Maggot
Lucilia sericata
Will only live in wet areas
Advertisement
Maggot Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Arthropoda
- Class
- Insecta
- Order
- Diptera
- Family
- Anthomyiidae
- Genus
- Lucilia
- Scientific Name
- Lucilia sericata
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Maggot Conservation Status
Maggot Facts
- Prey
- None, only consumes decaying matter.
- Group Behavior
- Group
- Fun Fact
- Will only live in wet areas
- Biggest Threat
- Pest control
- Most Distinctive Feature
- Rice-like shape
- Other Name(s)
- Botfly maggot, fly larva, grub, maggot, surgical maggot.
- Gestation Period
- 24-48 hours
- Litter Size
- 150 or less
- Habitat
- Damp surfaces with decaying matter
- Predators
- Small mammals, birds, amphibians, and reptiles
- Diet
- Omnivore
- Type
- insect
- Common Name
- maggot
- Group
- group or grumble
View all of the Maggot images!
People may be disgusted by maggots since they are wormy and eat rotten and decaying matter, but they have their uses as fish bait and, when sterilized, as a clean-up crew on necrotic tissue.

Maggots are the larvae of a fly. They are legless creatures that are no bigger than a grain of rice. They are usually white, but some species (like the rat-tailed maggot) have a red or brown hue. If you want to avoid them, keep things clean and avoid traveling to humid regions because they require moisture to survive. Although they are omnivores, the right climate might cause this insect to be primarily carnivorous.
3 Incredible Facts!
- Finding maggots in humans is rare, but it is possible if they are exposed through spoiled or rancid food or if they become infected in a tropical region. Though less likely, an infection called myiasis is possible if the maggot travels through the anus to the intestines as well.
- These insects don’t typically feed on a live host. Instead, they often choose dead or decaying matter, regardless of whether it comes from humans or plants.
- The best way to eliminate maggots from a home is to pour boiling water over them. However, prevention through pest control methods, primarily cleaning, is the easiest option.
Classification
Maggots are the larvae, or soft-bodied grub, of a fly in the Order Diptera, particularly houseflies, cheese flies and blowflies, although about half of all fly species produce larvae that are considered maggots.
Appearance & Behavior
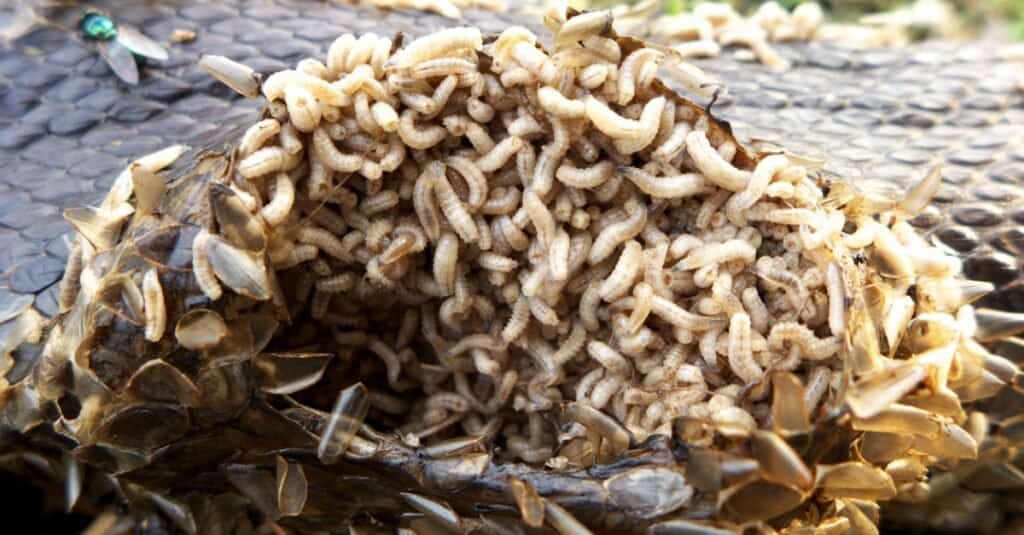

are small, legless fly larvae with two hooks that act like forks for eating plant and animal matter.
©iStock.com/SorJongAng
This type of insect is rather easy to identify. For the most part, it is rather small, reaching up to 25mm or 1 inch in length. This creature is completely legless since it doesn’t develop legs until it is further along in its lifecycle. With two little hooks on one end that act like forks, they can feed on plant and animal matter. The rat-tailed maggot is an exception, featuring a long tail on its body. Rat-tailed maggots specifically come from the drone fly.
These invertebrates tend to live in groups because they all start as eggs. They don’t rely on each other as food sources, but they are often born from the same mother, and their brief lifespan forces them to coexist. A group of maggots is called a grumble, and they are primarily driven by the need to feed. They aren’t aggressive in the pursuit of other animals, but they focus on survival through adulthood.
Even though the diet of a maggot is largely carnivorous, they don’t hunt. The plant and animal matter they consume is already in a state of decay since it is dead. They do not have any preference for any particular animal.
Habitat
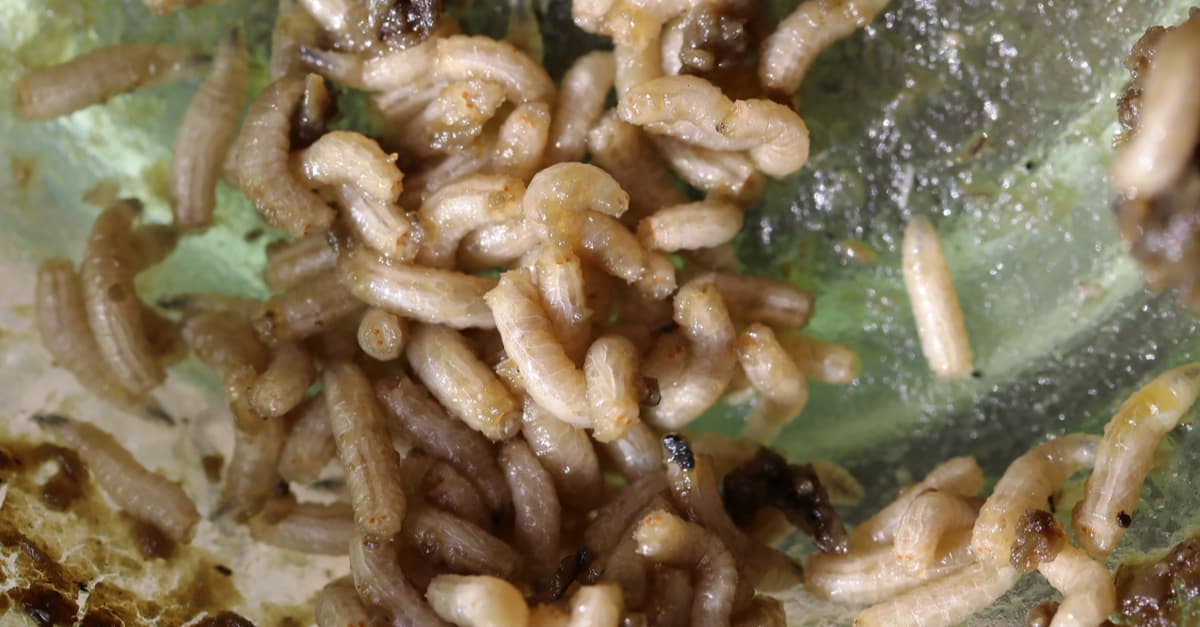

Maggots are voracious devourers of dead and rotting matter, so their habitat is anywhere they find food to eat.
©Astrid Gast/Shutterstock.com
The majority of these larvae find a habitat wherever they have food to eat. They’ll seek out areas with rotting food, organic material, filth, and decaying matter, regardless of the source. You might even find them in a poorly kept kitchen among the spoiled food or even in pet food. To avoid a call to pest control, keep your home free of these insects by maintaining cleanliness. Never allow trash to be strewn through an area, and don’t keep any food past its expiration date. The best pest control is to clean up immediately after meals or after a mess is made.
Typically, they seek out live tissue to live in as a habitat or eat from as a food source. However, there are extreme cases that may allow the insect to survive in a human body. Maggots in humans are rare, but it causes an infection called myiasis. This infection allows maggots to get in humans via contaminated food or directly through the anus, moving into the intestines. The infection rarely occurs in the United States, but it is common in tropical regions like Africa and South America.
Due to the brief larvae stage of the life cycle, this insect doesn’t typically have time to migrate. As an adult, flies can survive nearly anywhere.
Predators & Threats
Due to their small size, maggots tend to be on the menu for many animals, including the rove beetle. Since they can remain in their soil stage for some time, they are used as food for beetles and other small insects. Their food typically includes waste, fruits, and vegetables that have overripened, fermented substances, and plant/animal matter in a state of decay. Only in extreme cases do maggots ever feed on tissues involving something living.
The only threats seem to be the potential for being eaten or killed off in pest control. However, no conservation efforts are being made to protect them due to the nuisance of the fly.
Also known as grubs, these animals are at the bottom of the food chain. Many species of wild birds, foxes, raccoons, frogs, lizards, turtles, salamanders, and snakes. Amphibians will also eat maggots if the opportunity arises.
Reproduction, Babies, and Lifespan
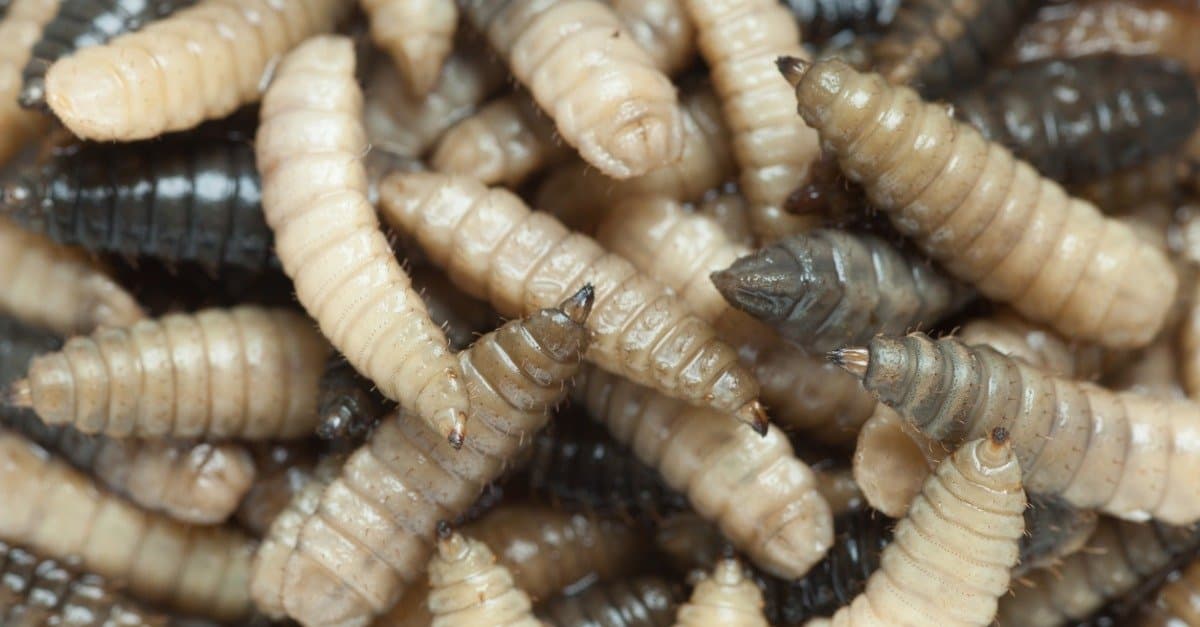

Maggots are the larva stage of a fly’s life cycle, which is only about a month long.
©iStock.com/okugawa
Maggots are born from female flies. To get sperm from the male, the female will put her ovipositor into the male’s genital opening. The mating is not a quick process, taking up to two hours to get the highest number of useful sperm. Although they are not monogamous by choice, the short life cycle of the female fly (about 1 month) leaves her only enough time to mate with one partner. The female lays about 500 to 2,000 eggs in her brief lifetime, though they are laid in batches of no more than 150 each time.
Maggots are the larva stage of the fly’s life cycle. They are the babies of flies, they are born within a day of the fly eggs being laid, and they do not need the mother or father to nurture them. Some fly eggs hatch in as little as 7 hours. Maggots are unable to see actual images, but they have photoreceptors from birth that let them see the brightness of their surroundings.
The average lifespan of a fly is about a month. It spends about 3-5 days in a heavy feeding stage before it reaches the pupal stage. From hatching, it takes 14-36 days to go from an egg to an adult fly.
Population
Determining the number of maggots in the world is nearly impossible. There is no natural regulation for these baby flies in the world, and they appear in the thousands within a day of eggs being laid by the female. Their population is not typically appreciated among the people who encounter them, and there is no current conservation effort in favor of them. When you see a larva, your first thought is probably to call pest control.
Use
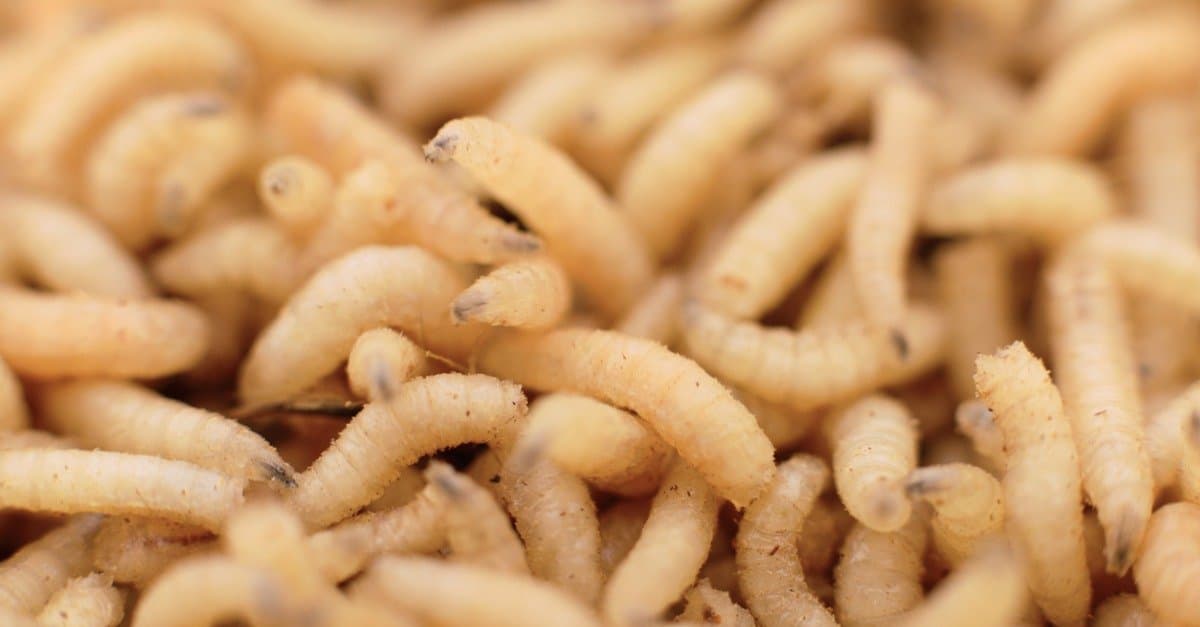

Maggots make good fish bait and are an important indicator of time of death for forensic scientists.
©iStock.com/Tsekhmister
Anglers use maggots commercially to catch non-predatory fish. They are actually one of the most popular baits for anglers in Europe. What fishers do is throw large handfuls of maggots into the area of water they are targeting. This then attracts the fish to the area making them easier to catch.
Live maggots of certain species of flies have also been used for wound healing and cleaning. Although, only the right species is used, otherwise it would cause the wound more harm. In controlled, sterile settings overseen by medical professionals, live, disinfected maggots may be introduced into any non-healing skin of soft wounds in a human or animal. The species of maggots used is called “Lucilia sericata,” and it is one of the only species cleared for marketing outside of the United States.
Additionally, the use of maggots is present in forensic science. The presence and development of maggots on corpses are useful to the estimation of time since death. By studying the insects present at a crime scene, forensic entomologists can find out the approximate time of death to help solve crimes.
View all 164 animals that start with MMaggot FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What is a maggot?
It is the larvae stage of a fly’s life cycle, hatching from fly eggs. It takes up to 36 days for a fly to go from an egg to adulthood.
What do maggot eggs look like?
Fly eggs look a lot like soft grains of rice, releasing legless white worms in the larvae stage. They particularly thrive in rotting plant or animal matter.
What happens if you eat a maggot?
You won’t likely be in any real danger if you consume one of these insects by accident. However, if you ate it as the result of eating food that has already gone bad, you put yourself at risk of food poisoning, which can be a serious medical issue that lasts for days of discomfort.
How long does it take for a maggot to hatch?
The total hatching time varies from two hours to three days, depending on their progression. Once it is hatched, the larvae will become a fly within six hours to five months.
What does a maggot look like?
It looks like a short white worm that is less than a quarter of an inch in length.
How do I kill a maggot?
There are multiple ways to kill them. Pouring boiling water over them is a quick solution, killing them instantly. However, to ensure that they do not survive, add a mixture of 1.5 cups of hydrogen peroxide and a cup of bleach to each gallon poured. Some people try to pour salt on them to dehydrate the insect since it thrives on moisture.
Can maggots harm humans?
Not directly. Food poisoning from eating infested food is a major risk, but the reason is due to the food, rather than the maggots. They feed on plants and animals that are already decaying, so they won’t pose a threat to living humans.
What causes maggots?
They arise in an area if there is improperly stored trash, rotting dead animals, or dog feces. The female fly uses these types of areas to lay their eggs, and their presence can be dangerous for pets.
Are maggots good or bad?
Maggots aren’t much of a threat but finding them in a home is a good indication that there are messes that need to be cleaned as soon as possible.
Are maggots inside humans?
Maggots can grow inside a host, living within the stomach, intestines, and mouth in cases of myiasis.
What are maggots a sign of?
Maggots are a sign of decaying plant or animal matter, as this is what attracts the female fly to lay their eggs.
Are maggots carnivores, herbivores, or omnivores?
For the most part, maggots are carnivorous. However, some species are omnivores as well.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- dengarden, Available here: https://dengarden.com/pest-control/getridofmaggots
- Wikipedia, Available here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Maggot
- petsonmom.com, Available here: https://animals.mom.com/habitats-maggots-6765.html
- Wikipedia, Available here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Myiasis
- mentalfloss.com, Available here: https://www.mentalfloss.com/article/89968/15-facts-about-maggots
- MYMOVE, Available here: https://www.mymove.com/pest-control/guides/remove-maggots/
- MedicalNewsToday, Available here: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/325319