Iguanodon
Advertisement
Iguanodon Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Iguanodon Conservation Status
Iguanodon Facts
- Diet
- Herbivore
View all of the Iguanodon images!
The Iguanodon is a large herbivorous dinosaur that lived in the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous periods (between 161.2 to 99.6 million years ago). The fossil distribution shows the species lived predominantly in Europe but might have lived in North Africa and North America as well. The Iguanodon was first identified and named based on a handful of teeth fossils discovered in the 19th century. The teeth looked like they were from a giant iguana, hence the name Iguanodon.
Taxonomy
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Reptilia
Order: Ornithischia
Family: Iguanodontidae
Genus: Iguanodon
Description & Size
Iguanodon is a genus of Iguanodontian dinosaurs that lived between the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous periods. Initially, many species were classified as a part of this genus. However, later taxonomic revision has now narrowed it down. Currently, only two Iguanodon species exist: the Iguanodon bernissartensis and Iguanodon ottingeri. The I. bernissartensis is the type species of this genus.
The Iguanodon is closely related to the duck-billed dinosaurs. Scientists believed that this bulky herbivore was both bipedal and quadrupedal. This means either walking on two legs or all fours. The type I. bernissartensis might have weighed as much as 3.4 tons on average and was about 9 -11 m (30 – 36 ft) long. However, paleontologists have uncovered Iguanodon fossils that were as much as 13 meters long.
Iguanodons had large narrow skills with toothless beaks that were probably composed of keratin. The teeth look similar to that of the Iguana, which is the basis of its name. The Iguanodon had powerful legs but was most likely unable to run very fast. Perhaps the most notable physical trait of this ancient dinosaur is the presence of a spiked thumb on their forelimbs. This conical thumb spike was as long as the other fingers and fused to the wrist. Initially, scientists erroneously thought the spike was on the Iguanodon’s head.
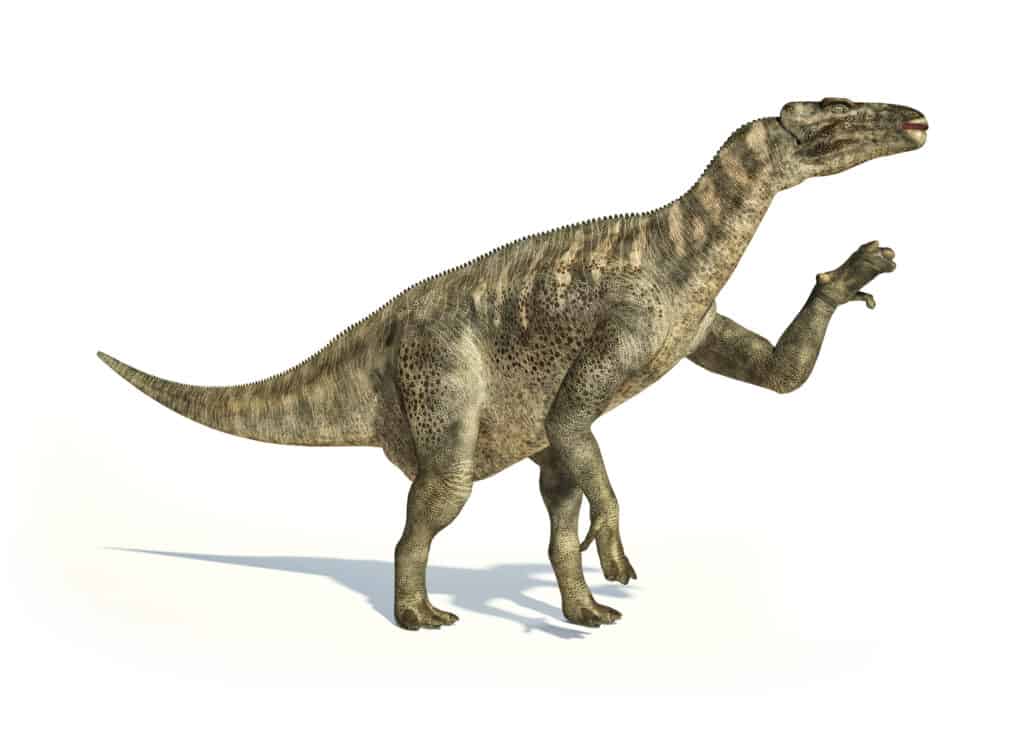

Perhaps the most notable physical trait of the Iguanodon is the presence of a spiked thumb on their forelimbs, as seen here.
©iStock.com/leonello
Diet – What Did Iguanodons Eat?
The Iguanodon’s teeth look like that of an herbivorous reptile. However, scientists are still unsure about what it takes and how it eats it. The Iguanodon had a well-developed jaw which meant it could eat a wide range of plants. Given its size, experts believed it could access tree foliage from trees as high as 4–5m. The Iguanodon’s diet probably included horsetails, conifers, and cycads, the dominant plant species on the European continent at the time.
Habitat – When and Where Iguanodons Lived
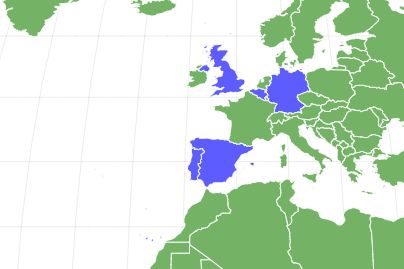
The Iguanodon most likely lived in forests, coastal inlets, swamplands, and islands in what is now present-day Europe during the mid-Jurassic to late Cretaceous. Some paleontologists think Iguanodons lived in herds. However, there is no conclusive evidence to support the fact that they nested together; Iguanodon fossils lived across Europe in various countries, including Belgium, Germany, Portugal, Spain, and the UK.
Threats and Predators of Iguanodons
As a plant-eating dinosaur, the Iguanodon was at risk of attack by any large predators living within the same habitat range. The Torvosaurus gurneyi is one of the largest predators in Europe around the same period as the Iguanodon. There is a good chance that this carnivore dinosaur might have preyed on the Iguanodon. Other predator species that co-existed with it include Razanandrongobe sakalavae, Baryonyx walkeri, Neovenator salerii, and the Megalosaurus.
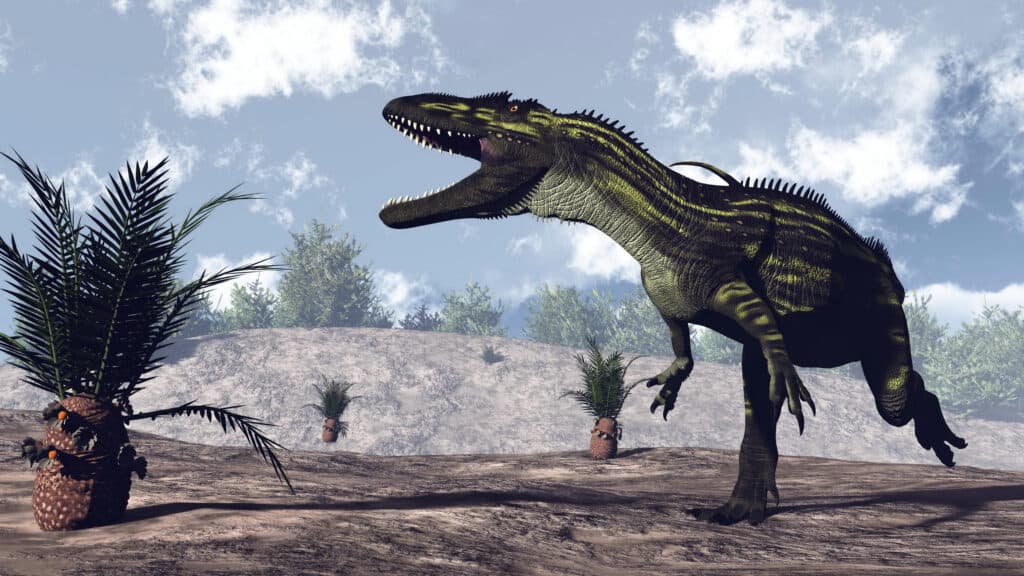

The
Torvosaurus gurneyi, or, Torvosaurus, was likely a major predator to the Iguanodon.
©iStock.com/Elenarts108
Discoveries and Fossils – Where Iguanodons were Found
Iguanodon bernissartensis was first described in 1881. The species in this genus are best known for the various fossil remains that scientists dug up in the Sainte-Barbe Clays Formation at Bernissart as well as other locations across Europe.
Scientists identified the first iguanodon fossil in 1825. English physician, Gideon Mantell, found the single tooth. The discovery was significant since it was the second identified dinosaur species. The fossil tooth served as evidence that dinosaurs were reptiles. The genus name is based on the description of the tooth, which Mantell observed to be similar to that of the Iguana.
Workers at a quarry in Maidstone, Kent, recovered a semi-intact fossil from the Lower Greensand Formation in 1834, which Mantell was able to link with the previously identified teeth fossil. However, perhaps the most significant find is that of 35 fossils found in great condition in a coal mine in Brussels. This discovery provided a deeper understanding of this genus of dinosaurs. Since they found the fossil remains in groups, scientists think the Iguanodon could have moved in herds. Scientists have also confirmed fossilized tracks of this ancient animal in deposits from the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous period.
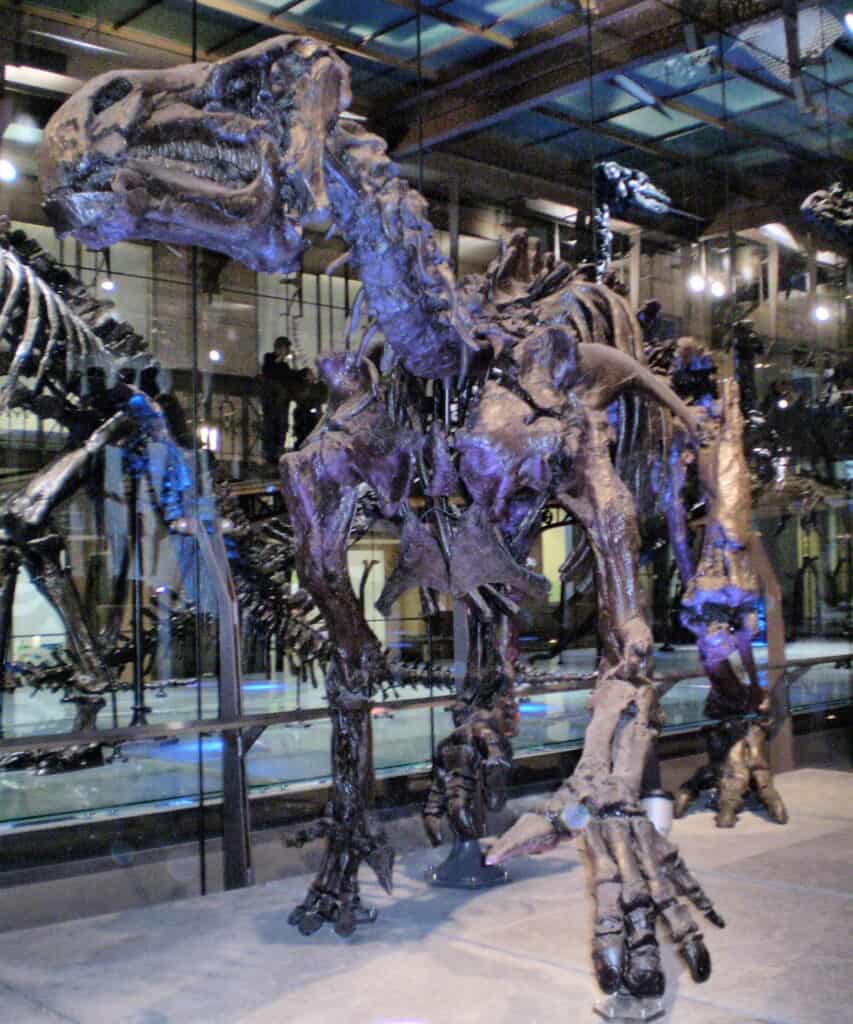

Many Iguanodon fossils were dug up in the Sainte-Barbe Clays Formation at Bernissart.
©By Ben2 – Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=3166764 – License
Extinction: When Did Iguanodons Die Out?
The Iguanodons lived on earth during the Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous period. They probably went extinct between 126 -122 million years ago. According to paleontologists, the disappearance was gradual. They gradually lost numbers until the entire population died off.
Similar Animals to The Iguanodon
- Megalosaurus buckendii: This is the first dinosaur fossil that was formally named. It was discovered in 1822 in present-day England and might have lived during the mid-Jurassic period as well.
- Hylaeosaurus: This is an herbivorous dinosaur that lived about 136 million years ago. It was the first dinosaur fossil to be put on display, along with the megalosaurus and Iguanodon.
- Hadrosauridae: the flat-billed dinosaur is a close relative of the Iguanodon.
Iguanodon FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
When was the Iguanodon Alive?
The Iguanodon lived in the Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous period, which is between 161.2 million to 99.6 million years ago.
How big was the Iguanodon
One of the largest dinosaurs of its time, the Iguanodon was about 8.9 ft. tall and was about 33 ft in length. This animal might have weighed between 8,800 – 11,000lbs.
What did the Iguanodon feed on
Since it was an herbivore, this dinosaur fed on trees and plants. It was tall enough to forage directly from plants like horsetails, conifers, and cycads.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- , Available here: https://www.britannica.com/animal/Iguanodon
- , Available here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Iguanodon
- , Available here: https://www.nhm.ac.uk/discover/dino-directory/iguanodon.html
- , Available here: https://ark.fandom.com/wiki/Iguanodon