Bearded Dragon
Pogona Vitticeps
Can grow to up 24 inches long!
Advertisement
Bearded Dragon Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Reptilia
- Order
- Squamata
- Family
- Agamidae
- Genus
- Pogona
- Scientific Name
- Pogona Vitticeps
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Bearded Dragon Conservation Status
Bearded Dragon Facts
- Main Prey
- Insects, Mice, Leaves
- Distinctive Feature
- Pronounced beard when scared and morphs skin colour
- Habitat
- Arid forest and desert
- Predators
- Birds, Snakes, Crocodiles
- Diet
- Omnivore
- Average Litter Size
- 15
- Lifestyle
- Solitary
- Favorite Food
- Insects
- Type
- Reptile
- Slogan
- Can grow to up 24 inches long!
View all of the Bearded Dragon images!

“A bearded dragon can change the color of its beard according to its mood”
Bearded dragons live in Central and Southern Australia.
See all of our expert product reviews.
They are omnivores that can live to be 15 years or older. This animal uses the beard of spines under its chin to communicate its moods to other animals. A bearded dragon is cold-blooded, so it needs to live in warm temperatures.
This reptile is a popular pet because it’s affectionate and curious. Learn about the most friendly wild animals in the world here.
5 Bearded Dragon Facts
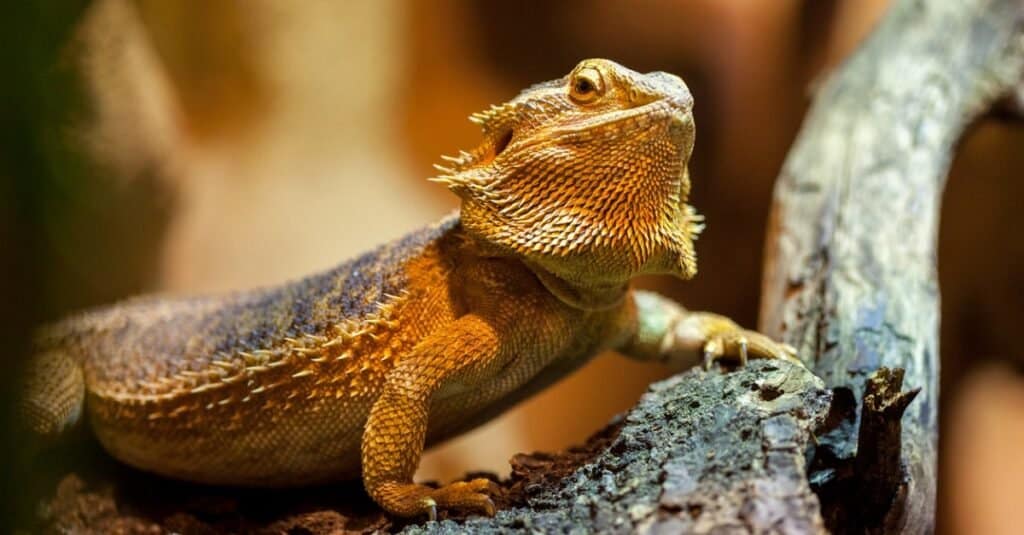

Some bearded dragons can grow up to 2 feet long
©iStock.com/huettenhoelscher
• A bearded dragon can grow to be 2 feet long
• Some bearded dragons go into a type of hibernation in cold weather
• Bearded dragons live in woodlands, deserts, and savannas
• These reptiles lay on rocks to sun themselves and raise their body temperature
Health and Entertainment for your Bearded Dragon
See all of our expert product reviews.
Evolution and Origins of Bearded Dragons
Bearded dragons are a type of lizard that originated from the common reptilian trunk about 250 million years ago. This branch of ancient reptilians is actually much older than the branch that would eventually lead to the dinosaurs and birds.
In fact, One ancestor, Pogona barbata, had a lot of yellow pigment in its mouth so any Pogona today with the same characteristic has at least some P. barbata bloodline.
These days, Bearded dragons are now found in many deserts and other dry climates in Australia.
Scientific Name
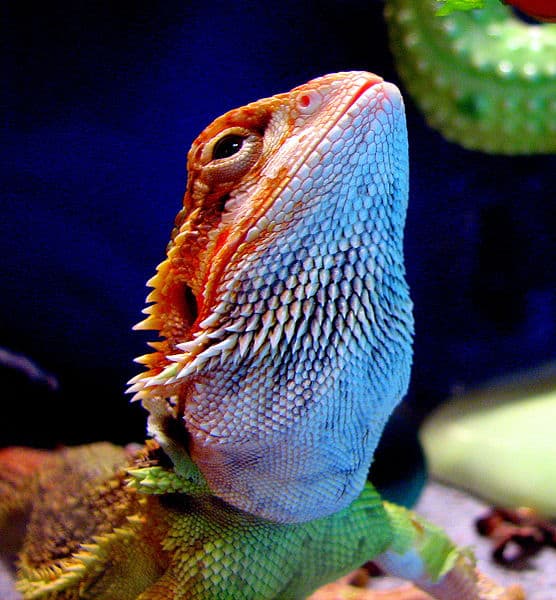

The bearded dragon’s scientific name is
Pogona VitticepsThe bearded dragon is this reptile’s common name while its scientific name is Pogona Vitticeps. Look a little further into the taxonomy of this reptile and you’ll see it belongs to the Agamidae family and its classification is Reptilia.
The scientific name of this animal comes from the Greek words Pogona (Pogon) meaning beard and Vitticeps meaning striped beard.
List of Types of Bearded Dragons
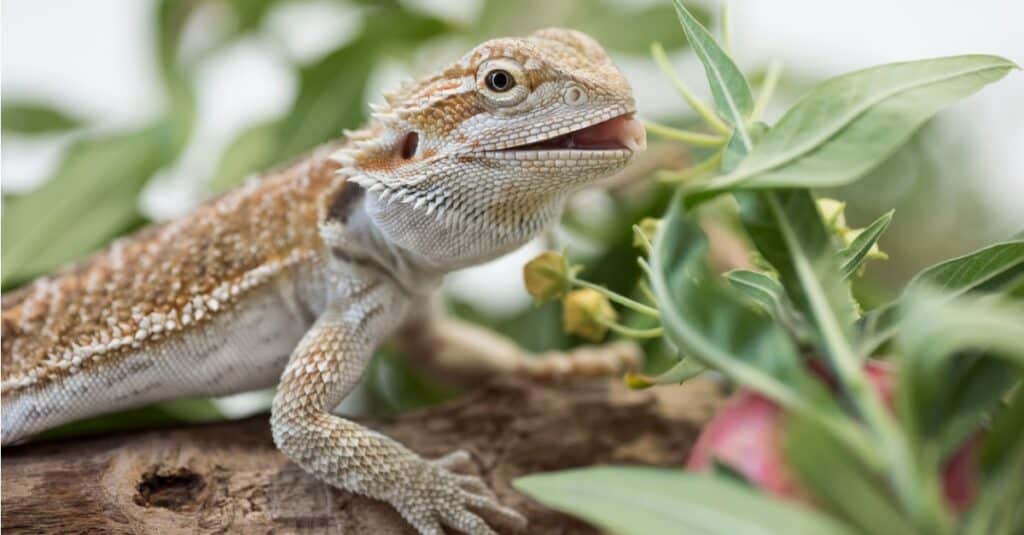

The central bearded dragon (
Pogona vitticeps)
©iStock.com/JeannetteKatzir
Central Bearded Dragon: The central bearded dragon (Pogona vitticeps) is also known as the inland bearded dragon. It is also the most common species found as a pet.
Eastern Bearded Dragon: The eastern bearded dragon (Pogona barbata), also known as the common bearded dragon or simply bearded lizard. Despite being a member of the toxic-bearing species, they are non-venomous however, they can bite.
Rankin’s Dragon Pogona Minor Dragon: Rankin’s dragon (Pogona henrylawsoni) is a species of Australian agamid lizard. It may also be called the pygmy bearded dragon. They are a smaller cousin of the common bearded dragon and are just as friendly.
Pogona Minor Dragon: Pogona minor minima, the Abrolhos bearded dragon or Abrolhos dwarf bearded dragon, is an agamid lizard. They produce relatively large clutches of eggs (about 30 eggs at once!)
List of Bearded Dragon Morphs
- Classic/Standard
- Leatherback
- Translucent
- Hypomelanistic
- Dunner
- German Giant
- Silkback
- Witblits
- Zero
- Wero
- Paradox
Appearance and Behavior
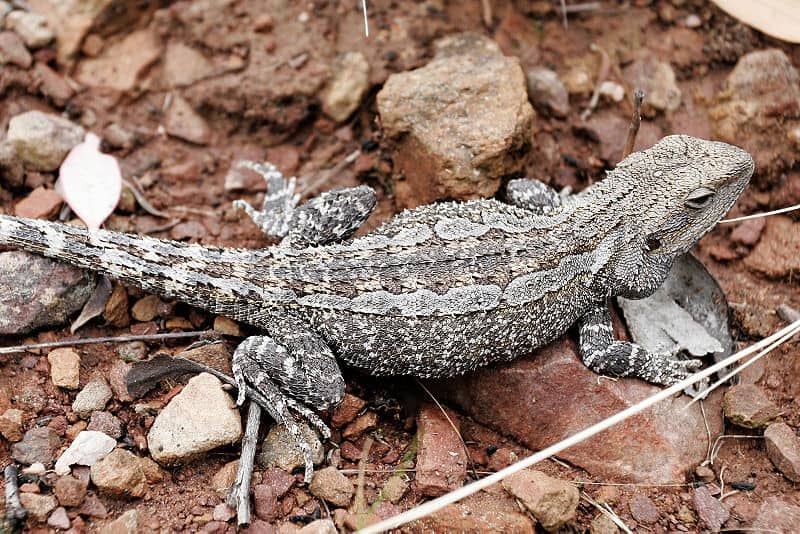

Bearded dragons have ear holes on the sides of their triangular head
A bearded dragon has yellowish, tan skin. It has a long body with a tail measuring more than half of its total length. A bearded dragon can measure up to 2 feet in length including its tail. An adult bearded dragon can weigh up to 18 ounces. Grab 2 cans of soup from your kitchen pantry and imagine that a bearded dragon’s weight is equal to about a can and a half.
This reptile has spines under its chin and along the sides of its body. Also, it has ear holes on the sides of its triangular head. A bearded dragon has four sturdy legs and sharp claws that help it to climb trees.
A bearded dragon protects itself from predators by changing color and blending into its environment. Plus, its scales and spiny skin help to protect it when a predator like a snake or a hawk tries to grab it. When this animal feels threatened, it puffs up its spiny beard and opens its mouth to make itself appear larger to enemies.
Bearded dragons are shy, solitary animals except during mating season. They can be aggressive only when they feel their territory is being threatened. Also, males can be aggressive while choosing a mate.
The spiny beard of a bearded dragon helps it to communicate in many ways. When this reptile changes the color of its beard and quickly bobs its head it is trying to show dominance over another male. When a bearded dragon bobs its head slowly and raises one of its legs, it is showing that it’s not a threat to another dragon in the area.
Habitat

There are 8 species of bearded dragons that live across the continent of Australia. They live in arid and subtropical environments including savannas, woodlands, and deserts. Lots of bearded dragons climb into trees and sit on branches to sun themselves.
Being up so high allows them to be on the lookout for predators in the area. Plus, they can change skin color blending in with the branch they’re sitting on. Other bearded dragons sun themselves on rocks. If this reptile sees a predator while sunning itself on a rock, it scurries into a crack between rocks to hide underground.
When the cold weather season starts in the autumn, bearded dragons go into a type of hibernation called brumation. While in brumation, this reptile is not completely asleep like a bear would be. The difference is it doesn’t eat during this period but does drink water to stay hydrated.
Diet

Bearded dragons are omnivores. They are not picky about their diet. They eat insects such as cockroaches, crickets, and locusts. In addition, they will snack on flowers, fruit, and leaves. Some bearded dragons eat lizards and small rodents such as mice.
These reptiles eat about once a day. If an adult bearded dragon is hunting crickets, it may eat 2 or 3 large ones. A baby bearded dragon that is growing quickly is likely to eat more than an adult reptile.
Fireflies and other insects that glow in the dark are poisonous to bearded iguanas. The chemical in a firefly’s body that makes it glow is harmful to a bearded dragon. In addition, bearded dragons do eat fruit, however, avocados are poisonous to them. For a complete list of foods bearded dragons eat, check out our “What Do Bearded Dragons Eat?” page.
Predators and Threats
Snakes, birds, dingoes, goannas, and crocodiles are all predators of a bearded dragon. An owl may fly down to a branch to grab a bearded dragon that’s sunning itself. Or, a dingo may capture a bearded dragon that’s lying on a rock to get some sun in the afternoon. Though a bearded dragon can run up to 9 miles an hour, it isn’t as fast as some of its predators.
The habitat of bearded dragons is threatened. When trees are cut down or land cleared, bearded dragons have no place to live. Also, some bearded dragons are caught and sold as exotic pets in other countries. This reduces the population in the wild. Fortunately, there are preserves in Australia where bearded dragons are cared for and protected from both of these threats. Their official conservation status is Least Concern.
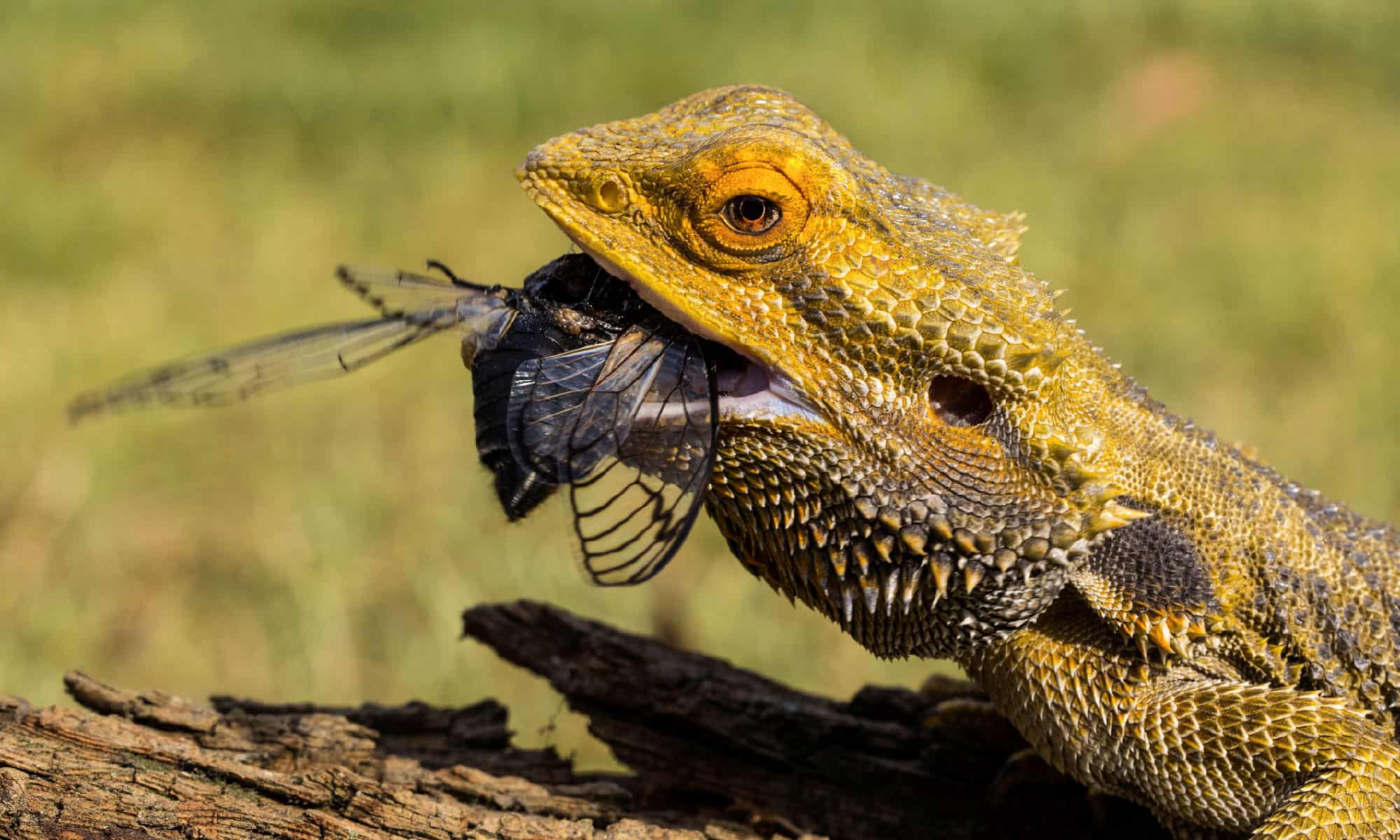

A bearded dragon feasting on a cicada.
©iStock.com/Ken Griffiths
Reproduction, Babies, and Lifespan
Bearded dragons mate in the spring and summertime. During mating season, a male bearded dragon bobs its head and stamps its feet to attract a female.
A female can lay from 11 to 30 eggs at a time. After mating with one male, a female may lay two or three different groups of eggs that number 11 to 30. A female bearded dragon may lay 9 groups or clutches of eggs in one year. The gestation period of this reptile is 55 to 75 days. This is a lot shorter than an iguana’s which is 90 to 120 days.
It’s possible for the sex of a bearded dragon to change while it’s incubating. A developing male can develop into a female bearded dragon if the temperature during incubation is especially hot.
It takes about three days for a baby bearded dragon to break out of its egg. Its birth weight is around one ounce and it’ll be about 3 to 4 inches long. A baby bearded dragon that is 4 inches in length is just a little longer than a crayon.
Baby bearded dragons are sometimes called hatchlings. Once a female bearded dragon lays her eggs, she doesn’t see them again. They are on their own immediately after they hatch.
Bearded dragons live for about 15 years. Pet bearded dragons may live a little longer because of the lack of threat from predators. These reptiles are sometimes vulnerable to respiratory infections and parasites but otherwise live healthy lives if they take in enough nutrition. The oldest bearded dragon is listed in the Guinness Book of World Records. This bearded dragon named Sebastian lived to be 18 years old. He died in 2016 in England.
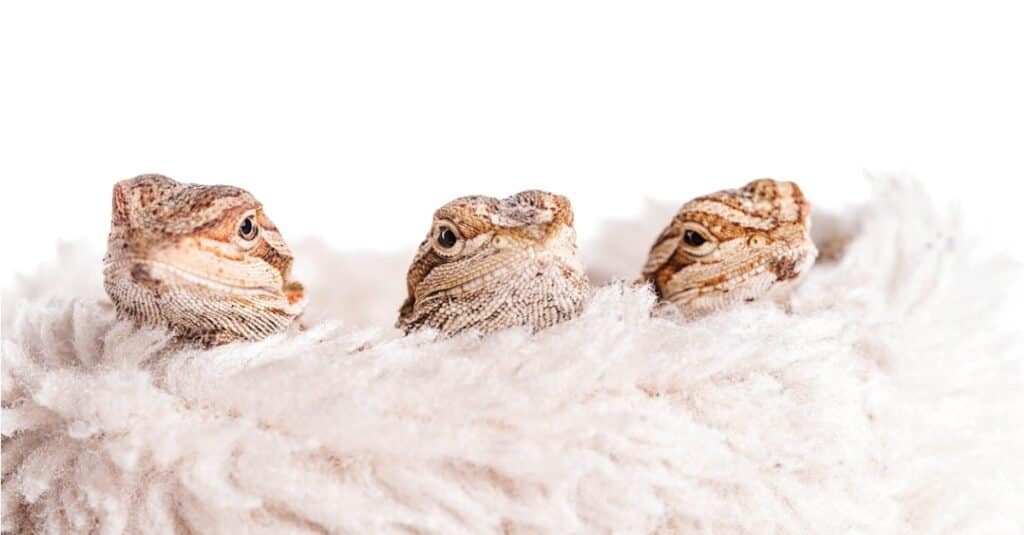

Baby bearded dragons
©iStock.com/Kaan Sezer
Male vs Female
There are several key differences between male and female bearded dragons, Males are typically about 20% larger in terms of weight. Most importantly, male bearded dragons will have two hemipenal bulges. There is where the sex organs of male bearded dragons are kept. In females, there will be a single bulge that’s centered on their bodies.
Population
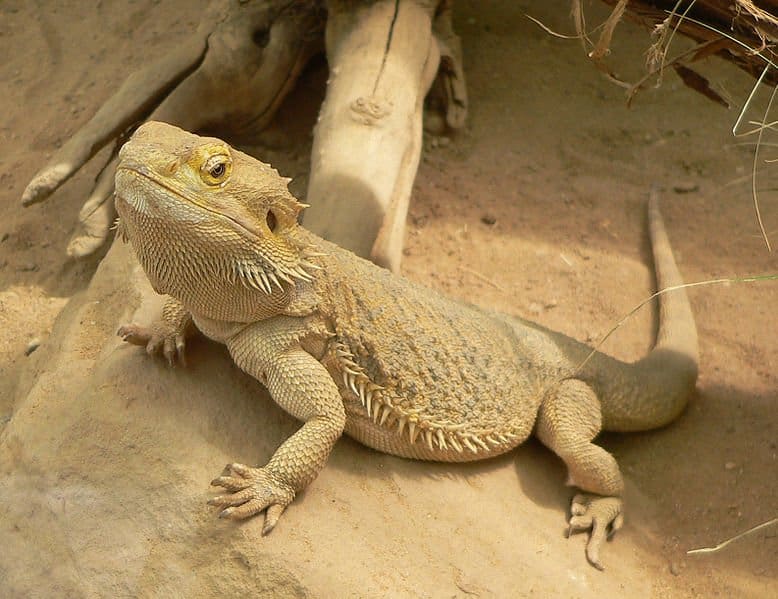

Bearded Dragon is the least concern as the official conservation statues
©Frank C. Müller, Baden-Baden, CC BY-SA 2.5, via Wikimedia Commons – License
The official conservation status of the bearded dragon is Least Concern. The population of these reptiles remains steady in Australia. Plus, there are over 900 bearded dragons living in zoos throughout the world. There are laws in Australia protecting bearded dragons from poachers who capture them and try to ship them out of the country. Today, many bearded dragons are bred outside of Australia.
Bearded Dragon as a Pet
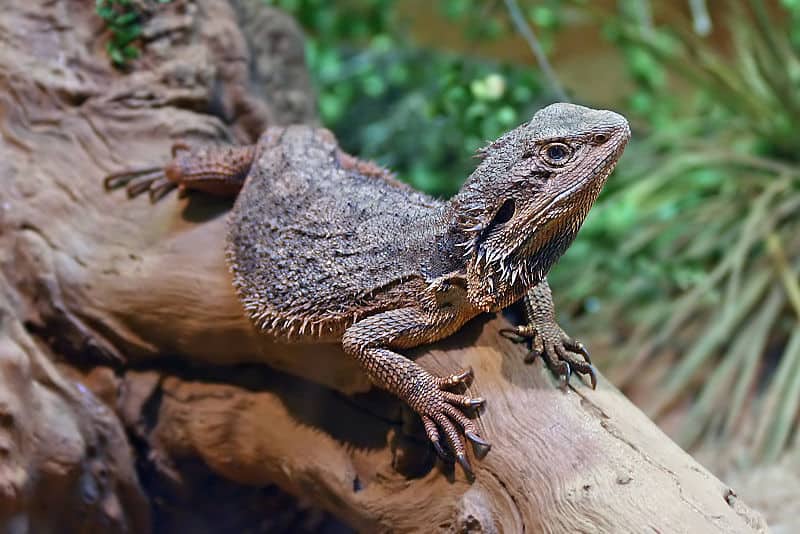

A pet bearded dragon makes a great family addition.
Bearded dragons are one of the more popular choices for pet lizards. In captivity, they generally grow up to 24″ long and live 10 years on average. When young, they eat an even mix of plants and insects, and as they mature their diet goes heavily plant-based, with only about 10% insects.
A terrarium of a minimum of 40 gallons would be needed to create a good habitat for your pet, and factors to take into account would include: heating, substrate, lighting, humidity, temperature, and decor.
View all 285 animals that start with BBearded Dragon FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are bearded dragons carnivores, herbivores or omnivores?
Bearded dragons are omnivores. They eat insects, fruit, leaves and sometimes rodents. What a bearded dragon eats depends on the food source available in the area. If there is a shortage of insects due to weather conditions, a bearded dragon may eat dry leaves for nourishment.
How do you take care of a bearded dragon?
If you have a bearded dragon as a pet, there are several things it needs to stay healthy. A spacious aquarium, branches to climb on, food and water bowls, a heat lamp, UVB light, nutritious food and a ventilated lid on the aquarium. One of the most important things to consider when caring for a bearded dragon is heat. They are cold-blooded animals that need the right amount and type of heat to keep them comfortable.
How do you tell the sex of a bearded dragon?
One way to determine the sex of your bearded dragon is to look at the base of its tail for hemipenal bulges. If your bearded dragon has them, then it’s a male. A second way to check your pet’s sex is to look for femoral pores on the underside of your bearded dragon’s back legs. If you see these pores, your pet is a male. A third way is to take a close look at your pet if you have two to compare. A male bearded dragon has a bigger head and body than a female.
Are bearded dragons friendly?
Yes. Bearded dragons are curious and affectionate. The only exception would be a male defending his territory during breeding season. Or, if a bearded dragon feels threatened by someone or something, it could act in an aggressive way.
How long does a bearded dragon live?
Bearded dragons usually live around 15 years. If they receive a balanced diet and avoid predators they can live long, healthy lives.
Are bearded dragons dangerous?
No. A wild bearded dragon will try to avoid human contact by escaping into a crevice or running up a tree. A tame bearded dragon that is a pet in someone’s home will probably want a lot of attention and affection from its owner.
What Kingdom do Bearded Dragons belong to?
Bearded Dragons belong to the Kingdom Animalia.
What phylum do Bearded Dragons belong to?
Bearded Dragons belong to the phylum Chordata.
What class do Bearded Dragons belong to?
Bearded Dragons belong to the class Reptilia.
What family do Bearded Dragons belong to?
Bearded Dragons belong to the family Agamidae.
What order do Bearded Dragons belong to?
Bearded Dragons belong to the order Squamata.
What genus do Bearded Dragons belong to?
Bearded Dragons belong to the genus Pogona.
What type of covering do Bearded Dragons have?
Bearded Dragons are covered in Scales.
In what type of habitat do Bearded Dragons live?
Bearded Dragons live in arid forests and deserts.
What is the main prey for Bearded Dragons?
Bearded Dragons prey on insects, mice, and leaves.
What are some distinguishing features of Bearded Dragons?
Bearded Dragons have pronounced beards when scared and can morph their skin color.
What are some predators of Bearded Dragons?
Predators of Bearded Dragons include birds, snakes, and crocodiles.
What is the average litter size for a Bearded Dragon?
The average litter size for a Bearded Dragon is 15.
What is an interesting fact about Bearded Dragons?
Bearded Dragons can grow to up 24 inches long!
What is the scientific name for the Bearded Dragon?
The scientific name for the Bearded Dragon is Pogona Vitticeps.
What is the difference between a bearded dragon and a chameleon?
The greatest differences between a bearded dragon and chameleon are their size, tails, and eyes. Bearded dragons are smaller than chameleons. Although they share a similar body length, most of a bearded dragon’s body length comes from their somewhat thin tails. Chameleons also weigh more than bearded dragons, but they can be incredibly small, too.
What's the difference between a bearded dragon and an iguana?
Bearded dragons and iguanas differ in 5 key ways including morphology and diet.
How to say Bearded Dragon in ...
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- David Burnie, Dorling Kindersley (2011) Animal, The Definitive Visual Guide To The World's Wildlife
- Tom Jackson, Lorenz Books (2007) The World Encyclopedia Of Animals
- David Burnie, Kingfisher (2011) The Kingfisher Animal Encyclopedia
- Richard Mackay, University of California Press (2009) The Atlas Of Endangered Species
- David Burnie, Dorling Kindersley (2008) Illustrated Encyclopedia Of Animals
- Dorling Kindersley (2006) Dorling Kindersley Encyclopedia Of Animals