Executioner Wasp
Polistes carnifex
The Executioner Wasp's sting is one of the most painful in the world.
Advertisement
Executioner Wasp Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Arthropoda
- Class
- Insecta
- Order
- Hymenoptera
- Family
- Vespidae
- Genus
- Polistes
- Scientific Name
- Polistes carnifex
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Executioner Wasp Conservation Status
Executioner Wasp Facts
- Prey
- caterpillar
- Main Prey
- caterpillar
- Name Of Young
- Larvae
- Group Behavior
- Colonial Nesting
- Fun Fact
- The Executioner Wasp's sting is one of the most painful in the world.
- Wingspan
- 3 inches
- Habitat
- Central and South America
- Diet
- Omnivore
- Lifestyle
- Social
- Favorite Food
- moth and butterfly catarpillar
View all of the Executioner Wasp images!
The Executioner Wasp’s sting is one of the most painful in the world.
Summary
The Executioner Wasp (Polistes carnifex) is a large wasp native to central and South America. The wasp is one of the largest wasps in South America. It is most popular for its painful string, which is supposedly more painful than the sting of the Asian Hornet and Bullet ant. The Executioner Wasp’s name is a reference to its painful sting. Despite their notorious reputation, the Executioner Wasp is a beneficial insect because it aids pollination and hunts garden pests.
Executioner Wasp: Species, Types, and Scientific name
The Executioner Wasp (Polistes carnifex) is a large vespid wasp that belongs to the cosmopolitan genus Polistes. The family Vespidae where this Wasp belongs, has close to 5000 species of eusocial and solitary wasps. The Executioner Wasp belongs to a group of wasps known as paper wasps. These paper wasps construct their nest with wood fibers that they have masticated to the consistency of paper mache.
Since this Wasp is native to non-English speaking countries, it did not have an English name for a long time. The Polistes carnifex got the name “Executioner Wasp” in 2010. The name originates from the Latin meaning of the species name “carnifex”, which means hangman or executioner.
The wasp has several native names across various locations in South America. In Paraguay, for instance, it is known as “kava mainomby,” which translates as the “hummingbird wasp.” It is also called kava alazán or “brown wasp,” Although this name is usually applied to another wasp species. In Mexico, the Wasp is commonly called a’ma xtíya cháda, which means “huarache-nest wasp.”
Appearance: How To Identify Executioner Wasp
The Executioner Wasp is the largest in Central and South America. It is also one of the largest wasps in the Polistes genus. On average, the body length of this Wasp is about 2.4 to 2.7cm (0.9 to 1.06 inches). However, it can reach lengths of up to 3.3cm (1.3inches).
Polistes carnifex is typically yellow with brown stripes on its abdomen. Their wings are large and narrow and are often tinted brown. Their head is a predominant yellow color. However, the crown of the head may take on black color with reddish-brown stripes. Their legs are dark-colored, while the antenna is typically yellow as well.
The Executioner Wasp has many physical features that distinguish it from other species of wasps in the same genus. This includes a lack of grooves on the underside of their heads, wide cheek plates, and compact tergite.
Habitat: Where to Find Executioner Wasp
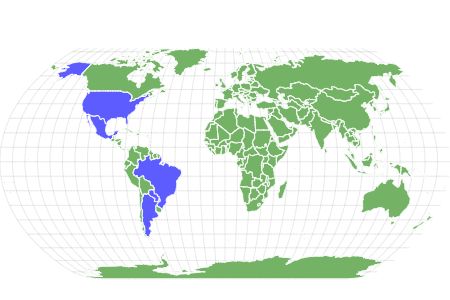
The Polistes carnifex is mostly found in Central and South America, where they originated. Their most notable range is in Argentina and Paraguay, but they exist sparingly in Brazil, Mexico, and up north in the United States.
In places where they’re found, members of this species live in coastal and humid climates with open areas like evergreen tropical forests and wooded habitats with no heavy rains. Like many vespid wasps, the Polistes carnifex is known to build small colonies. The colony is typically started by a solitary queen, who builds a nest on tree branches or under the eaves of buildings. The foraging adults would typically bring out prey to their nest to feed developing larvae housed in separate cells within the nest.
Diet: What Do Executioner Wasps Eat?
The Executioner Wasp is a beneficial insect because it feeds on pollen and nectar. During the feeding process, it ends up pollinating the plant. Additionally, they hunt insects and pests for food as well.
What Do Executioner Wasps Eat?
Executioner Wasps feed mainly on the caterpillar of moths and butterflies. The adult wasp kills the caterpillar, chews it up, and rolls it into a ball that they bring back to their nest to feed their larvae. The nectar from various flowers is an important source of carbohydrates for this insect.
What Eats Executioner Wasps?
The Executioner Wasp has a lot of natural enemies. This includes other insects like dragonflies and praying mantis. Spiders and centipedes may also prey on them. Larger predators such as birds, amphibians, and reptiles may also attack these wasps to feed on them. Small mammals like mice, weasels, and badgers also feed on wasps. The Executioner Wasp’s potent sting protects it against many predators.
Prevention: How To Get Rid Of Executioner Wasps
This wasp is feared because of its extremely painful sting. However, they are not really aggressive. They’re rarely a problem since they prefer to make their nests in open places. But in some cases, the female might make its nests under the eaves of buildings. In this case, it is always best to invite a professional to remove the wasps instead of trying to do so yourself.
Similar Animals
View all 117 animals that start with EExecutioner Wasp FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are Executioner Wasps Dangerous?
The Executioner Wasp’s sting is believed to be the most painful and venomous in the world. When threatened, the Wasp delivers a potent sting ranked at level four (the highest level) on the Schmidt pain index.
Is Executioner wasp aggressive?
Despite their painful sting, executioner wasps are not aggressive. They do not attack humans unless one gets too close to their nest, especially if it contains wasp larvae.
Where Do Executioner Wasps Live?
The executioner wasp’s native range is in Central and South America. It is commonly found in Mexico, Paraguay, Argentina, and some parts of Brazil. The species prefers to live in humid coastal areas and open areas like evergreen tropical forests.
What happens if you get stung by an Executioner Wasp?
The executioner wasp’s sting contains a painful venom that contains high amounts of histamines and norepinephrines. In addition to being extremely painful, the sting site will be swollen for days. Also, the venom breaks down living cells and tissues around the sting site.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- Insect Real / Theo James, Available here: https://www.insectrealm.com/5-interesting-facts-about-the-executioner-wasp/
- Wikipedia, Available here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polistes_carnifex
- Candide, Available here: https://candide.com/ZA/insects/5d987779-250f-49df-8393-9cc2aa7fb1f0
- Wikipedia, Available here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vespidae