Suckerfish
Found in rivers & streams across America!
Advertisement
Suckerfish Scientific Classification
Suckerfish Facts
- Prey
- Algae, zooplankton, insects, small invertebrates, crustaceans, and plants
- Fun Fact
- Found in rivers & streams across America!
- Biggest Threat
- Pollution and dams
- Gestation Period
- Average of 10 days to eggs hatching
- Habitat
- Freshwater streams and lakes
- Predators
- Trout, bass, catfish, and walleye
- Diet
- Omnivore
- Number Of Species
- 79
- Location
- United States, Russia, and China
- Slogan
- Commonly found throughout America!
View all of the Suckerfish images!
Suckerfish belong to the family Catostomidae and live in freshwater environments across the world. It’s believed that suckerfish first evolved roughly 50 million years ago and today more than 79 species have been identified.
Although suckerfish are bony fish, they’ve historically been an important food source and can be found in streams and rivers across not only America but also other countries such as China.
Suckerfish are different from the species Hypostomus plecostomus, which is commonly called the ‘suckermouth catfish.’ The species is commonly used in aquariums and is frequently called the ‘janitor fish’ as it cleans algae buildup.
Remoras are another fish family often colloquially called ‘suckerfish’ thanks to their sucker-like organ that allows them to attach to large marine animals like sharks.

Suckerfish Facts
- Long-living fish: A suckerfish named the bigmouth buffalo (Ictiobus cyprinellus) is believed to be the longest-living freshwater fish on Earth! A study that used carbon dating estimated one bigmouth buffalo fish lived to be 112 years old!
Classification and Scientific Name
Suckerfish belong to the order Cypriniformes and the family Catostomidae. As of November 2020, there are 79 described species across 13 genera.
Examples of scientific names for specific suckerfish species includes:
- Black redhorse: Moxostoma duquesni
- White sucker: Catostomus comm
And specific generas include:
- Carpiodes
- Catostomus
- Chasmistes
- Cycleptus
- Deltistes
- Erimyzon
- Hypentelium
- Ictiobus
- Minytrema
- Moxostroma
- Myxocyprinus
- Thoburnia
- Xyauchen
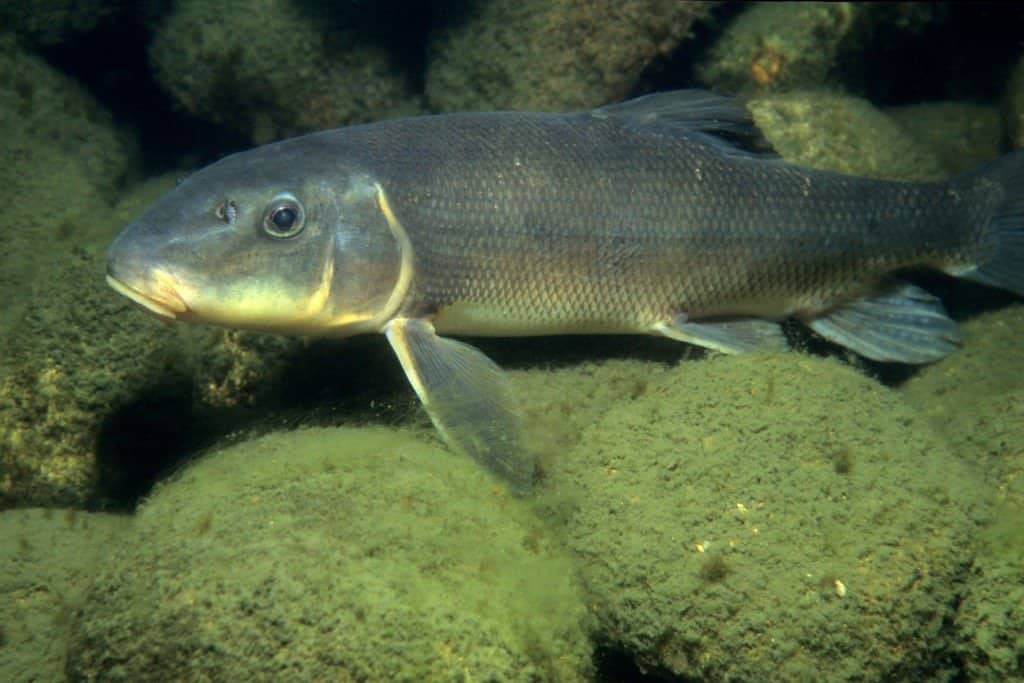

Suckerfish belong to the order Cypriniformes and the family Catostomidae.
©RLS Photo/Shutterstock.com
Types of Suckerfish
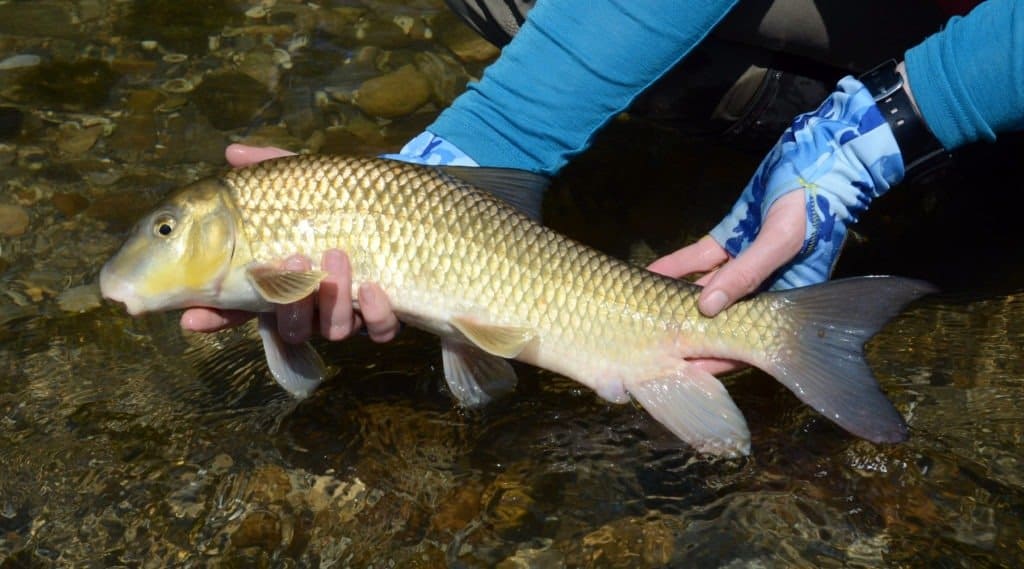

River redhorse is another sucker fish that was once quite common across the Mississippi watershed.
©M Huston/Shutterstock.com
With 79 identified species, there is a substantial amount of diversity across suckerfish species. Some of the most well-known include:
- White Sucker – The white sucker is found in streams and lakes across the Mississippi watershed. Typically a smaller sucker species weighing little more than 2 pounds, white suckers have occasionally reached sizes of 8 pounds. Thanks to its large distribution, the white sucker is sometimes known as the ‘common sucker.’
- River Redhorse – River redhorse is another sucker fish that was once quite common across the Mississippi watershed. However, in recent decades their range has declined. While ‘redhorse’ is often synonymous with suckers in local areas, there are a number of different species with ‘redhorse’ in their name. Other examples include the golden redhorse, silver redhorse, shorthead redhorse, and greater redhorse.
- Blue Suckers – Considered Near Threatened by the IUCN. Like other suckerfish, their population appears to be declining due to pollution and dam construction that has impacted their preferred environments.
- Smallmouth Buffalo – These suckers can be found in other areas but mainly near the Mississippi River and its tributaries. They resemble carp, and typically like faster-moving water yet can be found in lakes. They are closely related to other buffalo suckers.
- Northern Hogsucker – These suckers typically locate themselves in warmer waters that have a good downstream to provide them with rocks, pebbles, and other particles to scrape nutrients off. While they are not a threatened species, they do share a relationship with other species, and this sympathetic relationship causes issues for their survival in certain locations.
History and Evolution
While there are many different types of Suckerfish that live in many different parts of the world and have their own specific adaptations, they all have evolved to find a way to procure food where other fish and animals have not. It is a great testament to nature that proves that life finds a way or gets pushed to the side!
These different species of suckers evolved because individual members had physical characteristics that allowed them to outlive other members, and these more fit examples passed their specific genes onto their offspring and so forth through time.
Appearance

For suckerfish, the name ‘suckers’ is derived from their lips, which are thick and help the fish cling to the bottoms of streams and other freshwater habitats.
©MM Stock/Shutterstock.com
Suckerfish can grow to be up to about 3 feet (1 meter) long. Most species are between 1 to 2 feet. The largest species of sucker fish is the bigmouth buffalo, which can reach a maximum of 79 pounds (36 kg). An example of a smaller sucker species would be the blue sucker, which has an average mass of 5.5 pounds.
The name ‘suckers’ is derived from their lips, which are thick and help the fish cling to the bottoms of streams and other freshwater habitats.
Distribution, Habitat, and Prey
The vast majority of suckerfish species live in freshwater streams and lakes across the United States and North America. They can be particularly common in slower-moving channels of rivers or in reservoirs. Outside of North America, fish in the Catostomidae family can be found in Russia and a single species lives in China.
Suckers are bottom feeders and live on an omnivorous diet. They’ll consume algae, zooplankton, insects, small invertebrates, crustaceans, and plants.
Predators
Smaller suckerfish are preyed on by larger fish such as trout, bass, catfish, and walleye. Species such as buffalo fish that can reach larger sizes are generally not preyed upon once fully grown.
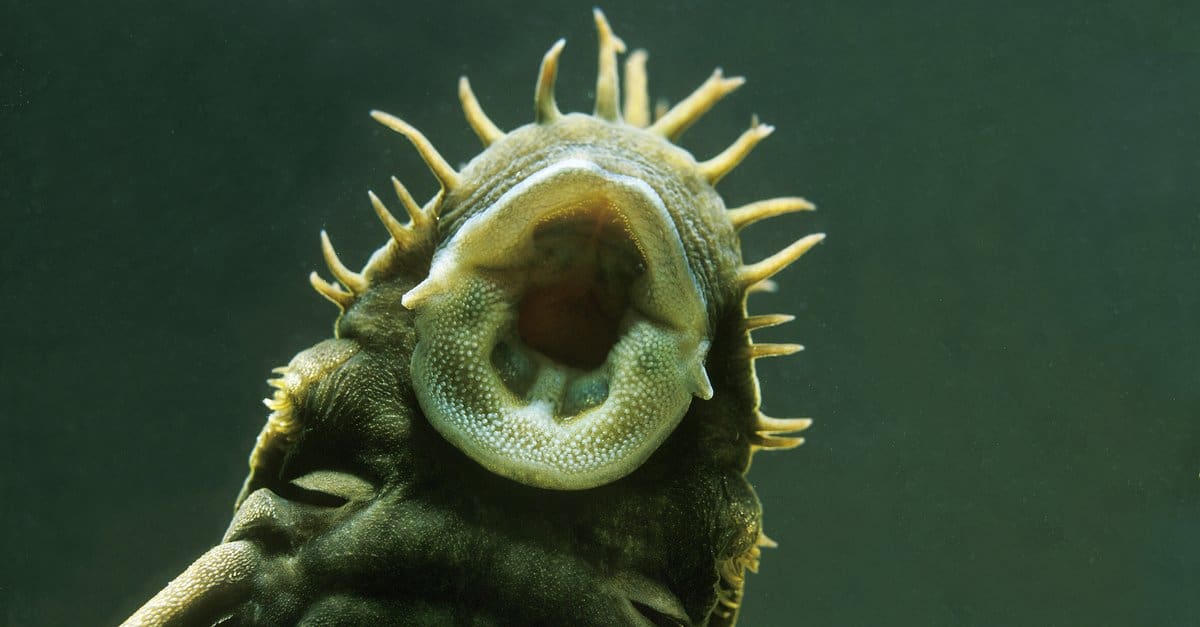

Suckerfish have thick lips that help the fish cling to the bottoms of streams and other freshwater habitats.
©slowmotiongli/Shutterstock.com
Fishing & Cooking
Suckerfish were a dietary staple for earlier civilizations, especially across America where Native Americans fished for this widely available and abundant species.
Today, the consumption of suckerfish varies. Smaller species like the white sucker are often used as bait. Larger sucker species need to be carefully cleaned to remove bones. Once cleaned, suckers are often fried. The meat is often described as sweet and flavorful.
View all 293 animals that start with SSuckerfish FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are Sucker Fish herbivores, carnivores, or omnivores?
Sucker Fish are Omnivores, meaning they eat both plants and other animals.
What Kingdom do Sucker Fish belong to?
Sucker Fish belong to the Kingdom Animalia.
What is the biggest threat to the Sucker Fish?
The biggest threats to Sucker Fish are pollution and dams.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- John Paxton, William Eschmeyer (1970) Encyclopedia of Fishes
- Animal Diversity Web, Available here: https://animaldiversity.org/accounts/Catostomidae/classification/
- Springfield News-Leader, Available here: https://www.news-leader.com/story/news/local/ozarks/2019/05/10/ozarks-tradition-grabbing-eating-sucker-fish-creeks-fishing/1151434001/
















