Advertisement
Pelycosaurs Scientific Classification
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Pelycosaurs Conservation Status
Pelycosaurs Facts
- Diet
- Omnivore
Pelycosaurs Physical Characteristics
- Weight
- 100kg-150kg (200lb -300lb)
- Length
- 3 m (118.11 inches)
- Venomous
- No
- Aggression
- Low
View all of the Pelycosaurs images!
The pelycosaurs are a group of small, primitive mammal-like reptiles that lived during the Late Paleozoic era. They were the dominant land animals for millions of years during the Permian period. Although they’re popularly grouped with the dinosaurs, Pelycosaurs are not dinosaurs. They lived and went extinct before the first dinosaurs came on the scene. The group is considered the earliest and most primitive synapsids, a group of animals that evolved into mammals.
Description & Size
In the past, the pelycosaurs were considered a separate order. However, it is no longer an order, and the term is no longer used in modern paleontology. Pelycosaurs are a group of synapsids that appear to have had direct ancestral links to present-day mammals.
Scientists often consider the pelycosaurs as an intermediate group between reptiles and mammals which is why they’re commonly called mammal-like reptiles. In terms of appearance, they resemble giant lizards, but they’re not reptiles at all. Some of the most notable genera in this group include the Dimetrodon, Ophiacodon, Edaphosaurus, and Sphenacodon.
Some species were quite large, growing to a length of 3 meters (10 ft) or more, although most species were much smaller. Unlike many of the present-day reptiles, pelycosaurs did not have scales all over their body. However, scientists think some species might have had horny scutes on some part of their body while the remaining part had naked, glandular skin similar to that of mammals.
At least two groups of pelycosaurs had a tall sail on their backs. The sails typically consisted of elongated vertebral spines that rose vertically to a height of up to one meter on their back. The sail was covered by highly vascularized skin and probably assisted them with thermoregulation. Scientists also think they might have been used for mating displays. However, it is important to note that not all pelycosaurs had a sail. At least two groups had massive sails; the edaphosaurids and sphenacodontids.
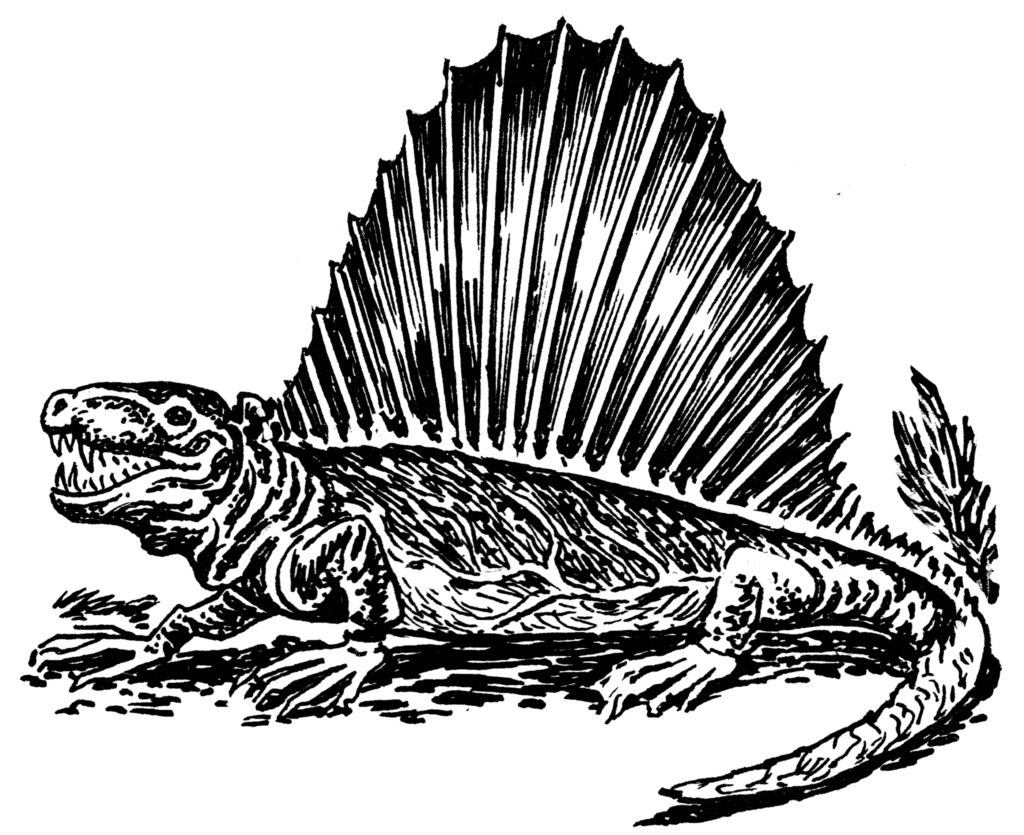
Pelycosaurs are often mistaken for reptiles. However, that is incorrect as they were discovered to have only one opening in their skull vs. two, which is a keynote feature of a reptile.
©Pearson Scott Foresman, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons – License
Diet – What Did Pelycosaurs Eat?
Pelycosaurs were a diverse group that exhibited varying traits and habits. The Dimetrodon, one of the largest and most popular Pelycosaur, was a carnivore with large, powerful jaws and sharp teeth for tearing into flesh.
However, not all Pelycosaurs were carnivorous. Some, such as the Caseidae and the Edaphosauridae, were herbivorous. The most popular plant-eating pelycosaurs were the Edaphosaurus. It was slightly smaller than the Dimetrodon, with a small skull and large peg-like teeth that it might have used for grinding and crushing plants.
Habitat – When and Where Pelycosaurs Lived
The Pelycosaurs lived during the Permian period, a time when all the earth’s landmass was connected as a single supercontinent known as Pangea. This massive global terrestrial habitat supported the development of various vertebrate groups, including the pelycosaurs. Their fossils have been found in different locations all over the world, which is expected since the entire planet was a single land mass at the time.
Threats and Predators
Many Pelycosaurs were themselves large predators that enjoyed wide success against other groups. The Dimetrodon, for instance, was a powerful carnivore and a top predator during the Permian period. It had numerous sharp teeth that would have made it possible to feed on other large vertebrates. Scientists think its diet may have included other pelycosaurs as well.
Discoveries and Fossils – Where It was Found
Pelycosaur fossils have been found in various locations all over the world. The most notable finds have been in Europe and North America. However, a few late surviving forms have been discovered in South Africa and Russia.
In the United States, Pelycosaur fossils are among the most notable fossils in Early Permian deposits. They’re quite common in Texas and Oklahoma, where their discovery is common during oil exploration. Scientists consider the discovery of these fossils to be very important. Studying them provides great insights into the evolution of mammals.
Extinction – When Did It Die Out?
The pelycosaurs appeared towards the end of the Carboniferous period of the Paleozoic era. The Early Permian was the height of their existence; at this time, they dominated the terrestrial animal world for around 40 million years. They peaked in the early Permian and were the dominating terrestrial creatures for about 40 million years, but then saw a severe fall throughout the late Carboniferous and early Permian. A few continued into the Capitanian, but they experienced a sharp decline shortly afterward and were eventually succeeded by the therapsids as the dominant group of land animals
Similar Animals to The Pelycosaurs
Similar animals to the pelycosaurs include:
- Dinosaurs: This is one of the most successful groups of animals to have ever lived. The dinosaurs were diverse in size and shape. They appeared shortly after the pelycosaurs went extinct.
- Therapsida: This is a group of synapsids that includes present-day mammals and their closest ancestors. This group evolved from the Pelycosaurs about 272 million years ago.
- Archosaurs: This refers to a group of synapsids that were the most dominant land animals during the Triassic. The dinosaurs evolved from the Archosaurs.
Related Animals
View all 192 animals that start with PPelycosaurs FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are Pelycosaurs Dinosaurs?
Although people erroneously group them as dinosaurs, the Pelycosaurs are not dinosaurs. They are a primitive group of synapsids that are more closely related to present-day mammals. They went extinct before the dinosaurs came on the scene.
What Did the Pelycosaurs Eat?
The Pelycosaurs had a varied diet. What they ate depended on their specific species. Some species, such as the Dimetrodon, were carnivorous. They had powerful jaws and sharp teeth for tearing into prey. However, many of the Pelycosaurs were herbivorous too. Examples include the Caseidae and the Edaphosauridae.
When Did Pelycosaurs Go Extinct?
The pelycosaurs came on the scene during the Carboniferous and reached the peak of their existence in the early part of the Permian period. They were the dominant group of land animals for up to 40 million years before going extinct towards the end of the Permian.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- Wikipedia, Available here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pelycosaur
- Berkeley, Available here: https://ucmp.berkeley.edu/synapsids/pelycosaurs.html
- New World Encyclopedia, Available here: https://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Pelycosaur
















