Louisiana is a southeastern state known for its vast swamps and bayous. More than 40% of the U.S.’s wetlands are in Louisiana. The state has rich, fertile soil and lush vegetation. Louisiana has a subtropical climate that features hot, humid summers with frequent rain showers and short, mild winters.
The state has three distinct types of vegetation. There are forests with pine trees, cypresses, and other hardwoods; prairies and dry grasslands; and marshlands dominated by live oaks. Louisiana’s mysterious swamps and bayous have long fascinated travelers and inspired countless myths and legends. These murky waters are home to hundreds of wild animals, including fish, turtles, alligators, snakes, rodents, and fur-bearing mammals like muskrats and beavers.
Wild Animals in Louisiana
Louisiana has many animals that are common to southern states, including squirrels, foxes, wolves, and shorebirds. You will find bobcats, catfish, blue crabs, black snakes, great blue herons, great horned owls, and brown pelicans.
It’s only natural, however, that this mysterious place would produce some unusual and exotic animals. Some of the state’s strange native inhabitants include the gopher tortoise, crayfish, southern leopard frog, and Louisiana pine snake. The American black bear can run up to 40mph. ©iStock.com/Lynn_Bystrom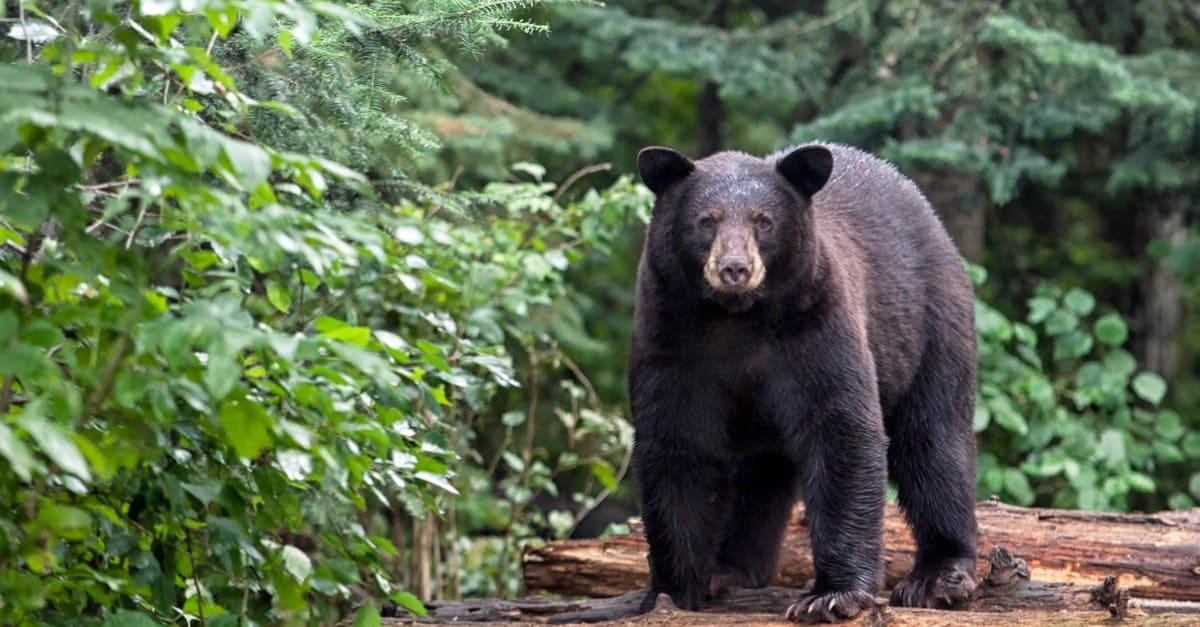
The Louisiana black bear is a subspecies of the North American black bear that is native to the state. The Louisiana black bear was endangered until recently, but its population is currently stable.
Louisiana has battled destructive invasive species, including apple snails, ticks, and fire ants. Various species of spiders can also be found in Louisiana.
The Rarest Animal in Louisiana
One of the rarest animals in the world, the white alligator, is native to Louisiana. White alligators are not albinos. They have a unique condition called leucism that causes loss of pigmentation.
White alligators are extremely fare. In fact, biologists believe there are only about 100 in the entire world. They can be found in freshwater lakes, marshes, swamps, and rivers in the southeastern region of the United States. White alligators are native to Louisiana.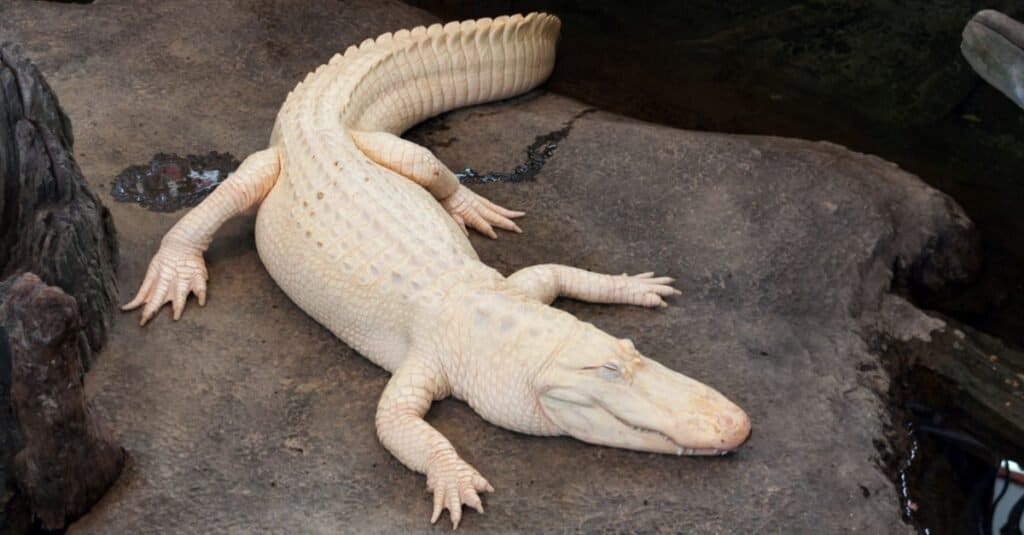
©one5zero/Shutterstock.com
The Official State Animal of Louisiana
The brown pelican is the state’s official animal. With a wingspan of 8 feet, it is the smallest of the pelican species. Pelicans hunt by diving into the sea and catching fish. Brown pelicans were on the endangered species list in 1970, but conservation efforts helped restore their populations.
This bird is an important cultural symbol for the people of Louisiana. A recent news item highlights their importance.
In 2010, a brown pelican tagged “Red 332” was rescued from the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. After cleaning oil from it and rehabilitating it, wildlife experts released the pelican in Brunswick, Georgia. In 2021, the bird was spotted in Louisiana at its old breeding grounds. It traveled 700 miles to return home. To people in Louisiana, this was a harbinger of genuine hope.
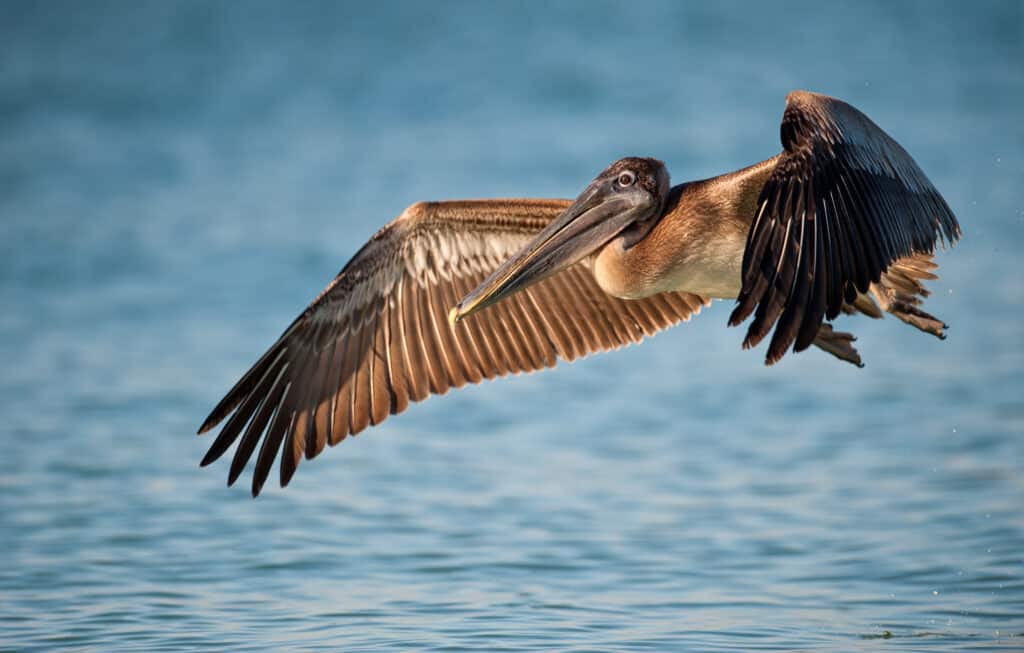

Brown pelicans have a wingspan of 8 feet and are the state animal of Louisiana.
©Nagel Photography/Shutterstock.com
The Two Largest Animals in Louisiana
Of all the varying wildlife in Louisiana, which is the biggest? There are two we have decided tower above or below the others: the North American black bear and the American alligator.
The American alligator is an armored reptile that resides in the swamps and freshwater areas of the state. This official state reptile can be anywhere from 6 to 14 feet long. The female weighs around 200 pounds and the male 500 pounds.
The North American black bear is even bigger. The average bear weighs 200-600 pounds. When on all fours, they are roughly 2 to 3 feet tall. Any standing body of water in Louisiana could house a gator, making swamps, rivers, lakes, and drainage pools all potentially dangerous. ©Deborah Ferrin/Shutterstock.com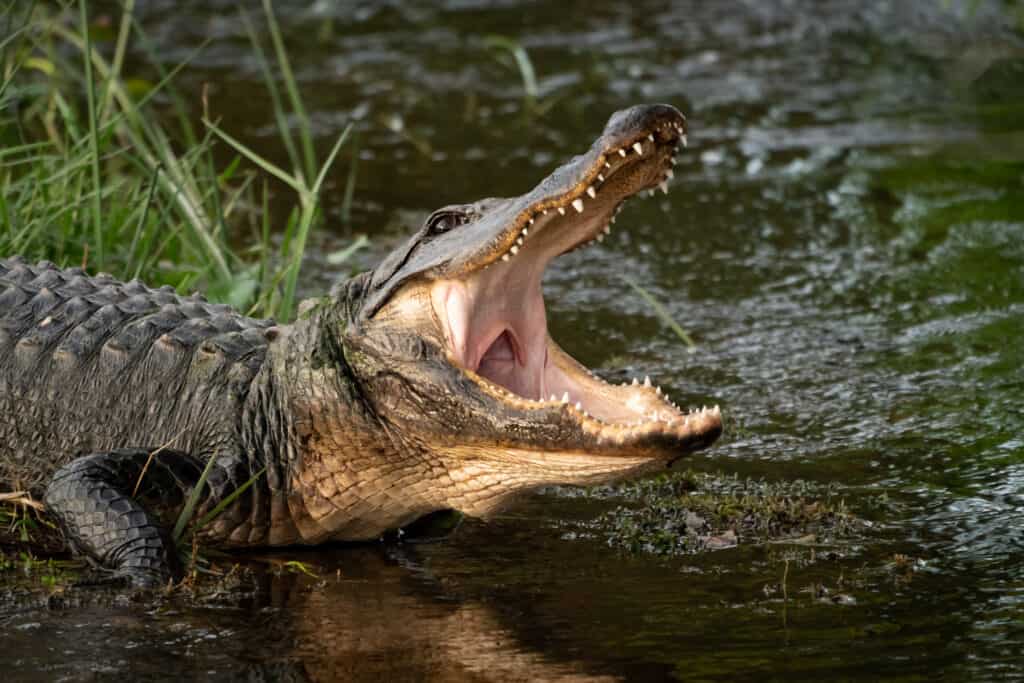
Where To Find The Top Wild Animals in Louisiana
Louisiana is home to a variety of species due to the varying habitats. In this Southern state, you will find marshes, bayous, swamps, wetlands, forests, woodlands, and even prairies. Regions with water, like the coastal marshes and swamps, make up about 40 percent of the state.
- Cypress Island Nature Preserve is a 9,500-acre stretch of cypress trees, tupelos and hardwood forest that is home to alligators, snakes and turtles. Lake Martin, which is part of the preserve, is a key nesting site for blue heron, egrets, white ibis and roseate spoonbills.
- Big Branch Marsh National Wildlife Refuge protects more than 15,000 acres of marshland and piney woods.
- The world-famous Atchafalaya Basin is the largest river swamp in the U.S. It combines bottomland hardwood forests in the north with brackish water and salt marshes in the south, where it borders the Gulf of Mexico. With almost 1 million acres of swampland, bayous and backwater lakes, it is an important habitat for reptiles, amphibians and mammals. More than 100 fish species, 250 bird species and 65 reptile and amphibian species live in the Atchafalaya. Nutria, foxes, beavers, rodents and otters find food and shelter here.
- Lake Maurepas is the 2nd largest lake in Louisiana and is a part of the Pontchartrain Basin, which covers 1,700,000 acres of abandoned delta in the southeastern part of the state. The water has low amounts of saline and contains many types of fish including mostly freshwater and some marine during times of higher salinity. In addition to fishing, hunting and trapping are popular here due to the population of white-tailed deer, squirrel, rabbit, and waterfowl.
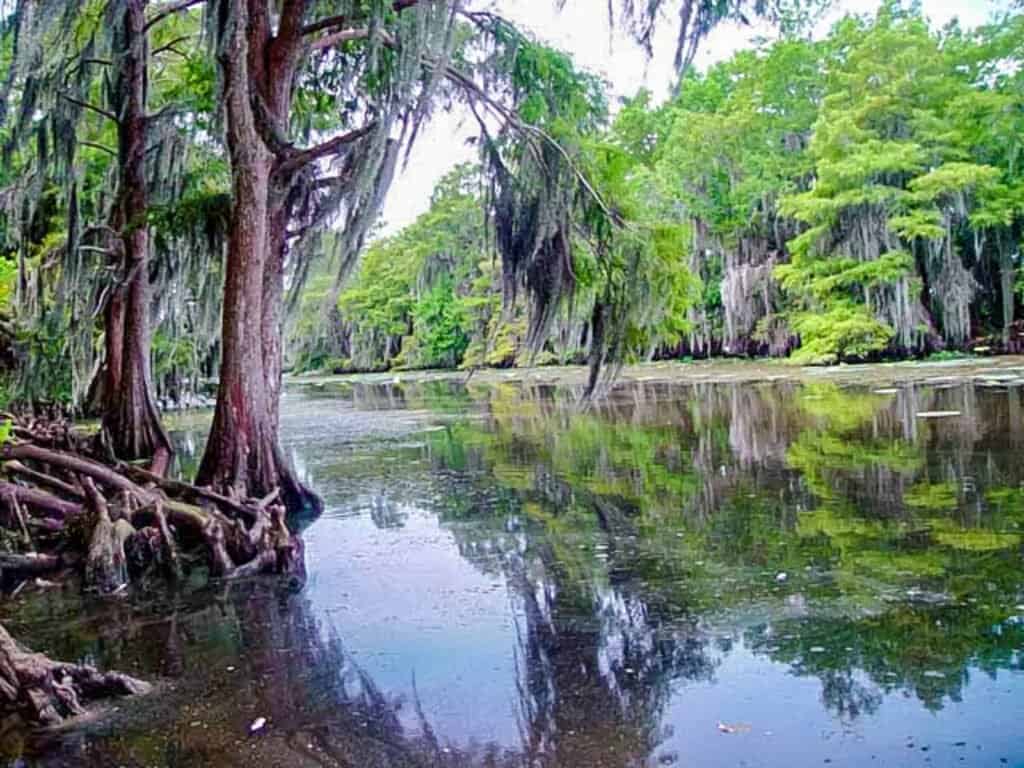

Lake Maurepas is the second largest lake located entirely in Louisiana known for a laid-back, undeveloped atmosphere and environment
©iStock.com/undefined undefined
The Most Dangerous Animals in Louisiana Today
When people think about dangerous animals in Louisiana, they may assume it’s the alligator. In fact, Louisiana and Florida are home to the most alligators in the country, with about 2 million in Louisiana alone. But are alligators actually the most dangerous animal in Louisiana? The answer is no because they rarely attack humans, and when they do, they often don’t end in death. There are only about unprovoked 7 alligator attacks a year.
Louisiana is home, however, to 3 venomous and poisonous creatures you will definitely want to avoid. The eastern diamondback rattle snake is a pit viper that can take down a human with its lethal venom. Death by snake is very rare. Then, brown recluse spiders, which are the size of a dime, and black widows, which are black with a distinctive red hourglass mark on their backs, can be found hiding under rocks or even in people’s basements in Louisiana. Any human bitten by one of these spiders should immediately seek medical attention. Here are two more dangerous animals in Louisiana:
Tarantula hawk wasp: This large, strange wasp preys on tarantulas by sweeping them up and repeatedly injecting venom into their heads. If that doesn’t scare you, consider that its sting, although rare, is excruciating. Researchers have described the pain as “unrelenting” and as second only to the sting of the bullet ant. The good news is that the pain only lasts a few minutes and does not cause serious damage.
Coral snake: These red-banded snakes have venom potent enough to cause paralysis in an adult human. They like to hide in bushes and shrubs, and they don’t give any warning before they strike. The tarantula hawk wasp has an extremely painful sting. ©iStock.com/Rainbohm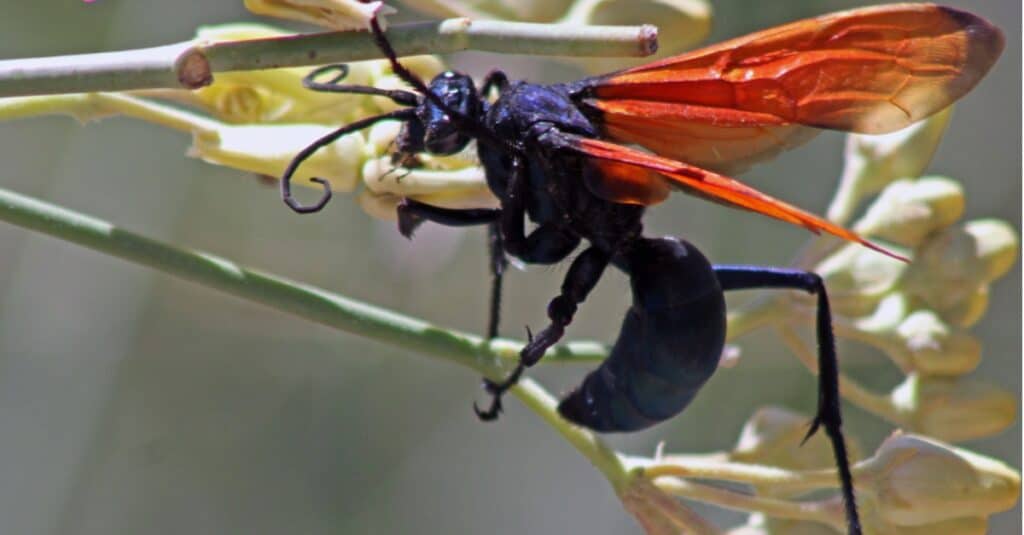
Endangered Animals in Louisiana
Louisiana has suffered from environmental damage. Decades of reliance on the petroleum industry caused widespread water pollution. Hurricane Katrina and the Deepwater Horizon oil spill devastated the state’s waters. The oil spill was especially dangerous to brown pelicans. Nearly 6,000 pelicans died in the spill. The state’s human and natural inhabitants have shown resilience in the face of these problems, and Louisiana’s important ecosystems are on the road to recovery.
- The West Indian manatee (Trichecus manatus) is a gentle aquatic mammal that lives in the warm coastal waters of Louisiana. Manatees are endangered and protected under the Marine Mammal Protection Act.
- The long-tailed weasel (Mustela frenata) is a native weasel with a long body and short legs. It usually lives near water, including marshes, swamps and riverbanks. It is one of the rarest animals in Louisiana.
- Alligators were once endangered in Louisiana, but these apex predators have made a full comeback. There are more than 1 million wild alligators living in the state’s marshes, rivers and lakes and another million on alligator farms. The state’s alligator management program, managed by the Department of Wildlife and Fisheries, is recognized internationally as a conservation success story and a model for sustainability.
- The gopher tortoise (Gopherus polyphemus) lives in the coastal plains of Louisiana. In the wild, this tortoise can live 40 to 60 years. Listed as threatened under the Endangered Species Act, it is listed as critically imperiled by the state of Louisiana. The state has instituted controlled fires in gopher tortoise habitats, which improve the habitat for tortoises, wild turkeys, quail and grouse.
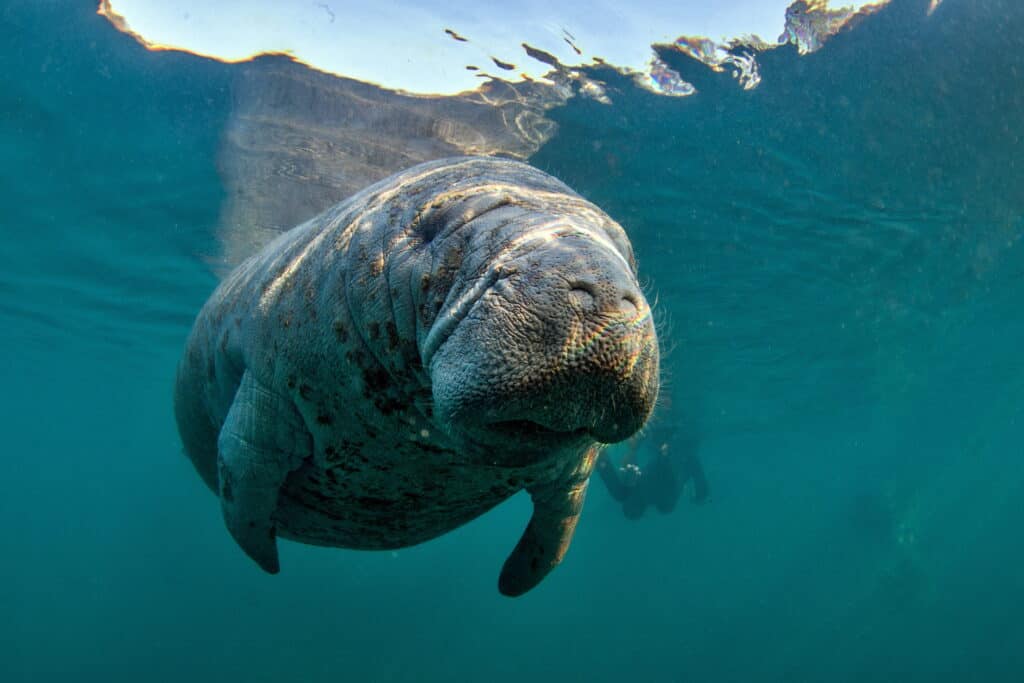

Manatees cannot survive temperatures below 60 °F (15 °C).
©Tomas Kotouc/Shutterstock.com
Mysterious Marshes
Louisiana’s wetlands, swamps, and bayous are among the most fascinating and important ecosystems in the country. Despite some setbacks, the state has taken steps to protect its precious natural resources. The dark, mysterious waters of Louisiana’s swamps and wetlands continue to be safe havens for many wild creatures.
If traveling to the swamps of Louisiana, you may want to be on the lookout for more than alligators and cypress trees. Cajun legend has it that a swamp monster, known as the Rougarou, lurks about the swamps. This shape-shifter has a human body with the head of a wolf but can shift into human form as desired.
Another mysterious being found in the swamps is the fishing spider. They reside in the roots of cypress and tupelo trees before they go fishing for a meal. These 3 inch spiders will create air bubbles to house their bodies, enabling them to travel underwater. They will catch minnows with their poisonous bites.
Native Plants in Louisiana
The Pelican State is home to a large number of plant species. From the Magnolia blossom, to the bald cypress, native plants in Louisiana have the perfect environment to thrive. These plants are interesting and worth exploring.
The bald cypress is found throughout Southern swamps and is one of Louisiana’s state trees. Massive in size, this conifer grows to around 70 feet tall and 25 feet wide. Some ancient bald cypresses date back 150 years and are even larger. While they are found in the swamps, bald cypresses can grow in both dry and wet environments.
The magnolia tree is undoubtedly a symbol of the South, and they thrive across Louisiana. These gorgeous trees have been around a long time; in fact, their fossils date them back 100 million years, ranking them some of the first flowering plants. They were believed to be pollinated by beetles. Southern magnolia flowers are well-known for their sweet, lemony fragrance, and which is often used in aromatherapy to induce a calm feeling and atmosphere. ©iStock.com/Dwbenjam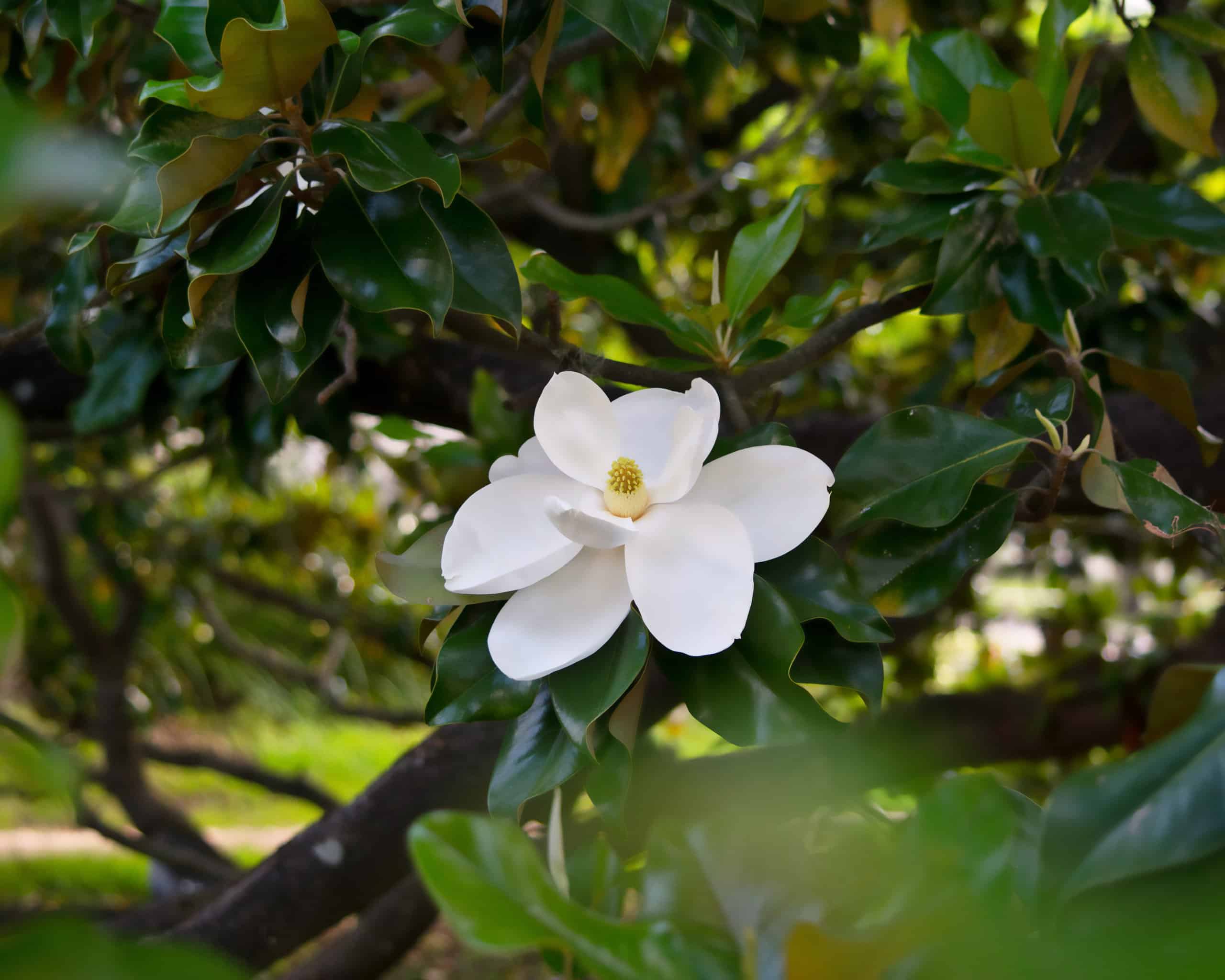
Flag of Louisiana
The flag of Louisiana consists of a blue field featuring a pelican and its young in a nest above a ribbon emblazoned with the state motto “Union Justice Confidence.”
The pelican on the flag is tearing at its breast to feed her young. Interestingly, pelicans do not feed their young in this way. Instead, they regurgitate food and feed them with their bills directly into their baby’s mouths. The picture, however, is supposed to symbolize self-sacrifice and dedication to family.
More Articles Related to Louisiana
Read about:
- extinct animals that lived in Louisiana.
- the best national parks in Louisiana.
- the types of hawks in Louisiana.
- the best aquariums in Louisiana.
- the best dog parks in New Orleans, Louisiana.
- the longest biking trail in Louisiana.
- the largest largemouth ever caught in Louisiana.
- the largest flathead catfish ever caught in Louisiana.
- the largest striped bass ever caught in Louisiana.
- the best fishing spots in Louisiana in the summer.
- the best fish to catch in Louisiana in the summer.
- the best places to camp in Louisiana.
- the largest wild hog ever caught in Louisiana.
- Louisiana Garden Snakes: Identifying the Most Common Snakes in Your Garden
- Discover the Largest Alligator Gar Ever Caught in Louisiana
- Discover the Louisiana Town With the State’s Worst Air Quality
- Discover the Largest Swordish Ever Caught in Louisiana
Louisianian Animals

Admiral Butterfly
Stunningly beautiful wings

Albino (Amelanistic) Corn Snake
Albino corn snakes make great beginner snakes.

American Eel
Don't eat raw eel! Their blood is poisonous to humans when consumed raw.

Armyworm
They are so named because they "march" in armies of worms from one crop to another in search of food

Bagworm Moth Caterpillar
They continually enlarge their protective cases

Banded Water Snake
Some water snakes defend themselves violently.

Beewolf wasp
They hunt bees

Blue Tang
One of the most colorful members of the genus Acanthurus

Brown Water Snake
Has more scales than any other water snake on the continent: 27 to 33 rows of dorsal scales!

Cane Spider
Cane spiders don't spin webs to catch prey

Catahoula Leopard
The state of Louisiana's only native dog breed

Clearnose Skate
The skate with translucent nose patches

Common Yellowthroat
The Common Yellowthroat stays close to the ground and uses stealth to survive!

Corn Snake
Corn snakes are partly arboreal and are excellent climbers.

Crocodylomorph
Crocodylomorphs include extinct ancient species as well as 26 living species today.

De Kay’s Brown Snake
They have specialized jaws for removing snails from shells.

Eastern Diamondback Rattlesnake
This is the biggest venomous snake in North America, with a few that reach 8 feet long.

Eastern Fence Lizard
Females are usually larger than males.

Eastern Glass Lizard
When the glass lizard loses its tail it can grow another one. But the new tail lacks the markings of the old one and is usually shorter.

Eastern Hognose Snake
Eastern hognose snakes are venomous, but only to frogs and toads.

Eastern Woodrat
The eastern woodrat mating ritual involves a potentially deadly fight between the male and female before reproduction begins!

Flea
Adult fleas can jump up to 7 inches in the air

Fox Squirrel
Although it is a tree squirrel, it spends most of its time on the ground.

Giant Desert Centipede
They are the largest centipede in North America

Gopher Tortoise
It is the only species of tortoise native to Florida.

Harlequin Coral Snake
Red touches yellow kills a fellow, red touches black a friend of Jack.

Jack Crevalle
One of the biggest species in the Caranx genus

Jackrabbit
They can run as fast as 45 mph.

Kentucky Warbler
The Kentucky Warbler appears to wear bright yellow cat-eye glasses!

King Snake
King Snakes eat other types of snakes.
Labahoula
The AKC does not recognize this breed or the parent breed Catahoula

Ladyfish
Ladyfish are aggressive fighter when hooked, making them a favorite of anglers.

Mealybug
They have a symbiotic relationship with ants.

Mockingbird
Mockingbirds are incredible mimics that can learn hundreds of songs!

Mourning Warbler
The Mourning Warbler was named for its gray head, which resembles a mourning veil!

Mud Snake
Mud snakes can lay over 100 eggs at a single time!
Nematode
Nematodes range in size from 1/10 of an inch to 28 feet long

Orb Weaver
Females are about four times the size of males

Owl
The owl can rotate its head some 270 degrees

Polyphemus Moth
The Polyphemus moth doesn’t and can't eat, except when it's a caterpillar!

Pompano Fish
They are bottom-feeders

Pygmy Rattlesnake
Pygmy rattlesnakes’ rattle is so small it can only be heard from about three feet away.

Quahog Clam
Their hinged shell protects their soft body

Queen Snake
Queen snakes have armor-like scales on the top of their head

Rat Snakes
Rat snakes are constrictors from the Colubridae family of snakes.

Red-Bellied Woodpecker
Red-Bellied Woodpeckers will often steal the nests of other birds.

Red-Shouldered Hawk
Red-Shouldered Hawks reuse the same nesting area each year.

Rooster
Will mate with the entire flock!

Rough Earth Snake
It has a pointed snout that is uses to burrow into moist soil.

Rough Green Snake
Rough green snakes are great pet snakes because they're low-maintenance.

Seagull
Some gulls are capable of using tools

Smokybrown Cockroach
Has up to 45 eggs per egg case

Smooth Earth Snake
Valeria Biddle Blaney (1828-1900) collected the first specimen in Maryland.

Southern Black Racer
These snakes live underground, beneath piles of leaf litter or in thickets, and they are expert swimmers.

Texas Rat Snake
The Texas rat snake is one of the most common subspecies of the western rat snake in the wild.

Tree Cricket
They make music with their wings

Western Rat Snake
Western rat snakes have special scales on their belly that help them climb up trees.
Louisianian Animals List
- Admiral Butterfly
- Agkistrodon Contortrix
- Albino (Amelanistic) Corn Snake
- American Eel
- Armyworm
- Bagworm Moth Caterpillar
- Banded Water Snake
- Basilosaurus
- Beewolf wasp
- Blue Tang
- Brown Water Snake
- Cane Spider
- Catahoula Leopard
- Clearnose Skate
- Common Yellowthroat
- Congo Snake
- Corn Snake
- Crocodylomorph
- De Kay’s Brown Snake
- Eastern Diamondback Rattlesnake
- Eastern Fence Lizard
- Eastern Glass Lizard
- Eastern Hognose Snake
- Eastern Woodrat
- Flea
- Fox Squirrel
- Giant Desert Centipede
- Gopher Tortoise
- Harlequin Coral Snake
- Jack Crevalle
- Jackrabbit
- Kentucky Warbler
- King Snake
- Labahoula
- Ladyfish
- Mealybug
- Milk Snake
- Mockingbird
- Mourning Warbler
- Mud Snake
- Nematode
- Orb Weaver
- Owl
- Polyphemus Moth
- Pompano Fish
- Pygmy Rattlesnake
- Quahog Clam
- Queen Snake
- Rat Snakes
- Red-Bellied Woodpecker
- Red-Shouldered Hawk
- Rooster
- Rough Earth Snake
- Rough Green Snake
- Seagull
- Smokybrown Cockroach
- Smooth Earth Snake
- Southeastern Blueberry Bee
- Southern Black Racer
- Swallowtail Butterfly
- Texas Rat Snake
- Tree Cricket
- Western Rat Snake
Animals in Louisiana FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What kind of animals live in Louisiana?
Animals common to most of the southeastern U.S. also live in Louisiana. Its large predators include bobcats, gray wolves, red foxes, and gray foxes. Louisiana has its own fox breed, the Louisiana fox. Louisiana also has a small population of red wolves, the rarest of the canid species. Its small predators include weasels and nutria, and its fur-bearing mammals include rodents, beavers and opossums.
Besides these common animals, Louisiana has many strange, exotic animals, including brown pelicans, southern leopard frogs, and white alligators.
What is the most dangerous animal in Louisiana?
Mosquito: Mosquitoes are everywhere in hot, humid Louisiana. They transmit the West Nile virus, which has caused more deaths than alligators, snakes, and poisonous spiders combined.
What dangerous animals are in Louisiana?
Louisiana has many dangerous animals. It has seven venomous snake species, including rattlesnakes, cottonmouths and coral snakes. It has a healthy population of alligators, which can be deadly if they feel threatened. Attacks on humans are rare, however, and Louisiana has not had any fatal alligator attacks on humans.
What is the most common animal in New Orleans?
City Park in New Orleans is a 1,300-acre wildlife preserve that is home to birds, wood ducks, turtles, and alligators. It has a fishing lake and a 60-acre bird sanctuary. Pelicans are the most common birds you will see in the city.
What types of ticks are in Louisiana?
Lousiana is home to a variety of ticks. The ticks you should be most worried about are American dog ticks, Gulf Coast ticks, and deer sticks.
What animals live on the Louisiana bayou?
The bayou is home to alligators, snakes and shorebirds. It also provides habitat for fur-bearing mammals, including beavers, otters, squirrels, muskrats and weasels. Tortoises and frogs also live in the bayou.










