Grass Spider
Agelenopsis
Their fangs aren't big enough to penetrate human skin.
Advertisement
Grass Spider Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Arthropoda
- Class
- Arachnida
- Order
- Araneae
- Family
- Agelenidae
- Genus
- Agelenopsis
- Scientific Name
- Agelenopsis
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Grass Spider Conservation Status
Grass Spider Facts
- Prey
- insects
- Name Of Young
- spiderling
- Group Behavior
- Solitary
- Solitary except during mating season
- Fun Fact
- Their fangs aren't big enough to penetrate human skin.
- Most Distinctive Feature
- Chevron patterns on abdomen
- Gestation Period
- Funnel Web Spiders, Ground Spiders, Sheet Web Spiders, and Funnel Weavers
- Habitat
- Grass, Lawns, Under rocks
- Predators
- Lizards, centipedes, birds
- Diet
- Insectivore
- Lifestyle
- Nocturnal
- Favorite Food
- Moths, Crickets, Aphids, Grasshoppers
- Common Name
- Grass Spider
- Number Of Species
- 14
- Location
- Canada, Kyrgyzstan, Mexico, Russia, Ukraine, United States
View all of the Grass Spider images!
Grass spiders are often found mainly in the grass, as you can determine by their name. But they might wander off to other places. They are one of the 1,200 funnel-web spider species that create a blackhole-shaped webs through their large spinnerets. You will often find these webs more than you will find the grass spider.
Grass Spider Species, Types, and Scientific Name
Grass spiders are known as the Agelenopsis by scientists. It was first described in 1869 and is Greek in origin. The term Agelenopsis consists of “Agelena”, which is a genus also known as Eurasian grass spiders, and “opsis”, which means “to look like”. It belongs to the family Agelenidae and the order Araneae.
It is often confused with the wolf spider and the hobo spider, because of the patterns on its head region. You will spot on either side of the midline two black lines that are slightly lighter and thinner than those on a wolf spider. Moreover, the abdomen of the grass spider has a series of dark chevrons, which are lighter than on wolf spiders. The grass spider contains venom, but with such small fangs, they are not dangerous to humans.
The grass spider has a few common names around the world. They are funnel web spiders, ground spiders, sheet web spiders, and funnel weavers. There are 14 known species of grass spiders.
They are:
- Agelenopsis actuosa
- Agelenopsis aleenae
- Agelenopsis aperta
- Agelenopsis emertoni
- Agelenopsis kastoni
- Agelenopsis longistyla
- Agelenopsis naevia
- Agelenopsis oklahoma
- Agelenopsis oregonensis
- Agelenopsis pennsylvanica
- Agelenopsis potteri
- Agelenopsis riechertae
- Agelenopsis spatula
- Agelenopsis utahana
Appearance: How To Identify the Grass Spider?
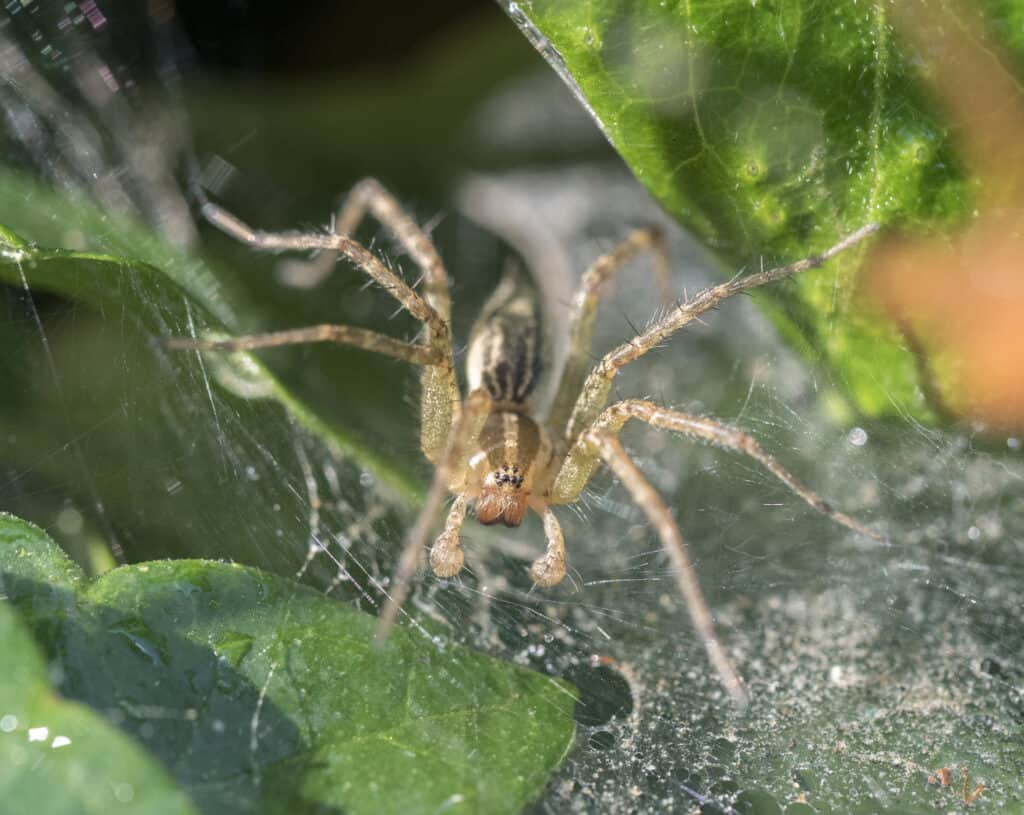

Funnel weaver spider, or grass spider, waiting for prey in web in garden.
©iStock.com/johnandersonphoto
Eggs
The eggs are in form of a sac that is laid by the female during the spring season. But the female grass spider dies shortly after hatching the eggs because of the drop in temperature. The baby spiders hatch after a while and go through eating, mating, and molting to eventually become adult spiders.
Adult
Grass spiders are about half an inch or three-quarters of an inch long. They exhibit sexual dimorphism, and the females are larger than the males. The females measure up to 0.39 to 0.78 inches while the males are around 0.31 to 0.70 inches long. They weigh just as much as a jumping spider, approximately 3 ounces.
It has a hard shell or carapace that is round in shape and has three distinct bands. Two of them run on either side of the middle band and are darkish brown in color. The middle band, however, is slightly lighter than the other two.
The grass spider is usually yellowish brown in color with chevron patterns that distinguish them from other similar spiders. But they show a mix of different colors on their body. The carapace is yellowish brown in color while the abdomen and the distinct part of the legs are relatively darker in color. The spinnerets are long structures on their abdomen but appear as short tails on the body.
The grass spider’s webs often identify it, rather than its physical appearance. You will find its web placed horizontally and formed as a sheet-like structure ending in a funnel. You can imagine it to resemble a black hole. The sheet extends up to 3 feet, while the funnel may measure up to a foot long.
The funnel portion of the web sits within a shelter that often leads down to the spider’s safe space. This may be a rock or any crevice. Prey may come on this web that sends the signal to the Grass Spider. This trap allows the Grass Spider to pounce on them.
The web is not that reliable for the spider, because it is not exceptionally sticky. Because of the shape, the prey falls inside the trap. This is why grass spiders are agile. They speed toward their prey and attack them, rather than waiting for the prey to stick to the web.
A grass spider is solitary in nature. You will not find it interacting with other of its species socially unless it is the mating season. But one grass spider may share its habitat with other grass spiders sometimes. Their behavior is mostly nocturnal where they avoid going out to hunt in the daylight to hide from predators. They will hunt and eat their prey at night.
Habitat: Where to Find Grass Spider?
Grass spiders mainly reside in North America. But they were introduced into various countries in Central Asia. Their population size is unknown, but they are in abundance in the northern parts of America.
If you wish to spot them, you can find them in dirty places in a house. They are not attracted to grime, but this is where their prey resides. Many small insects like ants are usually near food scraps or other dirty areas. Hence, these sites make as good as any place for the grass spiders to come and set up their webs.
However, this is only a rare instance where a male grass spider may find itself in homes. Otherwise, they are found in lawns, grass, gardens, ornamental plants and trees, along foundations, log piles, under rocks and lawn ornaments, tubs, window wells, and sinks. They tend to hide inside the funnel portion and come out only when there is prey nearby on their web.
Diet: What Do Grass Spiders Eat?
Grass spiders are carnivorous in nature and more specifically, insectivorous. They are pretty fast in locomoting, which serves as a great hunting technique for the Grass Spiders.
What Do Grass Spiders Eat?
They eat insects that are smaller than them. This includes insects found in the grass, like moths, crickets, grass bugs, aphids, grasshoppers, etc., or the ones found inside homes like ants.
What Eats Grass Spiders?
Their predators include lizards, birds, and centipedes.
Prevention: How to Get Rid of Grass Spiders?
Grass Spiders are not particularly dangerous to humans. They carry venom, but that is mostly for their prey. Moreover, they are very shy and not at all aggressive in nature. They may bite a human but only in self-defense or if provoked.
Reported grass spider bites have caused pain, swelling, redness, and itching. These symptoms usually stay with the victim for a time ranging anywhere between one day and ten days. Sometimes, a bacterial infection may occur. There have been no reports of a fatal grass spider bite.
Having said that, they may sometimes inhabit domestic homes. You might only find them due to their webs because they stay hidden in the funnel portion of the web that is situated within a shelter. But if you have small insects, you may find yourself encountering a grass spider infestation too. If that happens, you can opt to do a few things.
- Clean up leftover food, pet food, crumbs, and scraps around the house. Do not leave them lying around as they attract ants, which will call out the grass spiders.
- Mow your lawns frequently, because this is where they build large nests.
- Trim the bushes, hedges, and vegetation around your house and keep them neat to avoid building a grass spider habitat.
- Use a broom to remove spider webs that will force them to build their nests somewhere else.
Up Next…
Enjoying our spider-related articles? Take a look at a few others.
- Why Do Plagues Of Snakes And Spiders Follow Floods? – Find out why you see more of them after a flood.
- 10 Black Widow Facts – You’ve probably heard of these spiders, but do you know how incredible they actually are?
- Insects Vs Spiders – You can finally find out what the difference is between these two!
Grass Spider FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are grass spiders dangerous?
No, they are not dangerous. They do have venom, but that is to subdue prey. The most they will do to a human is bite, though their fangs are not penetrable to human skin. So, you will feel itching, redness, and swelling for anywhere between 1 to 14 days if bitten by a grass spider.
How many legs does the grass spider have?
Four pairs for a total of eight.
How fast is a grass spider?
They are very fast movers and one of the fastest spider species to exist.
How do you identify a grass spider?
They are identified on the basis of the color of the bands on their carapace and the chevron patterns on their abdomen.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- Smiths Pest Management, Available here: https://smithspestmanagement.com/blog/post/how-to-get-rid-of-grass-spiders/
- PSU, Available here: https://extension.psu.edu/grass-spiders
- MDC, Available here: https://mdc.mo.gov/discover-nature/field-guide/grass-spiders
- Insect Identification, Available here: https://www.insectidentification.org/insect-description.php?identification=Grass-Spider
- Western Exterminator, Available here: https://www.westernexterminator.com/spiders/everything-you-never-knew-about-grass-spiders/
- New Mexico Pest Control, Available here: https://newmexicopestcontrol.com/pest-info/spiders/grass-spider/
- Kidadl, Available here: https://kidadl.com/facts/animals/grass-spider-facts