Maned Wolf
Chyrsocyon brachyurus
Despite its name, the Maned Wolf is not actually a wolf.
Advertisement
Maned Wolf Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Mammalia
- Order
- Carnivora
- Family
- Canidae
- Genus
- Chrysocyon
- Scientific Name
- Chyrsocyon brachyurus
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Maned Wolf Conservation Status
Maned Wolf Facts
- Prey
- Small- to medium-sized animals including rodents, birds, fish, and rabbits; vegetable matter including tubers, fruit, and sugarcane
- Name Of Young
- Pup
- Group Behavior
- Solitary
- Fun Fact
- Despite its name, the Maned Wolf is not actually a wolf.
- Estimated Population Size
- 23,600
- Biggest Threat
- Habitat destruction
- Most Distinctive Feature
- Reddish brown or golden orange fur with a black mane
- Gestation Period
- 60 to 65 days
- Litter Size
- 2 to 6 pups
- Habitat
- Semi-open habitats such as grasslands, forests, and scrub prairies
- Predators
- Jaguars and pumas
- Diet
- Omnivore
- Lifestyle
- Nocturnal
- Crepuscular
- Common Name
- Maned Wolf
- Number Of Species
- 1
- Location
- Central and eastern South America
- Group
- Mammal
Maned Wolf Physical Characteristics
- Color
- Brown
- Black
- Orange
- Skin Type
- Fur
- Top Speed
- 47 mph
- Lifespan
- 12 to 15 years
- Weight
- 51 pounds
- Height
- 35 inches
- Length
- 39 inches (additional 18 inches including tail)
- Age of Sexual Maturity
- 1 year
- Age of Weaning
- 4 months
View all of the Maned Wolf images!
“The Maned Wolf is the largest canid in South America.”
The Maned Wolf is found in Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, and other countries in eastern and central South America. They have very long and skinny legs, making them the largest canine in South America. Their long legs almost make them look like a fox on stilts. In addition to these distinct legs, Maned Wolves also have a very easily recognizable black mane. Their fur is reddish-brown or golden-orange in color.
These canids are solitary animals. They do not hunt in packs, unlike many other canines. They can be found in grasslands, savannas, wetlands, forests, and marshes.
Incredible Maned Wolf Facts
• The Maned Wolf is not a wolf or a fox. Rather, it is the only species in the Chrysocyon genus.
• These animals communicate by marking their territory with urine or barking loudly.
• In addition to hunting small animals, they eat fruits and vegetables.
• Maned Wolves live an average of 12 to 15 years.
• Loss of their habitats is the greatest threat these animals face.

Scientific Name
The Maned Wolf’s scientific name is Chyrsocyon brachyurus. Chyrsocyon, which means golden dog, is the genus the animal belongs to. It is the only species in the genus. Brachyurus refers to the Maned Wolf’s tail. They are part of the Mammalia class and Canidae family.
Evolution And History
Originally thought to be closely related to true wolves, the mane wolf is actually a closer relative of wild dogs and wolf-like foxes, although they are still a distinct canid genus and species. This animal can trace its history back 6 million years ago to when many of the larger canids in South America became extinct. Fossils of the mane wolf dating back to the Pleiostine era have indicated that they are the only large canids to survive elimination. Its once closest relative, the Falkland Islands wolf, is now extinct.
Appearance And Behavior
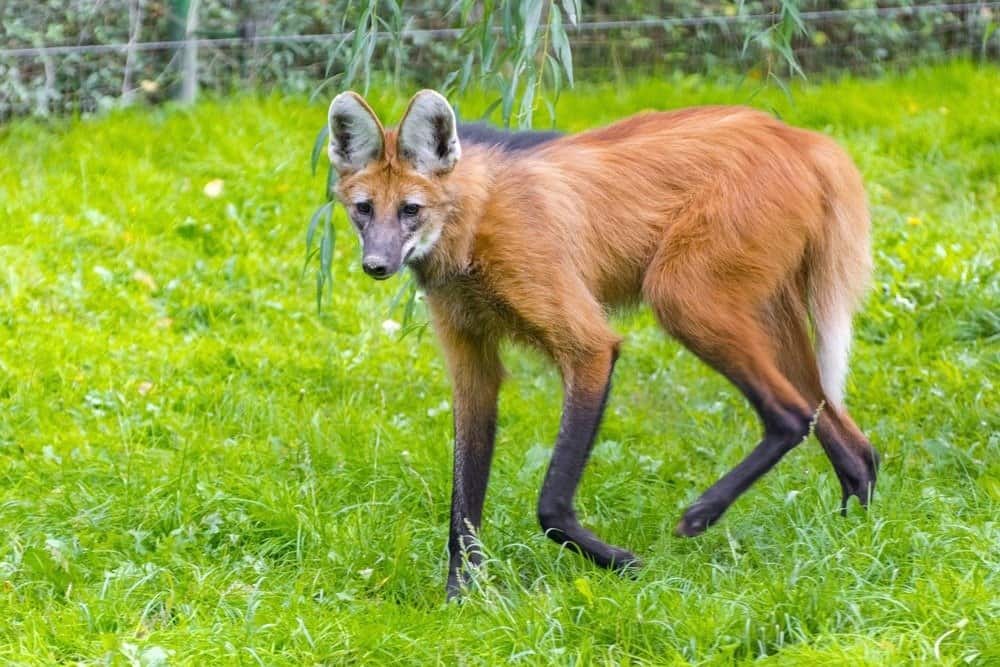

Maned wolves (Chrysocyon brachyurus) have long legs that are sometimes referred to as stilts.
©belizar/Shutterstock.com
The fur of these canids is golden orange to red/reddish-brown in color. As their name suggests, they also have a black mane that makes them easily identifiable. Maned Wolves also have very long black legs. These long legs sometimes referred to as stilts, are believed to be an adaptation to the very tall grasslands in their habitat. In fact, these animals are the tallest of all the wild canids.
Adults weigh about 51 pounds, which is about the weight of a large bag of dog food. Their body is about 39 inches long from their head to rear. Their tail adds another 18 inches or so to their total length. Maned Wolves are about 35 inches tall. Additionally, they are very large ears that are around 7 inches long.
Whereas Gray Wolves, African Hunting Dogs, and most other canid species form packs, the Maned Wolf is a solitary being. Most times, they will hunt alone. They are crepuscular animals, which means that they are most active during twilight hours (between 8:00 and 10:00 am and 8:00 and 10:00 pm).
These canids communicate using their urine. They use it to mark the spots where their pretty is buried and their hunting paths. Their urine’s smell is very distinct and easy to recognize; many people believe it smells similar to cannabis.
Habitat
These animals are found in central and eastern South America. Some of the countries they inhabit include Brazil, Paraguay, Argentina, Uruguay, Peru, and Bolivia. Maned Wolves live in the cerrado, which is the largest biome found in South America. This biome is made up of grasslands, forests (both wet and dry), wetlands, marshes, and savannas. It is also possible to find these canids hunting in the pastures around farmland, though they will not prey on farm livestock.
Diet
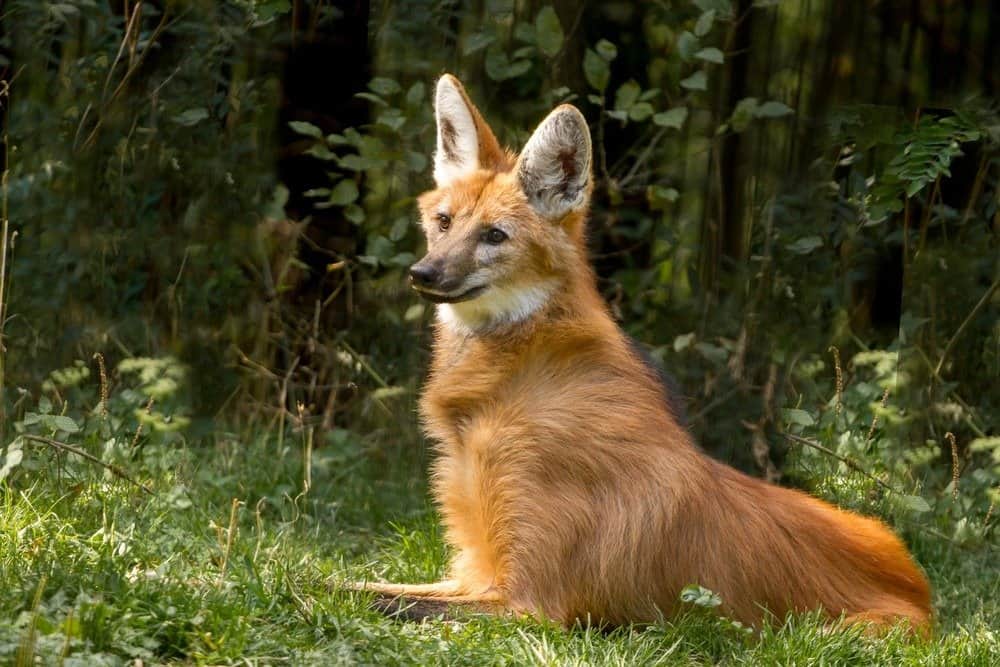

Maned wolves use their large ears to listen for animal sounds.
©Marie Dirgova/Shutterstock.com
Maned Wolves are omnivores, which means they eat both plants and animals. Plants can make up 50% or more of their diet. Some of the vegetation they enjoy eating includes fruit, vegetables, sugarcane, and tubers. One of their favorite foods is lobeira. Loberia means “fruit of the world” and is a small berry that resembles a tomato.
They also hunt to catch small- and medium-sized animals. Some of the animals they prey on include rabbits, mice and other rodents, pampas deer, armadillos, and giant anteaters. When hunting for food, they use their large ears to listen closely for animal sounds. They will rotate their ears to help them hear better. When they hear something, they use their feet to tap the ground to get their prey to come out.
The method they use to catch their prey can vary, depending on which type of animal they are catching. For example, they pounce after smaller animals that may be running away, dig to follow burrowing prey, or leap up to catch insects or birds. Their long legs help them move quickly to successfully capture their prey.
Predators And Threats
Maned Wolves face a few threats, both from their natural predators and humans. Large cats prey on them. The Jaguar is their biggest predator, but Pumas and other cats have also been known to hunt Maned Wolves.
Maned Wolves also get diseases such as parvovirus, rabies virus, distemper virus, and canine adenovirus. These diseases are a result of them sharing territory with domestic dogs. The animals can also be killed by Giant Kidney Worms. This parasite is a roundworm that attacks the animal’s kidneys.
Humans also pose a threat to Maned Wolves. They have been hunted in different parts of Brazil for their body parts. Their eyes, in particular, were thought to be good luck charms. While they are now protected by laws that prohibit hunting, some people still try to kill these animals.
Another major threat to these animals is habitat loss. Humans developing the lands where the Maned Wolf lives and hunts are resulting in less livable space for them and reduced animals to prey on in some areas. Automobile collisions also kill them.
While these animals are not considered endangered, there is concern that their numbers have been decreasing. The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) classified Mane Wolves as near-threatened.
Reproduction, Babies, And Lifespan
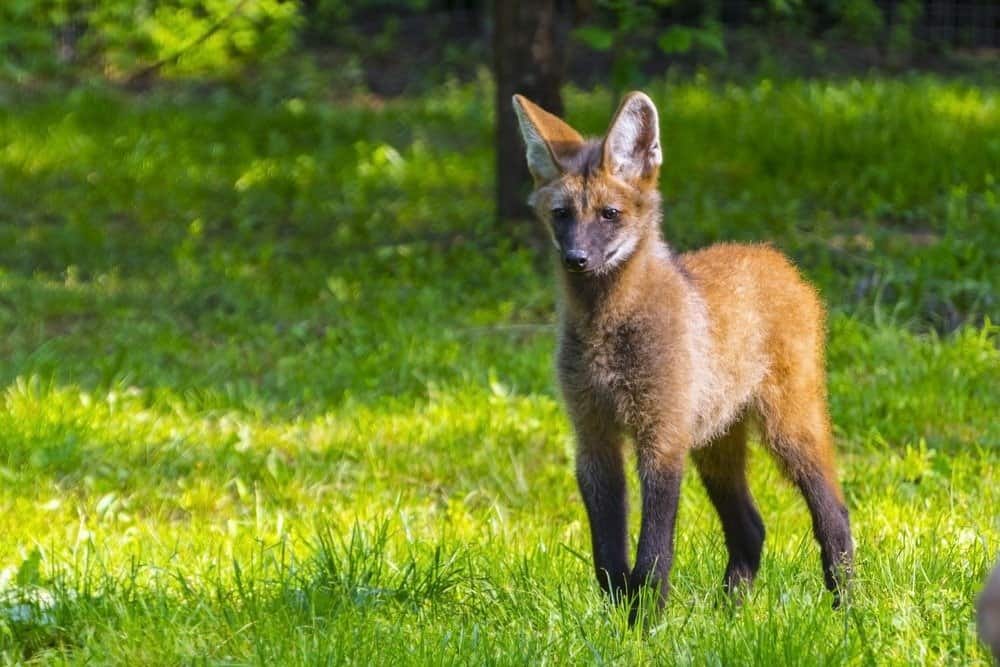

Maned Wolf puppies are very small, weighing about one pound.
©belizar/Shutterstock.com
The mating seasons for these canids are between November and April. Females only enter estrus once a year. Estrus is the set of physiological changes to a female’s body that occur due to the presence of reproductive hormones.
During courtship, males approach females and engage in an anogenital investigation. A female’s estrus period lasts for four days. During this period, copulation occurs. At the end of the four days, the male and female will engage in 15 minutes of intercourse. Unlike some other animals, male Maned Wolves also only produce sperm during the mating season.
The gestation period is between 60 and 65 days long. Two to six puppies will be born in each litter. When first born, the puppies are very small; they weigh just about 1 pound. For the first 10 weeks or so, the puppies will have black fur. After this time, it will turn red. Their eyes won’t open until they are about 9 days old.
The puppies are dependent on their parents for food during their first year. They are breastfed until they are up to 4 months old. After they are 3 weeks old, the puppies also receive regurgitated food from their parents. While the males may provide some help in caring for the young, the females are primarily responsible for this task.
While the exact lifespan of wild Maned Wolves is not known, scientists estimate that they have an average lifespan of between 12 and 15 years. One Maned Wolf at the São Paulo Zoo is reported to have lived 22 years.
Population
Sadly, the threats faced by these animals are causing their population to decrease. It is estimated that there are around 23,600 Maned Wolves left in the wild. They have a conservation status of near-threatened.
View all 164 animals that start with MManed Wolf FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are Maned Wolves carnivores, herbivores, or omnivores?
Maned Wolves are omnivores. In addition to hunting small to medium animals, they also eat plants.
What is a Maned Wolf?
A Maned Wolf is the largest canine found in South America. Maned Wolves look similar to foxes. However, they are not in the same genus as either foxes or wolves. They have a red/reddish-brown or golden orange coat, long black legs, and a black mane. They are a solitary animal that can be found in grasslands, marshes, wetlands, forests, and savannas.
How tall is a Maned Wolf?
Maned Wolves can be up to 35 inches tall. They have very long legs and have been compared to a fox on stilts.
Where do Maned Wolves live?
Maned Wolves live in central and eastern South America. They can be found in Brazil, Paraguay, Argentina, Bolivia, and Peru. Within these countries, they live in marshes, wetlands, forests, savannas, and grasslands.
What does a Maned Wolf eat?
As an omnivore, Maned Wolves eat both plants and animals. They eat lobeira, a berry similar to tomatoes, other fruits, and vegetables. They hunt for small- and medium-sized animals including rabbits, rodents, birds, fish, and insects.
Is the Maned Wolf endangered?
Maned Wolves are not currently considered endangered. However, their population has been decreasing and many are concerned about their future. They are currently listed as near-threatened by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
How many puppies do Maned Wolves have?
A litter of Maned Wolves will normally have between 2 and 6 puppies.
Do Maned Wolves attack humans?
Unless they feel threatened, a Maned Wolf will not attack humans. They are shy, and in most cases, will run when they see a human.
What Kingdom do Maned Wolves belong to?
Maned Wolves belong to the Kingdom Animalia.
What phylum do Maned Wolves belong to?
Maned Wolves belong to the phylum Chordata.
What class do Maned Wolves belong to?
Maned Wolves belong to the class Mammalia.
What family do Maned Wolves belong to?
Maned Wolves belong to the family Canidae.
What order do Maned Wolves belong to?
Maned Wolves belong to the order Carnivora.
What type of covering do Maned Wolves have?
Maned Wolves are covered in Fur.
What are some predators of Maned Wolves?
Predators of Maned Wolves include jaguars and pumas.
What is the scientific name for the Maned Wolf?
The scientific name for the Maned Wolf is Chyrsocyon brachyurus.
What is the lifespan of a Maned Wolf?
Maned Wolves can live for 12 to 15 years.
How many species of Maned Wolf are there?
There is 1 species of Maned Wolf.
What is the biggest threat to the Maned Wolf?
The biggest threat to Maned Wolves is habitat destruction.
What is an interesting fact about Maned Wolves?
Despite its name, the Maned Wolf is not actually a wolf.
How fast is a Maned Wolf?
A Maned Wolf can travel at speeds of up to 47 miles per hour.
What are the differences between a maned wolf and a Great Dane?
There are several differences between a maned wolf and a Great Dane. While they are both canines, the maned wolf belongs to a genus that only belongs the species. Great Danes are domesticated dogs while maned wolves are wild animals that live exclusively in South America.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- EOL, Available here: https://eol.org/pages/328686
- Wikipedia, Available here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Maned_wolf#Hunting_and_territoriality
- Smithsonian's National Zoo & Conservation Biology Institute, Available here: https://nationalzoo.si.edu/animals/maned-wolf#:~:text=The%20total%20population%20is%20believed,main%20threat%20to%20maned%20wolves.
- World Land Trust, Available here: https://www.worldlandtrust.org/species/mammals/manedwolf/
- Roaring Earth, Available here: https://roaring.earth/neither-fox-nor-wolf/