Parrot
Can live for up to 100 years!
Advertisement
Parrot Scientific Classification
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Parrot Conservation Status
Parrot Facts
- Diet
- Omnivore
- Lifestyle
- Solitary
- Favorite Food
- Fruit
- Type
- Bird
- Average Clutch Size
- 2
- Slogan
- Can live for up to 100 years!
View all of the Parrot images!
Parrots are popular as pets, offering raucous and gaudy entertainment.
Parrots, of the order Psittaciformes, are known for their wittiness, amusement, and intelligence, though they have an incredibly affectionate side as well. They are famous for the extensive imitation, including human words and multitudes of sounds.
See all of our expert product reviews.
6 Incredible Parrot Facts!
- Frequently found in tropical areas, like the Rainforest.
- The term “parrot” umbrellas a wide array of birds – 372 different species, to be exact. Some of the familiar species include the grey parrot, the macaw, and the monk parakeet.
- Known for their bright coloration, easy to spot in their natural habitat. To see some of the most beautiful parrots in the world check out ‘The 10 Most Beautiful Parrots in the World.’
- As one of the most intelligent species of bird, parrot brain development is strikingly similar to that of humans.
- These birds are capable of imitating many different sounds with advanced vocal cords, and often mimic human speech.
- The largest parrot in the world is the Kākāpō, a flightless bird from New Zealand, reaching 9 lbs in weight!
The word “parrot” is believed to come from the early 16th century, based on the French word “perrot.” “Perrot” is a variation of the name “Peter,” which means “stone” or “rock” in the original Greek root.
You can check out more incredible facts about parrots.

Scientific Name
Parrots belong to the kingdom Animalia and the phylum Chordata. Their class is Aves and their clade is Psittacopassarae. The scientific name for parrot is Psittaciformes. The family is broken down into three superfamiles. True parrots are called Psittacoidea. Cockatoos are Cacatuoidea. New Zealand parrots are called Strigopoidea. There are 398 species of parrot in the world!
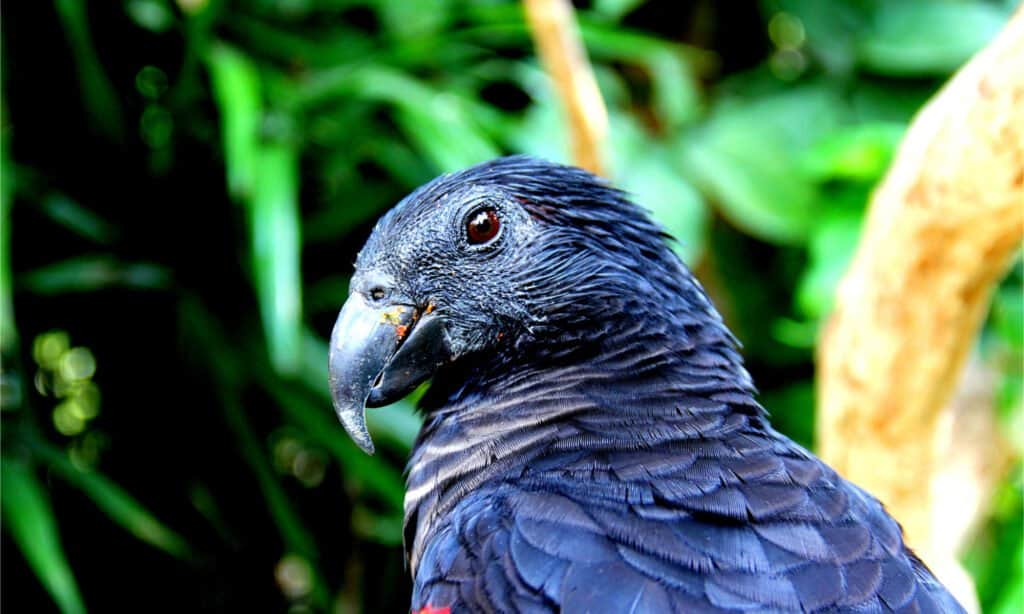

The scientific name for parrot is Psittaciformes
©Quatro212/Shutterstock.com
Health and Entertainment for your Parrot
See all of our expert product reviews.
Evolution
Molecular data has suggested that the cockatoos and other psittaciforms split from each other prior to the K/T boundary at 65 million years ago (MYA). Further parrot lineages started to form around 60-65 MYA when Australia and New Guinea were first separated from East Antarctica. It is estimated that the major parrot families were established by 30 MYA, when Australia, Antarctica, and South America had completely separated.
According to fossil data calibrated at 50 MYA, this split happened 45.04 MYA, shortly before Australia’s separation from Antarctica. Parrots in Neotropical regions began to evolve 33 MYA, when South America parted from West Antarctica.
Evidence suggests that Australia is the origin of parrots due to the high number of endemic genera, some of which are close to the base of the psittaciform tree. Additionally, the split of New Zealand taxa is an indication that their origin was in Gondwana during the Cretaceous. The cockatoos form a monophyletic group (one common ancestor) while many parrots are polyphyletic (more than one common ancestor). There is no clear relationship between some parrot species and other modern birds. This study suggests that Aves evolved during the Cretaceous and parrots are an ancient lineage with no close evolutionary relatives. Many scientists are working to unravel this mystery.
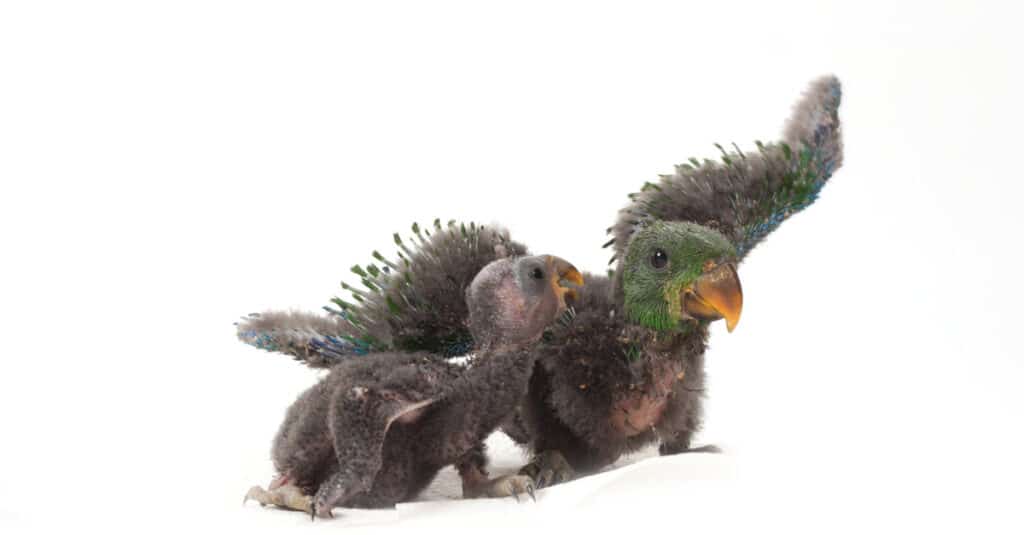

Parrots originated from Australia many millions of years ago.
©Bryoni Castelijn/Shutterstock.com
Common Types of Parrots
- Grey Parrot – The grey parrot is a medium sized bird native to Africa. They are predominantly grey with black bills and red tail feathers.
- Macaw – Macaws range in size from small (like the Hahn’s Macaw, measuring around 12 inches long) to large (like theHyacinth macaw, measuring around 40 inches long). Macaws are native to Mexico, Central America, and South America. These birds have long tails and large beaks.
- Cockatiel – Cockatiels are small birds with pointed tails that are endemic to Australia. Pet cockatiels have been bred to exhibit a variety of colors. Wild cockatiels are generally grey with white flashes on either wing and orange spots on the sides of their face.
- Budgerigar – Also known as the parakeet, this bird is small and long-tailed bird. These birds are bright green with yellow heads and black barring on the wings. Budgerigars are local to Australia.
- Amazon Parrot – Amazon parrots are medium sized, short-tailed parrots native to South America, Central America, and the Caribbean. These birds are primarily green with bright accenting colors, differing by the species.
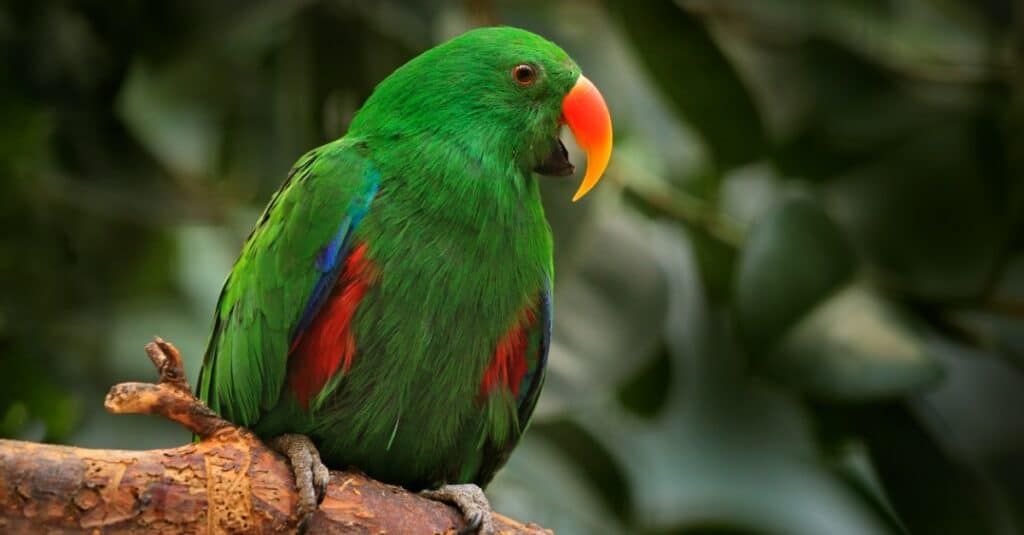

Eclectus Parrot are found in Western Papuan Islands, New Guinea.
©iStock.com/Ondrej Prosicky
Appearance and Behavior
Parrots vary in their bright colored feathers and each species varies in its pigmentation. Most people think of a these birds as bright green, accented by beautiful, strong, curved bills. Standing upright, parrots perch and even walk around upright with their clawed feet.
Not all of these species are one color, such as the macaw, which range from black, red, or yellow. Macaws, like the majority of parrots, are not sexually dimorphic, meaning there is no visual difference between males and females.
In temperament, these birds tend to be affectionate, earning them status as well-loved pets for centuries. Their high energy levels may be more than a novice pet owner can handle, but these creatures express empathy at a unique level. However, the humans that they reside with play a huge role in a bird’s mood and behavior.
Do be cautious – some species are incredibly dangerous and aggressive if provoked. The Senegal parrot, for example, is rather small, but they will bite down hard with their sharp beak if they feel threatened, causing substantial pain and possible injury.
Most often parrots will only attack if in danger, a natural “fight or flight” response to protect themselves from harm. In captivity, whether in a zoo or home, parrots may throw food around and tear up their surroundings if agitated or fearful. Parrots are chatty throughout the day and night, filling their homes with an array of loud vocalizations and potential imitations.
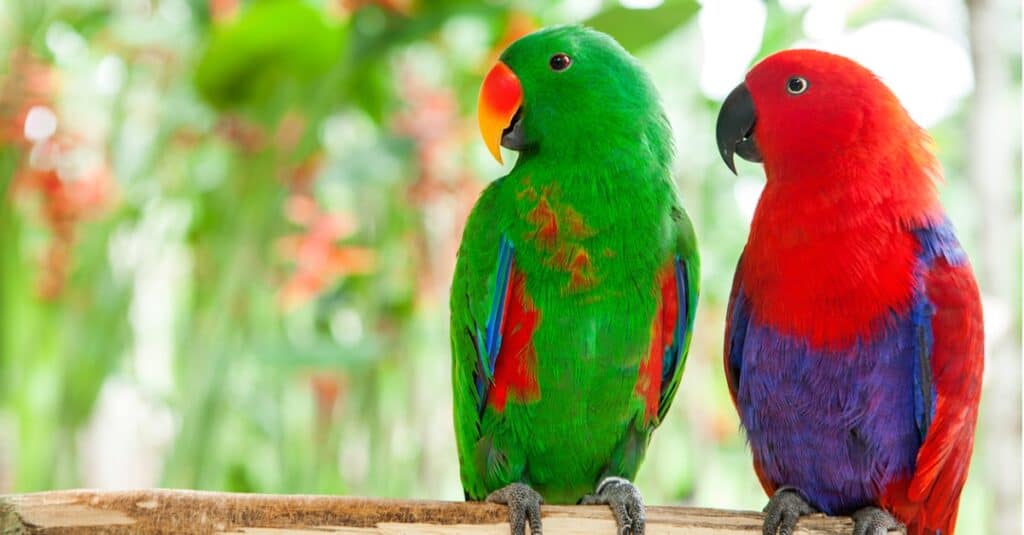

This parrot’s chirp can reach up to 115 decibels.
©iStock.com/redchanka
Personality
Parrots are incredibly smart and witty. If kept as a pet, they form a tight bond and are mostly friendly and social. They enjoy being close to the social activity in the home, allowing them to build trust and form lasting relationships.
Highly energetic, parrots have surprisingly short attention spans. However, they make plenty of time to provide a dramatic display of their emotions, thanks to the empathetic nature of the bird. As these birds spend more time with its human owner, it may start to imitate common phrases and sounds that it hears.
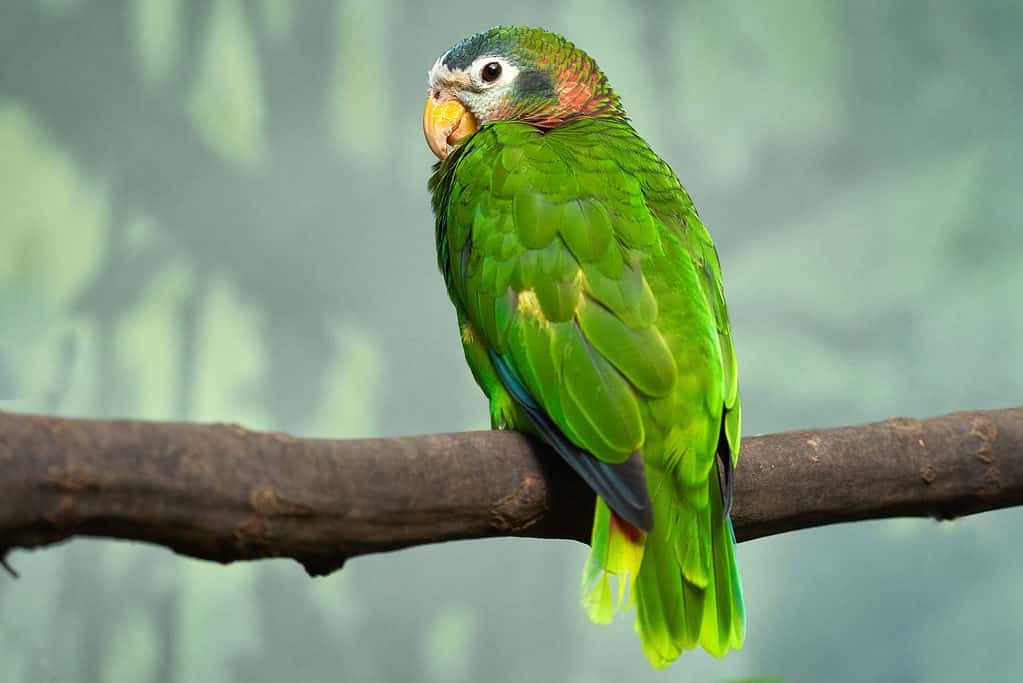

The yellow-billed parrot is one of the many feathered residents of Jamaica.
©Ondrej Prosicky/Shutterstock.com
Habitat
Parrots often thrive in tropical areas, due to the warm and humid climate. However, they don’t necessarily require this habitat to survive, which is why so many of the birds reside in warm climates worldwide. Apart from pet stores, there species naturally span across Australia, South America, and Central America.
Most wild parrots will build a place to rest in broad-leafed deciduous trees and bright tropical plants while domesticated ones are able to adapt to their present home environments.
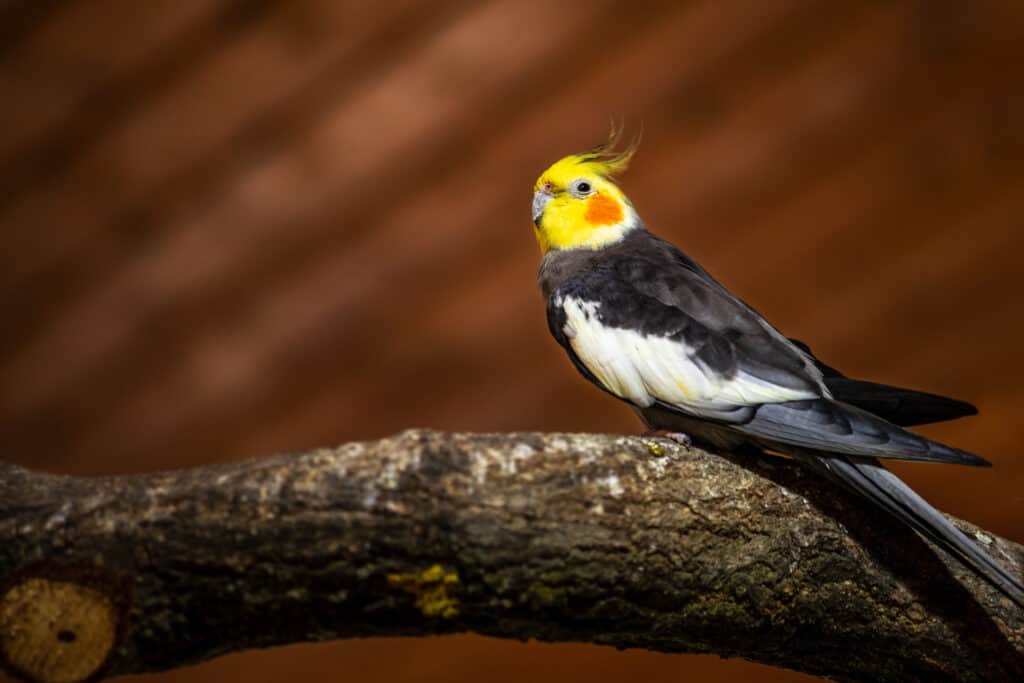

Grey-yellow female budgie cockatiel parrot thrives in tropical areas.
©iStock.com/Vronja_Photon
Diet
Omnivorous in nature, these birds have a varied diet. As a pet, diet should mimic that of a wild parrot’s, including raw or steamed vegetables, fruits, nuts, seeds, and whole grains (like rice, oats, quinoa, barley, or buckwheat). If available, an organic diet best supports a parrot, preventing them from ingesting dangerous chemicals that may cause health problems.
Most of the bird’s typical diet consists of fruits, nuts, seeds, flowers, and buds. Some species thrive (almost) exclusively on nectar. While they will consume both raw and cooked vegetables, the only animals that have to worry about their predatory nature are insects. If a parrot fails to find insects to eat, they will occasionally hunt snails, mice, or snakes instead.

Predators and Threats
Like all living animals, parrots are an important contributor to the natural food chain. They are both prey and predator in the wild, falling victim to raptorial birds that are larger than them.
However, the main threat to these birds is humans. Human activities – like deforestation, encroachment, industrialization, etc. – destroy their natural habitat. Along with the loss of habitat, human activities also weaken and damage the forests where parrots abide, preventing these birds and other animals from maintaining a consistent source of food, interrupting reproductive and growth cycles as well.
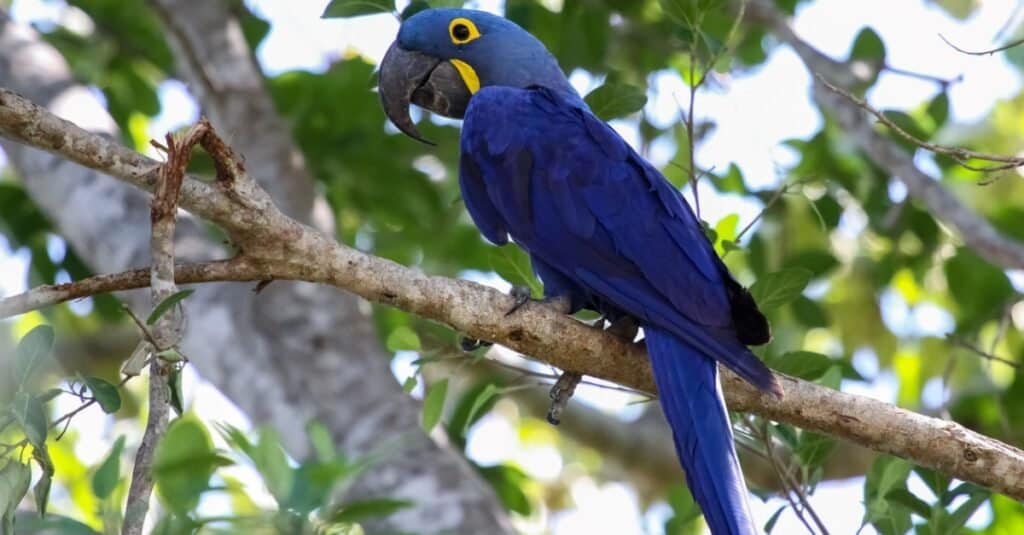

The hyacinth macaw is the largest flying parrot.
©iStock.com/Uwe-Bergwitz
Reproduction and Lifespan
Most species are monogamous, meaning they remain with the same partner for their entire lives. When these birds choose a breeding partner for themselves, they stay together throughout the non-breeding seasons as well.
Parrots prefer to mate with the changing seasons of their environment, mainly the warmer time of the year. Most often, the reproductive process starts during the spring months, due to the higher temperatures and the ample availability of food sources for offspring. During these months, parrots begin naturally releasing sex hormones, attracting opposite sexes for mating.
Like many other birds, parrots lay eggs. At one time, they usually lay about two to eight eggs. An incubation of about 18 to 30 days occurs before hatching. Parrot offspring are simply called “chicks” like many other avian species.
Small parrots tend to live for about 15 to 20 years, while larger species can live up to 80 years. A handful of these specie have broken records for living for 100 years! When considering an avian companion, it is crucial to understand that it is, potentially, a lifetime commitment.
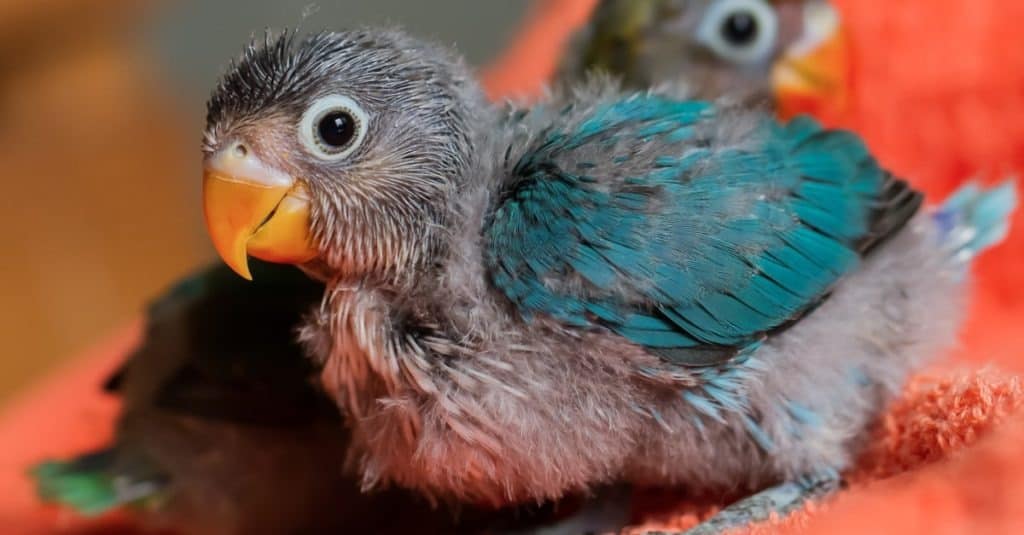

Parrots are monogamous, meaning they remain with the same partner for their entire lives. This can be up to 100 years!
©Shark_749/Shutterstock.com
Population
The exact number of parrots around the world is currently not well known. However, there are more than 350 species of parrots that exist in different parts of the world including a macaw, grey parrot, and monk parakeet.
Since parrots as a group were declared “not extinct” by the International Union for Conservation of Nature, no conservation efforts have been made on a broader scale. However, as recently as the last decade, the trading and habitat destruction of parrots led nearly 50% of these species to become endangered. Half of these species are now considered “critically endangered.” Some species – like the citron-crested cockatoo – are sold so frequently on the black market that local governments have imposed restrictions.
While some laws protect against trading and hunting, thanks to The Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species, parrots are largely still kept in captivity as pets or zoo attractions.Some of the zoos in the United States popular for their parrot exhibits include the San Diego Zoo, the Houston Zoo, and the Cincinnati Zoo and Botanical Garden.
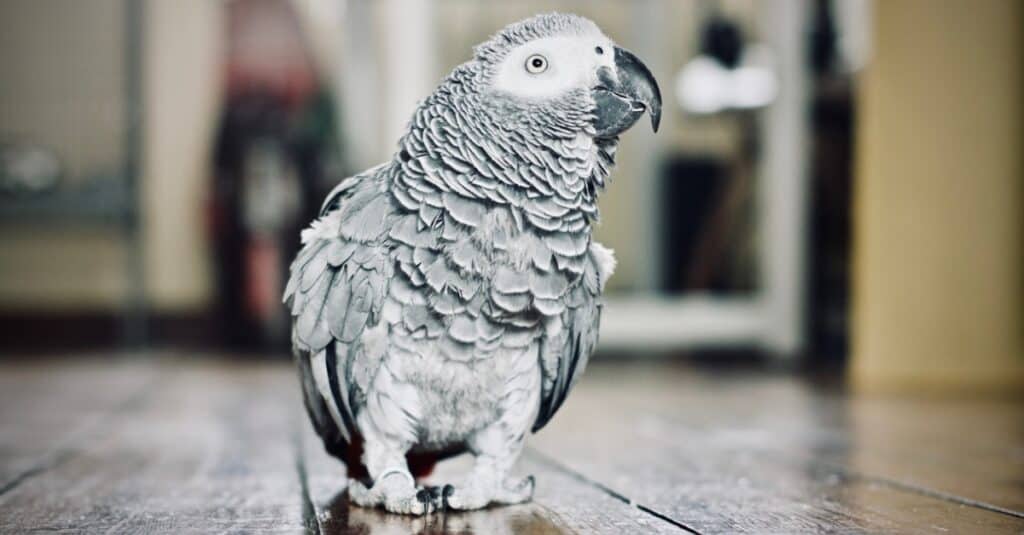

The African Grey Parrot can learn around 1,000 words. There are 350 types of parrtos in the world.
©iStock.com/Adrian Black
Conservation
Sadly, nearly a third of all parrot species are facing the danger of extinction. Human activity is typically the cause of this serious issue, with habitat loss and fragmentation being the largest problem. Illegal capture and poaching of nests also play a significant role. Other threats include climate change, disease, and environmental pollution. All of these factors have a negative effect on wild parrot populations.
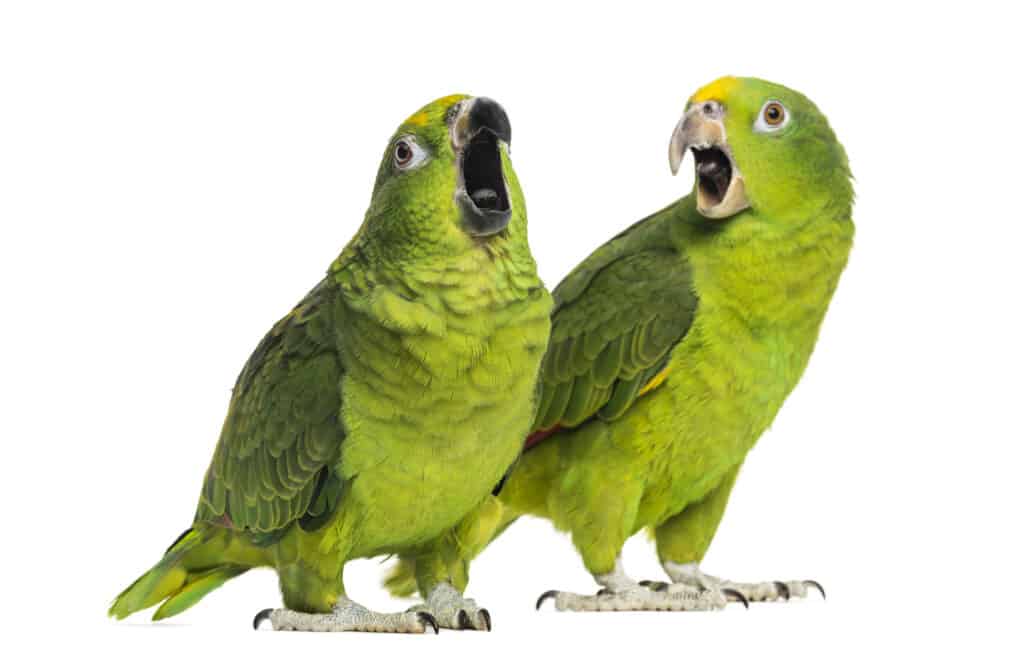

Parrots are critically endangered. Many parrot species have less than 50 living members on earth.
©iStock.com/GlobalP
Owner Tips
Before owning a bird, especially intelligent and highly attentive parrots, it is crucial to understand that these birds live for decades and require constant stimulation. All over the world, wild birds are illegally taken from their natural habitats and sold as pets. Tragically, almost 80% of these captured birds die before reaching their destination, killed by disease, starvation, trauma, or injury. Perpetrators capture these birds by violent means of cutting down trees or slicing through nests, resulting in destroyed habitats, affecting other bird and animal populations. While protectionshave been enacted to prevent such brutality, these rules are difficult to enforce and easy to get around. While certain bird species are able to reproduce in captivity, many of them are still being plucked from the wild.
Unfortunately, many pet owners do not research their companions before owning a bird and grow tired or annoyed by the animals. Some birds escape while others are released, resulting in feral populations. These non-native birds may introduce disease or invasive species to their new surroundings, detrimental to native bird and animal populations. If you are unable to further care for your domesticated bird, make sure to take it to a humane organization for it to be rehomed.
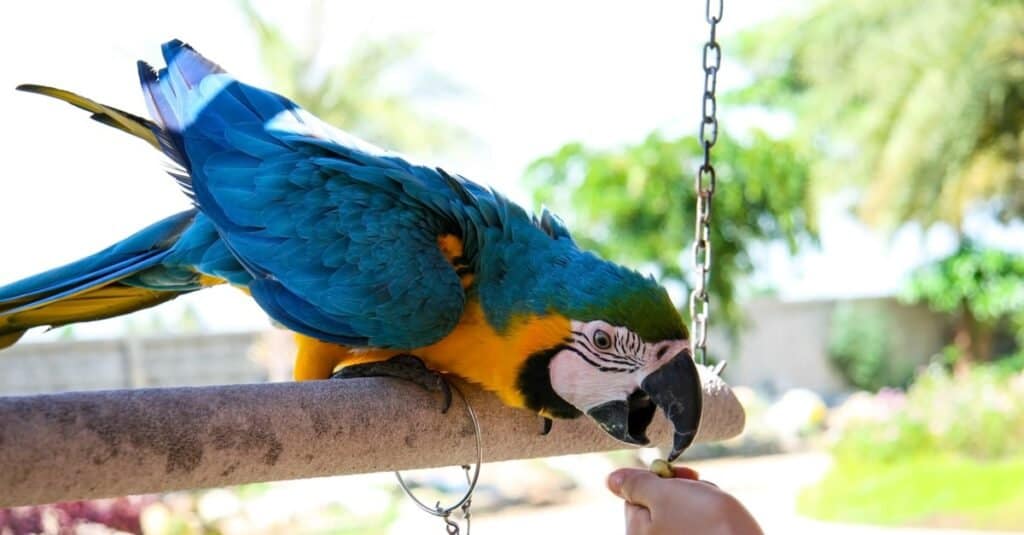

Before owning a bird, especially intelligent and highly attentive parrots, it is crucial to understand that these birds live for decades and require constant stimulation.
©TumCruise/Shutterstock.com
Intelligence and Learning
Some grey parrots have known a highly sensitive ability to associate words with meanings and be able to form simple sentences. These characteristics are common among crows, ravens, and parrots. Parrots are considered to be the most intelligent birds, their brain-to-body size ratio is comparable to that of great apes and other higher primates. Instead of using the cerebral cortex like mammals do, birds use the mediorostral HVC for cognition.
Not only have parrots shown how smart they are through scientific testing, but the use of their language ability is astounding. Additionally, some parrots have even been known to use tools and solve puzzles.
Learning early in life for these animals is very important and much of that learning comes from socially interactive environments. Social interactions are sometimes practiced with siblings or several other species. Parrots are known to form strong bonds with their playmates and owners.
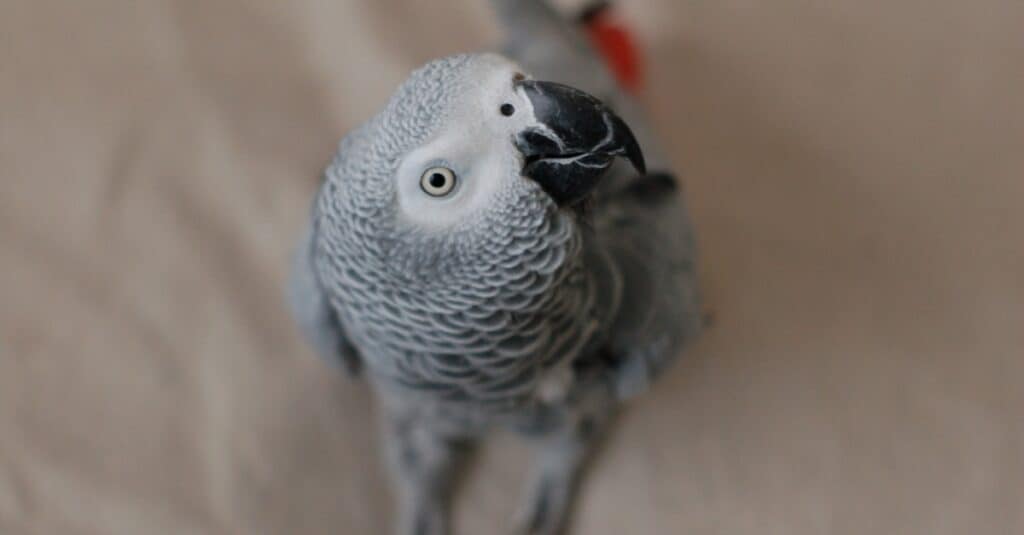

Not only have parrots shown how smart they are through scientific testing, but the use of their language ability is astounding. Additionally, some parrots have even been known to use tools and solve puzzles.
©iStock.com/Lilly Nonamaker
Parrot FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are Parrots herbivores, carnivores, or omnivores?
Parrots are omnivorous in nature which means that they eat meat as well as vegetation. In the wild, they mostly feed on nuts, buds, seeds, flowers, and fruits.
What Kingdom do Parrots belong to?
Parrots belong to the Kingdom Animalia.
What class do Parrots belong to?
Parrots belong to the class Aves.
What phylum to Parrots belong to?
Parrots belong to the phylum Chordata.
What family do Parrots belong to?
Parrots belong to the family Psittacidae.
What order do Parrots belong to?
Parrots belong to the order Psittaciformes.
What type of covering do Parrots have?
Parrots are covered in Feathers.
In what type of habitat do Parrots live?
Parrots live in rainforests and tropical jungles.
What is the main prey for Parrots?
Parrots eat fruit, nuts, seeds, and insects.
What are some predators of Parrots?
Predators of Parrots include humans, monkeys, and large birds.
Is a parrot a bird?
Yes, the parrot is a bird.
Can a parrot talk?
Parrots are famous for imitating several sounds. These sounds can sometimes also include human speech.
Are parrots friendly?
Parrots are known to be friendly, affectionate, and easy-going. Most of the parrots socialize easily and also empathize with their humans.
What do parrots eat?
In the wild, parrots mostly feed on nuts, buds, seeds, flowers, and fruits. However, when kept as pets, they can be fed raw or steamed vegetables and fruits, whole grains, pseudo-grains, and oats.
Can parrots fly?
Yes, parrots can fly, and their flying skills are often considered remarkable.
Do parrots migrate?
Some species of parrots are known to have migratory instincts.
How many eggs do parrots lay?
At one time, parrots lay, about two to eight eggs.
How fast does a parrot fly?
The flying speed of parrots can range anywhere between 40 mph to 50 mph.
What is a parrot’s wingspan?
Different species of parrots have different wingspans. Some of them have wingspans of about 41 to 45 inches.
When do parrots leave the nest?
When chicks leave their nests is unknown, but their incubation period ranges from 18 to 30 days after which the eggs hatch.
What are some distinguishing features of Parrots?
Parrots have large, colorful bodies and curved beaks.
What is an interesting fact about Parrots?
Parrots can live for up to 100 years!
What is the lifespan of a Parrot?
Parrots can live for 40 to 80 years.
How do Parrots have babies?
Parrots lay eggs.
What's the difference between macaws and parrots?
There are some differences between parrots and macaws, even though all macaws are technically parrots. Macaws are larger than most parrot varieties, and parrots are found in more locations worldwide compared to macaws.
Are parakeets different from parrots?
Parakeets are parrot species, but they differ in size, appearance behavior, and lifespan.
What are the differences between toucan and parrot?
The main differences between a toucan and a parrot are that they aren’t closely related, toucans have extremely large bills, and parrots are found globally while toucans are only found in South America.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- Britannica / Accessed January 14, 2021
- Science Kids / Accessed January 14, 2021
- Wikipedia / Accessed January 14, 2021
- Four Seasons Animal Hospital / Accessed January 14, 2021
- The Spruce / Accessed January 14, 2021
- Resources / Accessed January 14, 2021
- Live Science / Accessed January 14, 2021
- What are the major predators on parrots in the wild? / Accessed January 14, 2021
- Pars Trade Hungary KFT / Accessed January 14, 2021
- San Diego Zoo / Accessed January 14, 2021