Beewolf wasp
Beewolf wasps hunt bees to feed to their young!
Advertisement
Beewolf wasp Scientific Classification
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Beewolf wasp Conservation Status
Beewolf wasp Facts
- Main Prey
- Bees
- Name Of Young
- Larvae
- Group Behavior
- Solitary except during mating season
- Fun Fact
- Beewolf wasps hunt bees to feed to their young!
- Biggest Threat
- Habitat loss
- Most Distinctive Feature
- Venomous stinger
- Other Name(s)
- Beewolf, bee-hunter, bee-killer wasp
- Habitat
- Soil
- Predators
- Birds, insects, reptiles, amphibians, mammals
- Diet
- Omnivore
- Lifestyle
- Diurnal
- Favorite Food
- Nectar, pollen
- Common Name
- Beewolf
- Special Features
- Venomous stinger
- Number Of Species
- 136
- Location
- North America, South America, Europe, Africa, Asia
- Slogan
- They hunt bees
- Group
- Swarm
- Nesting Location
- Soil/ground
Beewolf wasp Physical Characteristics
- Color
- Yellow
- Black
- Dark Brown
- Black-Brown
- Skin Type
- Exoskeleton
- Venomous
- Yes
- Aggression
- High
View all of the Beewolf wasp images!
Beewolf wasps are insects belonging to the genus Philanthus. These efficient predators hunt and paralyze various species of bees to feed their newly-hatched larvae. However, as adults, they feed on nectar and pollen. These solitary wasps are not generally dangerous to nonallergic humans, though they may sting if threatened. The IUCN does not currently include beewolves on their Red List.
Beewolf Wasp Species, Types, and Scientific Name
Beewolf wasps are any of 136 species belonging to the genus Philanthus. They are also known as beewolves, bee-hunters, and bee-killer wasps. Beewolves are part of the class Insecta and the order Hymenoptera (ants, bees, wasps, and sawflies). They further belong to the family Crabronidae (square-headed wasps, sand wasps, and allies) and the tribe Philanthini.
The genus Philanthus includes the following species:
- European beewolf (Philanthus triangulum)
- Bumblebeewolf (Philanthus bicinctus)
- Bohart’s beewolf (Philanthus boharti)
- Crowned philanthus (Philanthus coronatus)
- Levin’s beewolf (Philanthus levini)
- Loefling’s beewolf (Philanthus loeflingi)
- Michelbacher’s beewolf (Philanthus michelbacheri)
- Parker’s beewolf (Philanthus parkeri)
- Sanborn’s beewolf (Philanthus sanborni)
- Schuster’s beewolf (Philanthus schusteri)
Appearance: How to Identify the Beewolf Wasp
Beewolf wasps are large wasps with six jointed legs, antennae, wings, and stingers. Depending on the species, they grow between 0.47 and 0.7 inches in length. Though there may be slight variations in colors and patterns according to species, the European beewolf is the most iconic with its yellow face and black-striped yellow abdomen. Its thorax is dark, as is the back of its head, which carries a reddish-brown hue. Its antennae are notable for being unusually thick.
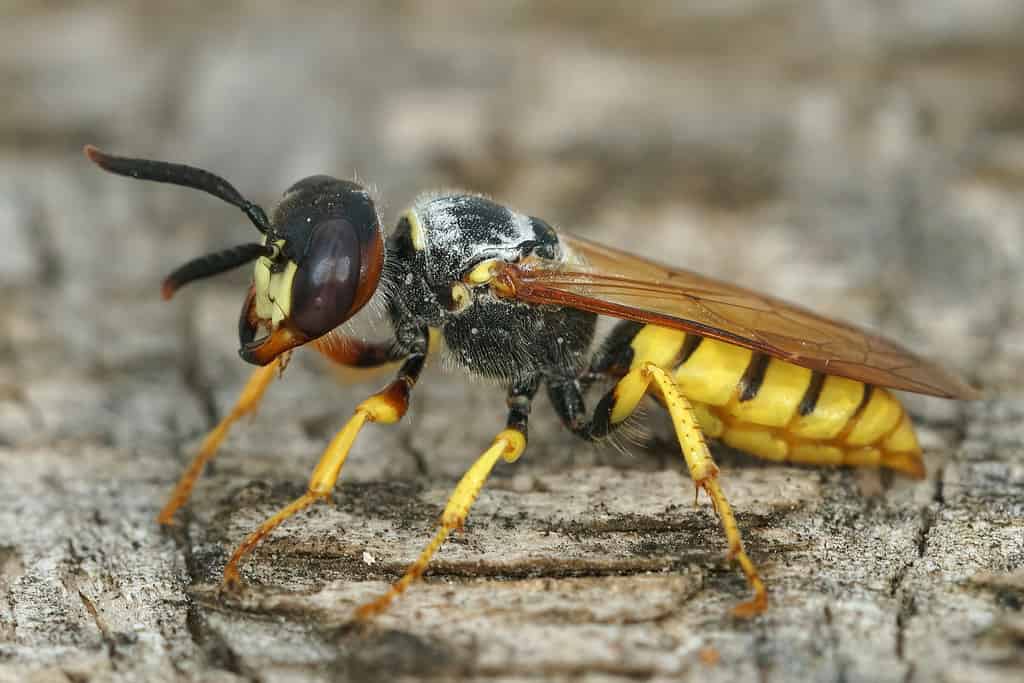

The European beewolf is the most iconic with its yellow face and black-striped yellow abdomen.
©iStock.com/Wirestock
Habitat: Where to Find the Beewolf Wasp
Beewolf wasps are primarily ground wasps, meaning they build their nests in the ground. Female European beewolves dig tunnels as long as 3.3 feet with as many as 34 side burrows leading to brood chambers. These diurnal insects are solitary except when mating or raising young.
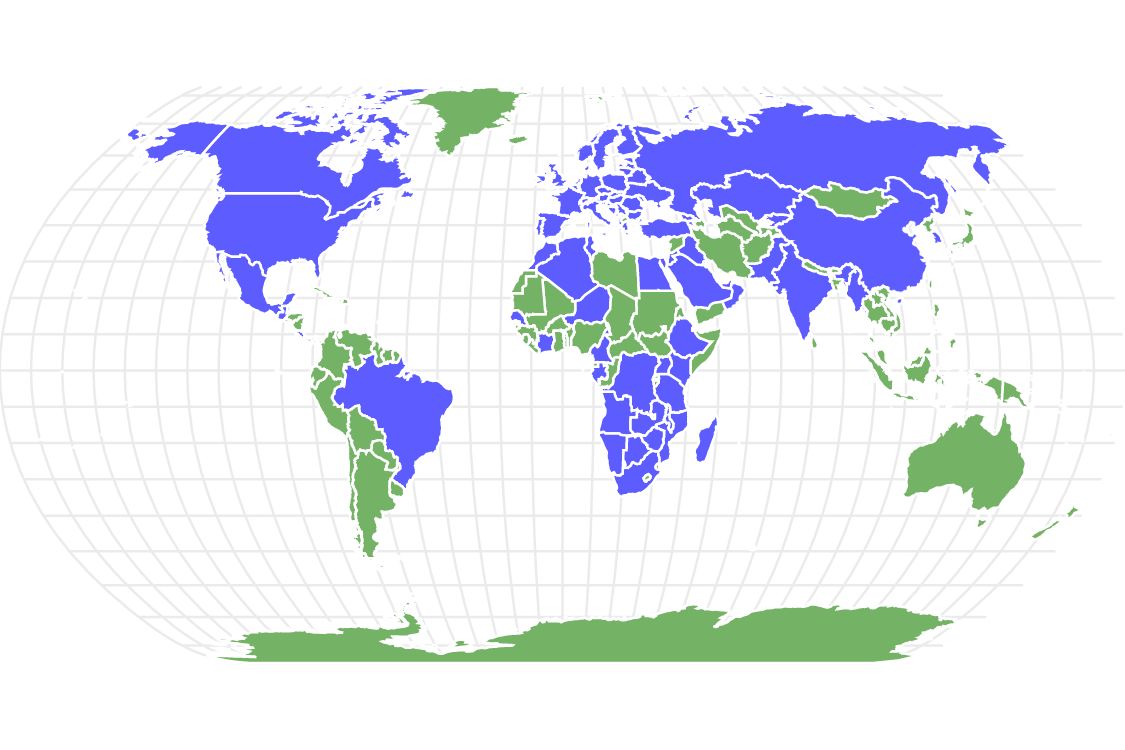
Beewolves inhabit countries in North America, South America, Europe, Africa, and Asia. They also occur in every U.S. state. Below is a table of countries with reported sightings of beewolf species:
| North America | South America | Europe | Africa | Asia |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Canada | Brazil | Albania | Algeria | China |
| Costa Rica | Armenia | Angola | India | |
| El Salvador | Austria | Botswana | Iraq | |
| Guatemala | Belarus | Cameroon | Jordan | |
| Mexico | Belgium | Côte d’Ivoire | Lebanon | |
| United States | Bosnia and Herzegovina | Egypt | Kazakhstan | |
| Bulgaria | Ethiopia | Kuwait | ||
| Croatia | Gabon | Kyrgyzstan | ||
| Cyprus | Kenya | Myanmar | ||
| Czechia | Madagascar | Oman | ||
| Denmark | Malawi | Pakistan | ||
| Estonia | Morocco | Saudi Arabia | ||
| Finland | Mozambique | South Korea | ||
| France | Namibia | Turkey | ||
| Georgia | Niger | United Arab Emirates | ||
| Germany | Senegal | |||
| Greece | South Africa | |||
| Hungary | Tanzania | |||
| Ireland | Tunisia | |||
| Italy | Uganda | |||
| Latvia | Zambia | |||
| Lithuania | Zimbabwe | |||
| Moldova | ||||
| Montenegro | ||||
| Netherlands | ||||
| Norway | ||||
| Poland | ||||
| Portugal | ||||
| Romania | ||||
| Russia | ||||
| Serbia | ||||
| Slovakia | ||||
| Slovenia | ||||
| Spain | ||||
| Sweden | ||||
| Switzerland | ||||
| Ukraine | ||||
| United Kingdom |
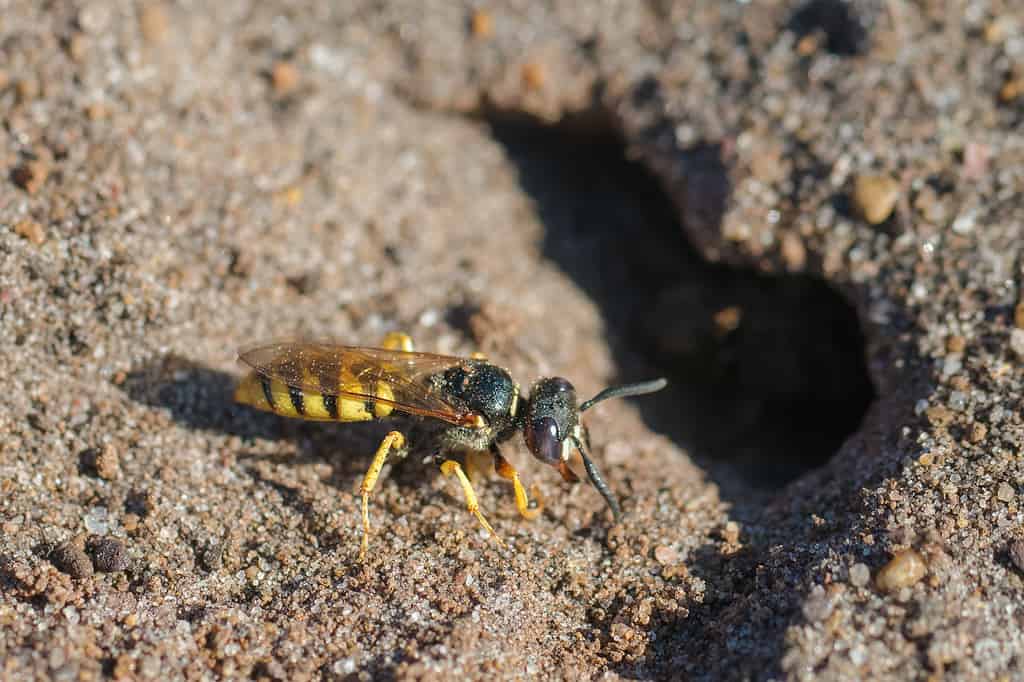

Female European beewolves dig tunnels as long as 3.3 feet with as many as 34 side burrows leading to brood chambers.
©iStock.com/ShaftInAction
Evolution and History
The order Hymenoptera (ants, bees, wasps, and sawflies) contains over 153,000 described extant species and as many as one million undescribed species. It first began to diversify between the Carboniferous and Triassic Periods some 329 to 239 million years ago. The earliest known fossils from this order came from the Triassic approximately 224 million years ago.
Bees likely originated within the family Crabronidae, which includes beewolves. The tribe most closely related to bees is Psenini. Bees diversified greatly within the Cretaceous Period (145.5 to 65.5 million years ago) with the rise of angiosperms (flowering plants), splitting off from extant wasps. Thus many pollinators, including beewolves, had a predatory origin.
Diet: What Do Beewolf Wasps Eat?
Beewolf wasps are highly predatory insects. Although the adults are primarily herbivorous, beewolf larvae are carnivorous.
What Do Beewolf Wasps Eat?
Adult beewolf wasps feed on nectar and pollen from flowers. However, beewolf larvae feed on the bodies of bees, especially sweat bees and honey bees. Adult female beewolves envenom their prey, paralyzing and dragging them back to their nests. Upon depositing up to six bees in each brood chamber, the wasps lay a single egg in each. After hatching, the larvae feed on the innards of the paralyzed bees.
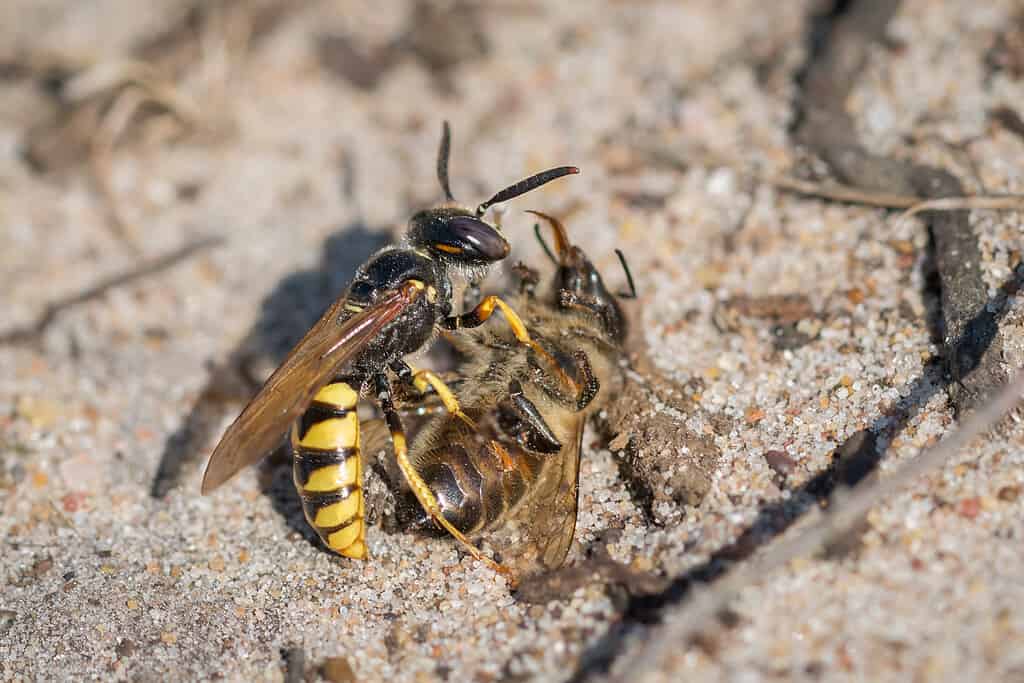

The name “beewolf” derives from the fact that these wasps prey on bees.
©iStock.com/ShaftInAction
What Eats Beewolf Wasps?
These wasps have a number of natural predators. Potential bird predators include sparrows, wrens, orioles, chickadees, warblers, and bluebirds. Predatory insects include spiders, dragonflies, and praying mantises. Some reptiles and amphibians like snakes, lizards, and frogs also prey on wasps. They may even fall victim to mammals like black bears and honey badgers. Beewolf larvae are especially vulnerable to burrowing insects like ants and beetles.
Prevention: How to Get Rid of Beewolf Wasps
Beewolves are not generally harmful to humans or property. In fact, they are valuable pollinators who contribute positively to their ecosystems. Despite the fact that the European beewolf preys on honeybees, their predation on its own is not usually enough to destroy valuable honeybee populations.
However, homeowners concerned about beewolf nests on their property may wish to spray the area with pesticides to kill the wasps. Spraying with white vinegar is a less invasive way of discouraging ground wasps like beewolves. Because they dislike the smell of vinegar, they will likely leave the area and not return to their nests.
Related Animals:
View all 285 animals that start with BBeewolf wasp FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are beewolf wasps dangerous?
Like any other wasp, beewolves may sting if threatened. However, their venom is not usually dangerous to nonallergic humans. Beewolves primarily use their venom to attack bees.
How many legs do beewolf wasps have?
As insects, beewolf wasps have six jointed legs (three pairs).
What do beewolf wasps eat?
Adult beewolves feed on nectar and pollen. However, beewolf larvae feed on the innards of paralyzed bees.
How do you identify beewolf wasps?
Beewolves are fairly large wasps with stingers. The European beewolf in particular has a yellow face and black-striped yellow abdomen. Its thorax and the back of its head are dark.
Are beewolf wasps endangered?
Beewolf wasps are not currently endangered.
Why are they called "beewolf" wasps?
The name “beewolf” derives from the fact that these wasps prey on bees. Two of the most common types of bees are honeybees and sweat bees.
Are beewolf wasps solitary?
Unlike many other types of wasps, beewolves are solitary.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- The Wildlife Trusts, Available here: https://www.wildlifetrusts.org/wildlife-explorer/invertebrates/bees-and-wasps/bee-wolf
- GBIF, Available here: https://www.gbif.org/species/1338932
- Current Biology, Available here: https://www.cell.com/current-biology/fulltext/S0960-9822(17)30059-3?_returnURL=https%3A%2F%2Flinkinghub.elsevier.com%2Fretrieve%2Fpii%2FS0960982217300593%3Fshowall%3Dtrue
- Current Biology, Available here: https://www.cell.com/current-biology/fulltext/S0960-9822(17)30353-6?_returnURL=https%3A%2F%2Flinkinghub.elsevier.com%2Fretrieve%2Fpii%2FS0960982217303536%3Fshowall%3Dtrue
- Britannica, Available here: https://www.britannica.com/science/animal-behavior/Instinctive-learning#ref497915
- Integrated Taxonomic Information System , Available here: https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=154338#null
- Bug Guide, Available here: https://bugguide.net/node/view/4345
- Encyclopedia of Life, Available here: https://eol.org/pages/3798401