Goose
During its migration, the goose flies in V formations to conserve energy.
Advertisement
Goose Scientific Classification
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Goose Conservation Status
Goose Facts
- Main Prey
- Grass, Seeds, Berries
- Fun Fact
- During its migration, the goose flies in V formations to conserve energy.
- Distinctive Feature
- Long neck and noisy communication calls
- Wingspan
- 4.2 to 6.1 feet
- Incubation Period
- 1 month
- Habitat
- Large ponds, rivers and lake shores
- Diet
- Omnivore
- Lifestyle
- Flock
- Favorite Food
- Grass
- Type
- Bird
- Average Clutch Size
- 5
- Slogan
- There are 29 different species!
- Nesting Location
- Ground
- Age of Molting
- A few months
- Migratory
- 1

The goose is among a group of large waterfowl that resides in the Northern Hemisphere.
This bird’s loud, aggressive behavior has become something of a running joke in modern media (epitomized by the popular action puzzle video game, Untitled Goose Game), but as a very caring parent, it is usually just trying to protect its young from danger.
The Canada goose is the most common species in North America, but the bird has adapted to live in many different regions around the world.
An Amazing Bird: 4 Goose Facts!

Fossils of these birds have been found dating back some 10 to 12 million years ago.
©Rogney Piedra Arencibia/Shutterstock.com
Here are a few amazing geese facts:
- Geese domestication was a somewhat common job or pastime in Ancient Egypt, Rome, and Greece. The Roman naturalist Pliny (200s AD) once told an amusing anecdote of a pet goose that was inseparable from its owner.
- Today most domesticated birds are descended from the graylag, the swan goose, and a few other species for the purpose of cultivating their feathers (which end up in quilts, pillows, and coats) or meat and paste (most commonly in foie gras). They have been artificially selected for polygamous behavior to improve their reproductive efficiency.
- The goose is a bird that has made an indelible mark on human culture as a harbinger of the winter and an important component of numerous idioms and phrases. “Killing the goose that lays the golden eggs” is a reference to one of Aesop’s Fables as a warning against greedy behavior.
- Fossils of these birds have been found dating back some 10 to 12 million years ago.
- The term goose can refer to not just the bird itself, but also the adult female specifically. She’s sometimes called a hen to avoid confusion. An adult male is generally referred to as a gander.
List of Types of Geese
Here is a full list of all different sub-species of geese:
- Canada goose
- Greylag goose
- Snow goose
- Swan goose
- Greater white-fronted goose
- Barnacle goose
- Brant
- Bar-headed goose
- Cackling goose
- Domestic swan goose
- Tula Fighting Goose
- Bean goose
- Ross’s goose
- Nene (Hawaiian Goose)
- Emperor goose
- Pink-footed goose
- Lesser white-fronted goose
- Red-breasted goose
- Anser serrirostris
Where to Find Them

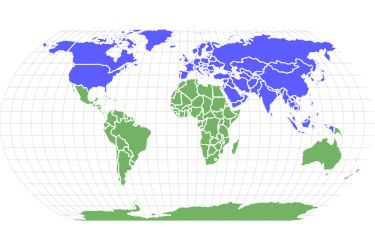
Geese are found in Europe, Asia, and North America.
©Erni/Shutterstock.com
The goose is a bird that has evolved over millions of years to live near the freshwater rivers, lakes, ponds, and streams of Europe, Asia, and North America. Most species prefer temperate or Arctic climates, but the Hawaiian species is an obvious exception since it lives in tropical climates.
Evolution and Origins
The European domestic goose is descended from wild greylag goose. In fact, based on its pink bill, the coloration suggests that it is more likely from the eastern subspecies (Anser anser rubrirostris) than the nominate western subspecies.
There are two key types of domestic geese. The first were thought to have origins in Europe. They may have also been descendants of the wild Greylag goose, and the second are suggested to have their origins in Asia, and may be descendants of the wild Swan goose.
Nests
The bird’s nest is a very simple construction of leaves, grass, twigs, mosses, and lichen in the ground, sometimes near an elevated area.
Scientific Name

Geese belong to the family of Anatidae
©Krasula/Shutterstock.com
Closely related to ducks, swans, and other waterfowl, these birds belong to the family of Anatidae, which appears to derive from the Latin anas for a duck. “Goose” is not really a single classification at all. Instead, it is generally defined as any member of two different genera: Anser, which includes the grey and white geese, and Branta, which includes the black geese.
There are some 16 or 17 recognized species, including Canada, the barnacle, the white-fronted, the snow, the swan goose, and the brant. Several more species (among them the magpie and the pygmy goose) are not true geese at all, despite their names.
Size, Appearance & Behavior
These birds are very recognizable due to their plump body, slender neck, and humped bill that tapers at the end of the mouth. Although physically similar to the closely related swan, they usually exhibit grey or black feathers all over their smaller body with a black or orange bill.
The terms gray, white, and black goose generally refers to the color of the neck and head (the black goose has an additional white mark around the chin as well). The largest species are Canadian geese, which weigh in at about 14 pounds and reach some 43 inches in length. The male gender tends to be slightly larger than the female, but the sexes are otherwise similar in color and appearance.
The social life of these birds revolves around large flocks called gaggles (though in the air they’re called skeins). When defending against threats or interacting with other members, these flocks are a loud cacophony of honks and cries. Sometimes, when they are particularly angry, they will vibrate their neck feathers in defiance.
After triumphing over a foe, they will emit a kind of victory cry as well. As members of the waterfowl family, these birds are obviously excellent swimmers and flyers, but the more forward position of their feet compared with swans and ducks also makes them better walkers as well.
Geese are able to sleep while staying alert by shutting down one-half of their brain. This is called the unihemispheric method and is shared with other animals like dolphins.
![graylag goose [Anser anser]](https://a-z-animals.com/media/Goose-Graylag-1024x535.jpg)
©Bildagentur Zoonar GmbH/Shutterstock.com
Migration Timing and Pattern
These birds migrate in V formations, which allow them to conserve energy by taking advantage of the air currents created by the wings of those ahead of them. This is why they constantly trade places: the bird at the front expends more energy than the bird toward the back.
Migratory patterns vary by species. Canada geese, for instance, travel as far south as Mexico and the Southern United States in the winter, sometimes up to 3,000 miles along a single route. Hawaiian geese (also called the nene) remain mostly within the island chain of their birth all year round.
A Herbivorous Bird

These birds are mostly herbivorous grazers; the bill and mouth are specially adapted for grasping and tearing at vegetation.
What does the goose eat?
The bird’s diet consists of sedges, grasses, grains, seeds, and aquatic plants. It will only sometimes resort to insects and fish.
Predators and Threats
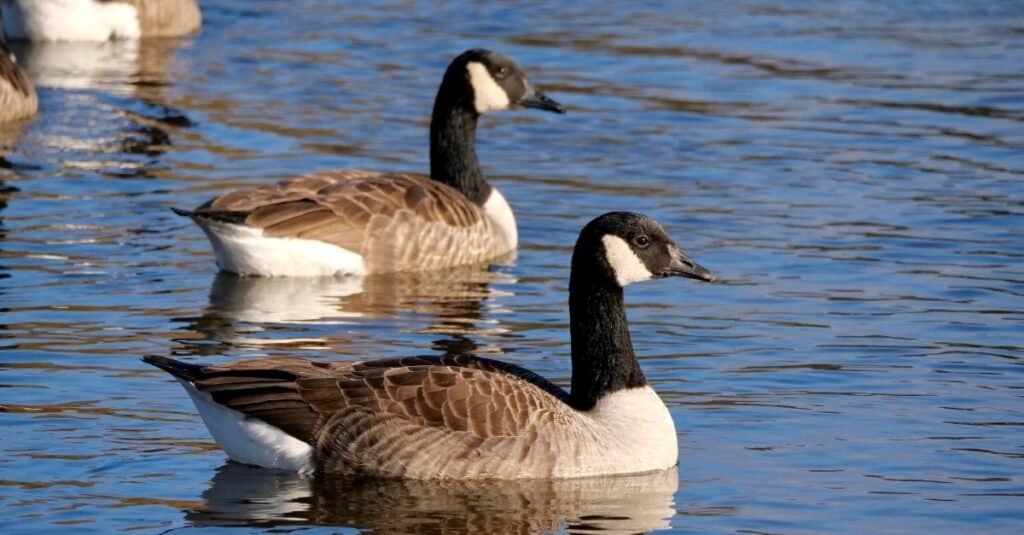

Geese face threats from hunting and habitat loss.
©iStock.com/yujie chen
These birds sometimes face threats from hunting, habitat loss, and predation (both natural and introduced species). These threats tend to be localized, however, and affect each population differently, rather than all geese as a whole.
What eats the goose?
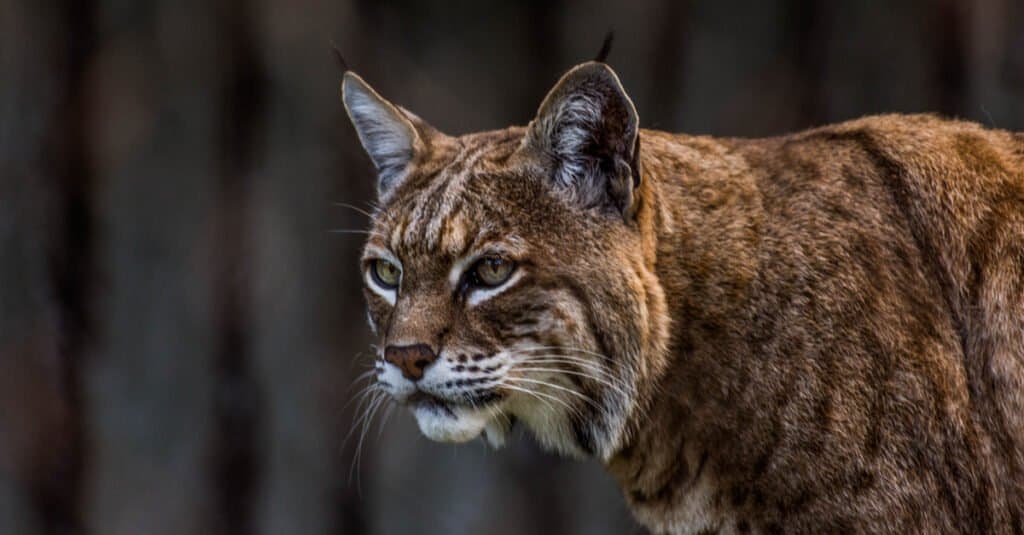

The bobcat is a natural enemy of Geese.
©Victor Arita/Shutterstock.com
Adult birds only have a few natural predators, including coyotes, bobcats, and humans. But eggs and juveniles make a tempting target for skunks, foxes, raccoons, crows, snakes, hawks, snapping turtles, and almost any other carnivorous animal of decent size. Since only the largest carnivores want to tussle with a full-sized goose, most of them resort to subterfuge and guile.
Reproduction, Babies, and Lifespan
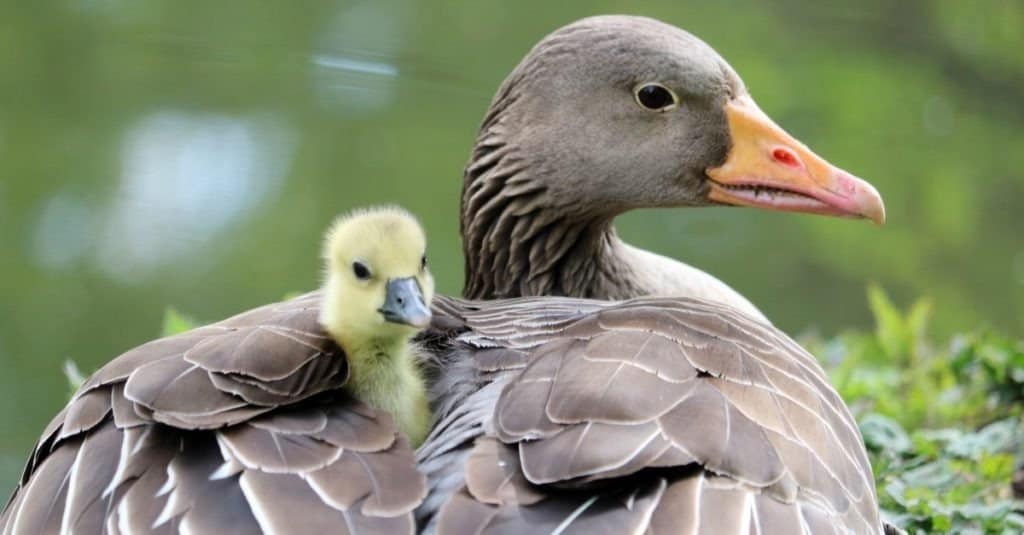

A goose and her baby.
©flagman_1/Shutterstock.com
These birds form lifelong monogamous bonds with a single partner. Together they produce a single clutch of white eggs (usually up to 10, depending on the species) in the spring breeding season. If one of the birds dies, then the surviving mate will find pair up with someone else within the same season.
Once she lays the eggs, the female has sole responsibility to incubate them, while the male gander stands guard to protect against threats. Emerging from the egg with downy feathers, the gosling has the ability to fend for itself almost immediately, but it remains under the protection of its parents for the first summer of its life.
The parents will lead the goslings in a single file line and hiss at anything that approaches. Geese have a life expectancy of around 10 to 15 years, but they have been known to live some 30 years in captivity.
Population
According to the IUCN Red List, most geese species are considered to be least concern, perhaps because they are rarely hunted enough to be threatened directly.
Of the 16 or so true geese species, only the swan, the red-breasted, the Hawaiian, and the white-fronted goose are vulnerable, while the emperor goose is near threatened.
View all 170 animals that start with GGoose FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are Geese herbivores, carnivores, or omnivores?
Geese are Omnivores, meaning they eat both plants and other animals.
What Kingdom do Geese belong to?
Geese belong to the Kingdom Animalia.
What class do Geese belong to?
Geese belong to the class Aves.
What phylum to Geese belong to?
Geese belong to the phylum Chordata.
Does the goose migrate?
Yes, most geese prefer to live in more temperate climates, so they migrate south for the winter.
How many eggs does the goose lay?
The goose can lay up to 10 eggs per clutch. However, five or six is the average number.
How fast does the goose fly?
The goose flies an average of about 40 miles per hour. If the winds are particularly favorable, then it can achieve a top speed of some 70 miles per hour.
What is the goose’s wingspan?
The largest geese have a wingspan of about 6 feet.
When do geese leave the nest?
The gosling usually leaves the nest soon after hatching and then gains its full flight feathers after about two months, right in time for the annual migration. But even after it matures, the goose may remain with the same flock for much of its life.
What is a baby goose called?
A baby goose is called a gosling.
Are geese dangerous?
Male geese can be quite aggressive about defending the nest, but these attacks on humans (which have increased as people intrude on natural goose habitats) are almost never more than amusing incidents that may result in bruises from their beak or wings. The worst injuries usually occur when people trip and fall as a result of a goose attack.
What is a female goose called?
A female goose is usually referred to as either a goose or a hen.
Is a goose a duck?
Geese and ducks are closely related, but the duck is a much smaller bird with a shorter neck and a variety of different colors and patterns. Ducks produce quacking sounds and tend to be more omnivorous.
How big do geese get?
Geese rarely grow longer than 4 feet from mouth to tail.
What family do Geese belong to?
Geese belong to the family Anatidae.
What order do Geese belong to?
Geese belong to the order Anseriformes.
What type of covering do Geese have?
Geese are covered in Feathers.
In what type of habitat do Geese live?
Geese live in large ponds, rivers, and lake shores.
What is the main prey for Geese?
Geese eat grass, seeds, and berries.
What are some predators of Geese?
Predators of Geese include foxes, owls, raccoons, and wild dogs.
What are some distinguishing features of Geese?
Geese have long necks and noisy communication calls.
What is an interesting fact about Geese?
There are 29 different species of Goose!
What is the lifespan of a Goose?
Geese can live for 12 to 26 years.
How do Geese have babies?
Geese lay eggs.
What's the difference between a goose and a duck?
Ducks and geese differ in their size, markings, diet, and species. You can learn more about them here!
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- Britannica, Available here: https://www.britannica.com/animal/goose-bird
- Thought Co, Available here: https://www.thoughtco.com/canada-goose-bird-facts-4584329