Tiger Trout
As tiger trout are sterile, they cannot produce offspring. However, they do have relatively long lifespans and can live up to 10 years in captivity.
Advertisement
Tiger Trout Scientific Classification
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Tiger Trout Conservation Status
Tiger Trout Facts
- Prey
- Small fish, invertebrates, insects, and larvae
- Group Behavior
- Solitary
- Fun Fact
- As tiger trout are sterile, they cannot produce offspring. However, they do have relatively long lifespans and can live up to 10 years in captivity.
- Biggest Threat
- Humans
- Predators
- Mergansers, Great blue heron, Pelicans, Kingfishers, Seals, Cod, River otters, minks
- Diet
- Carnivore
- Common Name
- Tiger trout
Tiger Trout Physical Characteristics
- Color
- Yellow
- Orange
- Grey-Brown
- Skin Type
- Scales
- Aggression
- High
View all of the Tiger Trout images!
Tiger trout (Salmo trutta/Salvelinus fontialis) are hybrids resulting from male Eastern brook trout and female brown trout cross-breeding. These unique offspring are sterile and usually do not naturally occur in the wild but are more often bred and reared in a hatchery. During the spawning season (in the fall), eggs are removed from a ripe female brown trout and fertilized by the milt taken from mature male Eastern brook trout. These hybrids will never be invasive because they cannot procreate.
Tiger trout derived their names from the squiggly patterns covering the sides of their bodies. However, some tiger trout have rosettes that closely resemble a leopard‘s spots. But it’s not just their appearance resembling the tiger, but also their attitude. These fish are extremely aggressive and have sharp teeth, making them stealthy predators.
Tiger Trout History
Without human interference, the tiger trout would not exist as the brown trout’s native range covers Eurasia, and the brook trout inhabits the freshwaters of North America. Therefore they would have never encountered one another in the wild. However, during the 1800s, widespread stocking of non-native gamefish began, and these two trout species started to establish wild populations alongside each other, and cross-breeding occurred soon after. The first recordings of stream-born tiger trout appear as early as 1944, and while this wild hybrid is still extremely rare, they have been documented several times since. However, tiger trout primarily result from fertilizing brown trout eggs with the milt from brook trout males. Trying to fertilize brook trout eggs with brown trout milt has proved unsuccessful because their eggs are too small. In addition, these two parent breeds have non-matching numbers of chromosomes, 84:80, so consequently, even if fertilization is successful in the wild, it generally fails to yield any offspring.
Three Amazing Tiger Trout Facts!
- Tiger trout are hybrids resulting from cross-breeding female brown trout and male brook trout.
- These hybrids are perfect for eliminating invasive species because of their high-prey drive and inability to reproduce.
- Tiger trout prefer colder water environments, especially lakes.
Tiger Trout Scientific Name
The tiger trout doesn’t have a valid scientific name. They are best described by combining their two parent breeds’ binomial names, Salmo trutta/Salveilnus fontinalis. They belong to the order Salmoniformes that mainly inhabit the waters of North America and Europe. Several members of this order possess primitive anatomical features representing an early stage in the evolution of modern bony fishes.
Tiger trout belong to the family Salmonidae, which includes some of the most sought-after gamefish in the world. They are famous for their delicious-tasting flesh and usually cost a pretty penny.
Tiger Trout Appearance
These hybrids closely resemble a labyrinth because of their grayish-brown bodies, covered with dark patterns. In addition, tiger trouts have bright orange and yellow bellies with square tail fins. Furthermore, their pectoral and pelvic fins are similar in color to their bellies. They have spotted patterns on their heads, very similar to the brown trout, and females aren’t as exuberant as the males. For example, females are generally tan and light brown in color, with fewer yellow and orange tones. Lastly, tiger trout can grow approximately 10 to 16 inches in length but can reach a maximum size of 20 inches. In addition, their weight ranges from two to five pounds.
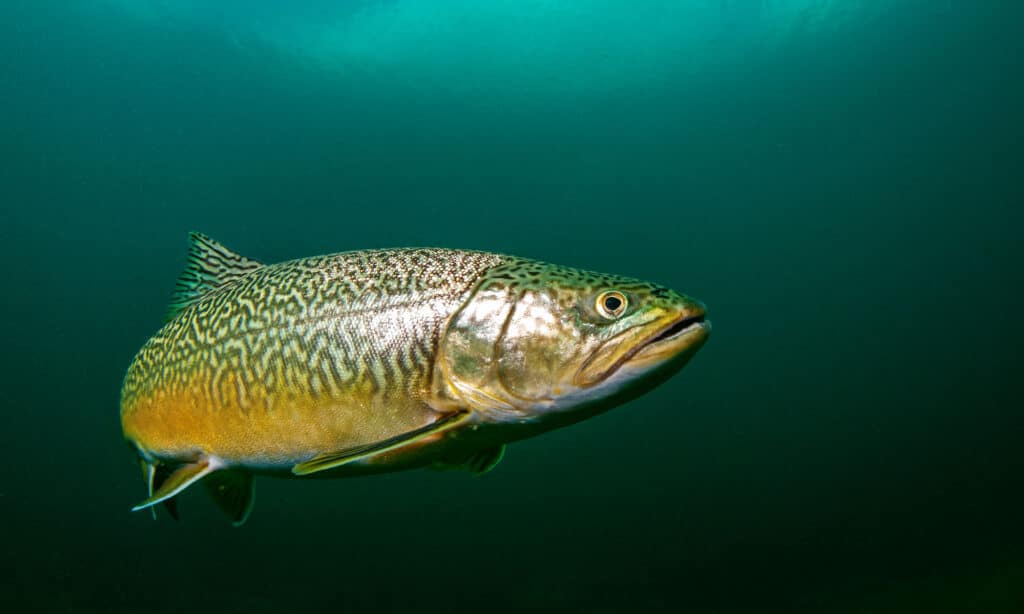

Tiger trout are hybrids and can’t produce offspring.
©MartinRejzek/Shutterstock.com
Tiger Trout Behavior
The tiger trout’s name is not only derived from its stripes. They also have a fierce attitude that can rival their furry namesake. These hybrids are aggressive piscivores with a fast growth rate. Additionally, they have proven effective at controlling invasive species, and since they can’t reproduce, there is no threat of their population sizes getting out of control.
Tiger Trout Habitat
Very few wild tiger trout exist, so these hybrids only occur in areas where they are produced. Therefore populations exist in places like:
- Indiana
- West Virginia
- Utah
- Wyoming
- Colorado
- Michigan
- Pennsylvania
- Washington State
- Minnesota
- New Jersey
- Ohio
- Nevada
- South Dakota
- Connecticut
- Montana
- Illinois
- Saskatchewan
- Canada
- New Zealand
- Australia
- United Kingdom
These freshwater fish thrive in colder temperatures, especially lakes, and usually prefer water with aquatic vegetation like freshwater algae.
Tiger Trout Diet
Tiger trouts are piscivores, which means that a large portion of their diet consists of fish. However, their primary diet includes a lot of invertebrates, insects, and larvae. Additionally, they are territorial fish, known for their aggressive feeding patterns and immense appetite. Other prey includes nymphs and streamers.
Tiger Trout Predators and Threats
Predators will differ depending on location, but trout usually fall prey to birds, mammals, and larger fish. Therefore predators include:
- Mergansers
- Great blue heron
- Pelicans
- Kingfishers
- Seals
- Cod
- River otters
- Mink
- Humans
Tiger Trout Reproduction, Babies, and Lifespan
As tiger trout are sterile, they cannot produce offspring. However, they do have relatively long lifespans and can live up to 10 years in captivity.
Tiger Trout Population
While there is no definite documentation about the population size of these hybrids, researchers believe there are around 238,000 individuals worldwide.
Similar Species
While these fish are a prize worth working for, they are very rare, and most anglers have to travel thousands of miles to find one. Therefore, they often seek out other similar species, which include:
Salmon
There are several species of salmon that belong to the family Salmonidae. They are primarily native to tributaries of the Pacific and North Atlantic Oceans. For example, there are seven species of Pacific salmon. There are five species in North America:
- Chinook
- Coho
- Chum
- Sockeye
- Pink
Additionally, there are two species in Asia, masu and amago, and lastly, Atlantic salmon.
The largest salmon from the family Salmonidae is the Chinook, or King Salmon, as they grow 24 to 36 inches in length, with a maximum of 4.9 feet. Their weight ranges from 10 to 50 pounds, but the heaviest on record is a whopping 130 pounds! The family’s smallest member is pink salmon, only growing up to 30 inches long and weighing between 3 and 5 pounds.
Their appearance varies widely between species. Their colors include green and silver with black stripes or spotted patterns.
Arctic Char
The Arctic char is mainly a freshwater fish scattered across the Northern polar belt. However, they have an extensive geographical range throughout North America, Greenland, and Scandinavian countries. While they are primarily freshwater fish that inhabit rivers and lakes, they also occur in certain coastal regions.
Arctic char are often mistaken for salmon and trout because their features and tastes are similar. The best time to catch these fish is during their migration season, as they swim from rivers to freshwater to spawn. Their spawning occurs in the fall, usually during the months of September to December. Once their eggs hatch, the offspring will spend five to seven months in the rivers before finding a permanent habitat. Their diet consists of insects, fish eggs, zooplankton, small crustaceans, snails, and small fish. However, they also fall prey to bears, otters, birds, and humans.
Alaskan Halibut
Alaskan halibut occur throughout most of Alaska’s marine waters. However, they can also be found along the continental shelf as far as southern California, the coasts of Japan, and Russia. They are quite large, some exceeding 400 pounds! In fact, the state record is a whopping 459 pounds and was caught in Unalaska Bay in 1996. Male halibuts grow slower than females and are smaller than females of the same age. On average, most halibut caught in sport fishery are between 5-15 years old, and males rarely exceed the 100-pound mark.
During their first year of life, their diet consists of plankton, but from one to three years old, they prefer krill and small fish. However, fish makes up most of their diet once they reach adulthood. Their preferred prey includes:
- Pollock
- Sablefish
- Cod
- Rockfish
- Octopus
- Herring
- Crabs
- Clams
- Smaller halibut
Tiger Trouts in Captivity
Since this species was created in captivity, they are great for large aquariums. However, they have many requirements and can be pretty high-maintenance, so they are not ideal for novice owners.
What Size Should the Tank Be?
You need a minimum 300-gallon tank for one tiger trout. They will require a larger tank if you plan to keep more than one.
What Are the Tank Requirements?
Besides having a 300-gallon tank, these fish need plenty of hiding places amongst rocks and driftwood. Also, they thrive in groups, which is strange because they are generally solitary, so it’s best to get more than one. You will need a robust filter system because they do best in an oxygen-rich environment. Furthermore, the temperature must be set between 72°F and 82°F for them to feel comfortable.
Tiger trout aren’t fussy when it comes to food and will eat nearly anything. However, when first introduced to the tank, they need live food like bloodworms until they have settled into their new surroundings. Once they are accustomed to their new home, you can feed them foods like krill or brine shrimp.
Tank Mates
In general, tiger trout are fine with other fish as long as there is enough space. However, they are territorial and aggressive, so these hybrids are not the best choice for aquariums with community fish. Additionally, they will eat smaller species and invertebrates, so only select larger species for the tank, two to three times their size. So, if you have enough space, good options are:
- Cichlids like peacocks or Oscars
- Catfish like giant danios
- Large plecos
In addition, avoid slow-moving or passive species like angelfish, guppies, discus, mollies, tetras, loaches, and small catfish. However, caution should always be taken when introducing any new species to the aquarium, as tiger trout are notorious for their aggressive behavior.
Are Tiger Trout Good to Eat?
Yes! Tiger trout is not only physically appealing, but they also taste delicious. In addition, these hybrids are often caught on light tackle, which is usually a pleasant surprise because they are so rare. You can prepare them like any other trout, but the preferred method is to pan-fry them. When cooking these tasty fish, use very little oil or butter. Season with a dash of wine vinegar or fresh lemon juice, salt, and pepper. Their flavor is so delectable that too many ingredients will spoil this fish.
What Biggest Recorded Tiger Trout Ever Caught?
The biggest tiger trout on record measured 44 inches long and weighed over 31 pounds! This beast of a fish was caught at Monroe Park Pond in Covington, Kentucky, by an angler named Doug Westmoreland in January 1998. While his achievement was legendary, Doug did not keep his prize; instead, he donated to a local fishing club.
Up Next
View all 133 animals that start with TTiger Trout FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What is the biggest tiger trout?
The biggest tiger trout on record measured 44 inches long and weighed over 31 pounds! This beast of a fish was caught at Monroe Park Pond in Covington, Kentucky, by an angler named Doug Westmoreland in January 1998. While his achievement was legendary, Doug did not keep his prize; instead, he donated to a local fishing club.
What two fish make a tiger trout?
Tiger trout (Salmo trutta/Salvelinus fontialis) are hybrids resulting from male Eastern brook trout and female brown trout cross-breeding.
Are tiger trout rare?
While there is no definite documentation about the population size of these hybrids, researchers believe there are around 238,000 individuals worldwide.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- Wikipedia, Available here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tiger_trout
- The Fisherman, Available here: https://www.thefisherman.com/article/freshwater-the-tiger-trout/
- iNaturalist, Available here: https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/705661-Salmo-trutta---Salvelinus-fontinalis