Grapevine Beetle
Pelidnota punctata
Although they feed on grapevine leaves, Grapevine beetles hardly cause serious damage to the plant.
Advertisement
Grapevine Beetle Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Arthropoda
- Class
- Insecta
- Order
- Cole
- Family
- Scarabaeidae
- Genus
- Pelidnota
- Scientific Name
- Pelidnota punctata
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Grapevine Beetle Conservation Status
Grapevine Beetle Facts
- Name Of Young
- Larvae
- Fun Fact
- Although they feed on grapevine leaves, Grapevine beetles hardly cause serious damage to the plant.
- Distinctive Feature
- four black spots on each side of their body
- Other Name(s)
- spotted pelidnota or spotted June beetle
- Habitat
- forests, thickets, and woods
- Diet
- Carnivore
View all of the Grapevine Beetle images!
Although they feed on grapevine leaves, Grapevine beetles hardly cause serious damage to the plant.
Summary
The Grapevine beetle is a type of Scarab beetle. It shares a similar appearance to the Japanese Beetles and June Beetles. In fact, this beetle is commonly called the spotted June beetle due to its similarity in appearance to the June beetle. As the name suggests, the Grapevine beetle is a pest of the grapevine plant. However, it does not have a serious negative impact on the growth and health of the plant, so it is not considered a serious pest.
Grapevine Beetle Species, Types, and Scientific Name
The Grapevine beetle (Pelidnota punctata) is also commonly known as the spotted June beetle or Spotted Pelidnota. They belong to a family of insects known as Scarab beetles (family Scarabaeidae). Other popular insects in the family include the dung beetles, Rhinoceros beetles, June beetles, and Japanese beetles. There are more than 30,000 insect species in the family Scarabaeidae found all over the world. About 1,400 of these species are found in North America.
Appearance: How To Identify Grapevine Beetle
Members of the Scarabaeidae are known for their stout bodies. These beetles typically have bright metallic colors. But probably their most notable feature is the club-shaped antenna made up of plates known as lamellae. They can fold this antenna into a ball or deploy it to sense their environments.
The Grapevine Beetle can either be a tan color or a darker shade of brown. They typically have an off-yellow or auburn red pattern with four black spots running on each side of their bodies. The color of the grapevine beetle’s legs can be brown or black, depending on where they’re found.
Grapevine beetles in the southern regions typically don’t have dark legs, while the northern ones have them. In some regional varieties, the edges of the beetle’s elytra are typically lined with a fine black line. Depending on the type you find, the spots may also be present or absent (GB beetles in northern regions have more spots than Southern ones).
Adults typically measure about 2.5 cm (1 inch) in length. However, in some cases, they may grow as large as 3 cm (1.2 in). Their eyes are usually on either side of their head and maybe tan or a dark shade of brown.
Habitat: Where To Find Grapevine Beetle
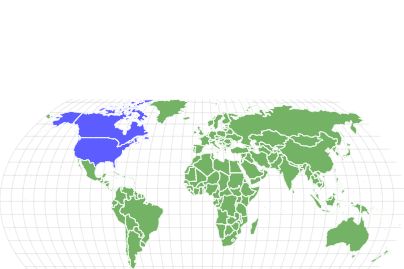
Grapevine beetles are native to North America. They’re most commonly found in the Northern and Central regions of the United States. The beetle is also quite common in eastern Canada. They’re pests of the grapevine plant in these places. However, farmers don’t consider them serious pests because they don’t do any major damage.
Grapevine beetles live in thickets, woods, and forests like many beetles. However, you may also see them in gardens and vineyards. They’re mostly seen during the Summer seasons. When they’re around human settlements, these beetles are typically drawn toward light.
Diet: What Do Grapevine Beetles Eat?
Female grapevine beetles lay eggs on rotten woods or tree stumps near a host plant. The larvae hatch from the egg and dig their way into the soil where it stays. The larvae feed on rotten wood and other decaying plant and animal matter in the soil as they develop into pupa form. Adults emerge from the pupa around July after a two-year cycle. As adults, they feed on grapevine leaves. However, they do relatively no damage to host plants.
What eats grapevine beetles?
Lizards, birds, toads, and rodents often feed on grapevine beetles. While they do not have any major defenses against predators, The beetles can fly at very high speed, which can help them get away from predators.
Prevention: How To Get Rid of Grapevine Beetle
Although they’re quite common in some parts of the United States and Canada, grapevine beetles are not considered serious pests. They have an appetite for grapevine leaves but do not cause significant damage.
If you wish to get rid of them, there are several simple ways to do this as well. Since they’re large beetles, you can easily handpick and remove them from the plant. The only challenge with this approach is that they’re nocturnal, making it difficult to find them. It is best to look for them in the evening or late at night.
Instead of handpicking them, some farmers may also spray a natural product known as Diatomaceous earth (DE) on the beetle’s body. You can also use an insecticidal soap spray to stun the bug before picking them off. Other natural control methods include introducing beneficial nematodes and milky spores that don’t harm beneficial insects in your garden.
View all 170 animals that start with GGrapevine Beetle FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are grapevine beetles dangerous?
No, grapevine beetles are harmless to both humans and pests. They do not have biting or stinging mouthparts. They are also not harmful to plants. Although adults feed on grapevine leaves, they’re not major pests in vineyards.
What's eating my grapevine leaves?
Due to their name, people often assume that grapevine beetles are responsible for the damage to their grapevine plant. However, this isn’t true. If there’s major damage to your grapevine plant, it was probably caused by other similar-looking bugs like the Japanese beetles.
How do you identify grapevine beetle?
The grapevine beetle is characterized by a tan color or a darker shade of brown. Their thick, serrated legs are typically brown or black. Their main distinguishing feature is the presence of dots on their elytra and thorax. Typically, they have 3 dots on each elytron and 1 on the thorax on each side of the body. The point where the thorax joins the abdomen is also characterized by a black or brown semicircle.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- Get Busy Gardening / AMY ANDRYCHOWICZ, Available here: https://getbusygardening.com/grapevine-beetle
- University of Wisconsin Milwaukee / College of Letters and Science, Available here: https://uwm.edu/field-station/grapevine-beetle/
- Insect Identification , Available here: https://www.insectidentification.org/insect-description.php?identification=Grapevine-Beetle
- Wikipedia, Available here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pelidnota_punctata