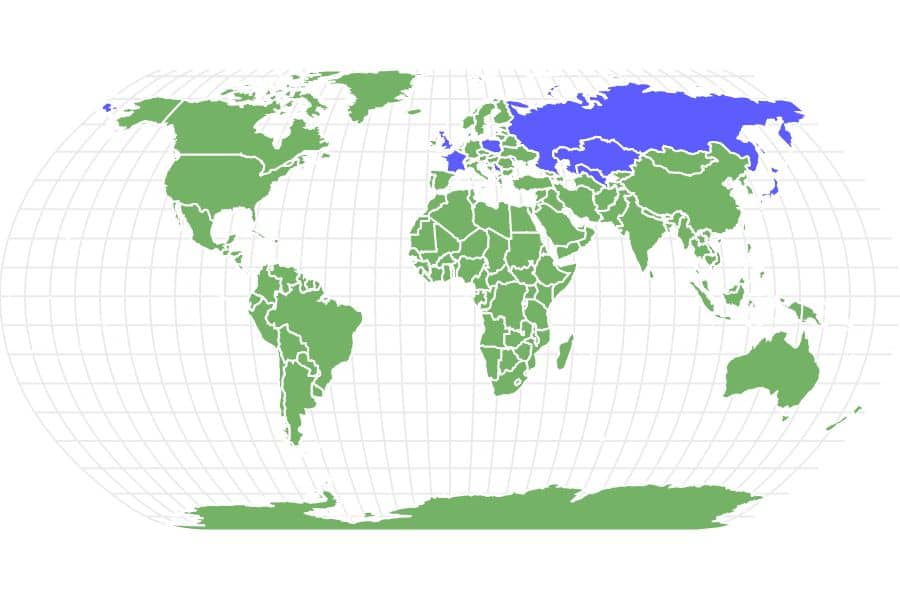
Crucian carp are freshwater fish living throughout the United Kingdom and most of Europe in ponds, lakes and slow-moving rivers. In fact, they are found from the UK to Russia, as far north as the Arctic Circle and as far south as central France and the Black Sea.
The fish are hearty and thrive despite high temperatures and low water oxygenation of summer and freezing temperatures of winter, even beneath layers of ice. They prefer densely vegetated waters at about 16 feet of depth (5m) where they spawn and their eggs attach to plants. But surprisingly, the fish can even survive almost-dried up pond, river or lake conditions by burying themselves in the mud.
In Britain, crucian carp are popularly sought after through sport fishing using rods, reels and tackle. They are not typically prepared as food in England, so this fishing is catch-and-release. They are also frequently caught in the Netherlands as part of angling sport. Worldwide, about 5.53 thousand tons of the fish are caught through fishing each year. The countries where fishing for crucian carp is most popular include Kazakhstan, Japan, Serbia, Moldova, Uzbekistan and Poland.
Predators and Prey
Crucian carp are naturally aggressive eaters, like all carp. They are omnivorous and eat water fleas, organic detritus, algae, zooplankton, aquatic weeds, small crustaceans, insects, larvae, fish eggs, small fish and small animals living in the lake, pond or river mud.
What eats crucian carp?
In Eastern European and Asian countries, people are a top consumer of crucian carp. Although the fish have a tough skin, scales and many small bones, the meat is considered a delicacy when properly prepared. In Poland, Russia and other regions, the fish is often prepared and served for holidays.
Like bass, European catfish, European smelt, blue tilapia, snakes and egrets, the northern pike is a major natural predator of the crucian carp. But the carp evades this big predator and others like it by changing its size. When pike are present in the same body of water, the carp grows larger and into a more disc-like, rotund shape, making the prey too big for a pike to fit in its mouth. This increases the carp’s odds of survival when faced by a predator. But the trade-off is that growing larger makes the fish’s immune system weaker. It is easier for an oversized crucian carp to catch and die from common illnesses.
What does the crucian carp eat?
Being omnivorous, the crucian carp has a wide variety of food options at its disposal in just about any body of water, even an aquarium. The fish, like its goldfish cousin, feeds on algae, organic detritus, aquatic weeds, zooplankton, insects and small animals living in the mud at the bottom of their habitat. They also eat other small fish, fish eggs, larvae, small crustaceans and water fleas.
Reproduction and Lifespan
The crucian carp spawns in weedy areas of its habitat. The adult fish is ready for reproduction at age two to four years, depending on its native region. They spawn in water temperatures of 64F (18C) or higher from May to July. Each female spawns with several males for a total of 3 to 5 egg releases per season. In one summer, the female can release up to 250,000 eggs. The eggs attach to weeds and other plant matter in shallow water, hatching in 2 to 3 days. At first, the young feed on the yolk sac from their eggs and later feed on plankton and algae before graduating to bigger foods. Although most crucian carp live about 10 years in the wild, they can live as long as 30 years in captivity.
Crucian Carp in Fishing and Cooking
The fish is a popular dish in Poland that is served with sour cream and called “karasie w śmietanie.” It is a pan fish dish traditionally served during the holidays. In Russia, the crucian carp is used in a borscht recipe called “borshch c karasej.” The fish also frequently finds its place on Chinese dinner tables such as in Chinese crucian carp soup.
Worldwide, the crucian carp is heavily farmed. In fact, it is the 9th most farm-raised fish at 1,957,337 tons per year. This worldwide awareness of crucian carp has made the fish popular in online gaming, particularly in games like Animal Crossing and Black Desert Online.
View all 235 animals that start with CCrucian Carp FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Where are crucian carp found?
Crucian carp are native to England but are also found throughout Europe and Asia. They live in lakes, ponds and slow-moving rivers from the Arctic Circle of Scandinavia to the Black Sea and central France, from the U.K. to Russia and Asia.
Can you eat crucian carp?
Crucian carp are tough-skinned, bony and scaly fish only typically eaten in some Eastern European and Asian countries. They are commonly prepared with sour cream for Polish holiday meals and as part of a Russian borscht. Chinese crucian carp soup is also quite popular in that country. In the regions where the fish is served, it is considered a delicacy.
Is there crucian carp in USA?
The crucian carp was once found near Chicago, Illinois in 1910. But the fish quickly vanished in that region. Although there were reports of a crucian carp sighting in Texas in the 1990s, that myth has since been proven untrue by the U.S. government. At this time, there are no known occurrences of crucian carp in North America.
Are crucian carp rare?
Crucian carp are abundant throughout the U.K., Europe and parts of Asia. They are not considered rare in these regions, by any means. Their conservation status worldwide is of “least concern” according to the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. In fact, crucian carp are so well known throughout the world that they are often included in popular video games like Animal Crossing and Black Desert Online.
How much is a crucian carp worth?
On the open market, a farm-raised crucian carp sells for about USD $0.41 to USD $0.59 per pound. But if you are playing the popular video game “Animal Crossing: New Horizons” in 2022, the crucian carp sells for 160 Bells. In Black Desert Online, another game, the fish is worth about 3720 in trade value.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- / Accessed March 1, 2022
- / Accessed March 1, 2022
- / Accessed March 1, 2022
- / Accessed March 1, 2022
- / Accessed March 1, 2022
- / Accessed March 1, 2022
- / Accessed March 1, 2022
- / Accessed March 1, 2022
- / Accessed March 1, 2022
- / Accessed March 1, 2022
- / Accessed March 1, 2022
- / Accessed March 1, 2022
- / Accessed March 1, 2022