Argentine Black and White Tegu
Salvator merianae
Argentine black and white tegus are popular pets due to their dog-like qualities, such as a docile nature, intelligence, loyalty, and companionship.
Advertisement
Argentine Black and White Tegu Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Reptilia
- Order
- Squamata
- Family
- Teiidae
- Genus
- Salvator
- Scientific Name
- Salvator merianae
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Argentine Black and White Tegu Conservation Status
Argentine Black and White Tegu Facts
- Prey
- Insects, small mammals, reptiles, birds, eggs, fruits, vegetables
- Name Of Young
- Hatchling
- Group Behavior
- Group
- Fun Fact
- Argentine black and white tegus are popular pets due to their dog-like qualities, such as a docile nature, intelligence, loyalty, and companionship.
- Estimated Population Size
- 1,000 to 10,000
- Biggest Threat
- Human activity
- Most Distinctive Feature
- Black and white beaded skin
- Incubation Period
- 40-75 days
- Litter Size
- 10-30
- Habitat
- Forests, shrubland, grassland, rivers, swamps, freshwater marshes, pastureland, rural gardens, and urban areas
- Predators
- Large birds, jaguars, snakes, and other larger predatory animals
- Diet
- Omnivore
- Average Litter Size
- 10-30
- Lifestyle
- Group
- Slogan
- giant lizard kept as pets
Argentine Black and White Tegu Physical Characteristics
- Color
- Black
- White
- Skin Type
- Scales
- Lifespan
- 10-15 years
- Weight
- 5-20 pounds
- Length
- 3-5 feet
- Age of Sexual Maturity
- 2-3 years
- Venomous
- No
- Aggression
- Low
View all of the Argentine Black and White Tegu images!
The Argentine black and white tegu is native to South America and is a popular pet due to its docile nature and intelligence. The tegu can grow up to five feet in length and have a lifespan of 10 to 12 years. It is an omnivorous animal, and its diet consists of small mammals, birds, lizards, frogs, and invertebrates. In the wild, these reptiles are found in tropical forests but can adapt to various habitats. Argentine black and white tegus are social creatures, and in captivity, they should be kept in pairs or groups. They require a spacious enclosure with plenty of hiding places, as well as access to UVB lighting and a basking spot. These reptiles are semi-aquatic, so their section should also include a water bowl or pond.
5 Incredible Argentine Black and White Tegu Facts
- The Argentine black and white tegu is the largest species of tegu lizard, reaching up to five feet in length in some cases.
- These lizards are native to South America and can be found in countries like Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, and Uruguay.
- Argentine black and white tegus make great pets due to their docile nature and dog-like qualities, such as loyalty and companionship.
- Argentine black and white tegus are known for their impressive intelligence as well.
- These lizards are also great swimmers and have been known to travel long distances across rivers in search of food or new territory.
Scientific Name
The Argentine black and white tegu is a giant lizard native to South America. The scientific name for this animal is known as Salvator merianae, while it gets its common name from its black and white coloration. Its scientific name is named in honor of German naturalist Maria Sibylla Merian.
Appearance
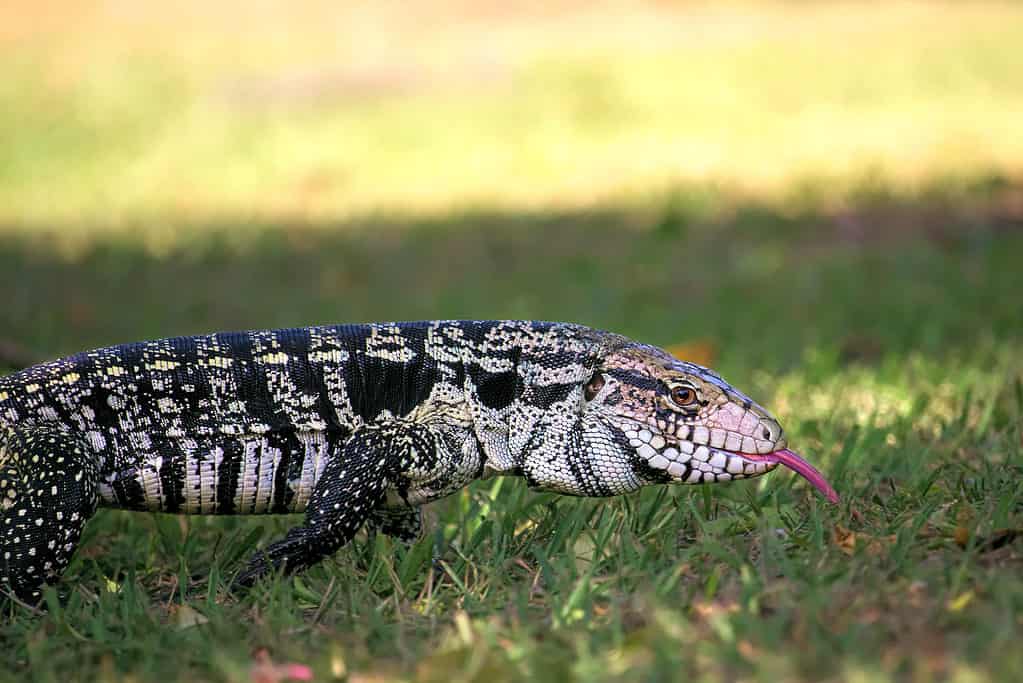

Healthy Argentine black and white tegus weigh between 15 and 20 pounds.
©Nelson Donizeti/Shutterstock.com
This incredible reptile is native to Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, and Uruguay. It is one of the most significant members of the tegu family, reaching lengths of up to five feet. On average, the females are much smaller than the males of this species, with females growing up to just three feet long. A healthy Argentine black and white tegu weighs around 15 to 20 pounds.
The Argentine black and white tegu is easily recognizable by its striking and mottled black-and-white beaded skin. However, the Argentine black and white tegu typically have bright green heads when they are first born. But the bright emerald color fades and becomes black as the young tegu sheds.
Evolution
The Argentine black and white tegu has undergone some evolutionary changes. One change is that it has become more adapted to living in captivity. This is likely because more people are keeping them as pets. Another difference is that the average size of the lizard has increased slightly over time. This could be due to better care and nutrition in captivity, or it could be a result of natural selection. Overall, the Argentine black and white tegu is a fascinating creature that has undergone some exciting changes over time.
Argentine Black and White Tegu Behavior
One of the coolest things about the Argentine black and white tegu is its behavior. When threatened, this lizard will hiss loudly and try to intimidate its attacker by inflating its body and opening its mouth wide. If that doesn’t work, the tegu will bite. And if all else fails, it will run away as fast as it can. An awesome adaptation of this reptile is that it can drop its tail on the floor as a distraction if attacked, giving it a moment to save itself by running away. And due to its sheer size, this lizard can also use its tail to strike its opponent.
The Argentine black and white tegu is a very intelligent reptile that can make an excellent pet for those willing to take the time and effort to care for them properly. They are active and curious animals that require much space to roam, so they might be better suited for life in a larger enclosure.
Argentine Black and White Tegu Habitat
The Argentine black and white tegu is found in Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, and Uruguay. Their habitats include subtropical and tropical moist lowland forests, subtropical and tropical dry shrubland, subtropical and tropical seasonally wet or flooded lowland grassland, rivers, swamps, freshwater marshes, pastureland, rural gardens, and urban areas. They also inhabit human-modified habitats such as agriculture (e.g., soybean fields) and livestock pastures. And since many consider this reptile a pet, Argentine black and white tegus have been found to live in human-made enclosures too.
Argentine Black and White Tegu Diet
These lizards are omnivorous, which means they eat both plants and animals. The Argentine black and white tegu’s diet consists of insects, small mammals, reptiles, birds, and eggs in the wild. They will also eat fruits and vegetables.
When in captivity, it is essential to provide a varied diet that includes all the food groups mentioned above. An excellent way to do this is by feeding them a mixture of commercially prepared reptile food and live prey items. It is also necessary to offer them a variety of fruits and vegetables so that they can get the nutrients they need.
What Eats the Argentine Black and White Tegu?
Large birds, jaguars, snakes, and other larger animals will eat a tegu.
What Does the Black and White Tegu Eat?
The black and white tegu can eat various foods, including insects, fruits, and vegetables.
Argentine Black and White Tegu Predators and Threats
One of the main predators of the Argentine black and white tegu is the jaguar. They are mighty hunters that use their sharp claws and teeth to kill their prey. Jaguars typically live in forested areas but have been known to venture into other habitats in search of food.
Another major predator of the Argentine black and white tegu is the boa constrictor. They kill their prey by wrapping their bodies around them and squeezing tightly until they suffocate. Boa constrictors typically live in tropical rainforests but have inhabited other habitats such as deserts or mountains.
In addition to predators, there are also some potential threats that Argentine black and white tegus may become victims of. One of these threats is disease. Some diseases that Argentine black and white tegus can contract include salmonella and cryptosporidiosis. These diseases can be transmitted through contact with contaminated food, water, or another infected animal. Therefore, if in captivity, owners need to provide their Argentine black and white tegus with clean food and water sources and regular vet check-ups to prevent disease transmission.
Another potential threat is injury from being stepped on or crushed. This can be avoided if an owner provides their pet with a suitable, safe enclosure with enough space to move around freely. Owners must ensure that their Argentine black and white tegu has plenty of room to exercise and explore without being at risk for injury.
Argentine Black and White Tegu Reproduction
Argentine black and white tegus use chemical cues to search for mates in the area. Female tegus more often take the lead in finding a potential mate by following these chemical scent trails. These reptiles mate in the spring right after hibernation when their hormones peak.
The Argentine black and white tegus are oviparous, which means they lay eggs. After mating, the female tegu will lay a clutch of 10 to 30 eggs in a nest she has dug herself, but some females may lay even more eggs, depending on their health. The eggs will then incubate for between 40 to 75 days before hatching. The female tegu potentially produces dozens of offspring over her lifetime.
Argentine Black and White Tegu Babies
As hatchings, the young tegus are born fully formed and independent in the beginning of spring. Unlike their adult counterparts, young tegus are born with an emerald green head with black markings. After shedding a few times over several months, this green color eventually fades and turns black.
When they first hatch, Argentine black and white tegu babies weigh only 0.35 ounces, but they quickly grow and can weigh up to 20 pounds in just 4 or 5 years, which is when they stop growing.
These young Argentine black and white tegus typically reach sexual maturity within two or three years when they are around 3 to 3.5 pounds. Then the cycle continues again.
Argentine Black and White Tegu Lifespan
Argentine black and white tegus typically live between 10 and 12 years in captivity, though some individuals have been known to live up to 15 years. Their lifespan is likely shorter in the wild due to predation and other factors. Several things can affect an Argentine black and white tegu’s lifespan, both positively and negatively. Proper diet and nutrition are essential for maintaining a healthy tegu and providing a clean and safe enclosure. Avoiding stressors such as handling too much or too little will also help them to live a long life. Some threats to the Argentine black and white tegu include, but are not limited to:
- Predators
- Disease
- Habitat loss
- Humans
Argentine Black and White Tegu Population
According to a study conducted in 2013, the estimated global population of Argentine black and white tegus is between 1,000 and 10,000. Most of these tegus are found in Argentina, where they are native, but they have also been introduced to other countries in South America, such as Brazil and Uruguay. Tegus are famous pets due to their docile nature and intelligence, which means that many of these reptiles are kept in captivity.
It is difficult to estimate how many tegus are kept as pets because there is no central registry. However, it is thought that the number of captive tegus far exceeds the number of wild ones. The popularity of tegus as pets has contributed to their decline in the wild. Tegus are often captured from the wild to be sold as pets, which puts pressure on wild populations. In addition, habitat loss and fragmentation due to human activity are significant threats to these animals.
Related Animals…
View all 194 animals that start with AArgentine Black and White Tegu FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are Argentine black and white tegus carnivores, herbivores, or omnivores?
The Argentine black and white tegu is omnivorous, as it eats both vegetation and meat.
Which countries is the Argentine black and white tegu found in?
The black and white tegu is found in South American countries such as Argentina and Brazil. But these reptiles are kept as pets all around the world.
What is the average lifespan of the Argentine black and white tegu?
The average lifespan of the black and white tegu is approximately 10-12 years, but sometimes up to 15 years in captivity.
Can you train tegus?
Argentine black and white tegus are highly intelligent animals that you can train with positive reinforcement. They have been known to understand cues, much like dogs.
Can Argentine black and white tegus hurt humans?
Argentine black and white tegus are not naturally aggressive, but if attacked, they may whip their tail or bite. They are not poisonous, but their sharp teeth can hurt!
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- Animal Spot, Available here: https://www.animalspot.net/argentine-black-and-white-tegu.html
- Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission, Available here: https://myfwc.com/wildlifehabitats/profiles/reptiles/argentine-black-and-white-tegu/