Alabama has a varied topography that ranges from steep hills to fertile flatlands, lakes, and rivers. Its coastline on the Gulf of Mexico includes 600 miles of tidal bay and bayou shoreline. Alabama has more than 60 types of natural habitat, including forests, woodlands, wetlands, glades, and prairies. The weather stays warm and humid most of the year, and snowfalls are rare.
Because of its topography and climate, Alabama is one of the most ecologically diverse states in the country. It ranks fifth in the country–and first among states east of the Mississippi–for biodiversity.
There are over 4,500 documented species in Alabama. Among these animals are:
- 62 native mammals.
- 22 species of rodents.
- 16 bat species.
- Four rabbit species.
- One marsupial: the opossum.
- 433 bird species, including some of the rarest bird species in the world.
Its rodents include gray squirrels, fox squirrels, chipmunks, and southern flying squirrels. Alabama’s predators include the bobcat, coyote, red fox, and gray fox. Its coastal waters are home to sharks, strange fish like the Clymene dolphin (Stenella clymene) and common marine mammals like the killer whale and California sea lion.
Bat species include the Mexican free-tailed bat, eastern red bat, and evening bat.
One of Alabama’s strange critters is the nine-banded armadillo (Herpailurus yagouaroundi). The state mammal of Texas, this small, armored beast spends its days eating insects and small reptiles.
The Official Animal of Alabama
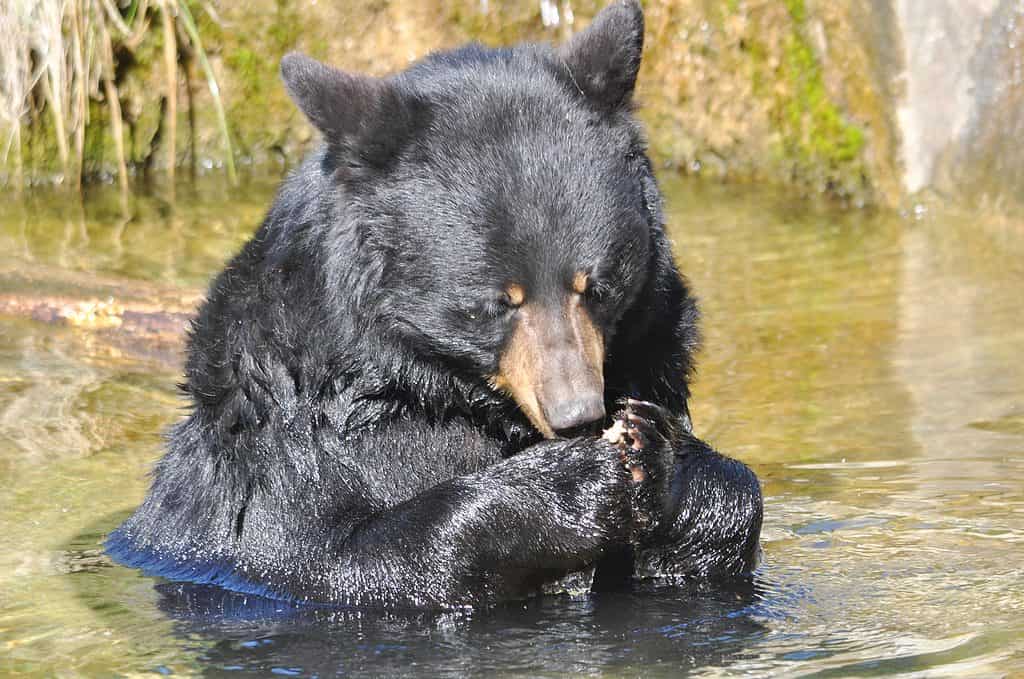

About 200 black bears call Alabama home
©Elizabeth Caron/Shutterstock.com
Alabama’s official state animal is the North American black bear (Ursus americanus). It shares this state mammal with West Virginia. Black bears were once rare in Alabama, but their population has grown recently.
Presently about 200 of these lumbering mammals known for having a sweet tooth, call the state home. Black bears are mainly found in three counties: Baldwin, Mobile, and Washington. However, they can also be found in northeast Alabama where they have settled down nicely in Cherokee, DeKalb, and Etowah counties.
The northern flicker (Colaptes auratus), also known as the yellowhammer is the state’s bird. As a matter of fact, it is actually the reason Alabama is referred to as the Yellowhammer State. The avian which is noted for its gray-brown speckled plumage, and in the case of males, a black or red bar beneath their beaks, can be found throughout the United States.
Alabama’s official amphibian is the red hills salamander. This strange creature lives in deep forest ravines and can grow 11 inches long. The red hill salamander is threatened because of habitat loss.
The Official Insect of Alabama
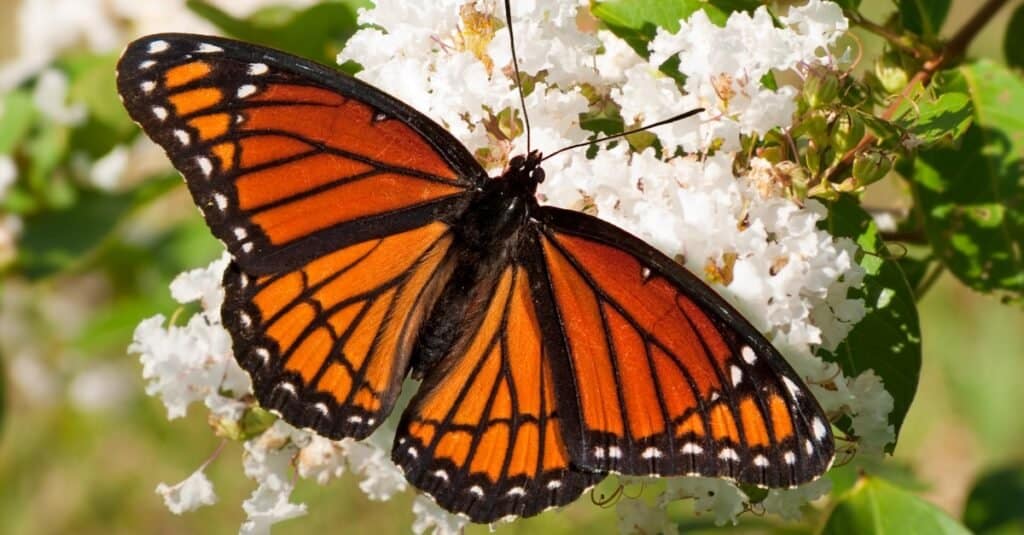

Monarch butterflies store the toxins from the milkweed on which they lay their eggs and which their larvae feed on
©Sari ONeal/Shutterstock.com
The official Alabama state insect is the Monarch butterfly. The Alabama legislature designated the local butterfly as the state insect in 1989. Authorities from Selma, which had dubbed the city the Butterfly Capital of Alabama in 1982, demanded the action.
Also known as Danaus plexippus, these arthropods are recognized by their large orange wings, prominent black veins, and white, pearl-shaped markings clusted at the borders of each wing, on thick black bands. Their migrations which are especially noteworthy and cover vast distances are fraught with risk. However, these beautiful butterflies protect themselves by storing the toxins from the milkweed on which they lay their eggs, and which sustains their larvae, in their bodies.
Where To Find the Top Wild Animals in Alabama
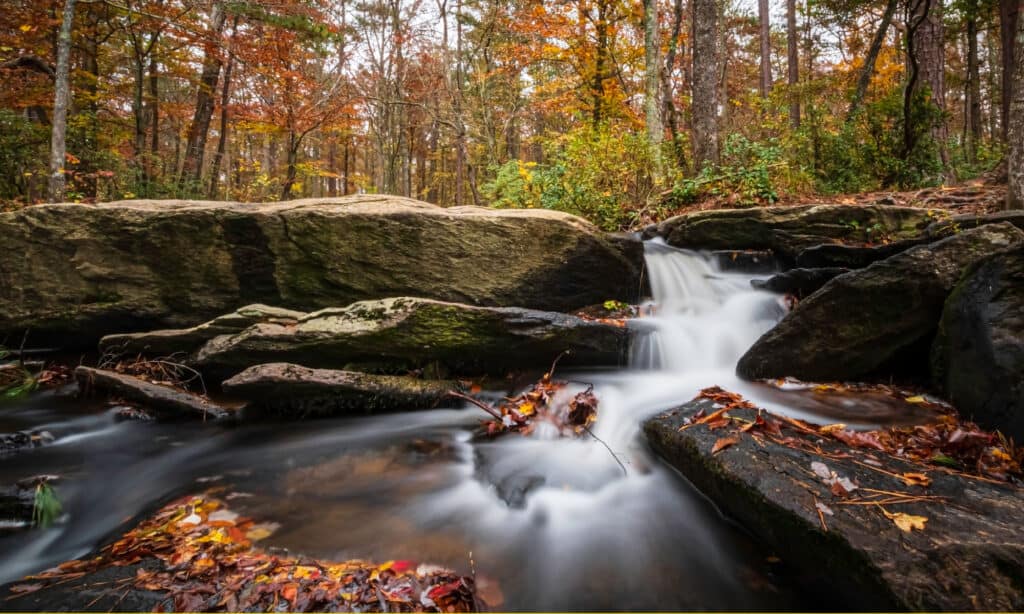

Talladega National Forest is home to several waterfalls and wide variety of wildlife
©iStock.com/Jacqueline Nix
More than 1 million people visit Alabama each year to view wildlife and birds. Alabama has dozens of reserves, national parks, and protected natural areas. They are all wonderful places to see the state’s most common animals.
- Eufaula National Wildlife Refuge is an 11,0000-acre wildlife and wetlands where you can see many of the state’s wildflowers, alligators, white-tail deer, great blue herons and wood ducks. The marshes provide safe haven for turtles, crayfish, frogs and minnows.
- The Alabama Wildlife Center is Alabama’s oldest and largest rehabilitation center for injured and orphaned wild birds. The center conducts education sessions with live birds to help people learn about barred owls, red-tailed hawks and other raptors.
- Oak Mountain State Park is a 10,000-acre park close to Birmingham. Talladega National Forest is a huge state park that has several waterfalls and many wildlife viewing opportunities.
- Birding tourism is a large part of Alabama’s economy. The Dauphin Island West End Acquisition Project is an 840-acre stretch of coastline that protects dunes, marshes and beaches. The piping plover and red knot are two of the rarest shorebirds that nest there.
- Bon Secours National Wildlife Refuge is a protected area for the Alabama beach mouse and other threatened species.
- Alligators are a popular tourist attraction in Alabama, and many people take swamp tours to see them in action. Alligator Alley in Dauphin is a railed boardwalk that allows visitor to view them safely from a distance.
The Largest Animal in Alabama
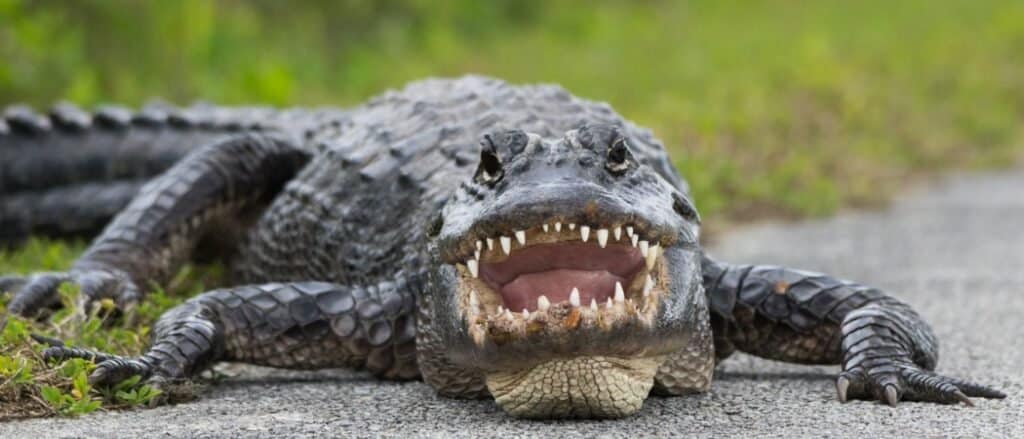

Alligators are capable of measuring 15 feet and weighing 1,000 lbs
©iStock.com/tobiasfrei
Alabama’s largest critter is the American Alligator (Alligator mississippiensis). Found in the lower part of the state, it is capable of reaching 15 feet in length and 1,000 lbs in weight. An example of a spectacular comeback, the reptile was once hunted to near extinction before protective measures which were set in place, enabling its numbers to spring to impressive levels, once more.
These apex predators tend to hang around lakes, reservoirs, rivers, swamps, and wetlands. In spite of their preference for the southern parts of the state, alligators have become a frequent occurrence in Huntsville. Alabama’s Alligator Alley is one of the very best places where you can observe these reptiles live in relative tranquility.
The Rarest Animal in Alabama
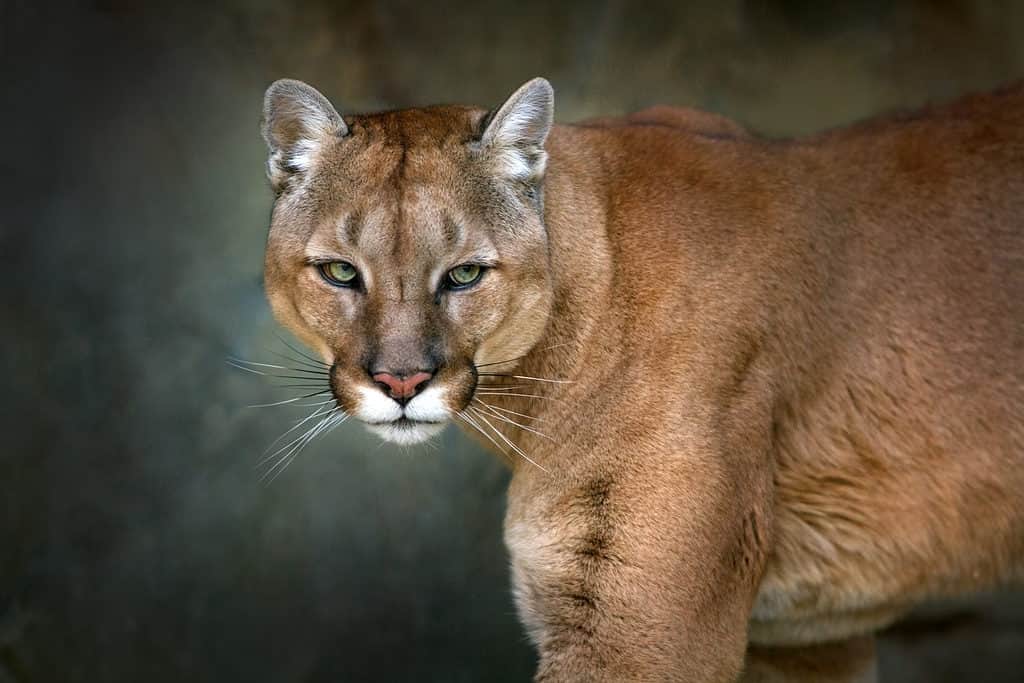

Cougars were extirpated from the Yellowhammer State in the 19th century
©Kwadrat/Shutterstock.com
Cougars are the rarest animals in Alabama at present. The wild felines which are known to be solitary by nature and capable of weighing 232 lbs at the most and measuring and measuring 7 feet in length once lived in the state. However their population became inexistent by the 19th century owing to encroachment on their habitat as well as extensive hunting.
And although nearby Florida has experienced its own success story, with numbers rising from just 20 to 200, Alabama has not been as fortunate. However, sightings of these cats have been reported, although certain experts assert that they are most likely felines released into the wild by their owners.
However, in 2008, a 140 lbs male was shot at West Point Lake which itself, sits on the shared border between Alabama and Georgia.
The Most Dangerous Animals in Alabama Today
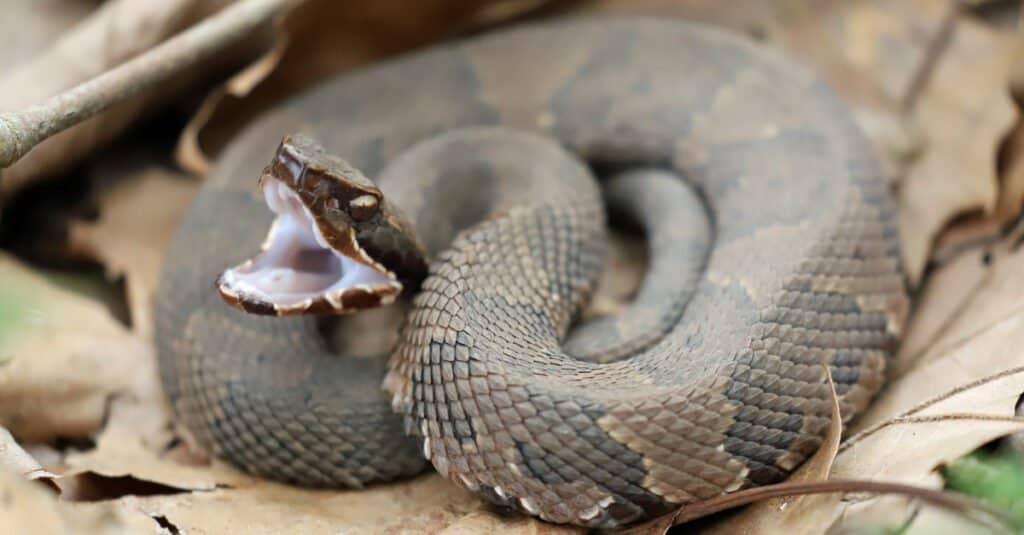

The cottonmouth is North America’s only venomous water snake
©KF2017/Shutterstock.com
There were 56 animal-related fatalities in Alabama between 1999 and 2003. The following are a couple of the most dangerous animals in Alabama:
Brown recluse spider: This tiny spider is mostly found in the northern part of the state. They enjoy warm places like bedding and boxes. Their bite causes intense pain, and their venom can cause tissue death.
Snakes: Alabama has six venomous snake species, including the cottonmouth or water moccasin, which is the only venomous water snake in North America. Fortunately, their bite is not deadly if you get prompt medical attention. Alabama is also home to some black snakes and copperhead snakes.
Endangered Animals
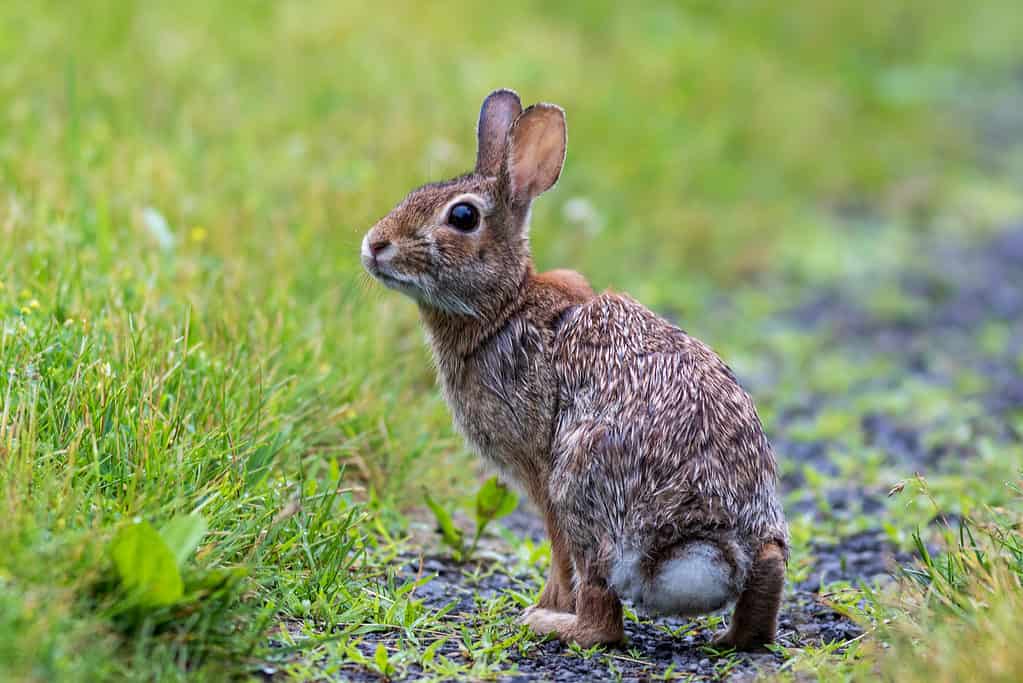

The Appalachian cottontail which can only be found in Northern Alabama is endangered
©Rabbitti/Shutterstock.com
Rice’s whale (Balaenoptera ricei) is a species of baleen whale native to the Gulf of Mexico. It is on the brink of extinction. These whales have not been a target of whaling activity, but they are highly sensitive to ecological disasters, underwater noises from vessel traffic and other human interference.
The Alabama beach mouse (Peromyscus polionotus ammobates) is one of the rarest mouse species in the world. It is found in only a few nature reserves and isolated areas of the state. It is one of the very few mouse species that live in sand dunes. Beach mice are a key part of the coastal dune ecosystem, and thriving mouse populations are a sign of dune health. The state has made protection of these mice one of its top conservation priorities.
The Appalachian cottontail (Sylvilagus obscurus) is found only in northern Alabama and is endangered. The marsh rabbit (Sylvilagus palustris) is also endangered.
Four species of animal once lived in Alabama but no longer occur there. They are the red wolf, cougar, elk and bison.
Check out more endangered animals living in Alabama.
Alligators, Armadillos and Alabama
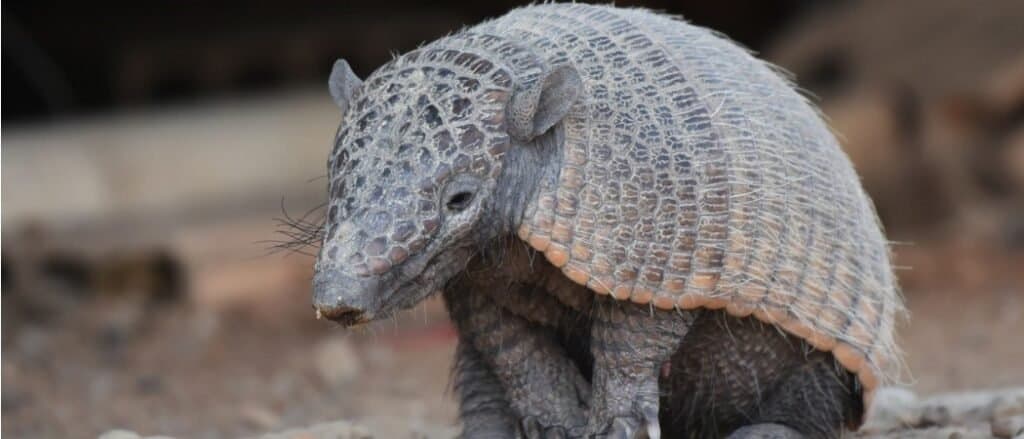

Armadillos can be found throughout Alabama except in eight counties, out of the state’s 67
©iStock.com/Rini Kools
Alabama is a wonderful place to watch wildlife and spot birds. Its mild weather and diverse habitats have allowed its native species to thrive. Continued conservation efforts will help protect endangered animals that help those ecosystems stay healthy.
Alabama takes special pride in having been the very first state to protect Alligators, in 1938. About 70,000 of these large reptiles call the Yellowhammer State home and enjoy federal as well as state protection. The harming, owning of, or harassing of an alligator is prohibited by law in Alabama.
Nine-banded armadillos were first spotted in the state in the 1940s, and at present reside in every county in the state with the exception of eight out of 67. They have a penchant for raiding quail and turkey nests for eggs and digging up gardens. However, residents can contact their local extension office for assistance with these adaptable creatures.
Native Plants in Alabama

The American elm is one of the many tree species native to Alabama
©Aejahn/Shutterstock.com
For lovers of flora and fauna, Alabama is the place to be. Located in the subtropical coniferous biome, you can find plants ranging from fireweed to ferns. The native plants in Alabama are worth exploring, as they flourish in diverse habitats.
Yellow or golden canna known for its ability to attract bees, butterflies, and dragonflies grows in the state, as do prickly white poppies known for their beautiful white flowers and leaves which are used as natural remedies. Tree species which grow in Alabama include, American beech, American elm, black cherry, pecan, river birch, sassafras, sourwood, southern red oak, sweetgum, white oak.
Alabamian Animals

Admiral Butterfly
Stunningly beautiful wings

Albino (Amelanistic) Corn Snake
Albino corn snakes make great beginner snakes.

American Eel
Don't eat raw eel! Their blood is poisonous to humans when consumed raw.

Armyworm
They are so named because they "march" in armies of worms from one crop to another in search of food

Bagworm Moth Caterpillar
They continually enlarge their protective cases

Banded Water Snake
Some water snakes defend themselves violently.

Beewolf wasp
They hunt bees

Blue Catfish
It's a strong fighter when caught on a fishing line

Blue Tang
One of the most colorful members of the genus Acanthurus

Brown Water Snake
Has more scales than any other water snake on the continent: 27 to 33 rows of dorsal scales!

Cane Spider
Cane spiders don't spin webs to catch prey

Clearnose Skate
The skate with translucent nose patches

Common Yellowthroat
The Common Yellowthroat stays close to the ground and uses stealth to survive!

Corn Snake
Corn snakes are partly arboreal and are excellent climbers.

Crocodylomorph
Crocodylomorphs include extinct ancient species as well as 26 living species today.

De Kay’s Brown Snake
They have specialized jaws for removing snails from shells.

Eastern Box Turtle
When injured or damaged, the shell of the eastern box turtle can regenerate

Eastern Diamondback Rattlesnake
This is the biggest venomous snake in North America, with a few that reach 8 feet long.

Eastern Fence Lizard
Females are usually larger than males.

Eastern Glass Lizard
When the glass lizard loses its tail it can grow another one. But the new tail lacks the markings of the old one and is usually shorter.

Eastern Hognose Snake
Eastern hognose snakes are venomous, but only to frogs and toads.

Eastern Woodrat
The eastern woodrat mating ritual involves a potentially deadly fight between the male and female before reproduction begins!

Flea
Adult fleas can jump up to 7 inches in the air

Florida Woods Cockroach
Often found on palmetto trees

Fox Squirrel
Although it is a tree squirrel, it spends most of its time on the ground.

Groundhog (Woodchuck)
They whistle to each other to warn of approaching danger!

Indigo Snake
Indigo snakes use brute force to overpower their prey.

Jack Crevalle
One of the biggest species in the Caranx genus

Jackrabbit
They can run as fast as 45 mph.

Kentucky Warbler
The Kentucky Warbler appears to wear bright yellow cat-eye glasses!

King Snake
King Snakes eat other types of snakes.

Ladyfish
Ladyfish are aggressive fighter when hooked, making them a favorite of anglers.

Mealybug
They have a symbiotic relationship with ants.

Mockingbird
Mockingbirds are incredible mimics that can learn hundreds of songs!

Mourning Warbler
The Mourning Warbler was named for its gray head, which resembles a mourning veil!

Needlefish
no stomach to digest food
Nematode
Nematodes range in size from 1/10 of an inch to 28 feet long

Orb Weaver
Females are about four times the size of males

Owl
The owl can rotate its head some 270 degrees

Pine Snake
Pine snakes bluff with the best, trying to scare you away.

Polyphemus Moth
The Polyphemus moth doesn’t and can't eat, except when it's a caterpillar!

Pompano Fish
They are bottom-feeders

Quahog Clam
Their hinged shell protects their soft body

Queen Snake
Queen snakes have armor-like scales on the top of their head

Rat Snakes
Rat snakes are constrictors from the Colubridae family of snakes.

Red-Bellied Woodpecker
Red-Bellied Woodpeckers will often steal the nests of other birds.

Red-Shouldered Hawk
Red-Shouldered Hawks reuse the same nesting area each year.

Rooster
Will mate with the entire flock!

Rough Earth Snake
It has a pointed snout that is uses to burrow into moist soil.

Rough Green Snake
Rough green snakes are great pet snakes because they're low-maintenance.

Scarlet Kingsnake
Scarlet kingsnake’s pattern is an example of Batesian mimicry.

Seagull
Some gulls are capable of using tools

Smallmouth Bass
A fierce fighter!

Smokybrown Cockroach
Has up to 45 eggs per egg case

Smooth Earth Snake
Valeria Biddle Blaney (1828-1900) collected the first specimen in Maryland.

Southern Black Racer
These snakes live underground, beneath piles of leaf litter or in thickets, and they are expert swimmers.

Tree Cricket
They make music with their wings
Alabamian Animals List
- Admiral Butterfly
- Agkistrodon Contortrix
- Albino (Amelanistic) Corn Snake
- American Eel
- Armyworm
- Bagworm Moth Caterpillar
- Banded Water Snake
- Basilosaurus
- Beewolf wasp
- Blue Catfish
- Blue Tang
- Brown Water Snake
- Cane Spider
- Clearnose Skate
- Common Yellowthroat
- Corn Snake
- Crocodylomorph
- De Kay’s Brown Snake
- Eastern Box Turtle
- Eastern Diamondback Rattlesnake
- Eastern Fence Lizard
- Eastern Glass Lizard
- Eastern Hognose Snake
- Eastern Woodrat
- Flea
- Florida Woods Cockroach
- Fox Squirrel
- Groundhog (Woodchuck)
- Indigo Snake
- Jack Crevalle
- Jackrabbit
- Kentucky Warbler
- King Snake
- Ladyfish
- Mealybug
- Milk Snake
- Mockingbird
- Mourning Warbler
- Needlefish
- Nematode
- Orb Weaver
- Owl
- Pine Snake
- Pine Snake
- Polyphemus Moth
- Pompano Fish
- Quahog Clam
- Queen Snake
- Rat Snakes
- Red-Bellied Woodpecker
- Red-Shouldered Hawk
- Rooster
- Rough Earth Snake
- Rough Green Snake
- Scarlet Kingsnake
- Seagull
- Smallmouth Bass
- Smokybrown Cockroach
- Smooth Earth Snake
- Southeastern Blueberry Bee
- Southern Black Racer
- Swallowtail Butterfly
- Tree Cricket
Animals in Alabama FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What rattlesnakes live in Alabama
Alabama is home to three rattlesnakes: the timber rattlesnake, pygmy rattlesnake, and the eastern diamondback rattlesnake.
What Animals Live in Alabama?
Alabama has a wonderful diversity of animals. It has many of the common North American forest animals, including white-tail deer, opossums, shrews, rodents and foxes. The prairie areas are home to rabbits, snakes and armadillos. Its coastal waters teem with marine mammals, fish and whales. Alabama has many wetlands that are home to shorebirds and alligators.
What Dangerous Animals Live in Alabama?
Alabama has alligators, black bears and wild boars. Although these large predators can be aggressive when provoked, attacks on humans are rare. The most dangerous animals are the state’s venomous snakes and spiders.
What Animal is Alabama Known For?
Alabama is probably best known for Big Al, the elephant mascot of the University of Alabama football team. Big Al appears on the team’s flag and as a costumed mascot at the team’s games. The team, known as the Crimson Tide, has one of the most passionate, devoted fan bases of any college football team in the country.
What Mammals Live in Alabama?
Alabama’s predators include bobcats, coyotes and wolves. Otters, beavers and minks are mammals that live near its rivers and lakes. Beavers were once extinct in Alabama, but they are now plentiful all over the state. Its rodents include groundhogs, squirrels and chipmunks. Marine mammals like sea lions and killer whales inhabit the coastal waters.










