Plesiosaur had a short tail and an extremely long neck
Advertisement
Plesiosaur Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Reptilia
- Order
- Plesiosauria
- Family
- Plesiosauridae
- Genus
- Plesiosaurs
- Scientific Name
- Plesiosaurus dolichodeirus
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Plesiosaur Conservation Status
Plesiosaur Facts
- Prey
- Fish, marine reptiles, cephalopods
- Main Prey
- Fish and cephalopods
- Fun Fact
- Plesiosaur had a short tail and an extremely long neck
- Estimated Population Size
- extinct
- Most Distinctive Feature
- extremely long neck
- Distinctive Feature
- elongated head
- Habitat
- Found in seas worldwide
- Diet
- Carnivore
View all of the Plesiosaur images!
Plesiosaurs were a group of marine animals that lived between the late Triassic to Cretaceous (about 215 to 66 million years ago), found in various seas worldwide, including the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. Plesiosaurs were the largest aquatic animals to swim in the ancient seas of their time and were prolific predators as well.
Plesiosaurs Description & Size
The name plesiosaur is derived from the Greek words plesios, meaning close to, and sauros, meaning lizard. The name alludes to the reptilian nature of their fossilized remains. Plesiosaurs were among the first marine fossils to be discovered.
Plesiosaur refers to any member of the order Plesiosauria. The order is further divided into two suborders; Plesiosauroidea and Pliosauroidea. Members of the sub-order Plesiosauroidea are often referred to as the true Plesiosaurs. One of their defining characteristics is their extremely long necks. Members of the second suborder Pliosauroidea are better known as Pliosaurs. They have short necks and elongated heads.
Plesiosaurs were characterized by a broad flat body with a very short tail. Their four limbs were modified into flippers with strong muscles attached to a wide bony plate formed by their pelvis and shoulder girdle. Their flippers are similar to a turtle’s, and aid underwater movement.
Despite spending their entire lives in the seas, Plesiosaurs were incapable of underwater breathing, an issued remedied by their long necks, or elongated heads! Many scientists believe the Plesiosaurs were warm-blooded mammals.
Although their size varies from one species to the other, the Plesiosaurs were the largest sea-dwelling animals of their time. The smallest members of this order were still up to two meters (6.5 feet) long. These smaller species would have been larger than present-day crocodiles. The larger ones reached up to 15 meters (49 feet), meaning they were smaller than ancient sea-monsters like the ichthyosaurs or living ones like the sperm whale.
Diet – What Did Plesiosaur Eat?
All orders of Plesiosaurs were carnivorous. However, since Plesiosaurs are divided into two morphological groups, the specific diet depends on the group you’re considering. The plesiosauromorph plesiosaurs (the group with long necks and small heads) were generally slower, and adapted to preying on smaller sea animals which they often caught by ambush or surprise. Their diet consisted of both hard and soft-bodied cephalopods with jaws adapted to bite through the hard shells of their preferred prey type.
The other group, the Pliosauromorph plesiosaurs (the group with short necks and large heads), are apex predators in their habitat. Their morphology would have made it possible for them to pursue prey by swimming at high speeds, taking on larger predators. The diet of the Pliosauromorph plesiosaurs consisted predominantly of soft-bodied prey, especially fish. They had large sharp teeth, adapted to gripping and ripping large animals apart.
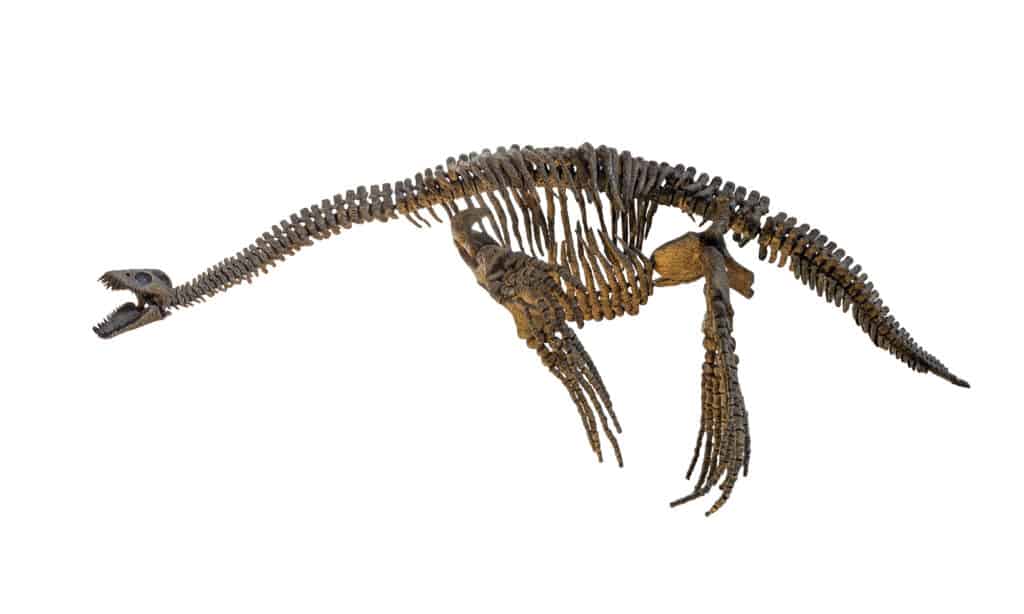

This skeleton of a
Plesiosaurusshows its incredibly long neck.
©Lefteris Papaulakis/Shutterstock.com
Habitat – When and Where It Lived
Plesiosaurs were found in oceans all over the world. Although most species lived in marine environments, some species spent part of their time in freshwater habitats. There are speculations that some species in this order visited terrestrial habitats occasionally to lay eggs as modern turtles do. However, there’s no evidence for this, especially considering that many experts believe the Plesiosaur to be a mammal.
Threats and Predators
Because of its massive size relative to the other animals in the ancient oceans where it lived, it’s obvious that the Plesiosaurs did not have many natural enemies. The lack of natural predators and abundance of prey allowed the members of these orders to thrive for millions of years. They lived alongside marine reptiles like mosasaurs and ichthyosaurs.
Discoveries and Fossils – Where It Was Found
Mary Anning discovered the first official fossil of a Plesiosaur in the early 1800s. It was among the first fossil vertebrates ever discovered and described by scientists. However, Though Anning’s discovery was the first official Plesiosaur fossil, many years earlier, in 1719, William Stukely had described a partial skeleton of a Plesiosaur, brought to his attention by Robert Darwin of Elston, the great-grandfather of Charles Darwin.
Since the 1800s, several other Plesiosaur specimens have been found, some in almost perfect conditions. One such near-complete specimen was discovered by fishermen off the coast of Somerset in the UK in 2002. The same year, an amateur paleontologist discovered another well-preserved (but less complete) skeleton in Yorkshire, England.
Extinction: When Did Plesiosaur Die Out?
The first appearance of the Plesiosaurs in the fossil record was during the Triassic, about 203 million years ago. However, their population experienced a major boom during the Jurassic, and they continued to thrive until their disappearance at the end of the Cretaceous. Experts think the Plesiosaurs disappeared during the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction about 66 million years ago.
Similar Animals to the Plesiosaur
Similar animals include:
- Pistosauroidea: This group of large marine mammals lived in the Early Triassic. Scientists believe that these were the early ancestors of the Plesiosaurs.
- Nothosaurs: This was a group of marine reptiles with a lifestyle similar to present-day seals. Nothosaurs hunted for prey underwater but often came ashore on beaches and rocks.
- Ichthyosaurs: This was an ancient group of fish-like marine reptiles that lived around the same time as the Plesiosaurs and might have shared the same habitat.
Related Animals
View all 192 animals that start with PPlesiosaur FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
When was the Plesiosaurs alive?
Plesiosaurs first appeared in the fossil record during the Triassic , about 203 million years ago. They thrived during the Jurassic until their disappearance at the end of the Cretaceous about 60 million years ago.
How big was the Plesiosaurs?
The largest Plesiosaurs reached lengths of up to 25 meters (82 feet). They had short necks and a head up to 3 meters (10 feet) long. However, some members of this group were significantly shorter than this. The smallest members of this order were about two meters (6.5 feet) long.
Is a plesiosaur a predator or prey?
All members of this order were predators of smaller animals, including cephalopods and fish. The type of prey they ate and how they hunted varied from one species to the other.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- Wikipedia, Available here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Plesiosaur
- Britannica, Available here: https://www.britannica.com/animal/plesiosaur
- New World Encyclopedia, Available here: https://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Plesiosaur
- McGill, Available here: https://www.cs.mcgill.ca/~rwest/wikispeedia/wpcd/wp/p/Plesiosaur.htm