Tenrec
Tenrecidae
While the Madagascar tenrec closely resembles a hedgehog, they are actually not related to one another.
Advertisement
Tenrec Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Mammalia
- Order
- Afrosoricida
- Family
- Tenrecidae
- Scientific Name
- Tenrecidae
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Tenrec Conservation Status
Tenrec Facts
- Prey
- insects and other invertabrates
- Main Prey
- insects
- Name Of Young
- baby tenrec
- Group Behavior
- Solitary
- Fun Fact
- While the Madagascar tenrec closely resembles a hedgehog, they are actually not related to one another.
- Estimated Population Size
- around 5-10 thousand
- Biggest Threat
- human activity and predators
- Most Distinctive Feature
- spines on their back
- Gestation Period
- 61-68 days
- Temperament
- shy
- Age Of Independence
- 4 weeks
- Litter Size
- up to 10
- Predators
- snakes, fossa, birds of prey, cats, dogs
- Diet
- Insectivore
- Average Litter Size
- 3-4
- Lifestyle
- Nocturnal
- Favorite Food
- insects
- Number Of Species
- 26
- Location
- madagascar
- Slogan
- Hedgeho-like nocturnal insectivore
View all of the Tenrec images!
While the Madagascar tenrec closely resembles a hedgehog, they are not related to each other.
Tenrec Summary
Tenrecs are small, insectivorous mammals that are only native to Madagascar. They are closely related to hedgehogs and have a similar appearance, although they sometimes lack the spines that hedgehogs have. They are nocturnal animals and spend most of their time in trees or burrows. There are two main types: the common tenrec and the greater tenrec. The common tenrec is the largest tenrec species and can grow up to two pounds. The greater tenrec is smaller, only growing to weigh around seven ounces. Both species are covered in fur, which can be either brown or black in coloration.
5 Incredible Facts
- The streaked tenrec is one of the only mammals known to use stridulation for communication. This means they make a chirping noise by rubbing their body parts together.
- They are native to Madagascar and can be found in various habitats, including rainforests, spiny forests, and dry scrubland.
- There are more than 26 species of tenrec, ranging in size from the common tenrec (about the size of a rabbit) to the giant tenrec.
- They are insectivores, and their diet consists mainly of insects, but they will also eat small vertebrates such as lizards and snakes when given a chance.
- They are nocturnal animals and spend most of the day sleeping in burrows or nests.
Tenrec Scientific Name
Tenrecs are in the family Tenrecidae. They are a family of small, spiny mammals found in Africa, Madagascar, and the Americas. They resemble hedgehogs, shrews, and moles; however, they are unrelated and have their evolutionary track.
Tenrec Appearance
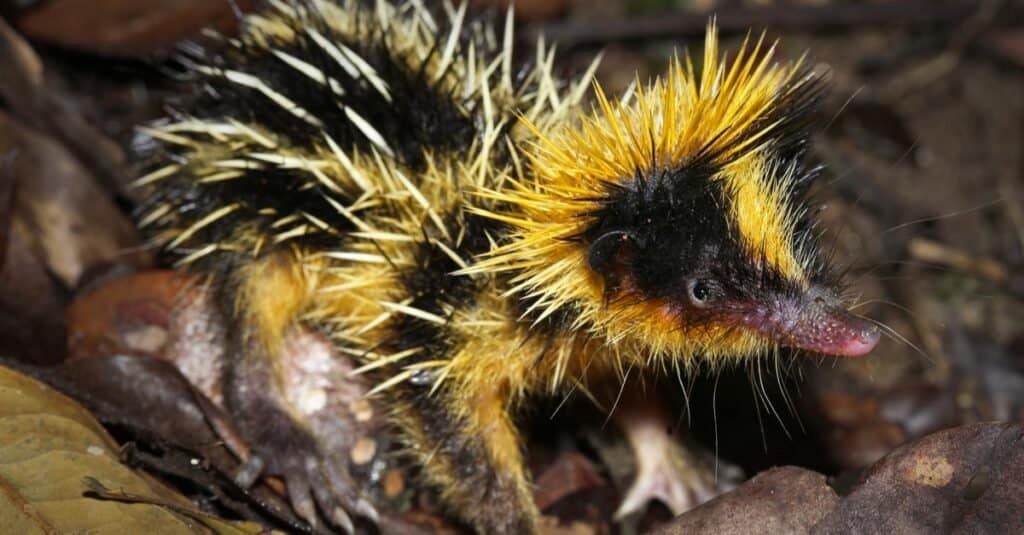

Tenrecs are small and round and can have quills all over their body.
©Ryan M. Bolton/Shutterstock.com
Tenrecs can have a unique appearance. They are small and round and can have quills all over their body. They are also covered in fur, which can be either brown or black. Their eyes are large and black, and they have a long snout. Overall, they look like a cross between a hedgehog and a mouse. They can be as small as 1.8 inches in length to as big as 15 inches. The largest species weighs around two pounds.
Tenrec Evolution
As we now know, the tenrecs are a family of small mammals native to Madagascar. They are in the same order related to other small mammals, such as rodents, rabbits, and moles. However, the family only includes the various tenrec species. The tenrec has undergone much evolution over their existence. They first appeared in Madagascar about 25 million years ago. Since then, they have adapted to their environment and evolved into the creatures we see today. There are many theories about why the tenrec animals have evolved. Some scientists believe it is because of their diet; others think it is because of their ability to reproduce quickly.
Behavior
Tenrecs are generally shy and solitary but can be very active when foraging for food. They eat insects, worms, snails, and other small invertebrates. When they feel threatened, they curl up into a ball, and some can even emit a loud clicking noise to warn predators. They are primarily active at night, so most species have adapted to be blind or have poor eyesight.
Habitat
Tenrecs are found in various habitats in Madagascar, including forests, grasslands, and urban areas. They are adaptable creatures that can survive in both hot and cold climates. Additionally, they can live in both wet and dry environments. Due to their ability to adapt to different conditions, it is challenging to say the ideal habitat for a tenrec. However, they do seem to prefer dense vegetation, as this provides ample hiding places from predators, and they do best in areas with a good amount of food readily available.
Diet
Tenrecs are insectivores, meaning their diet consists primarily of insects. However, they will also consume other small invertebrates, such as worms and spiders. They can be fed a diet of commercially available insectivore diets and live insects in captivity.
Predators and Threats
Unfortunately, the tenrec is at risk from predators and threats, and due to their small size, they are preyed upon by many different animals. The most common predators include owls, eagles, snakes, fossa, and cats. Additionally, these animals are also threatened by habitat loss and degradation. One of the main predators of the tenrec is the fossa, a unique to Madagascar predatory mammal. The fossa is a sizeable cat-like creature that preys on small mammals like the tenrec. These animals are also at risk from humans who hunt them for their meat or fur.
Several things can be done to help protect them and other unique animals only found in Madagascar from becoming extinct. The best place to start is to create protected areas for them to live. Educating people about the importance of these animals is also vital. The best way to help protect the tenrec is to raise awareness about their plight and work to conserve their habitat. We can also support organizations that are working to protect these animals.
Reproduction
The female tenrec will birth live young within 61-68 days of gestation and have a litter of up to 10 offspring. This reproductive strategy ensures at least some of the tenrec’s offspring will survive even if conditions are not ideal for raising young. It is just one of the many adaptations that make this animal well-suited to its environment.
Babies
The tenrec can have anywhere from 1-10 offspring at a time. The average litter size is 3-4. Offspring can be born fully furred and will open their eyes within 11-13 days. They will stay close to their mother for the first few weeks of life and be dependent on her. They are excellent parents and will care for their young until they are old enough to be on their own. There are two main types of tenrec animals: the common tenrec and the greater tenrec. Both kinds reproduce by giving birth to live young. The young tenrecs are born vulnerable and are usually weaned within four weeks. After that, they become independent and start to live on their own.
Lifespan
Tenrecs have a relatively short lifespan compared to other animals. The average lifespan is only about 10 years. While this may seem short, it is typical for small mammals like the tenrec. Many small mammals have less than ten years of lifespan due to their high metabolism and lack of defenses against predators and diseases. While their lifespan may be shorter than some other animals, it is typical for their size and species.
Some threats include predators, disease, parasites, and humans.
Tenrec Population
According to scientists, the population is hard to determine. However, around 2,500-5,000, individual tenrec animals are in the wild. Most of these animals are found in Madagascar, with smaller populations in other parts of Africa and Asia. They are listed as vulnerable due to their declining population. This decline is mainly due to habitat loss, fragmentation, and hunting pressure from humans. In addition, they are also affected by climate change and disease outbreaks. The good news is that several conservation efforts are underway to help protect them. For example, many organizations are working to raise awareness about this species and its plight. In addition, habitat protection and restoration projects are being carried out in their living areas.
Related Animals
View all 133 animals that start with TTenrec FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are tenrec carnivores, herbivores, or omnivores?
The tenrec is considered insectivorous as it almost exclusively feeds on insects and invertebrates.
Is the tenrec monogamous?
Some species of tenrec may show signs of monogamy. However, others breed with several partners.
Where is the tenrec commonly found?
The tenrec is a unique animal that can only be found in Madagascar.
What is the average lifespan of a tenrec?
The average lifespan of the tenrec in the wild is approximately 5-10 years of age.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.