Larder Beetle
Dermestes lardarius
Larder beetles were named based on their attraction to food storage rooms or cupboards, but they do not feed on stored food products.
Advertisement
Larder Beetle Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Arthropoda
- Class
- Insecta
- Order
- Coleoptera
- Family
- Dermestidae
- Genus
- Dermestes
- Scientific Name
- Dermestes lardarius
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Larder Beetle Conservation Status
Larder Beetle Facts
- Fun Fact
- Larder beetles were named based on their attraction to food storage rooms or cupboards, but they do not feed on stored food products.
- Diet
- Omnivore
- Favorite Food
- dried meats and fish, pet food, skins and hides, feathers, cheese
View all of the Larder Beetle images!
Larder beetles were named based on their attraction to food storage rooms or cupboards, although they do not feed on stored food products.
Summary
Dermestes lardarius (larder beetle) is a household pest commonly found in storage rooms in homes or food storage facilities. Despite their attraction to pantries (larders), larder beetles rarely feed on stored food products. They prefer to eat animal products such as dried meats, dried insects, leather, skins, feathers, and hides. They’re found in different locations all over the world.
Larder beetles Species, Types, and Scientific Name
Dermestes lardarius is a species of beetle commonly known as the larder beetle or moisture beetle. The beetle’s common name refers to their affinity for food storage rooms or storage facilities, otherwise known as larders.
The belong to the family Dermestidae and genus Dermestes. There are 92 species of beetles in this genus. The family of insects to which the larder beetle belongs is known as skin beetles or carpet beetles. They’re characterized by their love for animal products such as skin, hide, and leather. There are approximately 500 to 700 species of skin beetles all over the world.
Appearance: How To Identify Larder Beetles
The adult larder beetle is a small insect with a size varying between ⅓ to ⅜ inches (3.3cm to 3.7cm). It is typically dark brown in color. However, it may also have a pale-yellow band across the upper portion of its hardened chitinous wings (the elytra). The dots are usually arranged in a triangular shape. The legs and sternum of these insects are typically covered in a layer of hairy bristles which are yellow in color. This is also known as the setae.
The larval form of this beetle is a reddish-brown worm. It is typically hairy and may be about 1/2 inch in length. The most notable feature of the larvae is the presence of two-curved spines on their posterior end.
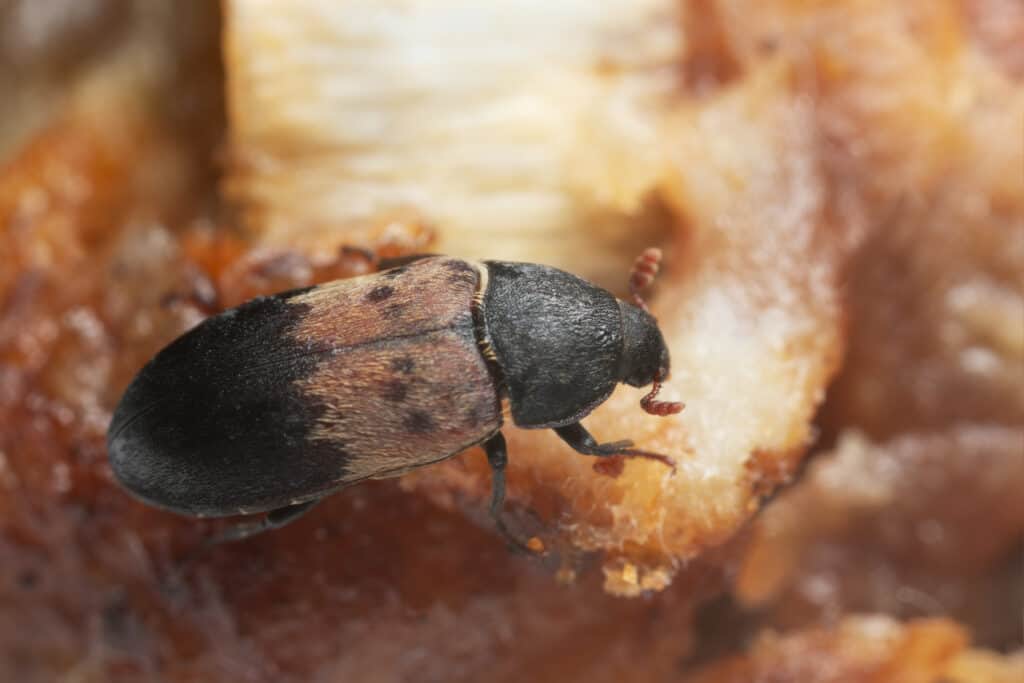

Larder beetles commonly inhabit food storage areas.
©Henrik Larsson/Shutterstock.com
Habitat: Where to Find Larder Beetles
Adult larder beetles naturally stay outdoors during the winter months. However, they may enter into buildings during the spring and summer months. When they enter buildings, they’re typically attracted to food pantries, kitchens, and other parts of the home where they’re likely to find the organic food matter that they feed on.
Larder beetles may also target attics, basements, and other parts of a building where dead insects, birds, or other animals may be found. The larval form typically bores into wood and similar materials like books, plastic cork, and foam insulation. Boring into structures like this helps to protect them from getting eaten by the other members of their own species that might want to cannibalize them.
Diet: What do Larder Beetles Eat?
Both the adult and larvae forms of this insect feed on animal products such as cured meat, hide, spoiled meat, dried fish, dead insects, pet food, furs, feathers, and leaders. They may also feed on dead animals such as rats and birds trapped in different parts of the home, such as chimneys, attics, and basements. Larder beetles are often classified as a type of carpet beetle. However, it doesn’t eat carpets directly. It only attacks carpets and other woolen products that have become soiled by organic matter like blood, oils, and other high-protein stains.
What Eats Larder Beetles?
Larder beetles practice cannibalism and occasionally feed on the larvae of the same species. Lizards, birds, and toads may also feed on these beetles. Rodents and other mammals like raccoons, shrews, moles, and hedgehogs may also feed on this beetle.
Prevention: How To Get Rid of Larder Beetles
When larder beetles enter buildings, they either do so in search of food or warmth. Thus, the first step in taking them out is to find their food sources and get rid of them. Without the food source, they’ll either leave or die off eventually. Sometimes the food source is large and noticeable, making it easy to get rid of. However, some food sources are more difficult to spot. For instance, dead mice hidden in the attic may be difficult to find and remove.
A large acute infestation or a recurring one indicates a renewable food source in the building, such as a cluster of dead insects. For food sources in hard-to-reach places, you may have no other choice than wait out the infestation. The beetles will disappear on their own when the food source is depleted. Regular cleaning helps eliminate the organic stains and grease they feed on.
You can also try bug-proofing your home by sealing off access points. This keeps both the larder beetles and the insects they feed on away. You may also spray the baseboard around their access point with insecticide or use dust or powder insecticides instead.
Related Insects
View all 98 animals that start with LLarder Beetle FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are larder beetles dangerous?
Since larder beetles don’t bite or sting, they’re not harmful to humans. They also don’t transmit any disease. However, they may contaminate food (especially dry pet food) and animal products such as hide or leather.
Why do I keep finding larder beetles?
Larder beetles are often attracted to indoor spaces with abundant food sources. This could be a dead swarm of insects in your attic or a dead mouse on your wall. The best way to keep this from happening is to eliminate these food sources as soon as you discover them.
What damage can larder beetles cause?
Larder beetles feed on high-protein materials. They commonly infest dry pests, making them inedible. They may also destroy preserved specimens and may damage carpets, leather, and other animal products. However, larder beetles cause the most significant damage in the larvae stage. In this stage, they bore into wood and other soft material until they mature. Serious structural damage may occur if the larvae are allowed to continue.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us? Contact the AZ Animals editorial team.
Sources
- University of Wisconsin, Available here: https://hort.extension.wisc.edu/articles/larder-beetles/
- University of Minnesota, Available here: https://extension.umn.edu/product-and-houseplant-pests/larder-beetles
- Wikipedia, Available here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dermestes_lardarius