Texas Blind Snake
Rena dulcis
These snakes grow to just 11 inches long
Advertisement
Texas Blind Snake Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Reptilia
- Order
- Squamata
- Family
- Leptotyphopidae
- Genus
- Rena
- Scientific Name
- Rena dulcis
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Texas Blind Snake Conservation Status
Texas Blind Snake Facts
- Prey
- Insect larvae, ants, termites
- Fun Fact
- These snakes grow to just 11 inches long
- Litter Size
- 1-6 eggs
Texas Blind Snake Physical Characteristics
- Color
- Brown
- Silver
- Pink
- Skin Type
- Scales
- Length
- 4-10 inches
- Venomous
- No
- Aggression
- Low
View all of the Texas Blind Snake images!
“These snakes grow to just 11 inches long.”
The Texas blind snake is sometimes called a Texas slender blind snake or a Texas thread snake. These are fitting names for a snake with a very narrow body that measures just four to eleven inches in length. The diet of this snake includes insect larvae, ants, and termites. It’s not venomous and lives in a woodland, savanna, or shrubland habitat. This small snake is docile and sometimes kept as a pet.

4 Texas Blind Snake Amazing Facts
- It doesn’t have any teeth, so it cannot bite its prey or humans
- These tiny snakes are known to eat the ants and parasites living in a nest full of eastern screech owl chicks
- They are sometimes found in homes living in moist, dark areas such as inside ductwork
- They can release an odor in an effort to deter predators such as armadillos
Where to Find a Texas Blind Snake
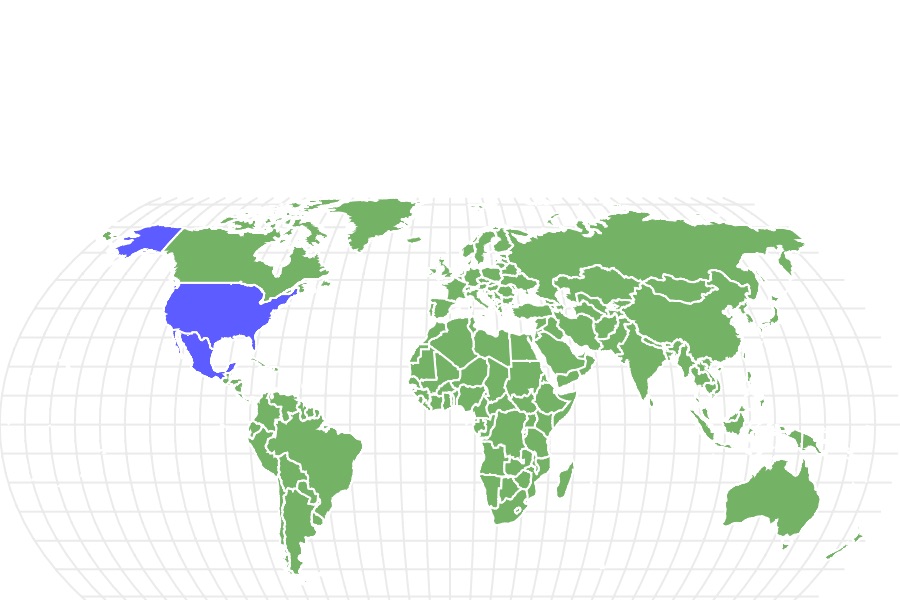
The Texas thread snake lives in the United States in North America. Specifically, it lives in Texas, Kansas, New Mexico, Arizona, and Oklahoma. It also lives in the northeastern part of Mexico.
These are burrowing snakes living underground in moist soil. They are known to show up above ground after heavy storms. Not surprisingly, they are often mistaken for earthworms! Just think of how many times you’ve seen earthworms on the sidewalk after a rainstorm.
Scientific Name
Rena dulcis is the scientific name of the Texas blind snake. Dulcis is a Latin word meaning sweet. It’s unclear what this description refers to. Its family is Leptotyphopidae, and it’s in the class Reptilia.
The subspecies of this snake are:
- Rena dulcis rubellum
- Rena dulcis supraorbicularis
Appearance
The Texas blind snake (Rena dulcis) is a small, slender snake that typically grows to an average of six inches in length. Its body is grayish-brown or black, and its underside is pinkish or tan. It has no eyes, hence the “blind” part of its name; instead, it has two pale spots just behind the head, which are thought to be light sensors. The scales on this species are smooth and shiny, arranged in 17 rows around its body. Its tail tapers off slowly towards the end and can sometimes be used for burrowing into loose soil or sand, as well as detecting prey through vibrations in the ground. As an adult, they feed mainly on ant larvae and eggs but also consume termites, beetles, grubs, earthworms, and other insects found underground.
Diet and Habitat
Texas blind snakes, also known as Texas Thread Snakes, are burrowing reptiles that primarily feed on invertebrates such as insects and their larvae. They can be found in a variety of habitats, from forests to deserts, but generally prefer moist soil with plenty of organic matter. Depending on the climate and availability of prey, they may eat other small invertebrates like earthworms or even small amphibians such as frogs or salamanders. They are non-venomous, so they use constriction to capture and subdue their prey before consuming it whole. Their diet is supplemented with decaying plant material which provides them with additional nutrients needed for survival.
Conservation and Threats
The Texas blind snake (Rena dulcis) is classified as Near Threatened according to the IUCN Red List. This means that, although it is not currently endangered, there is a risk of its population decreasing due to certain factors in the near future. The main threats that this species faces are habitat loss and degradation due to human activities such as urbanization and agricultural development. Other threats include road mortality, predation by non-native animals, and collection for the pet trade or scientific research. To ensure their survival, conservation efforts must be taken to protect their habitats from any further damage and limit any exploitation of these snakes for commercial purposes or personal entertainment.
The population of the Texas slender blind snake is estimated at more than 100,000 adults.
Appearance and Description

The Texas blind snake looks like an earthworm at first sight.
©LA Dawson / CC BY-SA 2.5 – License
The first thing to learn about the appearance of the Texas blind snake is it looks a lot like an earthworm. It has brown or reddish glistening skin with a silver tone to it. But, if you look closely at a Texas threadsnake and an earthworm, you’ll see the Texas threadsnake has scales while an earthworm does not.
Its eyes are two small black dots on its head. Their eyes look like they are buried beneath layers of opaque scales. The snake measures four to eleven inches long and is about the width of a pencil.
The Texas blind snake has a blunt head and no teeth, and its lower jaw is shorter than its upper one.
How to identify a Texas blind snake:
- Brown, reddish shiny scales with silver tones
- Two tiny black eyes beneath its opaque scales
- A blunt head
Reproduction and Lifespan
Texas blind snakes (Rena dulcis) reproduce by laying eggs. The females typically lay around 4-6 eggs at a time in a moist, dark location such as rotting logs or underground burrows. These eggs hatch after about two months, and the young snakes reach sexual maturity within one year. In terms of lifespan, Texas blind snakes usually live for 3 to 5 years in the wild but can survive up to 10 years with proper husbandry and care in captivity.
Pictures

The Texas blind snake looks like an earthworm at first sight.
©LA Dawson / CC BY-SA 2.5 – License
How Dangerous Are They?
The Texas slender blind snake is not poisonous. In fact, it has no teeth, so it doesn’t bite. Even if it did have teeth, this creature’s mouth and head are so small that its bite would be painless. You may not even notice it!
Though not dangerous, the Texas blind snake is sometimes called a nuisance by homeowners. These snakes can live inside ductwork or even beneath the foundation of a home. They don’t cause structural damage but can sometimes make their way into the living area of a home.
While the Texas blind snake doesn’t bite, it’s a good idea to wash your hands with soap and water after handling it. Someone who keeps this snake as a pet should certainly make it a habit to wash up after handling this snake. Snakes can sometimes carry bacteria on their scales that are not visible to a human’s eyes.
Behavior and Humans
Texas blind snakes are timid and hide underground the bulk of the time. When they are found in a home’s ductwork or elsewhere, they can be removed by a professional. However, these snakes eat insect larvae, termites, and ants, so some homeowners may decide to leave the snakes alone to conduct their business!
View all 133 animals that start with TTexas Blind Snake FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are Texas blind snakes venomous?
No, Texas blind snakes are not venomous.
How do Texas blind snakes hunt?
Despite its name, this snake is not completely blind. It can see some light but uses its sense of smell to track down chemical trails left by its prey of ants and termites. When it finds an insect or insect larvae, the Texas slender blind snake uses its lower jaw to rake the prey into its mouth and swallows it. This method of eating its prey has been compared to a household vacuum cleaner sucking up dirt from a carpet.
Are Texas blind snakes aggressive?
No. Texas blind snakes are docile and timid. Their gentle temperament has made them a popular pet with some reptile fans. Of course, just as it hides in the wild, a Texas blind snake kept as a pet is likely to hide in its enclosure as well.
Where do Texas blind snakes live?
They are found in the United States in Texas, Kansas, New Mexico, Oklahoma, and Arizona. Northeastern Mexico is another area where these snakes live.
What do Texas blind snakes eat?
They are called insectivores eating termites, ants, and insect larvae.
Are Texas blind snakes really blind?
No. They can see some light but depend on their sense of smell to detect chemical trails left by their insect prey.
Is Texas blind snake poisonous?
No, they aren’t poisonous.
Where are Texas blind snakes found?
They live in a woodland, shrubland, or savanna habitat. This snake uses its blunt snout like a shovel as it digs and burrows into the moist soil creating tunnels.
Sometimes they make their way out of their usual habitat and into a home where there are plenty of insects to eat.
How big do Texas blind snakes get?
These are considered very small snakes growing to a maximum length of 11 inches.
How do you get rid of Texas blind snakes in the house?
The best way to get rid of Texas blind threadsnakes is to make your home less appealing to them. Move piles of logs, debris, and other yard waste away from the outside of your home. These elements attract insects which makes your home attractive to these snakes.
Also, check for pathways that lead beneath your home to its foundation. Close up those pathways to discourage Texas blind snakes from finding a cozy place to live.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- EOL, Available here: https://eol.org/pages/792144
- Earth Touch News Network, Available here: https://www.earthtouchnews.com/natural-world/animal-behaviour/screech-owls-keep-blind-snakes-as-live-in-housekeepers/
- IUCN Redlist, Available here: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/64057/12740793
- The Reptile Database, Available here: https://reptile-database.reptarium.cz/species?genus=Rena&species=dulcis&search_param=%28%28search%3D%27Rena+dulcis%27%29%29
- USA Snakes, Available here: https://usasnakes.com/rena-dulcis-texas-blind-snake/
- Wikipedia, Available here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rena_dulcis
- The Pet Enthusiast, Available here: https://thepetenthusiast.com/snakes-that-look-like-worms/