Can drink up to 50 gallons a day!
Advertisement
African Bush Elephant Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Mammalia
- Order
- Proboscidea
- Family
- Elephantidae
- Genus
- Loxodonta
- Scientific Name
- Loxodonta africana africana
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
African Bush Elephant Conservation Status
African Bush Elephant Facts
- Prey
- Grass, Fruit, Roots
- Name Of Young
- Calf
- Group Behavior
- Herd
- Fun Fact
- Can drink up to 50 gallons a day!
- Estimated Population Size
- 300,000
- Biggest Threat
- Poaching and habitat loss
- Most Distinctive Feature
- Large, rounded ears
- Other Name(s)
- African Elephant
- Gestation Period
- 20 - 24 months
- Habitat
- Forest, savannah and flood plains
- Predators
- Human, Lion, Hyena
- Diet
- Herbivore
- Average Litter Size
- 1
- Lifestyle
- Diurnal
- Common Name
- African Bush Elephant
- Number Of Species
- 1
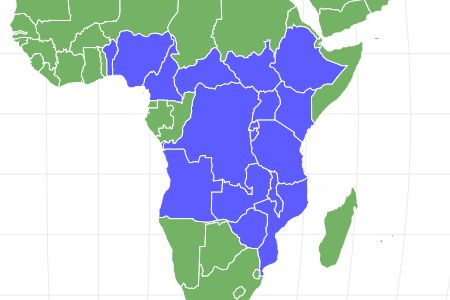
- Location
- central and southern Africa
- Slogan
- Can drink up to 50 gallons a day
- Group
- Mammal
African Bush Elephant Physical Characteristics
- Color
- Brown
- Grey
- Skin Type
- Leather
- Top Speed
- 25 mph
- Lifespan
- 60 - 70 years
- Weight
- 3,600kg - 5,400kg (7,900lbs - 12,000lbs)
- Height
- 3m - 3.5m (10ft - 12ft)
- Age of Sexual Maturity
- 11 - 20 years
- Age of Weaning
- 6 - 18 months
View all of the African Bush Elephant images!
Classification and Evolution
The African Bush Elephant is the largest of all living creatures on land today, with some individuals growing to weigh more than 6 tons. The elephant is thought to have been named after the Greek word for ivory, meaning that elephants were named for their uniquely long tusks.

Although many of the ancestors of the African bush elephant became extinct during the last ice age (including the Woolly Mammoth), there are three distinct species of Elephant remaining today which are the Asian elephant (of which there are a number of sub-species), the African bush elephant and the African forest elephant.
Although these two elephant species are very similar, the African bush elephant is considered to be larger than the African forest elephant, which has rounder ears and straighter tusks.
Evolution
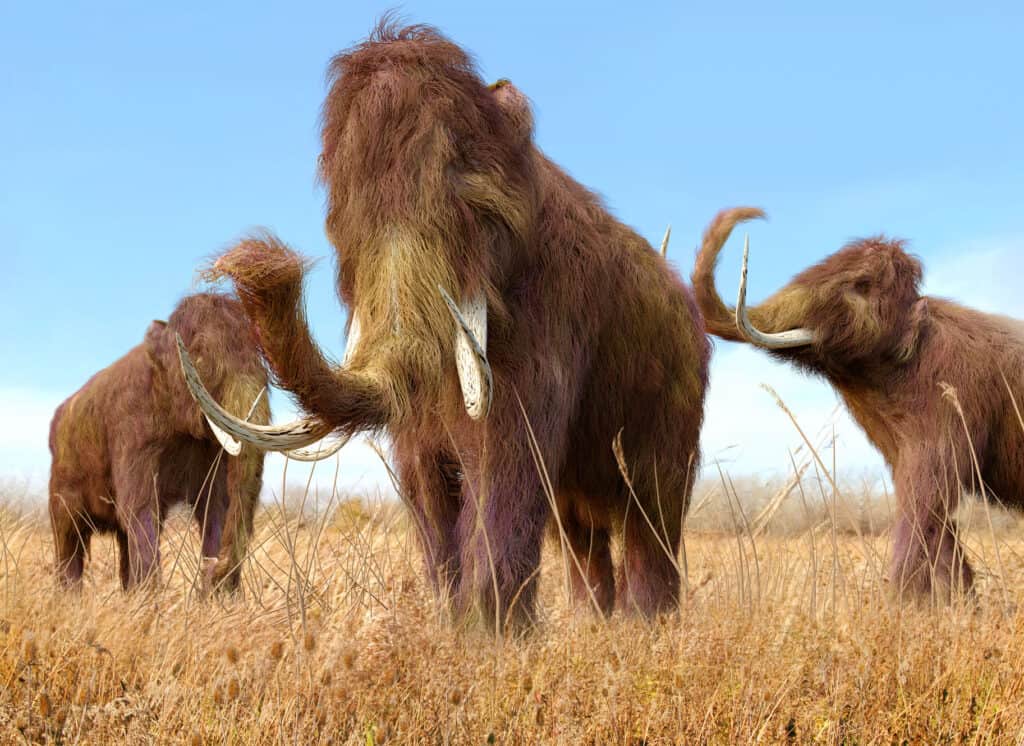

Woolly Mammoths are prehistoric ancestors of modern elephants.
©iStock.com/Aunt_Spray
Fossil records show that extinct proboscideans, large mammals with trunks and tusks, have been identified on every continent except Australia and Antarctica. The ancestor of these animals originated in Africa around 40 million years ago – and was trunkless. Moeritherium, about the size of modern pigs, is believed to be the animal that led to modern elephants – and is also an ancestor of manatees and dugongs.
Gomphotheres, tusked but with no trunks, were herbivores that roamed Africa, Eurasia, and the Americas during the Miocene, Pliocene, and Pleistocene epochs. These animals had given rise to the elephantids by the time of their extinction. Around the beginning of the Pleistocene, 5 million years ago, the Loxodonta arrived to be followed by the Elephas and Mammuthus. Loxodonta remained in Africa while Mammuthus ranged to Eurasia.
The ancestor of the Asian elephant, Elephas platycephus, arrived during the Pleistocene, as did the Mammuthus primigenious, the woolly mammoth. The African elephant, Loxodonta, appeared 1.5 million years ago and is the newest elephant species in evolutionary terms. It is larger than the Asian elephant in size and both males and females have tusks.
Anatomy and Appearance
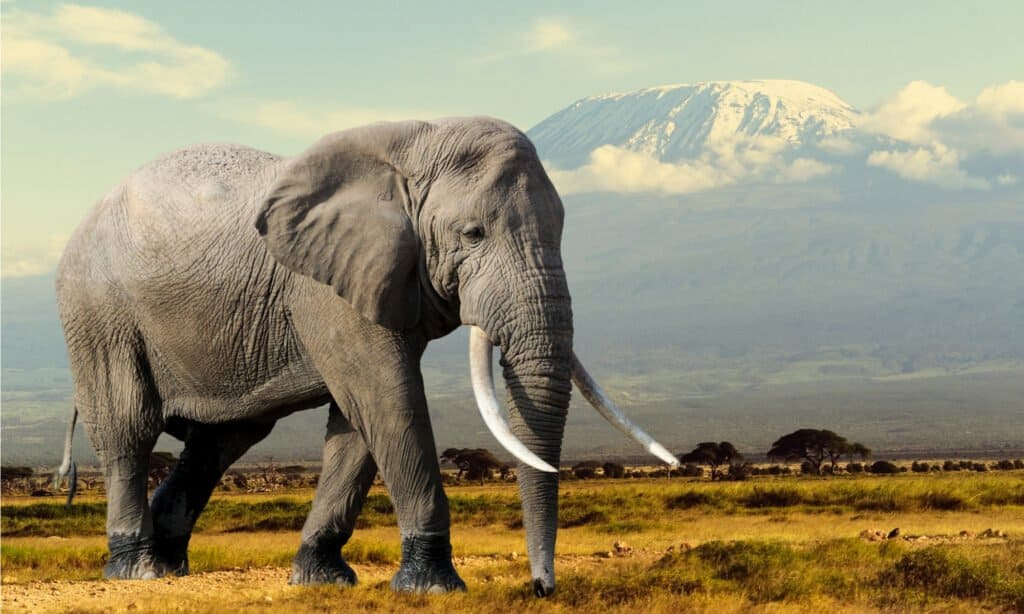

African elephants are the largest animals that walk the earth.
©Volodymyr Burdiak/Shutterstock.com
The African bush elephant is the largest known land mammal on Earth, with male African bush elephants reaching up to 3.5 meters in height and the females being slightly smaller at around 3 meters tall. The body of the African bush elephants can also grow to between 6 and 7 meters long.
The tusks of an African bush elephant can be nearly 2.5 meters in length and generally weigh between 50 and 100 pounds, which is about the same as a small adult Human. African bush elephants have four molar teeth each weighing about 5.0 kg and measuring about 12 inches long. As the front pair of molars wear down and drop out in pieces, the back pair shifts forward, and two new molars emerge in the back of the African bush elephant’s mouth.
African bush elephants replace their teeth six times during their lives but when the animal is between 40 to 60 years old, it no longer has teeth and will likely die of starvation, which is sadly a common cause of death of elephants in the African wilderness.
Distribution and Habitat
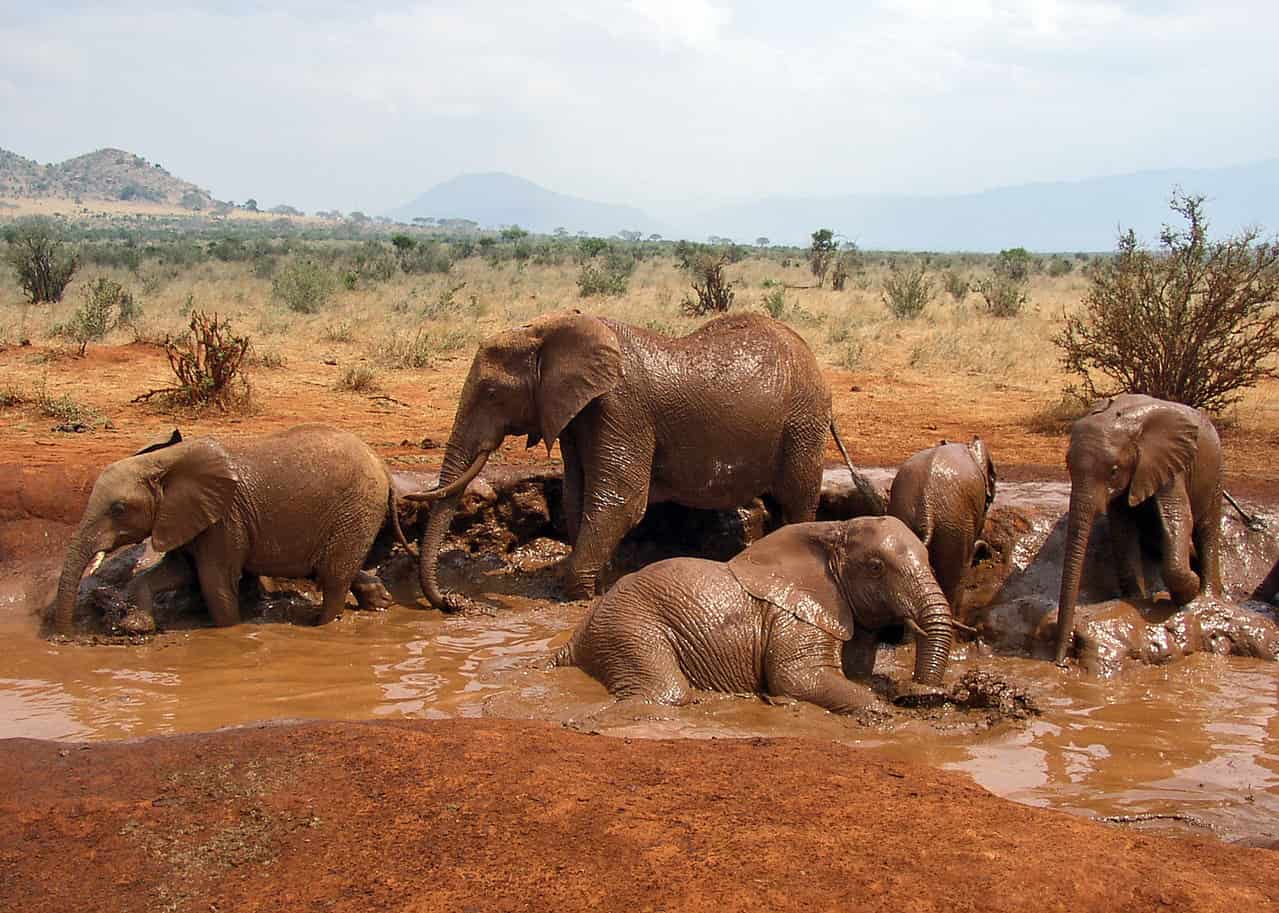

Herds of African bush elephants wander the plains and grasslands of Africa searching for food and waterholes.
©I, Mgiganteus, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons – License
Although the historical range of its ancestors ranged right into the Arctic Circle, today the African bush elephant is mainly found in central and southern Africa in nomadic herds that wander the plains and grasslands of Africa grazing for food and searching for waterholes. Unlike the slightly smaller African forest elephant, the African bush elephant inhabits the grassy savanna plains and shrubland of the African continent in groups that contain mothers and their calves. Generally, these herds contain around 10 individuals but it is not uncommon for family groups to join together, forming a clan that can contain over 1,000 elephants. This very social lifestyle means that the African bush elephants are less vulnerable on the open African plains.
Behavior and Lifestyle
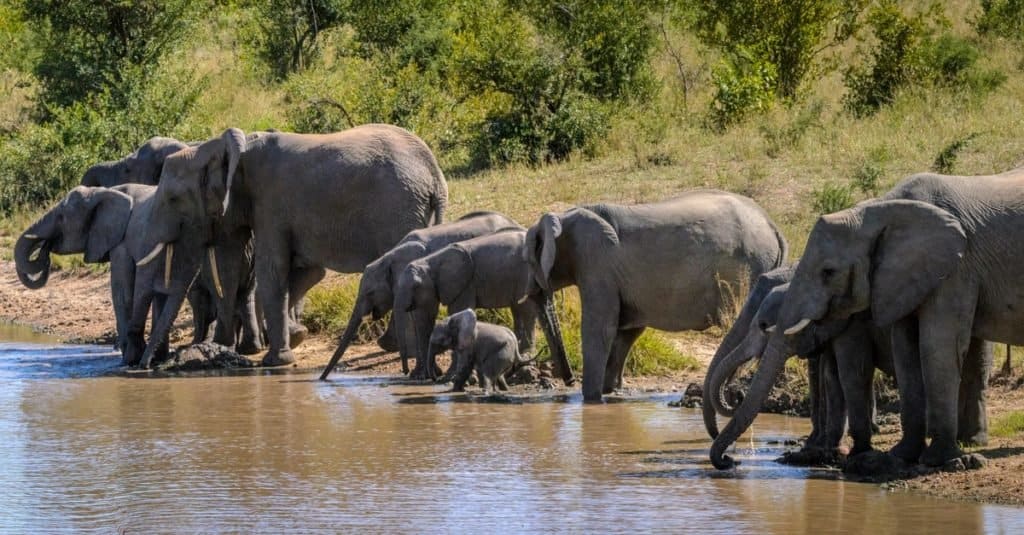

African bush elephants travel in family herds for protection from predators.
©Roger de la Harpe/Shutterstock.com
Not only is the African bush elephant an incredibly sociable mammal but it is also a very active one. Elephants are nomadic animals meaning that they are constantly on the move in search of food, so moving within these family herds allows them to have greater protection both from predators and from the elements.
The trunk of the African bush elephant is one of its most distinguishing features and this extra-long nose is not only flexible enough to gather and handle food but can also collect water. Its trunk, along with its tusks can also be used to defend itself from predators such as Lions, and to fight with other male elephants during the mating season.
African bush elephants are highly intelligent and emotional animals displaying behaviors that include giving and receiving love, caring deeply for the young, and grieving for dead relatives.
Reproduction and Life Cycles
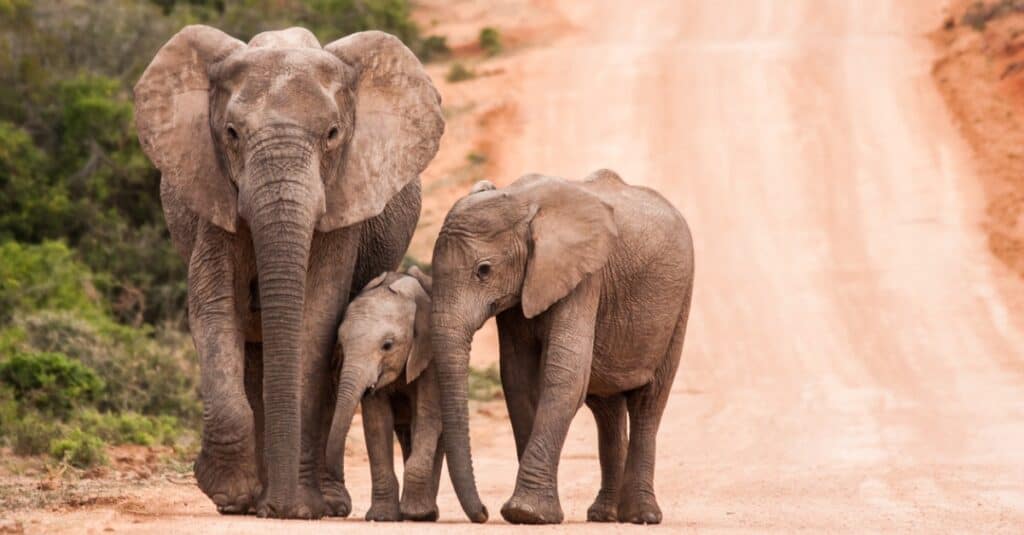

Female African bush elephants nurse their young for two years.
©iStock.com/WillieErasmus
African bush elephants tend to live relatively long lives, with their average life span lasting between 60 and 70 years, on average. Females reach sexual maturity (are able to reproduce) after 10 or 11 years but are thought to be most fertile between the ages of 25 and 45.
Male African bush elephants, however, often don’t reach sexual maturity until they are nearly 20 years old. After mating and a gestation period of up to 2 years, the female gives birth to a single calf (twins have been known but are extremely rare).
The calf is nursed for 2 years but will remain under the guidance and protection of the herd until it is old enough to support itself (around 6 years old). It is at this point that the tusks of the African bush elephant calf start to grow.
Diet

Despite its immense size, the African bush elephant is a herbivorous mammal meaning that it survives on a diet that solely consists of plants and plant matter. The bulk of the elephant’s diet is comprised of leaves and branches that are stripped off the trees and bushes using its trunk. The African bush elephant also grazes on fruits and grasses and uses its immense tusks for digging for roots in the ground and to strip the bark of trees. Food is fed into its mouth using the trunk, and the large, flat teeth of the elephant are then the perfect tool for grinding the vegetation and course plants down so that they can then be more easily digested.
African bush elephants are capable of tucking away 350 pounds of food each day – they’re also capable of gulping down 200 liters of water daily. As a matter of fact, the better part of their time is dedicated to finding the perfect spots of lush vegetation to enjoy a meal.
Their presence also spells good tidings for other species such as birds, honey badgers, meerkats, mongooses, and monkeys which love to sift through the dung left behind by elephants. In it, these mammals and avians get to eat the seeds and grains which have made it through the pachyderms’ digestive system in one piece.
Predators and Threats
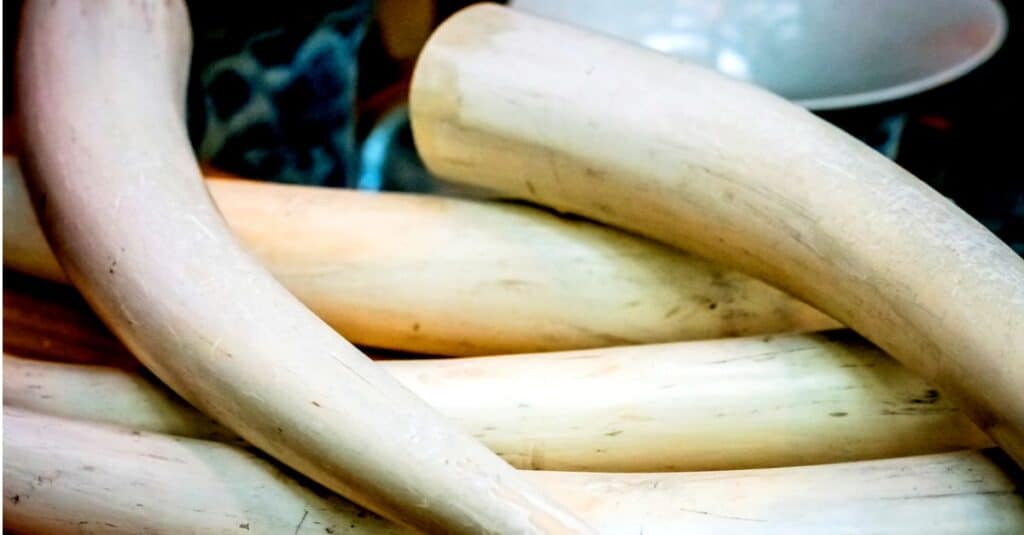

Humans that poach elephants for their tusks are the biggest threat to their survival.
©iStock.com/MagicColors
The African bush elephant has no real natural predators to threaten its survival, mainly due to its sheer size and the fact that they often remain within the safety of the herd.
African bush elephants are peaceful giants and can be seen cohabiting in their habitat with other large mammals and birds. Lions and Hyenas may occasionally be able to pick off a young elephant that has been separated from its mother; they have also been known to attack adults that are old and sick and therefore more vulnerable.
Humans that poach the elephants for their ivory tusks, classifying them as one of the “African Big Five,” are the biggest threat to their survival along with habitat loss across the continent.
Interesting Facts and Features
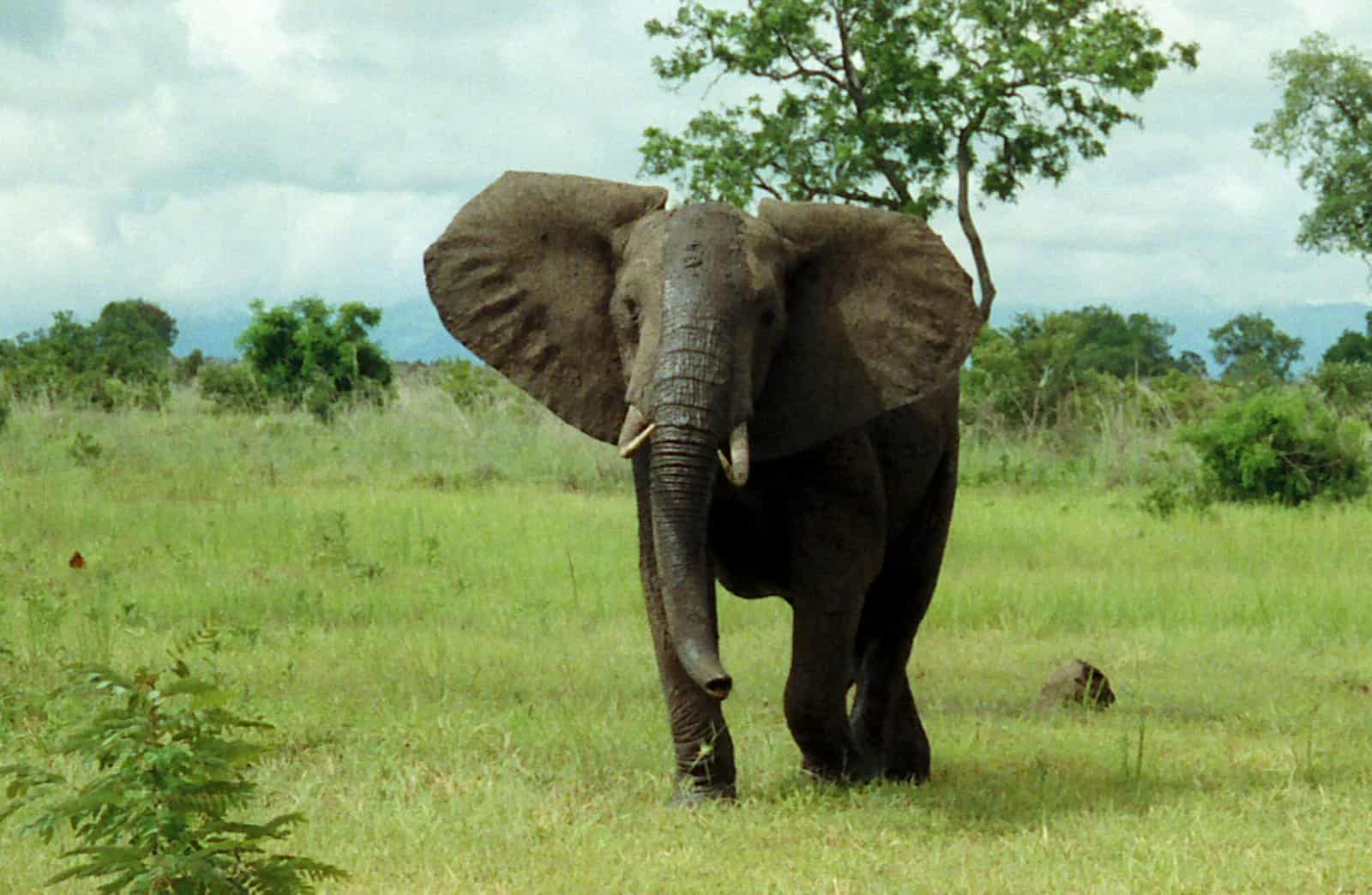

The ears of the African bush elephant are shaped like the African continent.
©Taken by Oliver Wright, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons – License
In the early 19th century, the story of the African bush elephant was very different with there being up to 5 million individuals thought to have been roaming the African continent. However, due to the increased demand for ivory, Africa’s elephant population is thought to have fallen as much as 85% in some areas.
The large ears of the African bush elephant are said by some to be shaped somewhat like Africa, but these large flaps of skin are not just for hearing, they are a vital tool in keeping the elephant cool in the African heat. Like many of the herbivores found throughout Africa, the calves can walk at birth to maximize their chances of survival. An adult African bush elephant can drink up to 50 gallons of water every day and is able to take 1.5 gallons of water into their trunks at a time.
Relationship with Humans
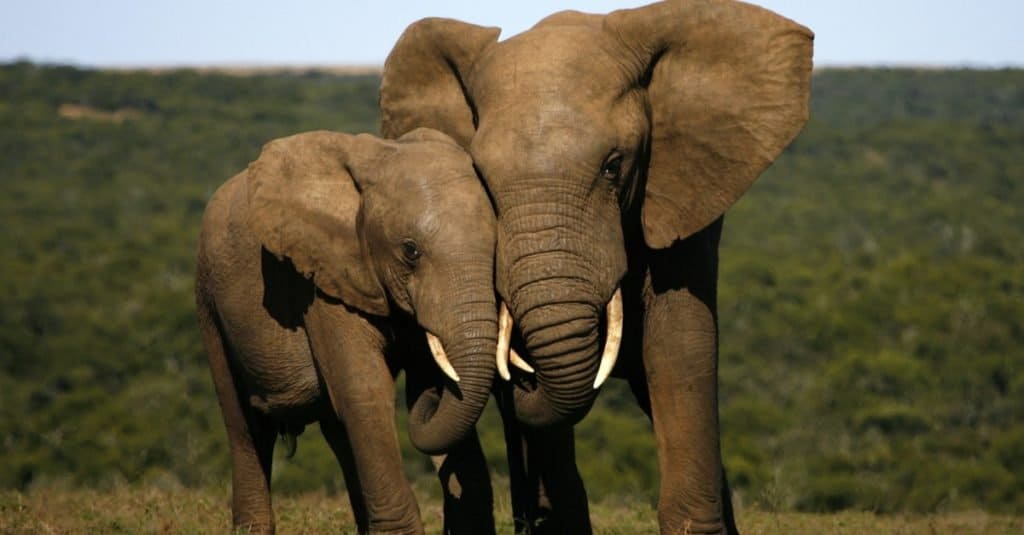

Protected status is helping elephant numbers to remain stable.
©JONATHAN PLEDGER/Shutterstock.com
Sadly, due to an increase of outside interest in Africa and its exotic wonders (particularly towards the mid-20th century), the African bush elephant population took a devastating decline toward extinction. After having been brutally killed by poachers for years for their ivory, elephants had vanished from much of their native habitat. In 1989 a worldwide elephant ivory hunting ban fell into place after the populations had dropped so dramatically across the continent. In northern and central parts of Africa, the African bush elephant is now rare and confined to protected areas, and although the story is similar in the south, South African elephant populations are thought to be doing better with an estimated 300,000 individuals in the region.
Conservation Status and Life Today
Today, although recovering, African bush elephant populations are still threatened by increasing levels of illegal poaching and habitat destruction. Deforestation in the elephant’s territory means that the animals lose both their food and shelter making them more vulnerable in the wild. Despite the ban, African bush elephants are also constantly threatened by poachers hunting the elephants for their ivory tusks.
View all 194 animals that start with AAfrican Bush Elephant FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are African Bush Elephants herbivores, carnivores, or omnivores?
African Bush Elephants are Herbivores, meaning they eat plants.
What Kingdom do African Bush Elephants belong to?
African Bush Elephants belong to the Kingdom Animalia.
What phylum do African Bush Elephants belong to?
African Bush Elephants belong to the phylum Chordata.
What class do African Bush Elephants belong to?
African Bush Elephants belong to the class Mammalia.
What family do African Bush Elephants belong to?
African Bush Elephants belong to the family Elephantidae.
What order do African Bush Elephants belong to?
African Bush Elephants belong to the order Proboscidea.
What genus do African Bush Elephants belong to?
African Bush Elephants belong to the genus Loxodonta.
What type of covering do African Bush Elephants have?
African Bush Elephants are covered in Leathery skin.
Where do African Bush Elephants live?
African Bush Elephants live in central and southern Africa.
In what type of habitat do African Bush Elephants live?
African Bush Elephants live in forests, savannas, and floodplains.
What are some predators of African Bush Elephants?
Predators of African Bush Elephants include humans, lions, and hyenas.
How many babies do African Bush Elephants have?
The average number of babies an African Bush Elephant has is 1.
What is an interesting fact about African Bush Elephants?
African Bush Elephants can drink up to 50 gallons of water a day.
What is the scientific name for the African Bush Elephant?
The scientific name for the African Bush Elephant is Loxodonta africana africana.
What is the lifespan of an African Bush Elephant?
African Bush Elephants can live for 60 to 70 years.
How many species of African Bush Elephant are there?
There is 1 species of African Bush Elephant.
What is the biggest threat to the African Bush Elephant?
The biggest threats to the African Bush Elephant are poaching and habitat loss.
What is another name for the African Bush Elephant?
The African Bush Elephant is also called the African elephant.
How many African Bush Elephants are left in the world?
There are 300,000 African Bush Elephants left in the world.
How fast is an African Bush Elephant?
An African Bush Elephant can travel at speeds of up to 25 miles per hour.
What's the difference between an African elephant and an Asian elephant?
The main differences between an African elephant and an Asian elephant have to do with their sizes and geographic location. Read about all of their differences here!
How to say African Bush Elephant in ...
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- David Burnie, Dorling Kindersley (2011) Animal, The Definitive Visual Guide To The World's Wildlife
- Tom Jackson, Lorenz Books (2007) The World Encyclopedia Of Animals
- David Burnie, Kingfisher (2011) The Kingfisher Animal Encyclopedia
- Richard Mackay, University of California Press (2009) The Atlas Of Endangered Species
- David Burnie, Dorling Kindersley (2008) Illustrated Encyclopedia Of Animals
- Dorling Kindersley (2006) Dorling Kindersley Encyclopedia Of Animals
- David W. Macdonald, Oxford University Press (2010) The Encyclopedia Of Mammals
- African Bush Elephant Classification, Available here: http://science.jrank.org/pages/2427/Elephant.html
- Evolution Of Elephants, Available here: http://www.buzzle.com/articles/evolution-of-elephants.html
- Elephant Intelligence, Available here: http://www.suite101.com/content/elephant-evolution-and-intelligence-a167231
- African Elephant Information, Available here: http://wwf.panda.org/what_we_do/endangered_species/elephants/african_elephants/
- About African Bush Elephants, Available here: http://www.nature.org/animals/mammals/animals/elephant.html