Russian Tortoise
Agrionemys horsfieldii
Known by at least five different names
Advertisement
Russian Tortoise Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Reptilia
- Order
- Testudines
- Family
- Testudinidae
- Genus
- Agrionemys
- Scientific Name
- Agrionemys horsfieldii
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Russian Tortoise Conservation Status
Russian Tortoise Facts
- Name Of Young
- hatchlings
- Group Behavior
- Semi-social
- Fun Fact
- Known by at least five different names
- Biggest Threat
- Humans
- Most Distinctive Feature
- Spiked tail
- Other Name(s)
- Central Asian Tortoise, Afghan Tortoise, Steppe Tortoise
- Gestation Period
- 56-84 days
- Litter Size
- five eggs
- Habitat
- arid steppes
- Predators
- Raccoon, fox, coyote
- Diet
- Herbivore
- Favorite Food
- grasses, flowers, leaves and other vegetation
- Type
- reptile
- Common Name
- Russian Tortoise
- Location
- Central Asia
- Group
- Social but territorial
View all of the Russian Tortoise images!

“A relatively small size, but big personality.”
The Russian Tortoise is one of five species of Mediterranean tortoises, which are in the reptile family. These tortoises live primarily in burrows.
Russian Tortoises prefer arid climates for their habitats, and as such are prone to shell rot in captivity if care is not taken to make sure they are kept dry enough or on dry enough terrain. Anyone who keeps a Russian Tortoise as a pet must vigorously maintain the humidity and temperature of their cage, in addition to monitoring their diet.
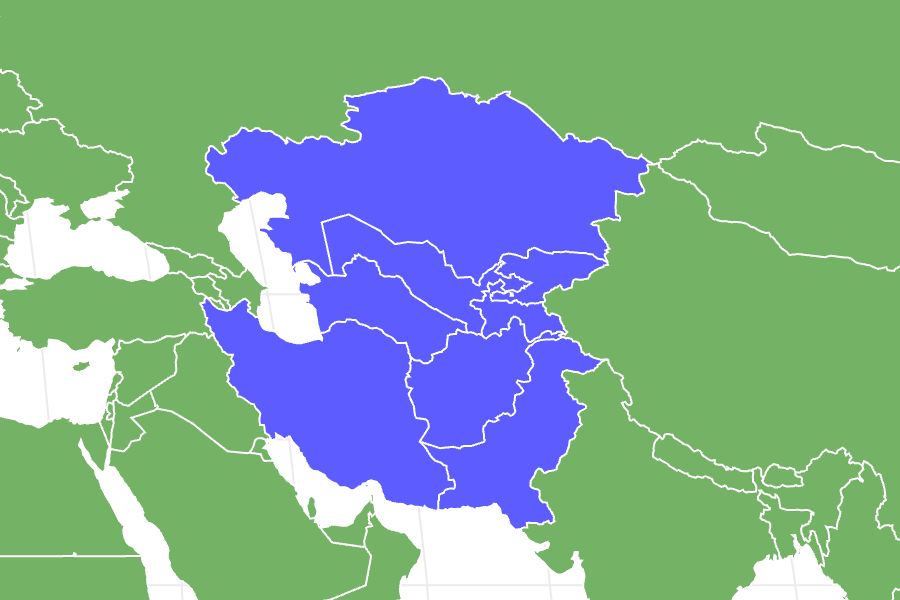
The Russian Tortoise is a threatened species in the family Testudinidae, which is native to southern Russia, Pakistan, Afghanistan, Iran, and a few other Central Asian countries.
5 Incredible Russian Tortoise Facts!
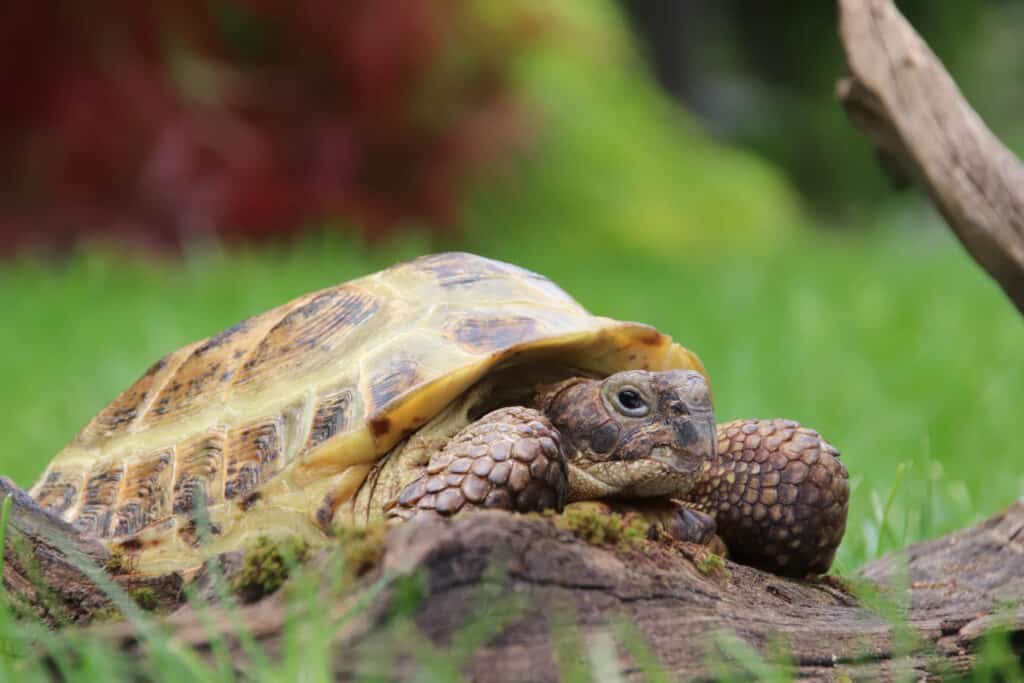

The gender of a Russian Tortoise is determined by the incubation temperature of its egg.
©Haoss/Shutterstock.com
A group of any species of tortoise is called a creep. Here are some facts about Russian Tortoises.
- Russian Tortoises hibernate for up to 6 months.
- A Russian Tortoise’s sex is determined by the temperature at which its egg is incubated.
- Russian Tortoises visit and have sleepovers in each other’s burrows.
- Russian Tortoises have 6 different common names.
- Russian tortoises have a very long lifespan, up to 50 years in captivity, up to 100 in the wild.
Scientific Name
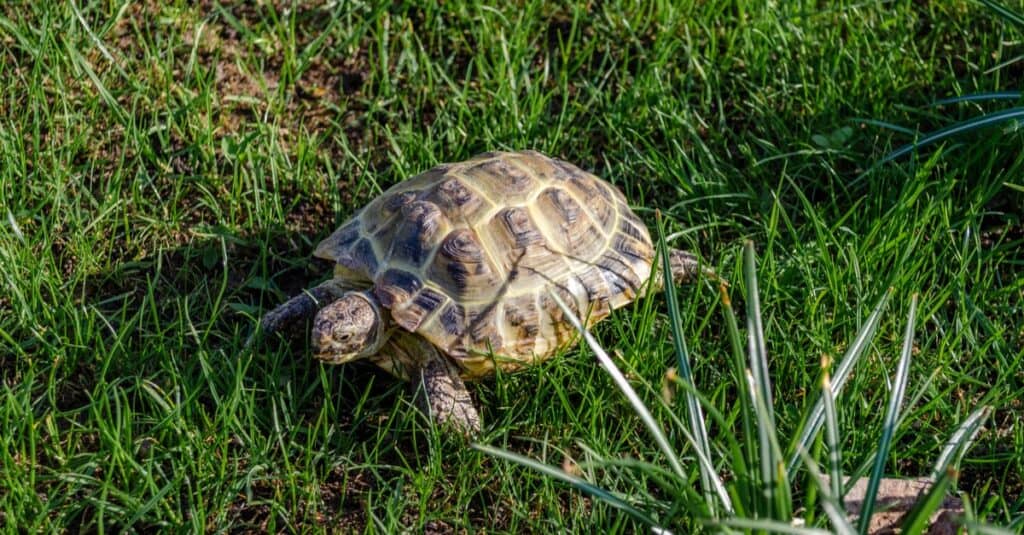

In contrast to the majority of animals, the Russian Tortoise is recognized by multiple scientific names.
©Alexandra Kovaleva/Shutterstock.com
Unlike most animals, the Russian Tortoise is actually known by several scientific names. You will find it listed as Agrionemys horsfieldii, Testudo horsfieldii, Testudo or Agrionemys horsfieldi, Medaestia horsfieldi, and several other names. The most commonly used ones are Testudo horsfieldii and Agrionemys horsfieldii.
The reason for this name diversity is likely a lack of communication between biologists back when the tortoise was first discovered, combined with a lack of understanding of its variety of shell colors. Some confusion may have arisen due to errors in transcription.
By the time further research was done into the species, different names were cataloged in many different places and therefore continued to be used. They are in the class Reptilia and the family Testudinidae.
Other Common Names for the Russian Tortoise
Just as it has many scientific names, the Russian Tortoise is known by many different common names, as well. To some, it is the Afghan tortoise. To others, it is known as the Central Asian tortoise. In some places, it is called Horsfield’s tortoise, which is where its scientific names stem from.
Thomas Horsfield was a doctor and scientist who documented a number of Indonesian plant and animal species over the course of his career. It may also be called the four-clawed tortoise because of its unusual number of claws, or even the Steppe tortoise because of the habitat where it is often found.
Appearance
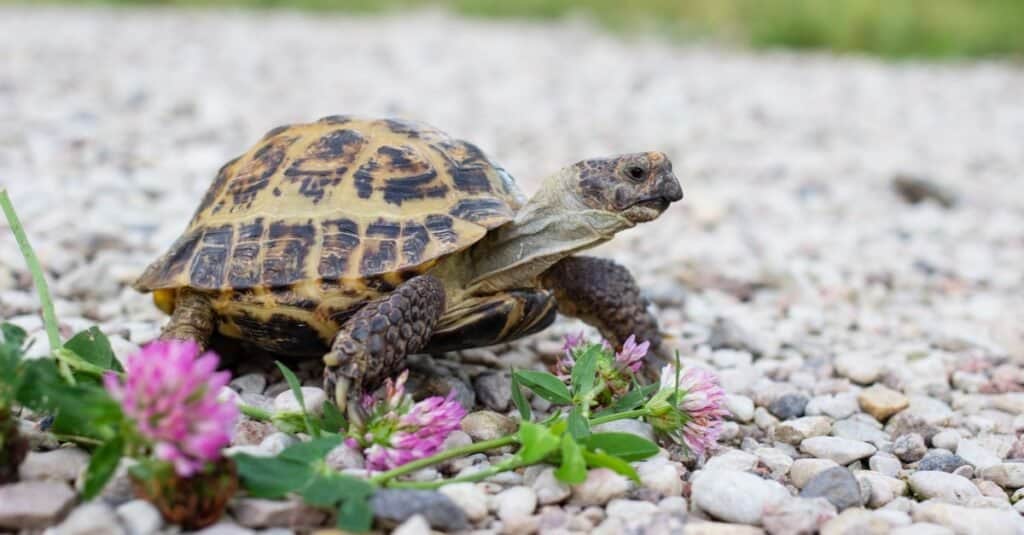

The carapaces, or shells, of Russian Tortoises exhibit a variety of colors, spanning from olive green to light tan, often adorned with markings in black or brown.
©Elena M. Tarasova/Shutterstock.com
Russian Tortoise carapaces, or what we frequently refer to as their shells, range in color from olive green to light tan, often with black or brown markings. The bottom of the shell is usually black or sometimes black and brown. Their skin is usually greenish-yellow.
Male Russian Tortoises have significantly larger tails than female tortoises do. They also have four claws and a small spike at the end of their tail. They reach lengths anywhere from about five up to 10 inches, though seven is about the average size.
These tortoises weigh between half a pound to two and a half pounds. By comparison, the largest tortoise ever recorded, Esmerelda, weighs about 670 pounds. This male tortoise of the Seychelles Islands is believed to be 170 years old.
Behavior

Russian Tortoises inhabit subterranean burrows that they excavate once the soil has been softened by the spring rains.
©Elena M. Tarasova/Shutterstock.com
Russian Tortoises live in underground burrows, which they dig out after the spring rains have softened the soil. They go into these burrows to avoid the higher temperatures of midday. They will pay visits to each other’s burrows, and sometimes multiple tortoises will sleep in the same burrow for a night.
However, they are very territorial and will fight over resources. The Russian Tortoise is said to make an excellent pet, though the trade of them is restricted in many countries, due to its small size and abundance of personality.
Habitat
These tortoises are like warm, dry places. Their natural habitat is rocky desert-like terrain. During the winter they need not only adequate sunlight but also a south-facing burrow for hibernation. In the summer, they need shade and a burrow to keep them out of the higher temperatures. They prefer temperatures between 70-90 degrees and humidity of less than 70%. They enjoy drier substrates, such as sand and rocky terrain, with sparse vegetation.
Diet

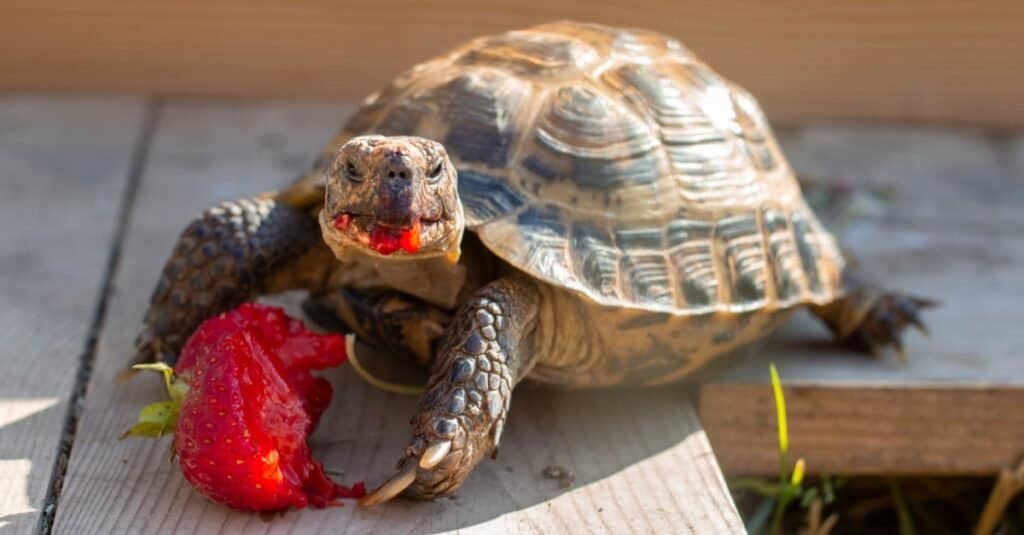
Russian Tortoises enjoy a diet rich in vegetation, such as leaves, grasses, and flowers. When kept as a pet, it is advisable to allow the tortoise to forage for their food in an area free from pesticides and other toxins, rather than strictly providing them with fresh fruits and vegetables.
They particularly enjoy hibiscus bushes and mulberry trees. When in captivity, their diet can be supplemented with kale, spinach, and other leafy greens, as well as broccoli. Since they are used to living where food is scarce, they are opportunistic eaters.
Predators and Threats
Russian Tortoises have a few natural predators in their native habitat, and still others when they are kept as pets. Dogs, cats, birds of prey, and humans are their main threats at home. When kept elsewhere, they may be at risk from coyotes, opossums, raccoons, skunks, foxes, snakes, and lizards. Humans, however, are their biggest threat, from habitat encroachment, poaching, pollution, climate change, and over-capture.
Reproduction and Life Cycle
A Russian Tortoise lays eggs in groups known as clutches. They do this up to three times per year. Each clutch contains up to five eggs. The sex of the hatchling is determined by how warm (female) or cool (male) the egg is kept during incubation. Each egg takes between 50-80 days to hatch. In the wild, these tortoises can live up to 100 years, though 80 is more common. In captivity, they rarely live beyond 40-50 years.
Population
The Russian Tortoise Population is listed as vulnerable, though this classification was last updated in 1996. The sale, trade, or import of them is now banned in Europe without a special license because of their conservation status. There is no information available about their current population numbers, as they have not been classified since 1996 and the IUCN lists their status as in need of update.
View all 114 animals that start with RRussian Tortoise FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Is a Russian tortoise a good pet?
Yes, they do. They are quite popular reptiles to keep as pets because they are so responsive to their owners and very active. With proper care, temperature, cage, and diet, their lifespan can be up to 40 years.
How much do Russian tortoises cost?
A Russian Tortoise costs anywhere between $200-400.
How big does a Russian tortoise get?
Russian Tortoises grow up to about eight to ten inches long, with a maximum weight of two and a half pounds.
What do I feed a Russian tortoise?
Their diet consists of vegetation. Allowing them to graze on safe outdoor plants is better than feeding them fresh fruits and vegetables alone, but they enjoy leafy greens like spinach.
How do I care for a Russian tortoise?
Their cage and/or any roaming area must be kept at a proper temperature and they must have the right diet. Allowing them to graze is better for them than only fruits and vegetables. They need a burrow if kept outdoors, sun and shade.
What are the key differences between male and female Russian tortoises?
The key differences between male and female Russian tortoises include size, appearance, color, reproduction, and behavior.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- Checklist of the Chelonians of the Wolrd, Available here: https://web.archive.org/web/20110501060224/http://www.cnah.org/pdf_files/851.pdf
- Pet MD, Available here: https://www.petmd.com/russian-tortoise-agrionemys-horsfieldii
- Arizona Exotic Animal Hospital, Available here: https://azeah.com/tortoises-turtles/basic-care-russian-tortoise
- Lafeber Vet, Available here: https://lafeber.com/vet/basic-information-sheet-russian-tortoise/
- Yarmouth Veterinary Center, Available here: https://yarmouthvetcenter.com/russian-tortoises.pml
- Biology Dictionary, Available here: https://biologydictionary.net/russian-tortoise/
- All Turtles, Available here: https://www.allturtles.com/russian-tortoise/
- Pet Russian Tortoise, Available here: https://petrussiantortoise.com/russian-tortoise-care/what-are-russian-tortoise-predators/
- Barrier Animal Care Clinic, Available here: https://www.barriervets.co.uk/exotics/horsfield-(russian)-tortoise
- California Turtle & Tortoise Club , Available here: https://tortoise.org/archives/russ.html
- Exotic Direct, Available here: https://www.exoticdirect.co.uk/news/tortoises-old-older-oldest
- Animalia, Available here: https://animalia.bio/russian-tortoise
- Reptile Direct, Available here: https://www.reptiledirect.com/russian-tortoise/
- Reptiles, Available here: https://www.reptilesmagazine.com/russian-tortoise-care-sheet/