Buffalo Fish
Species dependent
The oldest Buffalo fish recorded was 112 years old!
Advertisement
Buffalo Fish Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Actinopterygii
- Order
- Cypriniformes
- Family
- Catostomidae
- Genus
- Ictiobus
- Scientific Name
- Species dependent
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Buffalo Fish Conservation Status
Buffalo Fish Facts
- Prey
- Crustaceans
- Name Of Young
- Fry
- Group Behavior
- School
- Fun Fact
- The oldest Buffalo fish recorded was 112 years old!
- Biggest Threat
- Fishing
- Temperament
- Sociable
- Predators
- Larger fish and humans
View all of the Buffalo Fish images!
Buffalo fish have been known to live more than one hundred years!
Buffalo Fish Summary
The Buffalo fish, also known as the Ictiobus, is a large genus of freshwater fish that is one of the largest North American sucker fish. They can be found throughout the United States, Mexico, Guatemala, and Canada. Buffalo fish are often mistaken for carp due to the two fish’s similarities in appearance. These large fish thrive in a variety of different water systems, such as ponds, creeks, and lakes with temperate freshwater. They are native to North America and the genus belongs to five different species of Ictiobus.
3 Buffalo Fish Facts
- The largest of the Ictiobus fish genus can grow up to 82 pounds and reach up to 4 feet in size.
- The Bigmouth Buffalo fish (Ictiobus cyprinellus) has been known to live up to 112 years, and they fall under the category of an animal that’s lifespan can exceed 100 years, making them a supercentenarian.
- Buffalo fish consume just about anything that they can suck into their mouth, and they will filter inedible items like sand from their mouth and eat the edible pieces.
Buffalo Fish Species
Ictiobus describes a genus of five different freshwater sucker fish species. Each species classified as a Buffalo fish varies in size, with the largest of the Ictiobus genus being the Bigmouth Buffalo fish.
- Smallmouth Buffalo fish (Ictiobus bubalus)– A long-lived and stocky species that is found in the Mississippi river.
- Bigmouth Buffalo fish (Ictiobus cyprinellus)– One of the largest species in this genus and can grow up to 4 feet in size.
- Black Buffalo fish (Ictiobus niger)- North American species of Buffalo fish that was first discovered in Canada.
- Fleshylip Buffalo fish (Ictiobus labiosus)- A large demersal buffalo fish that is found throughout North America.
- Southern Buffalo fish (Ictiobus meridionalis)- A light-colored Buffalo fish that is long-lived and grows to an impressive size.
Buffalo Fish Appearance
The Buffalo fish has an olive coloration that is usually mixed with dark gray or golden scales. The appearance of the Buffalo fish differs according to the species, as the Southern Buffalo fish is considerably lighter in appearance than the Black Buffalo fish. Buffalo fish can reach a length of 4 feet; however, most species rarely exceed 2 feet in length.
This popular gamefish has a long dorsal fin that appears angular; their bodies are quite stocky, and they can weigh up to 82 pounds. However, most Buffalo fish only reach half their maximum weight. Although they are related to suckerfish, they do not have any barbels. Instead, they have an upturned mouth with thin sucker lips that they use to scrape algae off from rocks.
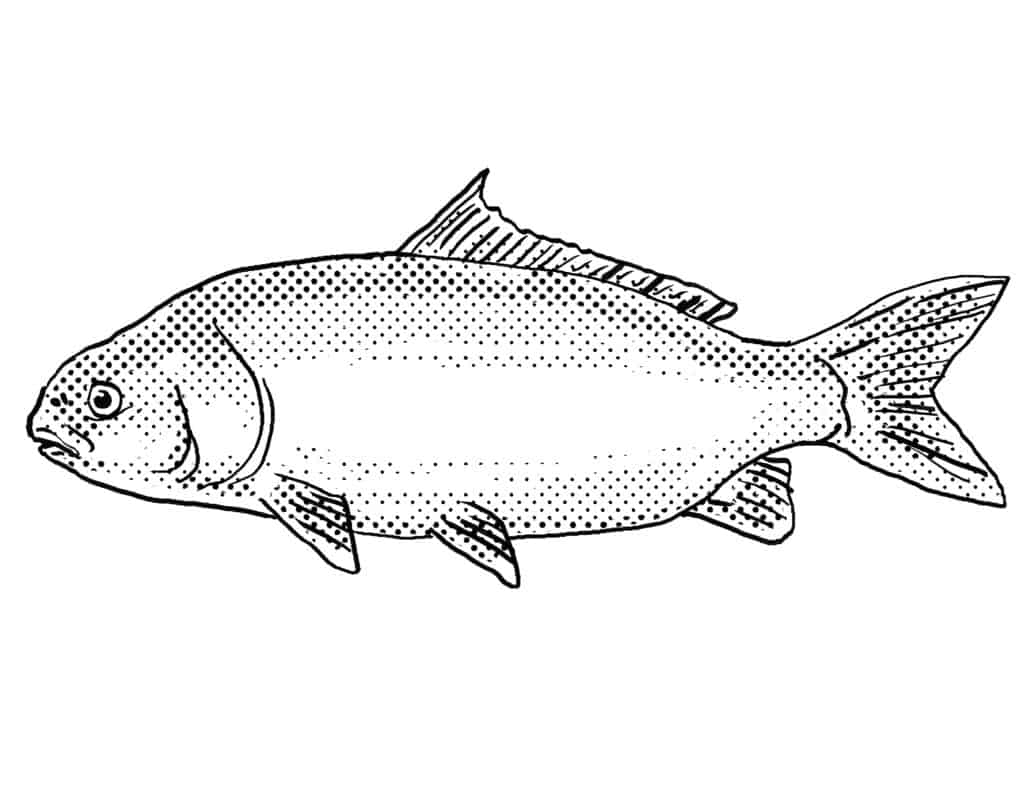
In this artist’s rendering, note the extended dorsal fin and stock body of the Buffalo fish.
©patrimonio designs ltd/Shutterstock.com
Buffalo Fish Distribution, Population, and Habitat
Distribution
Buffalo fish are native to North America, and they are distributed throughout Canada, Mexico, and Guatemala. Some species of Buffalo fish are found in larger regions, while others stick to a smaller geographical area. Each of the five species in the Ictiobus genus has its own geographical distribution, but they are all primarily from parts of Northern America from river basins or the Mississippi river.
Population
The Buffalo fish population is extensive throughout Northern America, and their population numbers are stable and have no cause for concern according to the IUCN red list. However, there are certain fish laws and regulations in some areas when it comes to Buffalo fish.
Habitat
The Buffalo fish lives in freshwater rivers, lakes, ponds, and creeks throughout North America. They live in shallow, sluggish waters where they swim at the bottom of the body of water, foraging through the muddy substrate and vegetation for food. Buffalo fish prefer to live in waters that contain a lot of vegetation because this is where they lay their eggs. The waters they inhabit are usually murky and contain mud as the main substrate.
Buffalo Fish Predators and Prey
Buffalo fish fall prey to larger fish, especially when they are juveniles. Since the Buffalo fish gets quite large and hide among dense vegetation, they usually stay out of predators’ way. One of the Buffalo fish’s main predators as adults is humans because they are a popular angler fish. The Buffalo fish’s low predator list may also be a contributing factor to how they can live for so long. Buffalo fish naturally prey on plankton, detritus, algae, insect larvae, small crustaceans, and other aquatic vegetation, making them omnivores.
Buffalo Fish in Fishing and Cooking
Fishing
Buffalo fishes were originally thought to be terrible gamefish because they were difficult to catch by a hook and line. Legal changes in 2010 have made Buffalo fish a target for bow fishing, which is why certain laws and fishing regulations were enacted in certain places. Buffalo fish are now considered to be a popular game fish and are great for fly-fishermen because they put up a fight. They can be caught with a fly rod and barbed hooks.
Cooking
Buffalo fish are considered to have a delicious taste with soft and juicy flesh in comparison to other fish like mackerel. Due to their reduced numbers since becoming a target for fishing, the Buffalo fish are not commonly caught to be eaten. They can be eaten raw or cooked, but they do contain a lot of bones that consumers should be cautious about when eating fish.
Buffalo Fish Reproduction and Lifespan
The Bigmouth Buffalo fish has been recorded to live up to 112 years, according to the measurement of their otolith ear bone by scientists. The Buffalo fish can live as short as 18 years of age, but the average lifespan reaches around 25 years. In captivity, the smallmouth buffalo fish only lives between 8 to 10 years, mainly because their environment is not as adequate as their large natural rivers and lakes that allow them to reach their full adult size.
Buffalo fish reproduce in waters that contain plenty of vegetation for their eggs to hatch and be hidden from predators. They travel upstream to reproduce and will usually migrate for this to be possible. Most Buffalo fish will travel in large groups to breeding grounds, where the females will release eggs and the males will fertilize them during spawning.
View all 285 animals that start with BBuffalo Fish FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Where are Buffalo fish found?
The geographical range of Buffalo fish is dependent on the species. All Buffalo fish are native to North America and can be found throughout Mexico, Guatemala, and Canada in the Mississippi river and river basins.
Are Buffalo fish the same as carp?
Buffalo fish are often confused with carp due to the similarities in the two species’ appearances and size. However, they are not related as the Buffalo fish is the largest member of the suckerfish family, while the carp is part of the minnow family.
What do Buffalo fish eat?
Buffalo fish are omnivores and generally eat anything that they can swallow. Their diet includes insect larvae, algae, detritus, plankton, aquatic plants, and crustaceans. They consume a lot of food and forage through muddy substrates or scrape their mouths against rocks with algae to capture their food.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- Wikipedia , Available here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ictiobus
- Biological Dictionary , Available here: https://biologydictionary.net/buffalo-fish/
- Fish Base , Available here: https://www.fishbase.se/summary/Ictiobus-bubalus.html

















