Below you can find a complete list of types of Salvadoran animals. We currently track 243 animals in El Salvador and are adding more every day!
El Salvador is the smallest country in Latin America. Known as the Land of Volcanoes, the country has frequent earthquakes and volcanic activity. For such a small country it has a diverse ecology with pine forests, mountain ranges, tropical dry forests, two volcanic ranges, and a coastline on the Pacific Ocean. El Salvador is the only country in Central America that does not have a coastline on the Caribbean Sea.
High in the mountains, there is a cloud forest at the summit of Monte Cristo Mountain. The area is home to spider monkeys, anteaters, and many species of birds including toucans. Orchids and wild ferns also adorn the exquisite cloud forest. Mango, coconut and palm trees line the country’s coastline.
Facts About the Animals of El Salvador
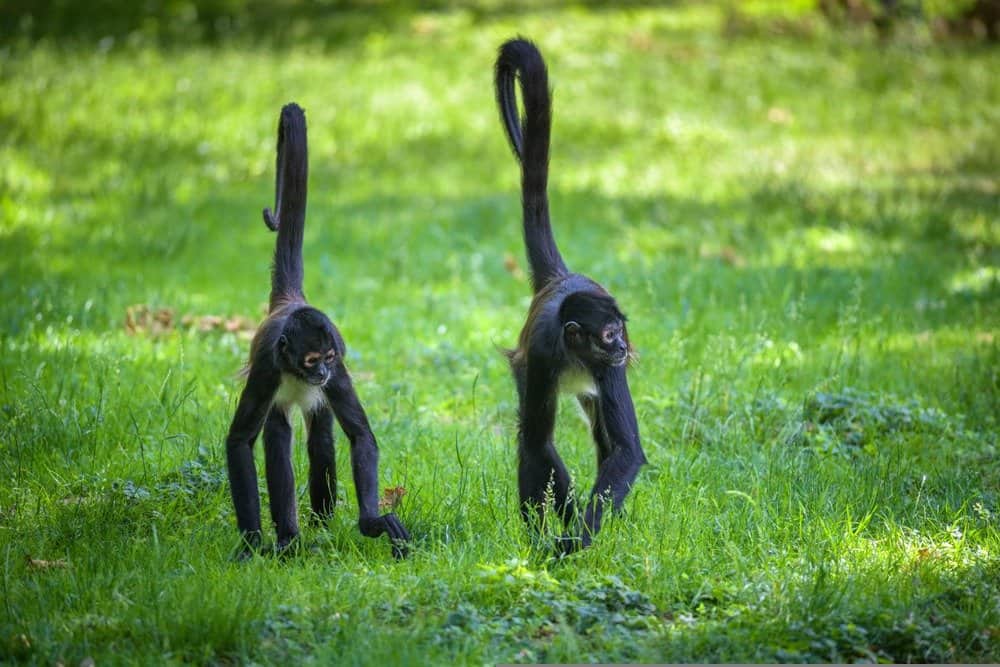

The best places to see spider monkeys in El Salvador are in national parks and private reserves.
©Nick Fox/Shutterstock.com
The most common types of animals in El Salvador are butterflies and birds, with hundreds of species of each. Popular birds are the quetzal, motmot, toucan, macaw, and kingfisher.
Since most of the land is under cultivation, national parks and private reserves are the best places to see popular mammals, including ocelots, spider monkeys, and white-tailed deer.
National Animal and National Bird of El Salvador
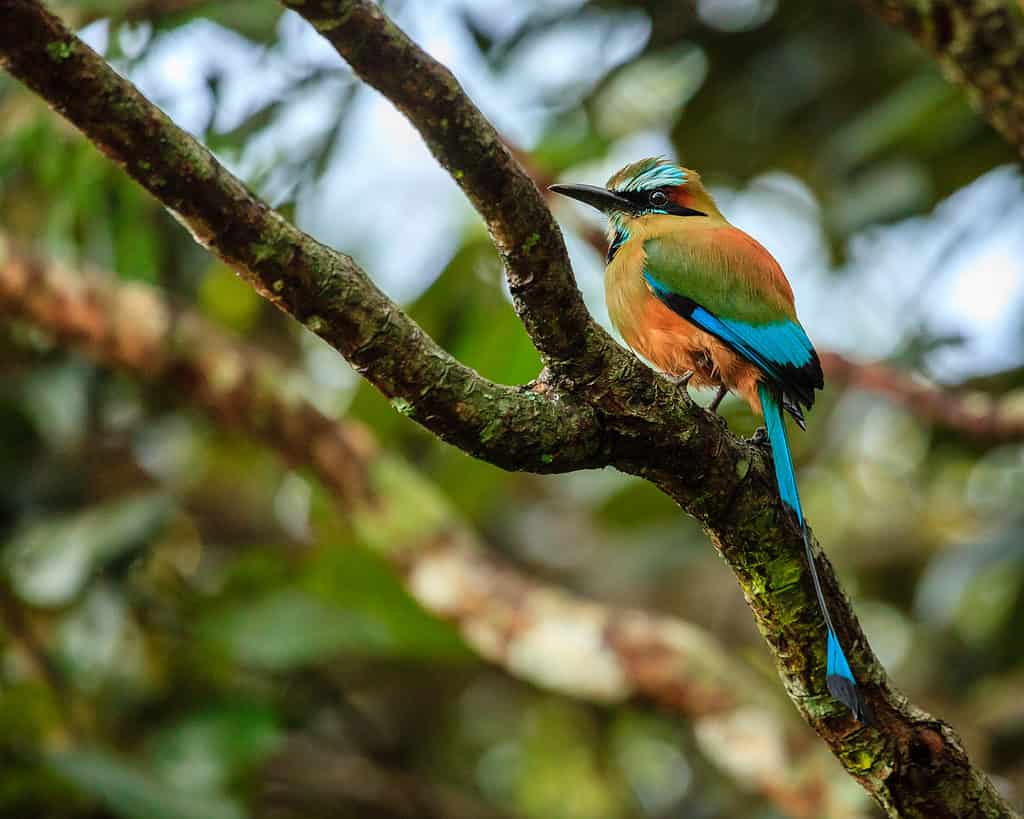

Turquoise-browed motmot (Eumomota superciliosa) is the national animal of El Salvador.
©iStock.com/alexeys
El Salvador’s national animal and the national bird is the turquoise-browed motmot (Eumomota superciliosa), a gorgeous, brightly colored tropical bird with a deep turquoise chest and bright blue patches on its head, chest, and long tail feathers. People in El Salvador call this native bird the “torogoz.” It is said to symbolize freedom, liberty, and the beauty of nature.
These birds are fairly easy to encounter in El Salvador, often seen perching in trees at the edge of forests and more out in the open than other tropical birds. Turquoise-browed motmots don’t build nests like other birds – instead, they dig long burrows in the ground along river banks.
Where To Find The Top Wildlife
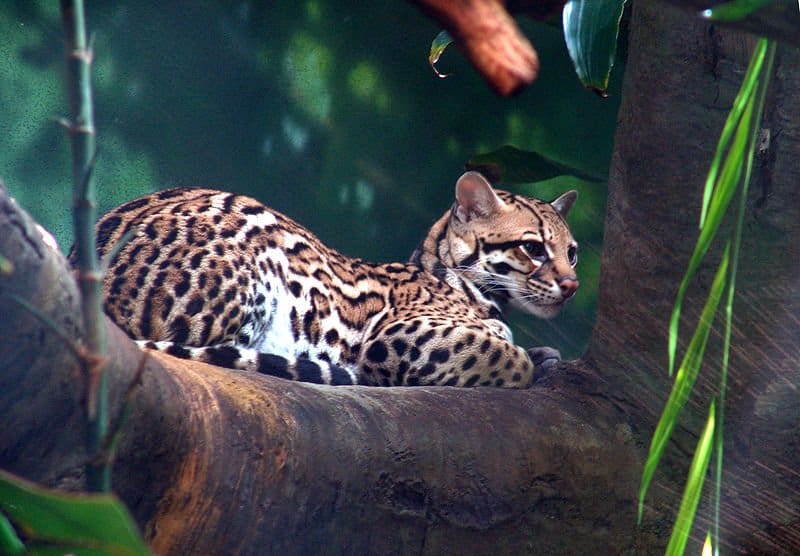

Ocelots can be seen at
Parque Nacional Montecristo
.
©Danleo, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons – License
The sad facts are that the country is facing the destruction of forests due to deforestation, leading many animals native to El Salvador to endangerment. The best places to see wild animals are in national parks and private reserves.
At Parque Nacional Cerro Verde, you can see emerald toucanets, motmots, and hummingbirds.
Parque Nacional Montecristo is a good place to spot ocelots, pumas and spider monkeys.
Cerro El Pital is the country’s highest peak. It’s a popular place to see catch sight of motmots and quetzals.
Largest Animal
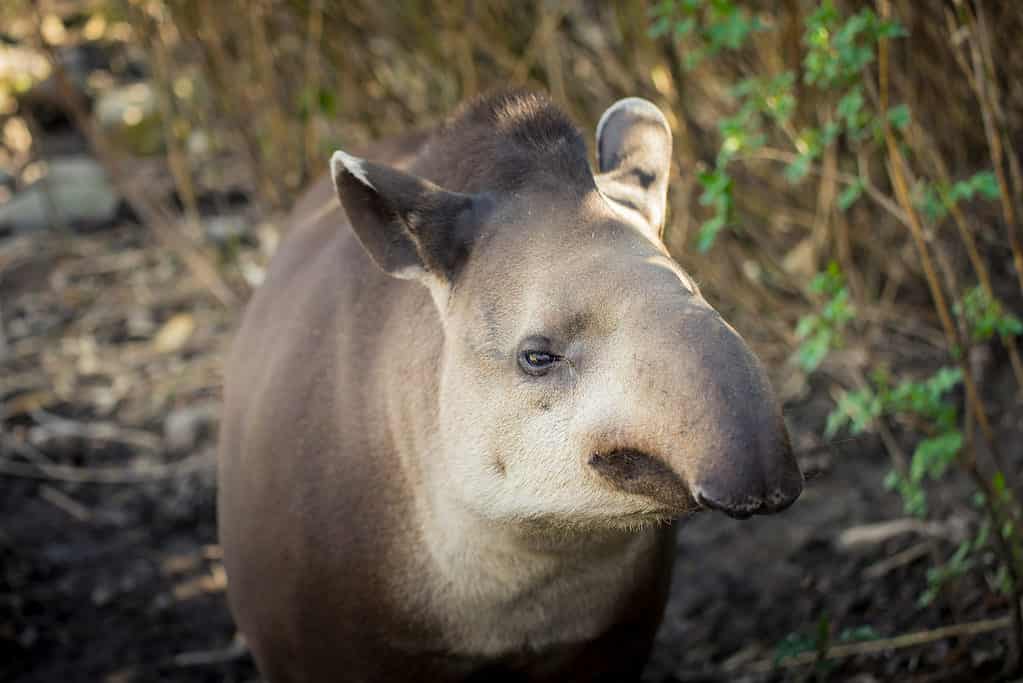

The Baird’s Tapir is the largest animal in El Salvador and can grow as large as 650 pounds.
©Silvia.cozzi/Shutterstock.com
Baird’s Tapir is the largest species of tapir and the largest land animal in El Salvador. This fascinating creature has a short tail and a long snout, which it uses like a snorkel to hide underwater. Stocky with short, mud-colored fur, this tapir’s feet are splayed to help it move on the muddy ground. Baird’s Tapir can reach lengths of 5 feet and weigh between 330 and 650 pounds.
These big herbivores eat leaves, fruits, twigs, small saplings, and aquatic vegetation. Their browsing behavior through the forest understory serves an essential task of seed dispersion. Baird’s tapirs can be found in the rainforests, swamps, mangroves, marshes, and flooded grasslands across Central America.
Mostly solitary creatures except for mothers caring for their young, Baird’s Tapirs are nocturnal but can also be active during the day. They escape predators by crashing their big bodies through dense vegetation or by jumping underwater. These animals are excellent swimmers and love to submerge themselves with only their snouts protruding from the water.
Rarest Animal
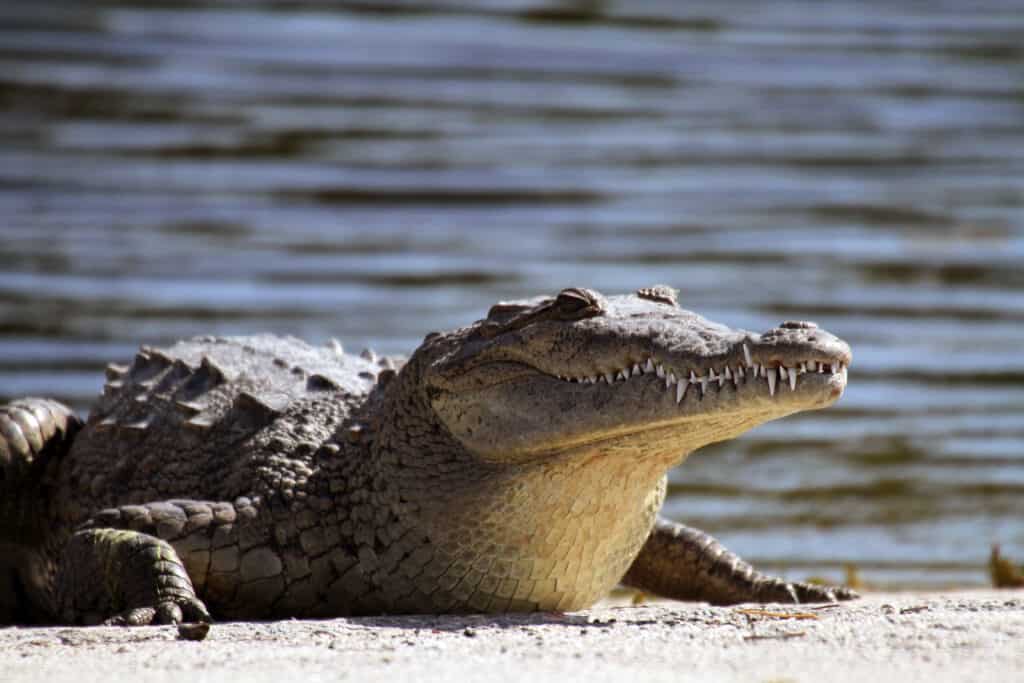

The American crocodile is one of the rarest animals in El Salvador, where it is listed as endangered.
©iStock.com/GriffinGillespie
It is difficult to decide which animal is the absolute rarest in El Salvador, but one endangered animal comes near the top of most lists – the American crocodile. These endangered crocs are native to southern Mexico, Central America, and South America as far as Peru and Venezuela. Other small populations can be found in Cuba, Jamaica, Hispaniola, and on the southern tip of Florida in the United States.
The American Crocodile is a large species able to grow nearly 20 feet long and can weigh up to 2,200 pounds. They inhabit both freshwater and saltwater habitats including mangrove swamps, brackish creeks, and coastal canals. Their diets consist of fish and other marine animals, small mammals, birds, and turtles. American crocodiles were once prized for their hides which were used to make belts and handbags. That practice is now banned – but habitat loss, pollution, and accidental deaths by fishing nets, cars, and boats still threaten the animal.
Native Birds
The Resplendent Quetzal is an important symbol of goodness and light in both Aztec and Mayan cultures. They can be seen in Montecristo National Park.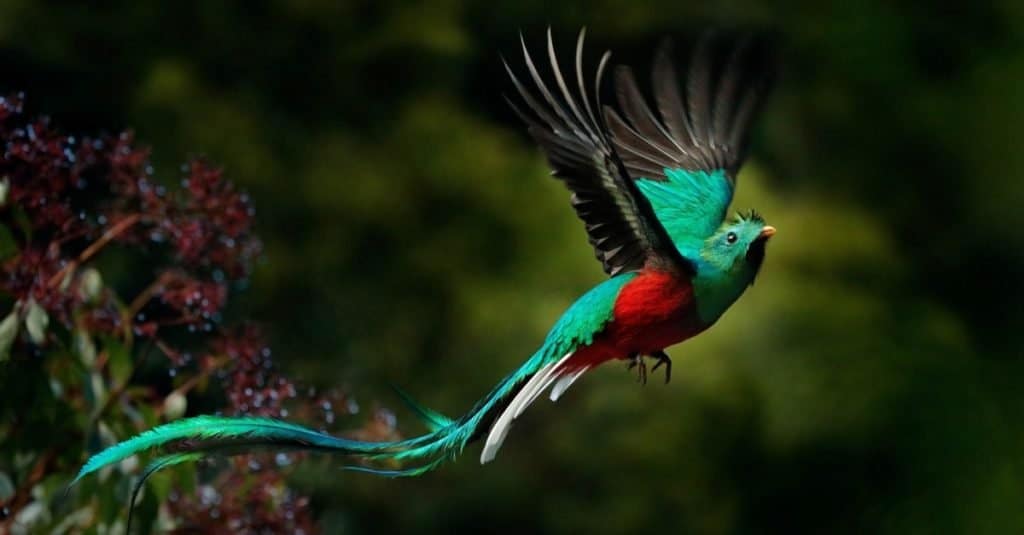
©Ondrej Prosicky/Shutterstock.com
El Salvador may be the smallest country in Central America but there is no lack of biodiversity. Unfortunately, due to the loss of habitat, many of these species remain only in protected natural areas and National Parks. Various species roam the unique habitats, here are several examples:
- Montecristo National Park – A respected cloud forest home to resplendent quetzal, fulvous owls, and the native, blue-throated motmot.
- Pine forests bordering Honduras – Many forests have suffered deforestation but a few remain and are habitats for species such as white-breasted hawks, fan-tailed warblers, orange-fronted parakeets, buffy-crowned wood partridges, and white-winged chachalacas.
- Volcanoes – Many volcanoes dot the country, ranging through multiple environments with cloud forests encircling. As a result of isolated habitats, rare species have evolved, including the Rufus Sabrewing.
Ornithologists all across the world are studying ecological change and developments in El Salvador, monitoring bird and other animal species in order to enact changes to protect and further the preservation of wildlife.
Native Fish
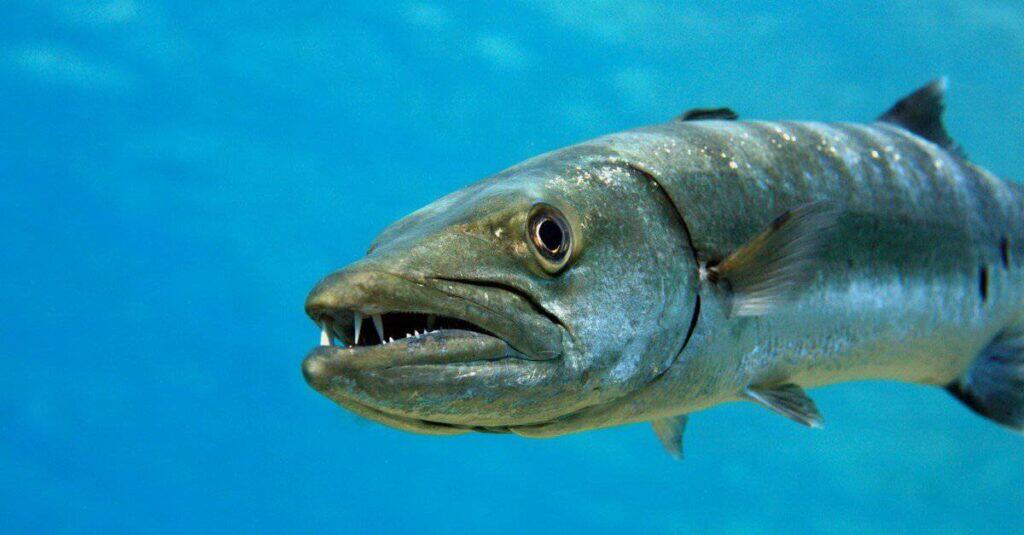

Barracudas have few predators because of their speed and size and can be found in El Salvador’s coastal waters.
©aquapix/Shutterstock.com
Located directly on the Pacific Ocean, the country of El Salvador is no stranger to fishing the waters. Close to the shore, small game fishing is quite easy. Further offshore is where the big game catches take place, with species such as marlin and large sailfish. Some popular catches include:
- Mackerel
- Dorado
- Wahoo
- Barracuda” data-wpil-keyword-link=”linked” data-old-href=”https://a-z-animals.com/animals/barracuda/” data-lasso-id=”60925″>Barracuda
- Red snapper
- Pargo
- Tunas
November through April is the best time to visit for a fishing trip but fishing is possible year-round.
Native Snakes
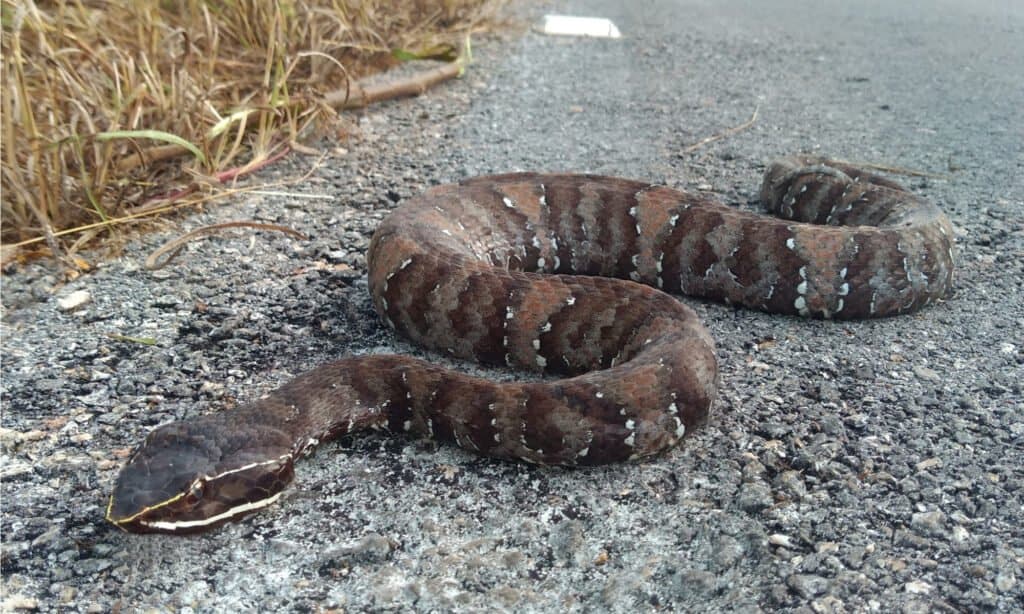

Cantils are venomous and native to El Salvador.
©Juan Pablo rosado/Shutterstock.com
Full of incredible species, some not-so-friendly critters exist in El Salvador as well. Six species of venomous snakes inhabit the country, namely:
- Cantils
- Jumping vipers
- Mountain pit vipers
- Hognosed pit vipers
- Central American rattlesnakes
- South American rattlesnakes – most dangerous; hemotoxic and neurotoxic venom
Other, non-venomous species can also pose a serious threat, such as boa constrictors measuring 10ft and over in length and weighing up to 100lb, easily able to crush and disable prey. Sea snakes can also be found off the shores of El Salvador, though relatively shy to humans.
The Most Dangerous Animals
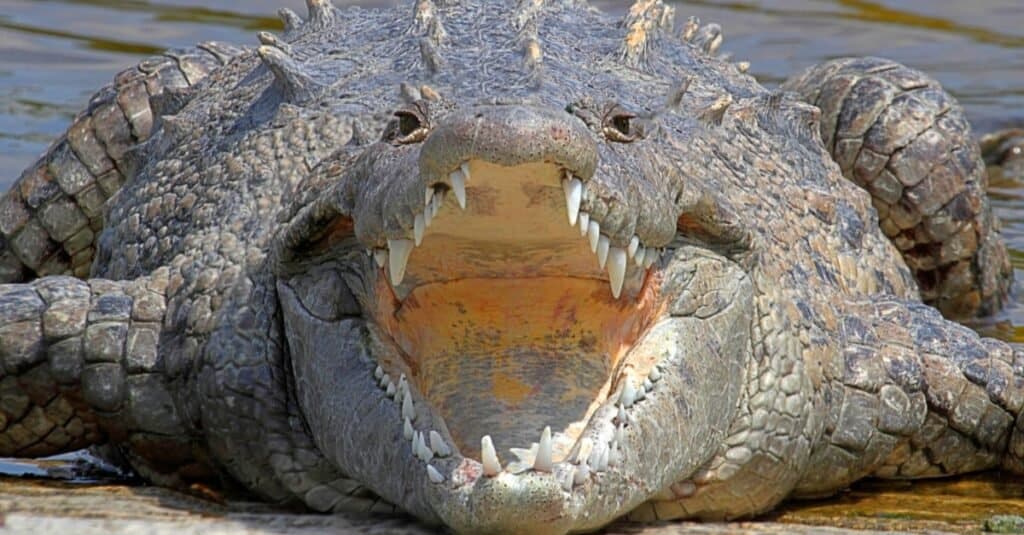

American crocodiles are endangered and dangerous animals in El Salvador.
©iStock.com/SteveByland
Animal attacks on humans are very rare in El Salvador. Its dangerous animals include the American crocodile (Crocodylus acutus), which can grow to 20 feet. The country also has dangerous snakes, poisonous centipedes, and scorpions.
Strangely, coyotes are considered to be dangerous animals – especially to a lone human encountering a pack, when they can be aggressive. Coyotes are numerous and can even be encountered in populated areas.
Zoos in El Salvador
It is hard to beat the outdoor views of El Salvador; however, visiting the National Zoo of El Salvador is an exciting adventure while in the country, as it is home to nearly 120 species, focused on Central American wildlife.
Endangered and Extinct Animals

Jaguars are native to El Salvador but are now extinct in the country.
©L-N/Shutterstock.com
The facts are grim. Over 90 species of animal are endangered or at risk of going extinct in El Salvador. These include animals native to El Salvador and others, including the American crocodile, cloud forest rice rat, hawksbill turtle, ocelot, margay, long-tailed otter, and the turquoise-browned motmot, which is the country’s national animal. Both jaguars and mountain lions are already extinct. Fortunately, the country’s government has recently taken steps to make conservation a priority.
Environmental restoration could lead to providing water necessary for agriculture and could restore native animal and plant species to the country. El Salvador’s flag features a coat of arms on a white stripe representing peace. ©iStock.com/Oleksii Liskonih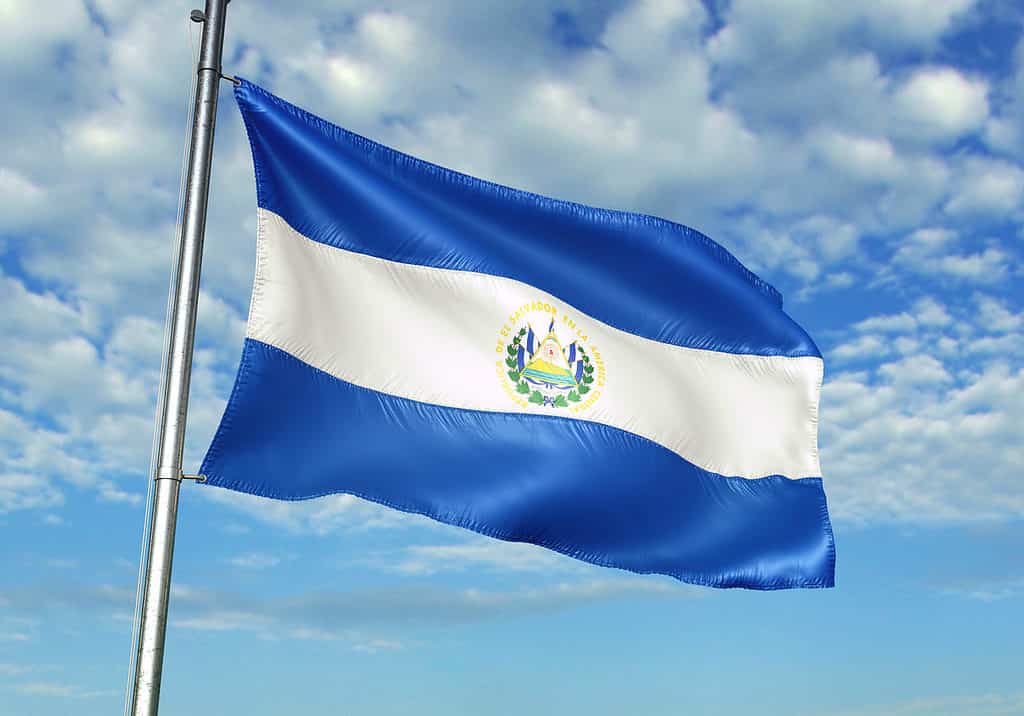
Flag of El Salvador
Adopted in 1912, the flag of El Salvador consists of a blue-white-blue horizontal triband and the El Salvador coat of arms in the middle. The top and bottom blue bands represent the ocean and the sky, while the white color represents peace.
The color blue is important to the people of El Salvador. The Native American cultures produced an indigo plant which they used to extract blue dyes. When Europeans invaded and colonized the area, they realized the wealth that could be made from indigo and turned El Salvador into one of the world’s greatest providers of indigo dye. Today, El Salvador is one of the few countries in the world that still cultivates indigo to produce blue dyes.
Salvadoran Animals

Acadian Flycatcher
Their nests are sloppily held together and have an abandoned appearance

Admiral Butterfly
Stunningly beautiful wings

Agouti
The agouti is one of the only animals that can crack open Brazil nut pods!

Amazon Parrot
These parrots can be trained to be "talking birds" that mimic human speech

Anole Lizard
There are just under 400 species, several of which change color.

Ant
First evolved 100 million years ago!

Anteater
Has the longest tongue of any animal in relation to its body size!

Armadillo
Can curl into a hard, protective ball!

Armyworm
They are so named because they "march" in armies of worms from one crop to another in search of food

Barn Owl
Found everywhere around the world!

Barn Swallow
Older offspring help care for new hatchlings.

Basilisk Lizard
Can run/walk on water.

Bat
Detects prey using echolocation!

Bear
There are 8 different species!

Bed Bugs
Bed bugs feed for 4-12 minutes.

Bee
Rock paintings of bees date back 15,000 years

Beetle
There are more than 350,000 different species

Beewolf wasp
They hunt bees

Bird
Not all birds are able to fly!

Biscuit Beetle
The biscuit beetle form a symbiotic relationship with yeast

Black Widow Spider
They typically prey on insects!

Blind Snake
The blind snake is often mistaken for a worm.

Blue grosbeak
Blue grosbeak parents take off the head, legs and wings of an insect before feeding it to their baby.

Blue Tanager (Blue-Grey Tanager)
They travel and forage in pairs or groups

Bobcat
About double the size of a domestic cat!

Booby
Seabirds found across the South Pacific!

Brazilian Treehopper
“Mild-Mannered Minimonsters”

Brown Dog Tick
Can live its entire life indoors

Burrowing Owl
The burrowing owl lives in underground burrows

Butterfly
There are thought to be up 17,500 species!

Caecilian
Some species' babies use their hooked or scraper-like teeth to peel off and eat their mother's skin

Caiman
Can grow to up 6 meters long!

Camel Cricket
The camel crickets that are found in the USA are light brown in color. They also have dark streaks all over their body.

Carpenter Ant
Carpenter ants can lift up to seven times their own weight with their teeth!

Cat
May have been domesticated up to 10,000 years ago.

Caterpillar
The larvae of a moth or butterfly!

Catfish
There are nearly 3,000 different species!

Cedar Waxwing
Their feathers have red, waxy tips that can be hard to identify unless you’re up close.

Centipede
There are about 3,000 documented species!

Chicken
First domesticated more than 10,000 years ago!

Cockroach
Dated to be around 300 million years old!

Codling Moth
Pupae are able to undergo diapause to survive poor fruit yield years and winter.

Collared Peccary
Form bands of up to 12 individuals!

Common Furniture Beetle
The common furniture beetle feeds exclusively on wood

Common House Spider
House spiders have the ability to eat most insects in a home.

Common Yellowthroat
The Common Yellowthroat stays close to the ground and uses stealth to survive!

Coral Snake
There are over 80 species of coral snake worldwide.

Cormorant
They can fly 35 mph and dive 150 feet below water.

Cow
There are nearly 1.5 billion worldwide!

Crab
There are 93 different crab groups

Crab Spider
Crab Spiders can mimic ants or bird droppings

Cricket
Male crickets can produce sounds by rubbing their wings together

Crocodile
Have changed little in 200 million years!

Crocodylomorph
Crocodylomorphs include extinct ancient species as well as 26 living species today.

Crow
A group of these birds is called a Murder.

De Kay’s Brown Snake
They have specialized jaws for removing snails from shells.

Dog
First domesticated in South-East Asia!

Dog Tick
Dog ticks feed on dogs and other mammals

Donkey
First domesticated 5,000 years ago!

Dragonfly
It's larvae are carnivorous!

Dubia Cockroach
The most popular species of feeder roach

Duck
Rows of tiny plates line their teeth!

Dung Beetle
The dung beetle can push objects many times its own weight

Dusky Shark
The Dusky Shark sometimes eats trash discarded by humans.

Dwarf Boa
Some species can change color from dark to light, and back again.

Earthworm
They are hermaphrodites, which means they have male and female organs

Earwig
There are nearly 2,000 different species!

Eel
Eels can be a mere few inches long to 13 feet!

Elegant Tern
Have a lifespan of 20 years or more

Emerald Toucanet
Emerald Toucanets spend their lives high in the canopy of tall forests, almost never coming to the ground!

Eyelash Viper
While the eyelash viper can be a pet, be cautious – they are extremely venomous!

False Widow Spider
False spiders actually prey on black widow spiders and other hazardous spiders

Fiddler Crab
The fiddler crab gets its name from the motion the males make with their over-sized claw during the mating ritual.

Firefly
The firefly produces some of the most efficient light in the world

Flamingo
Sleeps on just one leg!

Flea
Adult fleas can jump up to 7 inches in the air

Fly
There are more than 240,000 different species!

Flying Squirrel
Can glide up to 90 meters!

Frog
There are around 7,000 different species!

Fruit Fly
Fruit flies are among the most common research animals in the world

Fulvous Whistling Duck
They build a ramp from their nest, which leads to a nearby water source

Gar
Can grow to more than 3m long!

Gecko
There are thought to be over 2,000 species!

German Cockroach
The most common type of urban roach

Giant Leopard Moth
When giant leopard moths mate, their mating sessions last over 24 hours.

Glowworm
Found inhabiting dense woodland and caves!

Gnat
Males form large mating swarms at dusk

Grasshopper
There are 11,000 known species!

Great Blue Heron
Their wingspan is larger than an eagle’s; both males and females help hatch the eggs; rich in symbolism

Great Crested Flycatcher
This species makes use of some truly unusual nesting material, including snakeskin and garbage

Guppy
Also known as the Millionfish!

Hamster
Able to run as quickly backwards as forwards!

Hare
Can reach speeds of over 50 mph!

Harpy Eagle
Talon's the size of a grizzly bear's claws!

Harris’s Hawk
Their vision is eight times better than a human's

Hawk Moth Caterpillar
Many hawk moth caterpillars eat toxins from plants, but don’t sequester them the way milkweed butterflies do. Most toxins are excreted.

Hepatic Tanager (Red Tanager)
Parents and their young sing sweetly to each other

Hercules Beetle
This dynastine scarab beetle makes a weird huffing sound when it’s disturbed.

Herring Gull
They are loud, spirited birds with raucous cries that sound like bursts of laughter.

Honey Bee
There are only 8 recognized species!

Horse
Has evolved over 50 million years!

Horsefly
Horseflies have been seen performing Immelmann turns, much like fighter jets.

Housefly
The fly has no teeth

Howler Monkey
Spends 80% of it's time resting!
Human
Thought to have orignated 200,000 years ago!

Hummingbird
Beat their wings up to 80 times per second!

Huntsman Spider
Some huntsman spiders have an interesting way of moving around. Some cartwheel while others do handsprings or backflips.

Ibis
Found in swamps, marshes and wetlands!

Iguana
Uses visual signals to communicate!

Insects
There are an estimated 30 million species!

Jacana
The jacana has the ability to swim underwater

Jaguar
The largest feline on the American continent!

Jumping Spider
Some can jump 50 times the length of their bodies

Keel-Billed Toucan
It's beak can reach nearly 20 cm long!

Kentucky Warbler
The Kentucky Warbler appears to wear bright yellow cat-eye glasses!

Killdeer
The killdeer feigns injury to draw a predator away from its nest.

Kingfisher
Inhabits wetlands and woodlands worldwide!

Kinkajou
The kinkajou is a nimble forest-dwelling mammal of Central and South America.

Ladybug
There are more than 5,000 species worldwide!

Leech
Has 10 pairs of eyes!

Leopard Frog
They can jump up to three feet

Lizard
There are around 5,000 different species!

Lone Star Tick
Only females have the ‘lone star’ marking

Macaw
The largest species of parrot in the world!

MacGillivray’s Warbler
The complicated story of how MacGillivray’s Warblers got their name involves three ornithologists, a physician and a compromise.

Maggot
Will only live in wet areas

Magnolia Warbler
They line their nests with fungi strands

Margay
Margays are one of the world’s most highly adapted cat species for climbing trees!

Marine Toad
Produces a toxin used in arrow darts!

Mayfly
There are 2,500 known species worldwide!

Mealybug
They have a symbiotic relationship with ants.

Mexican Free-Tailed Bat
Some colonies have millions of bats

Millipede
Some species have a poisonous bite!

Mockingbird
Mockingbirds are incredible mimics that can learn hundreds of songs!

Mole
Primarily hunts and feeds on Earthworms!

Mole Cricket
Adult Mole crickets may fly as far as 5 miles during mating season and are active most of the year.

Molly
Known for their calm and peaceful nature!

Monarch Butterfly
During migration, Monarch Butterflies may travel 250 or more miles each day.

Mongrel
Has characteristics of two or more breeds!

Monkey
There are around 260 known species!

Moonglow Boa
Moonglow boas are the result of mixing three genetic traits.

Moorhen
Feeds on aquatic insects and water-spiders!

Morpho Butterfly
Collectors prize them for their bright wings

Mosquito
Only the female mosquito actually sucks blood

Moth
There are 250,000 different species!

Mountain Lion
Has no real natural predators!

Mourning Dove
It is almost always the male who makes the famous sad sound, which is a wooing call

Mourning Warbler
The Mourning Warbler was named for its gray head, which resembles a mourning veil!

Mouse
Found on every continent on Earth!

Mule
The offspring of a horse and donkey parents!

Muscovy Duck
Unlike most duck species, the Muscovy is silent and only makes noise when excited or threatened.
Nematode
Nematodes range in size from 1/10 of an inch to 28 feet long

No See Ums
There are more than 5,000 species.

Northern Harrier
They can reach speeds of 25 Mph but prefer to soar low and slow.

Northern Potoo
You can find them near golf courses in urban areas

Ocelot
Also known as the Painted Leopard!

Orange-Crowned Warbler
Often mistaken for the Tennessee Warblers, which are equally dull.

Orb Weaver
Females are about four times the size of males

Osprey
They reuse nesting sites for 70 years!

Otter
There are 13 different species worldwide

Owl
The owl can rotate its head some 270 degrees

Panther
Prefers to hunt at night than during the day!

Parrot
Can live for up to 100 years!

Pheasant
Females lay between 8 and 12 eggs per clutch!

Pigeon
They can find their way back to their nests from up to 1300 miles away.

Pit Viper
Pit vipers's fangs fold up into their mouths when they don't need them.

Poison Dart Frog
Inhabits the jungles of Central and South America!

Pompano Fish
They are bottom-feeders

Porcupine
There are 30 different species worldwide!

Praying Mantis
The mantis can turn its head 180 degrees.

Puma
Has longer back legs than front legs!

Quail
Inhabits woodland and forest areas worldwide!

Quetzal
The tail feathers of the male can be 1m long!

Rat
Omnivores that eat anything!

Rat Snakes
Rat snakes are constrictors from the Colubridae family of snakes.

Rattlesnake
Rattlesnakes may have evolved their rattle to warn bison away from them.

River Turtle
Inhabits freshwater habitats around the world!

Roadrunner
Roadrunners are one of the few animals that prey on rattlesnakes and tarantula hawk wasps.

Rodents
The capybara, the world’s largest rodent, likes to be in and around bodies of water. Because of this, the Catholic Church in South America decided that it was a fish, and people were allowed to eat it during Lent and First Fridays.

Rooster
Will mate with the entire flock!

Rose-Breasted Grosbeak
This bird is also called cut-throat because the male looks like his throat has been cut and has bled over his breast.

Roseate Spoonbill
The only Spoonbill in the western hemisphere!

Ruddy Duck
Ruddy duck breeding males have bright blue bills!
Saber-Toothed Tiger
Canines up to 7 inches long!

Sable Ferret
Ferrets were used during the Revolutionary War to keep down the rat population.

Salamander
There are more than 700 different species!

Sand Crab
The sand crab burrows beneath the sand with its tail

Scarlet Macaw
Like many parrots, the scarlet macaw is capable of vocal mimicry.

Scissor-tailed Flycatcher
Scissor-tailed flycatchers are known for their dramatically long tails!

Scorpion
There are around 2,000 known species!

Sea Eagle
The sea eagle tends to mate for life with a single partner

Seahorse
Males give birth to up to 1,000 offspring!

Sharp-Shinned Hawk
In captivity, sharp-shinned hawks can live up to 13 years. However, in the wild, this number is significantly reduced to 3 years!

Shrew
The spinal column of the shrew Scutisorex somereni is so strong and reinforced that it can support the weight of an adult human.

Shrimp
There are 2,000 different species worldwide!

Skink Lizard
Some skinks lay eggs in some habitats while giving birth to skinklets in other habitats.

Sloth
It's body temperature is between 30 - 34 degrees!

Slug
They glide around on one foot, which is aided by the slime they produce

Smokybrown Cockroach
Has up to 45 eggs per egg case

Snail
There are nearly 1,000 different species!

Snake
There are around 4,000 known species worldwide

Sparrow
There are 140 different species!

Spider Wasp
They prey on spiders to feed their larvae or they parasitize other spider wasps.

Spotted Skunk
Spotted skunks are known for their acrobatic abilities. They perform handstands before spraying their enemies.

Squirrel
Small rodents found in woodlands worldwide!

Stick Insect
There are more than 3,000 different species!

Summer Tanager
They remove bee stingers by rubbing them against a tree

Swainson’s Hawk
Their wings form a “V” shape when flying.

Swan
Populations have been affected by pollution!

Tarantula Hawk
Tarantula hawks are excellent pollinators, especially for milkweed.

Termite
Their mounds can be up to 9 meters tall!

Thrush
The American robin is called the robin because its red breast reminded European settlers of the robin back in the old country.

Tick
They inject hosts with a chemical that stops them from feeling the pain of the bite

Tiger Beetle
The adult tiger beetle is one of the fastest land insects in the world

Tortoise
Can live until they are more than 150 years old!

Toucan
There are more than 40 different species!

Tree Frog
Found in warmer jungles and forests!

Tree swallow
The tree swallow can make more than a dozen distinct vocalizations

Turtles
Some species of aquatic turtles can get up to 70 percent of their oxygen through their butt.

Umbrellabird
Migrates up and down the mountains!

Upland Sandpiper
They make jerky movements as they walk through the grass, searching for food.

Vampire Bat
Have a heat sensor on the end of their nose!

Vine Snake
A slender body and elongated snout give the vine snake a regal look.

Vinegaroon
Vinegaroons can spray 19 times before the glands are depleted

Vulture
There are 30 different species worldwide!

Wasp
There are around 75,000 recognised species!

Western Tanager
They migrate farther north than any other tanager.

White-Faced Capuchin
One of the world's most intelligent monkeys!

White Ferret / Albino Ferrets
There are two different types of white ferrets!

White-tail deer
White-tail deer are good swimmers

Willow Flycatcher
These birds live in the understory and are named for their propensity for flitting between willows and shrubs.

Wolf Spider
Carnivorous arachnid that hunts its prey.

Woodlouse
This animal can roll up into a ball

Woodpecker
There are 200 different species!

Worm
Doesn’t have eyes.

Yellow Bellied Sapsucker
The males are responsible for choosing the nesting tree most of the time. Luckily, cavity nests are often reused for multiple breeding seasons (up to 7 years.)

Yellow Spotted Lizard
Gives birth to live young.

Yellowthroat
They forage near the ground, searching leaves for insects
Salvadoran Animals List
- Acadian Flycatcher
- Admiral Butterfly
- Agouti
- Amazon Parrot
- Anole Lizard
- Ant
- Anteater
- Armadillo
- Armyworm
- Barn Owl
- Barn Swallow
- Basilisk Lizard
- Bat
- Bear
- Bed Bugs
- Bee
- Beetle
- Beewolf wasp
- Bird
- Biscuit Beetle
- Black and White Warbler
- Black Widow Spider
- Blind Snake
- Blue grosbeak
- Blue Tanager (Blue-Grey Tanager)
- Bobcat
- Booby
- Brazilian Treehopper
- Brown Dog Tick
- Burrowing Owl
- Butterfly
- Caecilian
- Caiman
- Camel Cricket
- Carpenter Ant
- Cat
- Caterpillar
- Catfish
- Cedar Waxwing
- Centipede
- Chicken
- Cockroach
- Codling Moth
- Collared Peccary
- Common Furniture Beetle
- Common House Spider
- Common Yellowthroat
- Coral Snake
- Cormorant
- Cow
- Crab
- Crab Spider
- Cricket
- Crocodile
- Crocodylomorph
- Crow
- Cuckoo
- De Kay’s Brown Snake
- Dog
- Dog Tick
- Donkey
- Dragonfly
- Dubia Cockroach
- Duck
- Dung Beetle
- Dusky Shark
- Dwarf Boa
- Earthworm
- Earwig
- Eel
- Elegant Tern
- Emerald Toucanet
- Eyelash Viper
- False Widow Spider
- Fiddler Crab
- Firefly
- Flamingo
- Flea
- Fly
- Flying Squirrel
- Frog
- Fruit Fly
- Fulvous Whistling Duck
- Gar
- Gecko
- German Cockroach
- Giant Leopard Moth
- Glowworm
- Gnat
- Grasshopper
- Great Blue Heron
- Great Crested Flycatcher
- Guppy
- Hamster
- Hare
- Harpy Eagle
- Harris’s Hawk
- Hawk Moth Caterpillar
- Hepatic Tanager (Red Tanager)
- Hercules Beetle
- Herring Gull
- Honey Bee
- Horse
- Horsefly
- Housefly
- Howler Monkey
- Human
- Hummingbird
- Huntsman Spider
- Ibis
- Iguana
- Insects
- Jacana
- Jaguar
- Jumping Spider
- Keel-Billed Toucan
- Kentucky Warbler
- Killdeer
- Kingfisher
- Kinkajou
- Ladybug
- Leech
- Leopard Frog
- Lizard
- Lone Star Tick
- Macaw
- MacGillivray’s Warbler
- Maggot
- Magnolia Warbler
- Margay
- Marine Toad
- Mayfly
- Mealybug
- Mexican Free-Tailed Bat
- Millipede
- Mockingbird
- Mole
- Mole Cricket
- Molly
- Monarch Butterfly
- Mongrel
- Monkey
- Moonglow Boa
- Moorhen
- Morpho Butterfly
- Mosquito
- Moth
- Mountain Lion
- Mourning Dove
- Mourning Warbler
- Mouse
- Mule
- Muscovy Duck
- Nematode
- No See Ums
- Northern Harrier
- Northern Potoo
- Ocelot
- Orange-Crowned Warbler
- Orb Weaver
- Osprey
- Otter
- Owl
- Ox
- Panther
- Parrot
- Pheasant
- Pigeon
- Pit Viper
- Poison Dart Frog
- Pompano Fish
- Porcupine
- Praying Mantis
- Puma
- Quail
- Quetzal
- Rat
- Rat Snakes
- Rattlesnake
- River Turtle
- Roadrunner
- Rodents
- Rooster
- Rose-Breasted Grosbeak
- Roseate Spoonbill
- Ruddy Duck
- Saber-Toothed Tiger
- Sable Ferret
- Salamander
- Sand Crab
- Scarlet Macaw
- Scissor-tailed Flycatcher
- Scorpion
- Sea Eagle
- Seahorse
- Sharp-Shinned Hawk
- Shrew
- Shrimp
- Skink Lizard
- Sloth
- Slug
- Smokybrown Cockroach
- Snail
- Snake
- Sparrow
- Spider Wasp
- Spotted Skunk
- Squirrel
- Stick Insect
- Summer Tanager
- Swainson’s Hawk
- Swallowtail Butterfly
- Swan
- Tarantula Hawk
- Termite
- Thrush
- Tick
- Tiger Beetle
- Tortoise
- Toucan
- Tree Frog
- Tree swallow
- Turkey
- Turtles
- Umbrellabird
- Upland Sandpiper
- Vampire Bat
- Vine Snake
- Vinegaroon
- Vulture
- Wasp
- Western Tanager
- White-Faced Capuchin
- White Ferret / Albino Ferrets
- White-tail deer
- Willow Flycatcher
- Wolf Spider
- Woodlouse
- Woodpecker
- Worm
- Yellow Bellied Sapsucker
- Yellow Spotted Lizard
- Yellowthroat








