Tiger Shark
Galeocerdo Cuvier
The fourth biggest species of shark in the world!
Advertisement
Tiger Shark Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Chondrichthyes
- Order
- Carcharhiniformes
- Family
- Carcharhinidae
- Genus
- Galeocerdo
- Scientific Name
- Galeocerdo Cuvier
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Tiger Shark Conservation Status
Tiger Shark Facts
- Main Prey
- Squid, Fish, Turtles
- Habitat
- Tropical coastal waters
- Predators
- Human
- Diet
- Carnivore
- Average Litter Size
- 35
View all of the Tiger Shark images!

The tiger shark, also known as a leopard shark, maneater shark, and spotted shark, is a warm, saltwater fish living in various areas throughout the world.
This is the only member of the Galeocerdo genus. It is known for the vertical dark stripes on its back and the fact that it eats many types of prey. It’s hunted by humans for its fins, cartilage, and oil.
5 Incredible Tiger Shark Facts
• A large litter: A female can have from 10 to 82 babies in one litter. Not surprisingly, she only has one litter of babies every three years.
• Speedy hunters: Though tiger sharks are fish that move slowly through the water most of the time, they use quick bursts of speed to capture prey. They can swim at a speed of around 20mph.
• Few predators: Killer whales and humans are their only predators. They are sometimes caught in commercial fishermen’s nets either deliberately or by accident.
• Garbage fish: Tiger sharks are sometimes referred to as garbage fish because they swallow a lot of items besides their prey. Plastic, empty cans, and license plates are just some of the items found in a tiger shark’s stomach.
• Powerful teeth: A tiger shark’s teeth are so strong and powerful that they can bite through a sea turtle’s shell or a clam.
Want more tiger shark facts? Check out ‘10 Mind-Blowing Tiger Shark Facts!‘
Classification and Scientific Name
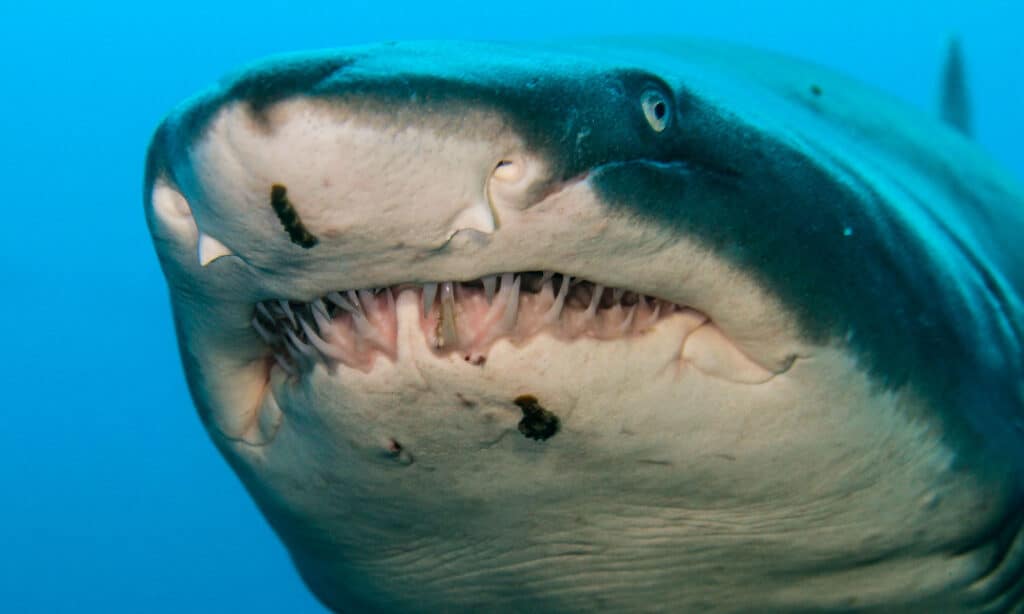

The scientific name of the tiger shark is
Galeocerdo cuvier
.
©Michael Rothschild/Shutterstock.com
The scientific name of the tiger shark is Galeocerdo cuvier. Galeocerdo cuvier comes from the Greek words Galeus (shark) and cerdo (fox). This relates to the sneaky way it approaches its prey. It’s also known as the maneater, leopard, and spotted a shark. It belongs to the Carcharhinidae family which contains 60 species. Its class is Chondrichthyes.
It belongs to the order Carcharhiniformes along with 270 other species of sharks including the Blacktip Reef Shark, Bull Shark, and Gray Reef Shark among many others. However, this species is the only member of the genus, Galeocerdo.
Species
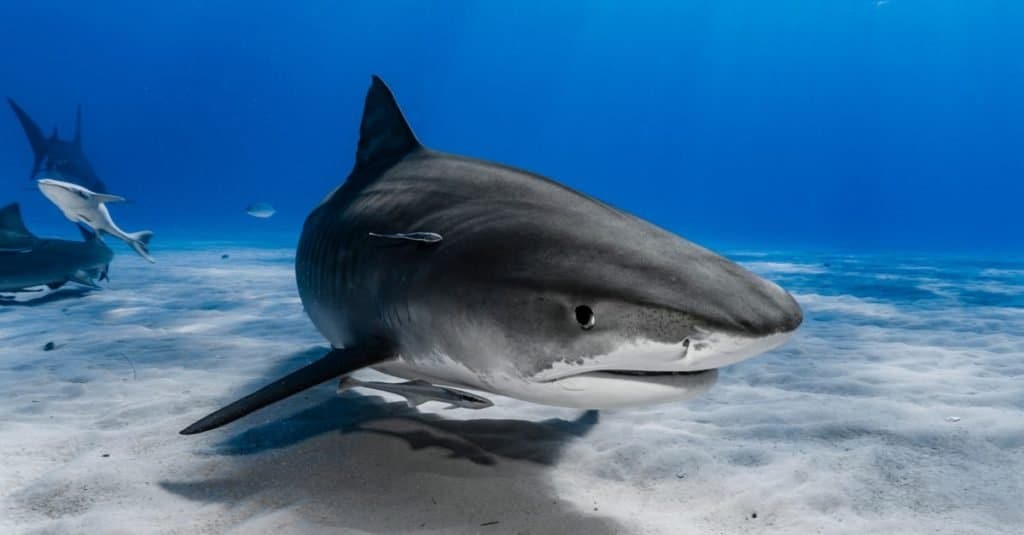

A Tiger Shark (Galeocerdo cuvier) swimming over the reef. Sharks have been swimming in the ocean for more than 400 million years.
©kaschibo/Shutterstock.com
There are 60 species of shark that belong to the same family (Carcharhinidae) also known as requiem sharks. There are 12 genera of this family. Some notable members of the requiem family include:
• Blacktip Reef Shark: Living in warm water this shark is easy to recognize by the black tips on its dorsal and other fins. This shark swims in shallow areas and is curious, but not aggressive when it encounters humans.
• Bull Shark: This shark lives in warm coastal waters and in rivers. They eat much of the same prey as tiger sharks but hunt during the day as well as at night.
• Gray Reef Shark: Has a blunt nose like a tiger shark and lives in warm waters gathering around reefs to find prey. This shark around 6 feet long and weighing around 70 lbs is much smaller in size than the tiger shark.
Here is a full list of tiger sharks:
- Galeocerdo
- Requiem sharks
- Sand tiger shark
- Ground sharks
- Carcharias
- White sharks
- Odontaspis
Evolution and Origins
The current tiger shark’s origin was formerly thought to have occurred around 5.3 million years ago. Nonetheless, the team was able to locate a number of 13.8 million-year-old fossil shark teeth, proving that they existed considerably earlier than previously thought.
The majority of scientists think sharks first appeared 400 million years ago. Before the dinosaurs, by 200 million years! They are said to have originated from a tiny fish with the shape of a leaf that lacked eyes, fins, and bones. Eventually, these fish evolved into the two major families of fish that exist today.
While fishing for swordfish in the southern Mediterranean, people unexpectedly snagged one male and one female Galeocerdo cuvier tiger shark specimen. This discovery proves beyond a shadow of a doubt that the tiger shark was found in the Mediterranean Sea’s waters at some point during their evolution.
Appearance
A tiger shark is a fish with smooth, gray skin, a white underside, and dark gray or black vertical stripes on its back. Its nose is rounded and broad. The teeth are curved toward the inside of its mouth. In addition, each of its teeth has a serrated edge. The design of their teeth helps them to bite through shells and the other hard exteriors of prey.
These sharks range from 10 to 14 feet in length. Their weight range is from 850 to 1,400 lbs. The longest tiger shark measured 24.6 feet while the heaviest weighed in at 1,780 lbs.
Its gray color helps it to blend into the murky water. Not surprisingly, this can also help a tiger shark to sneak up on prey swimming in the same area.
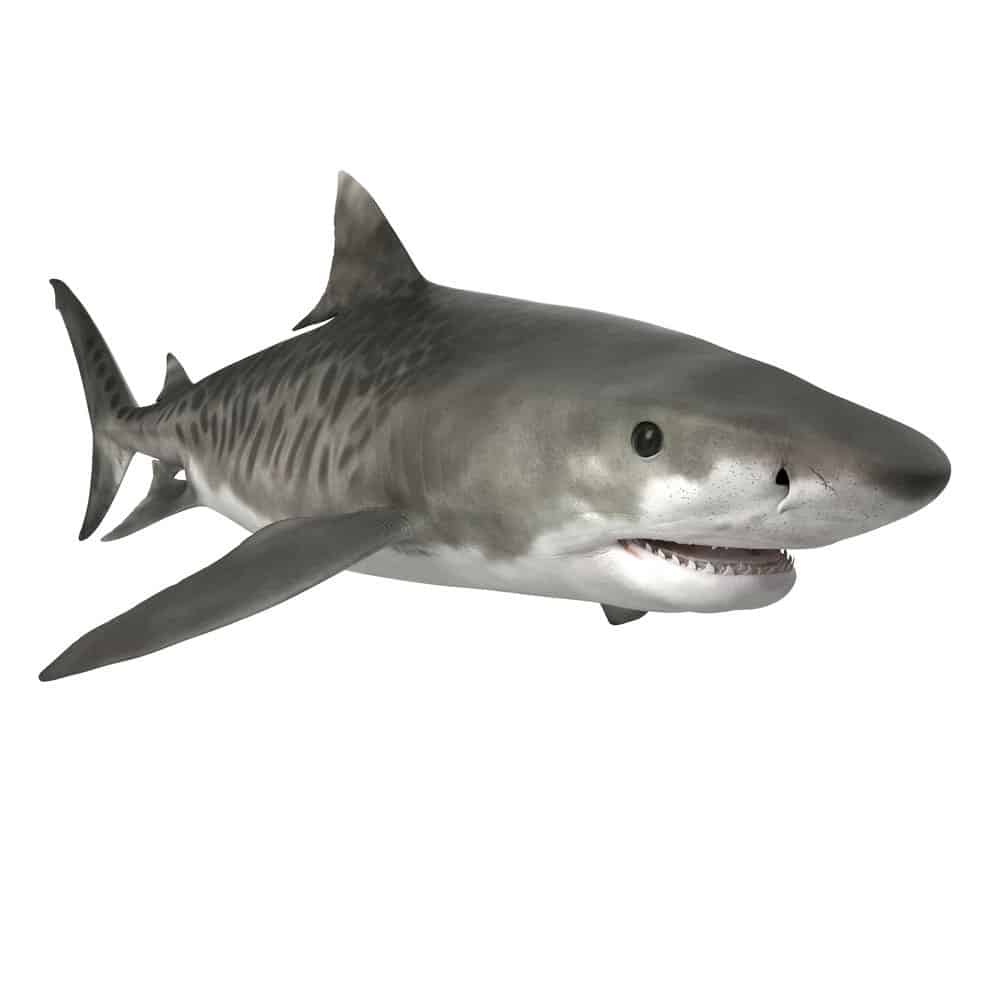

One of the most notable features is the stripes on its back. As it grows older, its stripes begin to fade.
©3DMI/Shutterstock.com
Tiger Shark Stripes
One of the most notable features is the stripes on its back. As it grows older, its stripes begin to fade.
Distribution, Population, and Habitat
The tiger shark lives in tropical waters in many places throughout the world. They are saltwater fish that have been seen around the central Pacific islands, in the Gulf of Mexico off North America and the Caribbean Sea. They have been seen off the coast of South America, China, Australia, Indonesia, Africa, and India. Though this shark spends time swimming near the surface, it normally swims at a depth of around 460 feet.
These sharks migrate with the change of seasons. When the weather turns cold, they move from temperate waters to tropical waters. Alternatively, when the warm weather returns, they move from a tropical habitat to a temperate one.
There is a lack of data regarding the population of this creature. However, the official conservation status is Near Threatened. Its numbers are decreasing due to poaching. They are hunted for their fins, their skin, and the oil contained in their liver. They are often caught in commercial fishing nets.
Predators and Prey

Killer whales and humans are both predators of adult tiger sharks. Killer whales are larger in size and weight than tiger sharks allowing them to overwhelm these fish. Humans capture baby and adult tiger sharks in commercial fishing nets and kill them for their skin, liver oil, and cartilage.
Baby tiger sharks are sometimes as small as 20 inches long at birth. This makes them vulnerable to being eaten by larger sharks and seals.
A tiger shark has a long list of prey. Some of the things these sharks hunt include squid, sea turtles, dolphins, smaller sharks, clams, rays, and sea birds. This shark will swallow things it finds in the ocean including plastic, license plates, and anything that looks tasty! They hunt at night which means they are even harder to see in the murky water.
For a complete analysis of what tiger sharks eat, check out our full ‘What do Tiger Sharks Eat? Their Diets Explained‘ article.
Reproduction and Lifespan
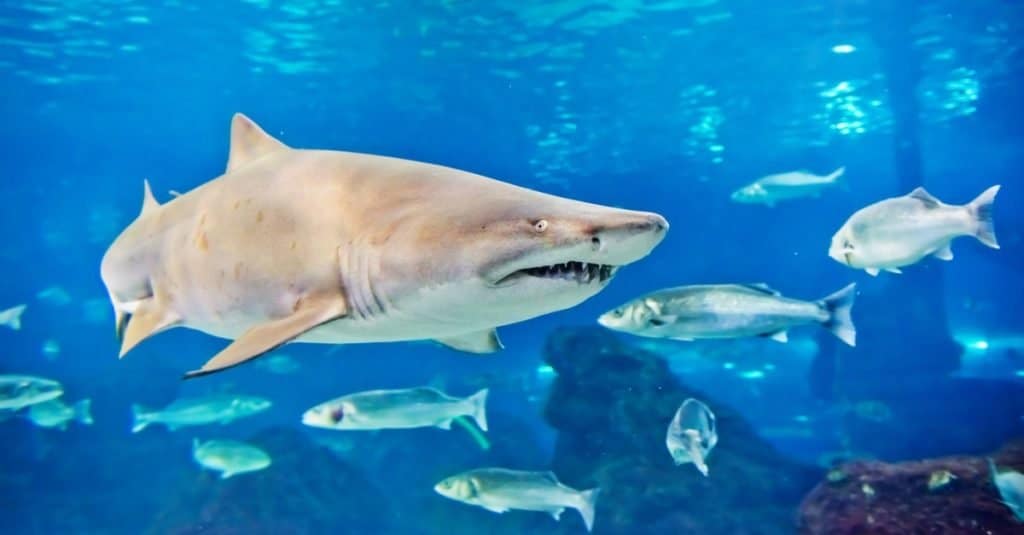

Sand tiger shark (Carcharias taurus) swimming with other fish in an aquarium.
©Valeri Potapova/Shutterstock.com
In the northern hemisphere, the breeding season of this shark goes from March to May while the breeding season in the southern hemisphere goes from November through the beginning of January. After the male mates with the female, the babies develop in eggs inside of the mother. After a 13- to 16-month gestation period, the female gives live birth. She can have from 10 to 80 babies or pups. A female tiger shark has a litter of pups just once every three years.
Shark pups can be from 20 to 30 inches in size at birth. Each baby leaves its mother right away to live independently. These sharks reach sexual maturity at about 7 to 10 years old. Tiger sharks live to be about 15 years old, but it seems they can live a lot longer — the oldest tiger shark on record was 50 years old!
Fishing and Cooking
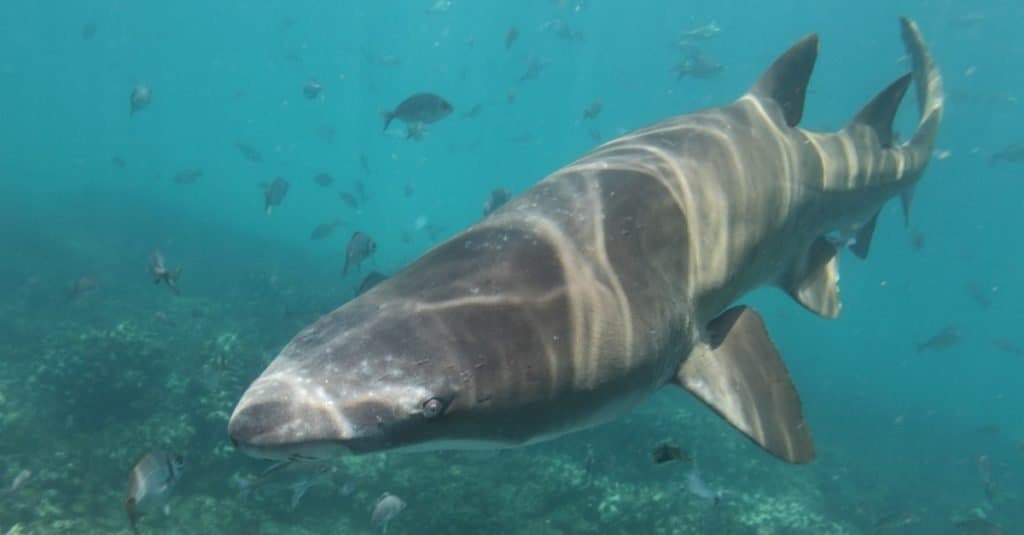

Sand tiger shark or grey nurse shark or spotted ragged-tooth shark, Carcharias taurus, Cape Infanta, South Africa, Indian Ocean
©Alessandro De Maddalena/Shutterstock.com
Tiger sharks are sometimes caught in commercial fishing nets by accident and sometimes deliberately. Either way, tiger sharks are usually killed for its skin, fins, cartilage, and the oil in its liver. The number that is caught in commercial fishing nets is not known.
This shark is not one that many humans eat. Its meat has a strange taste. Plus, this fish ingests lots of different items both edible and non-edible. This makes them even less appetizing.
View all 133 animals that start with TTiger Shark FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Where are tiger sharks found?
Tiger sharks live in tropical waters around North America, South America, Australia, India, China, Indonesia, and Africa.
What do tiger sharks eat?
Some of the prey of tiger sharks includes squid, clams, sea birds, rays, sea turtles, and smaller sharks.
Where do tiger sharks live?
Tiger sharks tend to swim along coasts, in river estuaries and harbors. They look for murky water where they can blend in and capture prey.
How big is a tiger shark?
A tiger shark is usually 10 to 14 feet long. They have a weight range of 850 to 1,400lbs.
What is the tiger shark’s scientific name?
Their scientific name is Galeocerdo cuvier.
Are tiger sharks dangerous?
Yes, they can be. These sharks are curious and can be dangerous when they mistake a human for prey. When these sharks see movement or reflections, they go over to investigate thinking it’s something to eat.
Harbors, river estuaries and reefs are the habitat of tiger sharks. Many people like to dive in these areas, so it’s not surprising tiger sharks and humans sometimes encounter each other.
What Kingdom do Tiger Sharks belong to?
Tiger Sharks belong to the Kingdom Animalia.
What phylum do Tiger Sharks belong to?
Tiger Sharks belong to the phylum Chordata.
What class do Tiger Sharks belong to?
Tiger Sharks belong to the class Chondrichthyes.
What family do Tiger Sharks belong to?
Tiger Sharks belong to the family Carcharhinidae.
What order do Tiger Sharks belong to?
Tiger Sharks belong to the order Carcharhiniformes.
What genus do Tiger Sharks belong to?
Tiger Sharks belong to the genus Galeocerdo.
What type of covering do Tiger Sharks have?
Tiger Sharks are covered in Smooth skin.
What are some predators of Tiger Sharks?
Predators of Tiger Sharks include humans.
How many babies do Tiger Sharks have?
The average number of babies a Tiger Shark has is 35.
What is an interesting fact about Tiger Sharks?
The Tiger Shark is the fourth biggest species of shark in the world!
What is the lifespan of a Tiger Shark?
Tiger Sharks can live for 30 to 40 years.
How fast is a Tiger Shark?
A Tiger Shark can travel at speeds of up to 20 miles per hour.
Who would win a fight: Tiger Shark Vs Great White Shark?
A great white shark would win a fight against a tiger shark.
The great white shark is too large and powerful for the smaller tiger shark to overcome. Even though the tiger shark would have difficulty ambushing the great white, unless it managed to deal a devastating blow to the bigger fish, it would be setting itself up for a bad counterattack.
What is the difference between a bull shark vs a tiger shark?
The main differences between bull and tiger sharks are that bull sharks are smaller, are freshwater tolerant, and prefer shallow waters. Tiger sharks are larger, can’t enter freshwater, and are usually in deeper water.
Who would win a fight: Tiger Shark Vs Crocodile?
A tiger shark would almost always kill a crocodile. Tiger shark wins 9 times out of 10.
In the open water, the tiger shark will always have the advantage over the crocodile. It can swim faster, maneuver better, and breathe underwater. If the fight goes below the water, the tiger shark almost always wins.
Who would win in a fight between a tiger shark and killer whale?
In the battle of tiger shark vs killer whale, the killer whale would likely win. Tiger sharks are large predators whose only real threat are killer whales!
What are the differences between the tiger shark and the sand tiger shark?
The major differences between the tiger shark and the sand tiger shark can be seen in their size, appearance, and reproductive processes
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- National Geographic, Available here: https://www.nationalgeographic.com/animals/fish/t/tiger-shark/
- Kids' Animal Facts, Available here: https://kidsanimalsfacts.com/tiger-shark-facts-for-kids/
- , Available here: https://www.dfo-mpo.gc.ca/species-especes/profiles-profils/tigershark-requintigre-eng.html